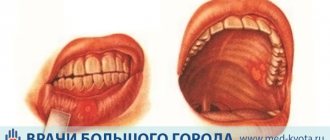
Even our distant ancestors knew how to diagnose diseases based on the condition of the back of the tongue. Depending on the nature of the plaque, its color, smell, and sensations in the patient himself, one can assume many pathological processes occurring not only in the oral cavity, but throughout the entire body.
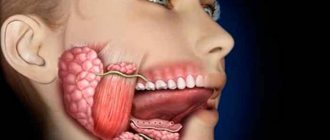
The dorsum of the tongue is divided into the anterior 2/3 (oral part) and the posterior third (pharyngeal part), covered with multilayered squamous unevenly keratinized epithelium, which is rapidly renewed. The tongue is a muscular organ with abundant innervation and a large number of blood vessels. On its back and lateral surfaces there are 4 types of papillae: filiform, grooved, mushroom-shaped and leaf-shaped. The perception of taste - sweet, bitter, sour and salty - is provided by taste buds and receptors, but the mechanism of obtaining taste sensations has not yet been fully studied.
The tongue is affected in almost all diseases of the oral cavity caused by various microflora (staphylococcus, streptococcus, fungi, protozoan spirochetes). The nature and degree of changes in the tongue are determined not only by the form of the disease, but also by the general condition of the human body.
Glossitis or inflammation of the tongue
Inflammation of the tongue most often appears due to an existing disease of the gastrointestinal tract, cardiovascular system, allergic reaction or metabolic disorder. That is, the disease develops against the background of another disease, and it can only be eliminated by being completely cured. There are infectious and non-infectious types of glossitis, the first includes various fungi and infections, the second can be caused by tongue injuries.
Diagnosis of diseases by language
— Thin plaque is a sign of an incipient disease, thick plaque is a sign of chronic disease. — Thickening of plaque indicates the progression of the disease, and clearing and reduction inspires optimism: health is getting better. - A coating covering the tongue indicates toxins in the stomach, small intestine or large intestine. — If plaque coats the base of the tongue, the doctor may suspect a problem with the intestines and kidneys. — If only the back of the tongue is coated, toxins are in the colon, — If the plaque is in the middle of the tongue, toxins are present in the stomach and small intestine. — A thin, easily removable whitish coating on the tongue and a metallic taste in the mouth always accompany acute gastroenteritis (damage to the stomach and small intestine), and a person’s job is to consult a doctor in time. And chronic gastroenteritis is always accompanied by a sticky, hard-to-remove gray coating with a putrid odor from the mouth and a pungent taste. - With a fatty, muddy coating of the tongue - stagnation of food, accumulation of mucus, etc. - with a spotted purple coating of the tongue - stagnation of blood. — A thin coating of the tongue indicates an incipient disease (or a superficial localization of the process), — A thick coating of the tongue indicates a chronic disease (or a deep localization of the process). - a whitish coating on the middle third with cracks along the edges signals: gastritis, gastric and duodenal ulcers are likely. - Whitish plaque at the root - enterocolitis. - White plaque around the edges and on the front third - lung disease. - Foamy plaque around the edges and on the front third - chronic bronchitis. - White plaque along the edges of the posterior third - kidney disease. - White coating over the entire surface - dysbacteriosis, thrush, stomatitis. - White and red spots (the so-called strawberry tongue) - scarlet fever. - Blue coating - typhus, dysentery. - Thick white color of plaque is evidence of intoxication, constipation. — White plaque indicates increased dryness of the digestive organs. — White plaque on the back third of the tongue indicates pathology of the large intestine; - In the middle third of the tongue - for problems with the duodenum. — The yellowish color of the plaque is a sign of problems in the gallbladder. Yellowness at the bottom of the tongue indicates developing jaundice. The tongue has turned yellow - disturbances in the functioning of the digestive organs, liver disease, and chronic cholecystitis are likely. With a yellow coating of the tongue, there is excess heat in the body. If the color is yellowish, there is excess bile in the gallbladder or a disorder in the liver. Yellow plaque increases with seasonal exacerbations of the liver and gallbladder. One of the signs of developing jaundice is yellowness in the lower part of the tongue, which is detected when it is raised to the palate.
Brown - diseases of the lungs and gastrointestinal tract. Brown plaque along the edge of the tongue (symmetrical with respect to the median fold) indicates bilateral pneumonia. - Black-brown coating, with cracks - With pellagra (deficiency of nicotinic acid and vitamin B) - the tongue is covered with a difficult-to-remove coating, reminiscent of a chessboard. In the late stage of pellagra, the tongue acquires a red tint with a varnished surface - “cardinal tongue”.
The dark color of the plaque indicates severe chronic dysfunction of the digestive organs, accompanied by dehydration. Black plaque indicates disturbances in the digestive system, especially in the pancreas and gall bladder, as well as disturbances in the acid-base balance of the blood due to dehydration.
The line running down the middle of the tongue indicates excitement running along the spinal column. If this line is curved, it may indicate a deformity or curvature of the spine.
Teeth prints on the front of the tongue and on its side surface indicate hidden neuroses. The deeper the imprints, the more pronounced the neurosis.
A curved or deviated tongue indicates an ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke, dysfunction of the cerebellum or cerebral circulation. Streaks of foam on both sides may indicate the presence of rheumatism. Flat ulcers indicate a tuberculous process in the body. A dry tongue with numerous cracks occurs in diabetic patients. A trembling tongue occurs in neurotic disorders and brain diseases.
Lacquered tongue.
The varnished tongue has a shiny, smooth, bright red surface due to atrophy of the taste buds. In some diseases, the number of papillae decreases, they become almost invisible, and sometimes are completely absent. Because of this, the tongue looks smooth and shiny, as does the entire mucous membrane of the mouth. Occurs in stomach cancer, the body’s inability to absorb vitamin B2, and chronic colitis. With pellagra (deficiency of nicotinic acid and vitamin B), the tongue is covered with a difficult-to-remove black-brown coating, with cracks resembling a chessboard. In the late stage of pellagra, the tongue acquires a red tint with a varnished surface - “cardinal tongue”.
"Geographical" language
In children, it is always a sign of food allergy, and the location of inflamed and non-inflamed areas of the mucous membrane (“continents” and “seas”) very accurately indicates the involvement of a particular organ of the digestive system in an allergic disease.
Geographic tongue, characterized by the presence on its surface of areas of varying color and size with deep grooves and reliefs, is typical for people with chronic damage to the gastrointestinal tract and some mental disorders. Geographic tongue occurs with chronic damage to the gastrointestinal tract, as well as with some forms of mental disorders. Using this language, you can almost immediately diagnose the allergic condition of individual organs. If bright red spots appear against the background of a normal pink color, then the disappearance of the papillae is a sign of anemia (anemia). An enlarged, uniformly red, but not crimson, varnished tongue is most often a sign of a metabolic disorder. And also - “Geographical” tongue (uneven desquamation and regeneration of the epithelium) - disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, helminthic infestations, diathesis, toxicosis of pregnant women. When your tongue gets stuck
The main signs of gastrointestinal diseases, in the tongue
When examining the tongue, attention is paid to the color, nature and location of plaque, the shape and features of the surface, and various formations on the tongue. Smoothness of the entire surface of the tongue indicates decreased secretion of gastric juice (hypocidal gastritis), which can occur as a result of stomach disease, but can be a consequence of other diseases (for example, liver and gallbladder diseases). Rough inflamed or non-inflamed papillae on the entire surface of the tongue are more often observed with increased secretion of gastric juice (hyperacid gastritis). Redness and slight soreness of the tip of the tongue (of course, not associated with its burn) definitely indicate some kind of disease of the pelvic organs: the sigmoid or rectum, bladder, uterus.
Swelling and redness of the right half of the tongue from tip to middle indicate inflammatory liver disease. The same changes on the left – disease of the spleen. The appearance of ulcers in these areas indicates the severity and chronic nature of the disease. The same changes in the middle part of the tongue and its edges on both sides indicate a serious lung disease (previously, they primarily meant Tuberculosis, now - chronic pneumonia and cancer).
Pathology of the digestive organs often leads to noticeable changes in the surface of the tongue. different parts of the tongue are connected to different organs of the body.
A thin, easily removable whitish coating on the tongue and a metallic taste in the mouth always accompany acute gastroenteritis (damage to the stomach and small intestine), and a person’s job is to consult a doctor in time. And chronic gastroenteritis is always accompanied by a sticky, hard-to-remove gray coating with a putrid odor from the mouth and a pungent taste.
Peptic ulcer of the stomach or duodenum is always accompanied by chronic gastroenteritis, so a gray coating on the tongue is a constant sign of these diseases, but with them another external symptom is added - inflammation of the edges of the oral mucosa around the necks of the front and root teeth of the lower jaw. By the nature and severity of inflammation of the mucous membrane around these teeth, one can judge in advance whether the peptic ulcer is exacerbating or subsiding.
Diagnosis by language - in photographs
A tongue without bones Indeed, the tongue itself cannot boast of a solid support. But the fold running along its middle accurately reflects the state of the human spine. Thus, a curvature of the fold at the tip of the tongue signals cervical osteochondrosis, in the middle - about problems in the thoracic region, at the root - about lumbar osteochondrosis. And teeth marks on the tongue, unless you accidentally bit it, indicate digestive disorders.
Signs of diseases that you can detect by diagnosing your tongue:
1. Excited state of the body (thickened, smooth median fold). 2. Curvature of the spine in the lumbar region. 3. Curvature of the spine in the thoracic region. 4. Curvature of the spine in the cervical region. 5. Chronic enterocolitis, dyspepsia (dental marks on the lateral surfaces of the tongue). 6. Thyrotoxicosis, neurasthenia, alcoholism (tremor of the tongue). 7. Chronic diseases of the large intestine (many small intertwined folds). 8. Kidneys are not working well. 9. Dysfunction of the large intestine. 10. Intoxication of the large intestine. 11. Intoxication of the gastrointestinal tract. 12. Weakness of cardiac activity. 13. Chronic bronchitis. 14. Bilateral pneumonia (brown plaque). 15. Pulmonary emphysema.
Tongue color
- the body, as doctors say, is very informative. Redness of the tip is a sign of weak cardiac activity, possibly incipient coronary artery disease. · Pale tongue - exhaustion. · Red - disorders in the cardiac and pulmonary systems, blood diseases, infectious diseases. · Dark red - the ailments are the same as with the red color, but the patient’s situation is much more serious. · Shiny smooth - anemia. · Purple - serious diseases of the blood and lungs. · Blue - disorders in the cardiovascular system, lungs, kidney problems. And one more thing... Your tongue will bring you to the doctor. So which specialist should you go to if you feel unwell? Language can give the right clue. - For example, - Dry tongue, numerous cracks - fever, diarrhea, diabetes, anemia. - Burning sensation - stress, vegetative neurosis, cervical osteochondrosis. - Swelling and redness on the right - hepatocholecystitis. - Swelling and redness on the left - diseases of the spleen. — Tremor (shaking) of the tongue is a manifestation of neurasthenic syndrome, vegetoneurosis, thyrotoxicosis. — “Geographical” tongue (uneven desquamation and regeneration of the epithelium) — disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract, helminthic infestations, diathesis, toxicosis of pregnant women. When your tongue gets stuck
Another sign of problems in the body is a decrease in taste sensations. If a person stops feeling sweet, sour, salty or bitter, diseases of the nervous and endocrine systems are likely. An overdose of medications, especially antibiotics, can also affect the tongue. This is a so-called drug disease caused by intoxication of the body. Plaque, cracks, erosions, herpetic rashes, but most often thrush may appear on the tongue. Having noticed these signals in time, you should immediately stop taking the medication and consult a doctor. To prevent your tongue from itching Do not forget to regularly show your tongue to yourself so as not to miss signals that not everything is fine in the body. By the way, it is better to show your tongue the way Albert Einstein did in the famous photograph - to do this you will have to stick it out as much as possible in order to see the root.
And one more thing - you need to examine the tongue when it is clean. It can be tidied up with a special tongue massager, which is sold in a pharmacy, or with a soft toothbrush. In addition to the hygienic benefits, this procedure, thanks to the massage, will have a very beneficial effect on the work of those organs with which the tongue, as it turns out, is deeply “tied”.
For our part, we can regularly clean the surface of the oral muscle from plaque using a silver or wooden spoon, followed by massaging the tongue with a soft toothbrush.
This simple procedure helps improve the condition of the entire body.
Of course, everyone knows that there are special devices for cleaning the tongue. And they appeared at least five centuries ago.
The story is told by Anna Yurievna Volkovich, candidate of cultural studies, senior researcher at the Military Medical Museum of the Russian Defense Ministry in St. Petersburg.
Even Avicenna, in his treatises, spoke of the need to cleanse the tongue of plaque, which gives an unpleasant odor to the breath. For these purposes, the famous doctor recommended cypress cones and slivers of trees rich in essential oils.
Armenian doctors who lived more than five hundred years ago also encouraged the use of improvised means. The first physical evidence was discovered in 1998 at excavations in China.
Archaeologists have found scrapers made of silver and coated with a thick layer of gold. They were intended for daily use by representatives of the ancient Chinese nobility. The widespread distribution of scrapers in China was also noted by the Russian doctor Pyasetsky, who visited the Celestial Empire in 1874. In his notes, he notes that local gourmets thoroughly clean their tongues before each meal. It was believed that this procedure allows one to better evaluate the taste of prepared dishes.
But tongue scrapers were also used by Europeans. For example, when the future Russian Emperor Paul and his wife were in France, Marie Antoinette and Louis XVI gave them a travel bag, which, among other things, contained a tongue scraper. Then they made a copy of it from a turtle shell, and Alexander I already used it.
Charles XII also had his own personal tongue cleaning device. It was made entirely of ivory, only three semilunar slits were cut on the working part, which increased the functionality of the scraper. The handle was decorated with a heraldic design.
But scrapers were not only the prerogative of kings and kings. The court people also took very good care of their oral cavity. They placed orders from silversmiths not only for jewelry and dishes, but also for various trinkets - mirrors, combs, perfume bottles and... tongue scrapers.
By the way, completely unique scrapers were made in Russia; there were no such scrapers anywhere else. They were silver spoons with several narrow semilunar slits. The handle had a special edge that was used to clean the midline of the tongue. In a word, all the subtleties of its anatomical structure were taken into account. In addition, silver disinfected the oral cavity and was a good prevention of inflammation.
In Western Europe, things were completely different. Scrapers made of ivory or horn with a working part in the form of a loop were common there. Such bone objects were very often combined with toothpicks or even scrapers to clean the buccal mucosa. Rich Europeans preferred silver scrapers coated with gold.
The structure of the scraper also developed according to its own laws. For several centuries it remained standard: the length of the handle was 8–9 cm, and the working part was relatively small. In the 18th century, travel and pocket personal hygiene products became very common; they were made very small. And then there was a tendency to increase the cleaning part itself, which made it possible to properly treat the root of the tongue.
Nowadays almost all scrapers are made of plastic. Therefore, products have to be changed quite often - much the same as toothbrushes. This is also natural because most modern scrapers have bristles. There are scrapers in which the working part is represented by a pointed end.
And recently they started producing very interesting toothbrushes: they have bristles on one side and a scraper on the other. Given such diversity, everyone can choose a model to suit their taste. We just need to remember that our tongue needs cleaning no less than our teeth. Source
Inflammation of the tongue causes
All reasons can be divided into several large classes:
- bacteria (streptococci and staphylococci), the number and presence of these bacteria is determined by taking a swab from the oral cavity;
- fungi (various types);
- viruses, for example, herpes;
- tissue injuries (burns, prostheses, mechanical damage);
- chronic use of alcohol and nicotine;
- ignoring the rules of personal hygiene;
- vitamin deficiency and reduced immunity.
These reasons, individually or in combination, can cause the development of glossitis.
Possible diseases and their symptoms
There can be many causes of tongue diseases, the main ones include:
- infection with viruses, bacteria, fungi;
- damage: thermal, chemical, mechanical;
- lack of oral hygiene;
- stress;
- smoking, alcohol, drugs.
Modern man has added piercing to the usual mechanical damage.
Diseases are divided into 3 types.
Acute inflammatory:
- Catarrhal glossitis - caused by acute respiratory viral infections, caries, dental plaque, smoking tobacco or mixtures. It is characterized by unpleasant sensations, loss of taste, plaque, and redness.
- Ulcerative glossitis - ulcers appear on the tongue, there is a grayish, dirty coating, and a strong odor from the oral cavity. Often the manifestation of ulcerative glossitis indicates a weakening of the body’s immune defense; it also appears with necrotizing stomatitis.
- Desquamative glossitis (geographic tongue) - characterized by an unpleasant taste in the mouth and the appearance of red spots. Indicates diseases associated with metabolic disorders in the body, gastrointestinal tract, and the occurrence of dysbacteriosis.
- An abscess appears due to mechanical, toxic, chemical, thermal damage. The tongue swells, it becomes difficult to speak, severe pain occurs, cracks and dryness may occur.
Acute inflammatory diseases on the tongue, photographs:
Catarrhal glossitis
Ulcerative glossitis
Desquamative glossitis
Abscess
Chronic:
- Leukoplakia – the organ turns red and thickens, which causes discomfort and difficulty speaking. A common cause is smoking, advanced dental diseases, and genetic predisposition.
- Hairy leukoplakia - the papillae become like separate threads, the shape of the tongue loses its boundaries, becomes uneven, wavy, the entire tongue and its root thicken. Manifests itself in HIV infection and tuberculosis.
- Hairy black tongue - there is hypertrophy of all papillae, unpleasant sensations. Often characterizes pathological changes in the gastrointestinal tract or infection of the body with fungi.
- Diamond-shaped glossitis - a diamond-shaped, smooth, small, red lesion appears on the back of the organ. Characterizes the occurrence of immune diseases.
Photos of chronic diseases:
Leukoplakia
Hairy leukoplakia
Black hairy tongue
Diamond-shaped glossitis
Infectious:
- Thrush (stomatitis caused by the Candida fungus) - causes itching, burning, loss of the ability to sense tastes, and fever. When the plaque is removed, red ulcers appear.
- Glossitis caused by herpes virus infection is characterized by the appearance of ulcers and small watery swellings. Severe pain occurs when eating food, water, and the temperature rises.
- Streptococcal impetigo - severe redness, rashes appear in the form of blisters. Caused by streptococcus entering the oral cavity.
- Lichen planus - rough red spots appear. Occurs when metabolic processes in the body fail, immunity is weakened, and manifests itself in stressful situations.
Photos of infectious diseases:
Herpes
Thrush
Ringworm Impetigo
If any deviations from the norm are detected in the appearance of the organ or changes in taste, you should contact a specialist to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
If the changes affect not only the tongue, but also the gums and teeth, then you need to contact a dentist. If changes affect the tongue or throat, then you need to make an appointment with a family doctor or therapist who will give a specialized referral.
Tongue inflammation symptoms
Symptoms of the disease vary depending on the type and cause of the disruption, but generally patients complain of:
- redness of the tongue
- swelling
- smell from the mouth
- presence of plaque or rash
- bleeding gums
- painful sensations
Do not ignore any symptoms and self-medicate. For competent advice, consult your doctor: therapist or dentist.
Color of disease
A normal tongue looks soft and tender, its movements are not constrained, the color is pink, and the coating is normally thin, white and moderately moist. With certain diseases, the color of the tongue changes.
- A dark red tongue indicates probable pneumonia, severe acute infectious disease, high fever caused by infection, ischemia or poisoning.
- A raspberry tongue signals the same diseases as a red one, but in a more severe form.
- A purple tint means that a severe infectious disease, disturbances in the circulatory and respiratory systems are possible.
- A thick white coating indicates food retention in the intestines, i.e. about constipation that has not yet become chronic.
- Yellow plaque indicates serious digestive disorders. The more intense the color and thicker the plaque, the more serious the disease and the likelihood of permanent accumulation of food in the stomach and intestines.
- A grayish coating indicates chronic, imperceptible diseases of the stomach and intestines. Dehydration and disruption of the acid-base balance in organs and tissues (high acidity) are also possible.
If you are a lover of strong tea or a heavy smoker, relax! A thick, grayish or yellow coating on the tongue indicates, rather, not a disease, but rather bad habits. Some foods and medications can also change the color of your tongue.
Read also: Nervous tic of the eyes and facial muscles: what to do and how to prevent
Inflammation of the tongue: various foci
The oral cavity, and in particular the tongue, consists of several parts, each of which can be susceptible to inflammatory processes:
- Inflammation of the papillae on the tongue
Inflammation of the papillae, or popularly “tipun”, is accompanied by increased sensitivity of the tongue, swelling and redness; patients complain of pain that occurs even during a simple conversation.
- Inflammation of the root of the tongue
Usually accompanied by pain when swallowing, a feeling of a lump in the throat, and soreness. The reason may be a terrible diagnosis - oncology. If there is constant and aching pain in the larynx and root of the tongue, immediately consult a doctor for an examination.
- Inflammation under the tongue
Under the tongue are a large salivary gland, muscles, blood vessels, the hyoid bone and the frenulum. The cause of inflammation under the tongue can be a sore throat (with the growth of the lesion), glossitis of the salivary gland, or trauma to the frenulum.
- Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the tongue
Inflammation of the mucous membrane is accompanied by the appearance of redness and ulcers in the mouth; the cause is usually a fungal infection that spreads quickly.
Infectious diseases of the tongue
Tongue lesions can be caused by fungal, viral, or bacterial infections. The nature of changes in the tongue depends not only on the underlying disease, but also on its stage, severity, and the state of immunity of the whole organism.
- Candidiasis is a disease caused by yeast-like fungi, widespread in the environment and normally present on the skin and mucous membranes. In the development of candidiasis, a major role is played by decreased immunity, weakening of the body's defenses, use of antibiotics, and chronic trauma to the tongue. With the pseudomembranous form, a white “curdled” coating is observed, which is easily removed from the back of the tongue, revealing a bright red, painful surface. With atrophic candidiasis in the oral cavity, pathological dryness, redness of the mucous membrane and severe pain can be observed. There is very little flying time.
- Herpetic glossitis is a disease of a viral nature, the occurrence of which is provoked by stress, hypothermia, the menstrual period, and acute respiratory infections. Single or multiple blisters are observed on the tongue; when opened, severely painful erosions are formed that tend to merge. The general condition of the body suffers: body temperature rises, headaches, pain in joints and muscles appear.
- Streptococcal impetigo of the tongue is a lesion caused by streptococcus, characterized by a rash of superficial blisters (phlycten) on a bright red background up to 1 cm with transparent contents. The lesions quickly open, revealing round, painful erosions.
Types of glossitis
Various causes of diseases have given rise to a whole classification of this disease; there are several types of glossitis, among which the most common are:
- Purulent-phlegmonous glossitis
It consists of ulcers of varying sizes on the tongue or oral cavity. The abscess requires surgical intervention, that is, excision by an experienced surgeon.
- Desquamative glossitis
Appears as a result of disruption of the gastrointestinal tract (gastrointestinal tract) or malfunction of the cardiovascular system, respectively, and treatment is prescribed after examination and elimination of the cause of the failure. In some cases, it can manifest itself during pregnancy due to changes occurring in the woman’s body and decreased immunity.
- Gunter's glossitis
This disease is a consequence of a deficiency of folic acid and vitamin B12; treatment occurs by normalizing the necessary elements and vitamins.
- Candidal glossitis
Dry throat and redness of the tongue are symptoms of candidal glossitis, which spreads due to infection with a fungus, against the background of reduced immunity.
Symptoms of glossitis
How to understand that inflammation is associated with glossitis? There are a number of symptoms by which you can recognize the disease yourself:
- Burning, irritation and pain.
- A feeling of foreignness, due to the fact that the tongue may swell and crack.
- Additionally, the palate swells, making swallowing more difficult.
- Color change: white coating, gray “villi”, red, bright scarlet surface, up to a burgundy tint.
- Another surface relief (“geographic tongue”, convex spots, growths, villi, torn or, on the contrary, tongue smooth without roughness).
- Absence or change in taste characteristics.
- Enlargement of the tongue, consequences: the palate, throat begins to pinch, painful eating and drinking.
- Violation of the speech apparatus.
- The sores may bleed.
- Impaired tongue mobility.
- The occurrence of purulent processes.
- Inflammation of the neck, chin. The process can encumber the lymph nodes.
- Increased secretion of saliva.
- Loss of sensation of the tongue on the back and tip.
- Burning throat - causes of symptoms, diagnosis of possible diseases and their treatment
- White plaque on the lips in children and adults - causes, treatment with medications and rinses
- Herpes on the tongue in children and adults - causes, symptoms, treatment with antiviral drugs
Inflammation of the tongue: treatment
For diagnosis and treatment, you need to see a doctor: a therapist or an otolaryngologist; you may need to consult a dentist. First of all, you need to establish the cause, because inflammation of the tongue can be only one of the symptoms. You will be asked to take a number of tests, including:
- general blood analysis
- swab from the affected part of the mouth
- blood test for viral infections
Based on the results, your doctor will be able to make a diagnosis and suggest one of the following types of treatment:
- anti-inflammatory drugs
- antiseptics for treating the oral cavity
- vitamin complexes to improve immunity
- mouth rinse infusions
Compliance with all instructions will allow you to quickly get rid of painful sensations and recover. During treatment, you may be prescribed a diet that excludes very hot or cold foods, fried, salty and sweet foods. Treatment time depends on the stage of the disease and its cause, so it can range from several days to several months. Treatment takes place at home, without hospitalization.
Treatment of candidiasis
Externally, the oral mucosa is treated with a solution of borax in glycerin at a 10% concentration. You should also rinse your mouth with chamomile decoction, soda solution and irrigate the mucous membrane with 2% boric acid. Tablets for oral administration with antifungal effect:
- Nystatin is a rather old, but proven and effective remedy for Candida fungus, tablets with a dosage of 250-500 thousand units. taken 3–4 times a day, it is not recommended to crush or chew them beforehand; the course of treatment is 10–14 days.
- Lamisil - tablets that need to be taken one per day (active substance content 250 mg), the course of therapy depends on the depth of damage to the epithelial layers and the duration of the disease.
- Terbinafine is a fungicidal agent, which will take from a week to 1-2 two months to be treated, take one tablet once a day with a dosage of 250 mg.
In case of fungal etiology of glossitis, drug therapy should be aimed at destroying the yeast-like pathogen from the Candida group
It must be remembered that candidal glossitis often accompanies long-term infectious diseases, for which the patient uses large doses of antibiotics. Sometimes it is enough to cancel antibacterial agents and apply external treatment to the tongue several times so that the symptoms of glossitis go away on their own.
Behavior in case of inflammation of the tongue
When the first symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor, because as we have found out, the reasons can be completely different: from harmless and easily treatable to complex complex diagnoses. In the event of illness, to maintain the health of your loved ones, use sterile masks (change every two hours), because many forms of infectious glossitis are very contagious.
- In order not to further irritate the already affected oral cavity, limit yourself to very salty and spicy foods; food should be at room temperature.
- If you have difficulty swallowing, use a blender to homogenize the food.
- Use individual devices to avoid infecting your family members.
Follow all the instructions, then you will quickly get rid of the symptoms and defeat the disease. Vitamin complexes will help strengthen the immune system and reduce the chances of a recurrence of the disease.
Treatment methods
Treatment includes measures to remove infection and bacteria with antiseptic drugs (tinctures, sprays, tablets, solutions).
For streptococci or Candida fungus, antibiotics of the penicillin group are prescribed. Rinsing with antiseptic solutions will help. Ointments and gels are used: Nystatin, Metrogyl denta, Pimafucin.
Glossitis caused by herpes virus infection is treated with Acyclovir, Zovirax, Viferon, Tebrofen ointment, Virumerz sirol. For glossitis, rinses with traditional anti-inflammatory drugs are also used, as well as medicinal solutions and oils: Chlorophyllipt, Chlorhexidine, Furacilin, Borax solution. For severe pain, use Novocaine, Lidocaine, and other painkillers.
To increase immunity and the body's resistance to viruses and bacteria, immunostimulating drugs and vitamins are prescribed.
In case of traumatic injury (frostbite, bites, cuts, injuries), medicinal and folk methods with antimicrobial, healing effects are used: Furacilin, manganese solution, Chlorhexidine, Aqua solution (soda, salt, iodine), herbal decoctions (chamomile, calendula, burdock), lotions with essential oils (tea tree, sea buckthorn, aloe, bergamot). Special gels and ointments are used: Oxolinic ointment, Methyluracil.
For stomatitis, decoctions and medicinal rinses are used, as well as: Actovegin, Cholisal.
Catarrhal glossitis and leukoplakia are treated with antiseptic drugs, such as Hexoral, Hexetedine, Kamistad, soda and iodine solutions.
For streptococcal impetigo and lichen planus, not only local remedies are used, but also antibiotics: Ceftriaxone, Meropenem. Lozenges: Faringosept, Septefril.
Ulcerative glossitis, abscesses and other problems associated with an incorrectly performed procedure or uncomfortable prostheses (crowns, implants) are treated surgically using local anesthesia, antibiotics and antiseptics.
The tongue takes part in the formation of speech, contributes to the complete processing of food in the oral cavity and is the strongest muscle. But its mucous membrane is very vulnerable to the action of many negative factors.
In addition to direct exposure to pathogenic microorganisms, thermal burns and injury from food or teeth, this organ also suffers from many internal diseases. Diseases of the tongue and their symptoms are varied, so such diseases must be treated under the strict supervision of a dentist, therapist, gastroenterologist or other specialist as indicated.
Prevention of tongue inflammation
Of course, it is better not to deal with inflammation of the tongue, because a person cannot even eat and talk calmly because of the pain. To prevent this disease, use the following measures:
- Daily oral hygiene
- Diagnosis of gastrointestinal diseases
- Regular visits to the dentist and therapist
- Proper nutrition (refusal of salty and fried foods, scalding drinks)
- Quitting smoking and alcohol
It is easier to prevent a disease than to treat it later. Treat yourself carefully - the tongue is an important indicator of your health and the consequences of various diseases will primarily be reflected on it. Take care of yourself and be healthy!
Taste sensations
Due to the fact that many taste buds are concentrated on the surface of the tongue, we know that cucumbers are salty, sugar is sweet, lemon is sour, and medicines are bitter. It turns out that the tongue is the first to make a critical assessment of the food that should enter our stomach.
At the same time, different areas of the tongue have unequal sensitivity to different taste substances. Typically, sweet is recognized by the tip of the tongue, and bitter by the root of the tongue. The taste buds themselves are extremely fragile creatures and without saliva would have long since failed. And so saliva dissolves dry substances that enter the mouth and stimulates taste buds.
It also washes away the remaining taste from the surface of the tongue, so that we can experience a whole series of consistent taste sensations within a short period of time. But, most importantly, the protein found in saliva has the ability to bind acids, protecting the oral mucosa and the taste buds located in it from their harmful effects.
As sad as it may be, not all of us are able to enjoy the taste. And this happens for a number of reasons. For example, due to frequent burns of the mucous membrane of the tongue, when we hastily throw too hot food into ourselves, or pour in a surrogate of unknown origin, causing a chemical burn.
A change in taste sensations or their loss can occur as a result of damage to the conduction pathways of the taste analyzer: for example, loss of taste in the anterior two-thirds of one half of the tongue is associated with damage to the lingual or facial nerve, in the posterior third of the tongue - with damage to the glossopharyngeal nerve. That is why doctors disapprove of a child’s early exposure to overly peppered or spicy foods, the abuse of which can lead to a distortion of the sense of taste.
In some cases, perversion of taste is caused by diseases of internal organs or metabolic disorders: a feeling of bitterness is noted in diseases of the gallbladder, a feeling of acidity in diseases of the stomach, a feeling of sweetness in the mouth in severe forms of diabetes.
How to prevent the development of the disease
After cured glossitis, the tongue may become inflamed again, so regular prevention of the disease is necessary. There are no specific recommendations for preventing this pathology. Therefore, you need to adhere to general rules of oral care.
You can only use high-quality pastes and rinses: “Forest Balsam”, Colgate, Listerine. Teeth should be brushed with brushes with medium-hard bristles, which should be changed approximately every two months. To prevent infection of the oral mucosa with fungi and viruses, you need to thoroughly wash your hands and utensils.
Nutrition must be correct and balanced. Eat very cold or hot food as little as possible, and do not eat too many salty and sour foods. The diet should contain proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins and minerals.
Baby supplies need to be disinfected
Prevention of glossitis in babies involves regular disinfection of bottles, pacifiers, and toys. You need to carefully select care products and carefully monitor the child’s reaction to them.
If you liked the article, please like it.
In the comments, please share your experience in identifying the signs of glossitis and treating this disease.
Types of inflammation of the oral mucosa
Inflammation of the oral mucosa is a key symptom in diseases such as:
- stomatitis;
- gingivitis;
- herpes stomatitis;
- traumatic inflammation of the mucous membrane.
In all these diseases, the symptoms will be the same: pain in the mouth, in the gum area, on the lips, cheeks, or severe sore throat. Often inflammation of the oral cavity is accompanied by suppuration if it is not treated in time. In mild cases, rinsing with medicinal herbs, teas, antiseptic solutions and, less often, antibiotics are usually used, but these are prescribed only by a doctor.
Inflammation of the mucous membrane in the mouth belongs to the group of dental diseases. As a rule, the mucous membrane tends to become inflamed due to certain changes in the human body, which should be paid attention to. In this case, injuries to the shell or its burns are considered isolated cases, for the treatment of which, if we are not talking about serious injuries, you can use folk remedies like the same rinses.
How does complicated pathology manifest itself?
Now let's talk about the symptoms of glossitis in an advanced stage. If the inflammation is not treated, abscesses will begin. They are characterized by acute pain that manifests itself locally. The tongue increases in size, speech loses intelligibility. The location of the abscess hurts even more.
During complications of the disease, the structure of the tongue will begin to change, and the swelling will become dense. Often mushroom-shaped growths appear over the entire surface of the tongue. When glossitis is accompanied by phlegmon, the swelling becomes pronounced and appears on the neck. The discomfort becomes even stronger, so it is almost impossible to chew food. It becomes difficult for the patient to breathe, and suffocation may begin. Signs of intoxication also appear:
- severe weakness;
- heat;
- enlarged lymph nodes.
Methods for diagnosing pathology
Before you begin to treat inflammation of the mouth and tongue, you need to establish an accurate diagnosis. Only after this can drug therapy be carried out. The main method is bacteriological examination. It is necessary to take a smear from the root of the tongue, palate, side and inner surface of the cheeks. This procedure allows you to identify the pathogen that caused inflammation of the papillae of the tongue.
All other measures are additional. They help assess the general condition and treat the pathologies that cause the symptoms of glossitis, which are described below. It would not hurt to conduct a histological diagnosis of tissues or do a general blood test. Biochemical studies can determine the condition of the kidneys and liver and identify possible autoimmune pathologies. You need to donate blood for TORCH infections, human immunodeficiency virus and sexually transmitted diseases. Doctors often prescribe an immunogram and stool tests. The tongue is also examined, including from the side. Alarm should be caused by changes in color, pronounced grooves or bumps.
Taking a smear
Why the oral mucosa becomes inflamed: causes and treatment
Inflammation of the mucous membrane in the mouth is a very common disease that dentists encounter almost every day. Naturally, in order to prescribe the correct treatment to the patient, you must first determine the cause of such inflammation. The most common causes of inflammation in the oral cavity are:
- poor oral hygiene;
- advanced caries and its untimely treatment;
- presence of tartar;
- incorrectly made dentures for teeth and other reasons.
Also, the mucous membrane in the mouth can become inflamed due to chronic diseases such as:
- diabetes;
- pathological stomach problems;
- problems with immunity;
- hormonal disorders;
- smoking;
- alcohol abuse;
- hormonal disorders during pregnancy and much more.
Naturally, when a patient comes to the doctor for an appointment with an inflamed mucous membrane in the mouth, the doctor is obliged to do a detailed examination and interview the patient to identify concomitant ailments, also take tests, allergy tests, and can, if necessary, prescribe an examination with other doctors.
And only after all the circumstances have been clarified, he prescribes a treatment regimen, since improper treatment can only aggravate both the inflammatory process and the general condition of the patient. So, for example, if inflammation of the mucous membrane began due to mechanical damage, then only antiseptic treatment of the injury site is suitable as treatment. If the cause of the inflammatory process is a burn in the mouth or frostbite, then anti-inflammatory drugs and even painkillers are added to the antiseptics if the inflammation is accompanied by pain.
If the cause of the disease is the interaction of the oral cavity with a chemically active substance, which often happens in children, then the mouth should be immediately washed with a neutralizing agent, washed with special baths, antiseptic drugs are used and pain-relieving applications are applied to the site of damage to the mucous membrane.
Another treatment will be when the inflammatory process was caused by an infection that appears against the background of diseases such as:
- herpes;
- flu;
- scarlet fever;
- chickenpox and other diseases.
In such cases, treatment includes general therapy, including immunomodulatory drugs, antiviral agents, vitamins, etc., as well as local treatment.
To treat inflammation, antifungal and antibacterial drugs are used if it is caused by Candida fungus or other harmful microorganisms.
Sometimes treatment includes filling or tooth extraction if such a need arises due to injury or severe disease.
In cases where the cause of inflammation is poor oral hygiene, the doctor may prescribe professional cleaning and conduct a hygiene lesson for the patient. If the inflammation is not too painful and is not severe, then such a preventive measure will be quite sufficient.
If inflammation is accompanied by the appearance of swelling or ulcers on the mucous membrane, and pain occurs when eating, then you should consult a doctor and begin treatment, otherwise the inflammation can become chronic and affect the lungs, bronchi and other organs.
Why is the mucous membrane injured?
Sometimes a person may complain of pain in the palate. Often such pain occurs when the mucous membrane is injured while drinking too hot drinks like tea or coffee. The skin on the mucous membrane is very thin and vulnerable, often its integrity is compromised due to ingestion of too hard food. Pain, as a rule, does not begin immediately, but after a few days. Thus, harmful microbes enter the resulting wound and the inflammatory process begins. To prevent this, you need to use an oil solution of vitamin A and rinse the cavity with herbal infusions.
Often, problems with the mucous membrane can arise if you overuse citrus fruits and even seeds, if you chew them with your teeth rather than your hands. So, you should control the consumption of sour fruits and other foods with “sourness”. If the mucous membrane is damaged, it should be treated with a thin layer of retinol ointment or antiseptic.
Read also: Sanitation of the oral cavity
Why does the mucous membrane peel off?
Peeling of the mucous membrane in the mouth is one of the symptoms of stomatitis or due to problems with neurology. The most common reasons for this phenomenon are the following:
- constant neuroses and stress, a constant load on the brain, quite often occurs among students during the session, when after passing it they have dental problems;
- chemical burn of the mucous membrane, which can be caused by vodka or low-quality alcohol in large doses;
- burn from hot food;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, however, they cause stomatitis extremely rarely.
If you have problems with the stomach, the lining begins to peel off completely unexpectedly, so you should immediately consult a doctor, who will actually conduct an examination and prescribe the necessary treatment regimen.
For chemical burns, treatment can be limited to the use of regenerative agents, if they are not too large. But if the problem is a decrease in immunity and nerves, you should start taking immunomodulators, vitamins and sedatives. We also must not forget about rinsing and treating the cavity with special medicines and folk remedies.
It is advisable to take immunomodulatory drugs during the inflammatory process, regardless of the reason that provoked it, since any inflammation is a consequence of a weakening of the body and it should be strengthened and restored.
Piercing and inflammation of the mucous membrane in the mouth: how are they related?
Sometimes the cause of inflammation in the mouth is tongue piercing, which, although extremely dangerous and painful, is still very popular among young people.
The fact is that before this procedure you should sanitize your entire mouth, and also prepare yourself for this operation at least a week in advance by taking a complex of vitamins and minerals.
Sometimes glossitis or an abscess may occur during this procedure, as the body tries to reject the foreign body; this can be avoided by carrying out preliminary procedures. However, such piercing for the mucous membrane is an extremely unpleasant thing, because even if everything heals, accidental injuries to the cavity in the presence of piercing in the mouth are quite common and dentists do not recommend piercing anything in the mouth , so as not to have problems with infections and all kinds of diseases of the oral cavity.
Features of inflammation in smokers
We should also talk about inflammation of the mucous membrane in the mouth of heavy smokers.
Like piercing lovers, they have a choice - the desire to stand out or health. The fact is that, despite all sorts of procedures, a smoking person is not able to protect himself from stomatitis one hundred percent, since the effect of nicotine is much stronger, it is capable of killing all the beneficial substances that appear in the body with the same vitamins.
Naturally, stomatitis in smokers occurs much more often than in non-smokers, and treatment of inflammation will simply be useless if a person does not immediately give up this bad habit. Treatment consists of rinsing and treating the lesions with special ointments.
By quitting smoking and receiving treatment, inflammation can quickly subside, but if a person continues to smoke, the inflammatory process can only get worse even with treatment, since nicotine has the property of corroding a thin layer of the mucous membrane and disrupting its protective properties.
Features of stomatitis in diabetics
This category of patients should also be discussed in detail, since with diabetes, the mucous membrane in the oral cavity is almost always inflamed, dehydrated and constantly cracking.
Treatment of the inflammatory process due to diabetes is extremely difficult; it is necessary to be especially strict about oral hygiene and constantly treat the oral cavity with medicinal agents, in particular, Metrogyl denta, which makes the membrane softer and moisturizes it, which is very important for diabetics.
Preventive measures to prevent any type of inflammation in the mouth are very simple: you need to regularly brush your teeth thoroughly, not only with a brush, but also with floss, to rid the cavity of bacteria and rinse your mouth every time after eating.
You should also carefully monitor your diet, make healthy food choices and avoid eating foods that cause gastrointestinal diseases. Naturally, you need to give up cigarettes and minimize your consumption of alcoholic beverages. It will not be superfluous to take vitamins, as well as means to strengthen the immune system.
Treatment of glossitis
Treatment of tongue glossitis necessarily begins with eliminating the main cause and correcting the disorders caused by the underlying disease. To reduce pain when eating, a gentle diet is recommended: pureed soups, boiled liquid porridges, pureed vegetables. For severe pain, it is suggested to make nutritional cocktails from eggs, sugar, milk and drink them through a tube.
A doctor of any specialty can meet with different types of glossitis at an appointment.
Local procedures:
- several times during the day, before and after meals, rinsing the mouth with disinfectant solutions (Furacilin, potassium permanganate, Chlorhexidine) is prescribed;
- for severe pain, applications with anesthetic drugs (Trimecaine, Pyromecaine, Lidocaine) are indicated;
- if the mucous membrane is dry, then the surface is lubricated with a glycerin mixture with Anestezin;
- To remove fibrin plaque and necrotic epithelium, cotton swabs soaked in a solution with proteolytic enzymes (Trypsin or Chymotrypsin) are used; for painful erosions and ulcers, they are used in applications.
After each procedure, the oral cavity is treated with an antiseptic solution and hydrogen peroxide to prevent re-infection and complications. To speed up healing, gel-like dental products are used (Vinizol, Solcoseryl, Retinol oil solution). They activate the process of tissue regeneration. Contains vitamin A, a little rose hips, and peach.
Depending on the type of glossitis, antifungal drugs, antibiotics are prescribed, antiviral (Acyclovir, Cycloferon) and anthelmintic treatment is carried out. Among immunomodulators, agents that increase local immunity are widely used (Imudon in absorbable tablets under the tongue, Lysozyme drops). The dosage is selected by the doctor individually.
For allergic and autoallergic processes, courses of corticosteroids in the form of ointments are indicated. It is dangerous to use them on your own, as they can cause atrophy of the tongue mucosa. Surgical treatment may be necessary for complications of infectious glossitis (abscessation, phlegmon), villous form. The keratinized part of the mucous membrane is removed and abscesses are opened.
What can you do at home?
Inpatient treatment is recommended in cases of advanced or complicated glossitis. Most patients are treated on an outpatient basis in accordance with the doctor's recommendations. It is necessary to regularly rinse, treat affected areas, and drink antibacterial or antifungal tablets.
For rinsing, special dental kits made from extracts of medicinal plants (Stomatofit, Rotokan) are recommended.
It is necessary to observe the time after the procedure before eating - at least two hours. Folk remedies can be used only after consultation with a doctor. The following have the greatest bactericidal effect and healing effect:
- raspberry leaves;
- coltsfoot;
- sage;
- chamomile and calendula flowers;
- bay leaves;
- celandine;
- Oak bark.
Eucalyptus and tea tree oil are effective for surface treatment. Healers suggest a method of rinsing your mouth with freshly squeezed potato juice. Glossitis is a painful disease. To prevent it, it is necessary to fulfill all the requirements of oral hygiene, treat carious teeth in a timely manner, and give up smoking and spicy food. Respect for your own body will help you avoid many problems.
Causes
There are several causes of glossitis:
- Injury to the tongue. One of the most common causes of the disease. Many victims do not attach much importance to microtraumas of the tongue, but even a slight bite of the tongue with teeth or a puncture with a sharp object (for example, a fish bone) can cause glossitis. Thermal burns can also contribute to the development of the disease, so doctors strongly do not recommend eating excessively hot food or drinking boiling water (for example, tea, coffee).
- Illiterate use of medications. Medicines (especially antibiotics) negatively affect the body's microflora and can contribute to the development of glossitis.
- Allergic reaction . Oral care using special rinses can lead to the development of an allergic reaction. Also, prolonged use of the same paste can cause an allergy to its components. The result is glossitis.
- Bad habits . Alcohol and cigarettes seriously disrupt the body's microflora, thereby weakening local immunity. People with weak immune systems are most likely to become victims of glossitis.
- Infectious diseases . Bacteria and fungi found in the esophagus and mouth are especially dangerous.
According to experts, a lack of vitamins in the body can also trigger the development of the disease.
The following types of glossitis are distinguished:
- Desquamative type of pathology develops due to gastrointestinal diseases or the presence of viral infections, most often observed in women.
- Candidal glossitis is a consequence of the increased presence of Candida fungi in the oral cavity.
- The folded appearance is considered a congenital pathology, characterized by the appearance of folds on the tongue.
- Rhomboid is a chronic disease, the symptoms of which appear periodically, while the patient only occasionally feels discomfort.
- Gunterovsky is a consequence of a lack of vitamins.
- The catarrhal form of the disease is the initial stage of glossitis, the main reason for the development of the disease is improper oral care.
- Atrophic glossitis develops with an infectious lesion of the oral cavity.
- The ulcerative form of the disease occurs when the tongue is injured or there is an infection in the oral cavity.
- Herpetic glossitis is caused by the herpes virus. Recognized as one of the most contagious types of the disease.
- Mycotic glossitis is not an independent disease, but is a consequence of fungal infections.
- Allergic glossitis is caused by intolerance and allergy to products used to treat the oral cavity.
- Interstitial glossitis causes syphilitic lesions of the tongue.
How is the treatment carried out?
Treatment of ulcerative glossitis in both adults and children should begin with eliminating the root cause of the problem, and this requires a thorough diagnosis. Only after identifying the source of the pathology can the doctor offer effective therapy. As for symptomatic treatment, to relieve acute inflammatory processes, specialists usually prescribe the drugs Hydrocortisone and Prednisopon. At an advanced stage and the presence of keratinized areas, they are removed surgically. Remember: only your doctor can prescribe medications; any attempts at self-medication can result in very unpleasant consequences.
To restore organ tissue, doctors usually prescribe rinse solutions with an antiseptic effect. These include “Furacilin” and “Chlorhexidine”. But to cope with pain, doctors usually prescribe drugs that have both anesthetic and antiseptic properties - Ledocaine and Kamistad. When answering the question of how to treat other forms of glossitis of the tongue, it is important to note that therapy is selected taking into account the type of pathology and the individual characteristics of the clinical picture.
Desquamative form of pathology
This form is widely known as “geographic language”. On the back of the organ, irregularly shaped light spots appear framed by a whitish coating. From the outside, the drawing somewhat resembles a map of the world, which is why the disease received its name among the common people. Most often, this type of glossitis becomes a consequence of pathological processes in internal organs and systems.
This is what geographic language looks like
Treatment is primarily aimed at achieving stable remission without exacerbations, since the desquamative type of the disease itself most often has a chronic form. Regular treatment of the organ and tissues of the oral cavity is required using anti-inflammatory gels and solutions, such as Chlorophyllipt or Karotolin. If the patient complains of severe pain, novocaine blockades and phonophoresis (ultrasound exposure simultaneously with drug therapy) are prescribed. The patient will also have to follow a special diet and take B vitamins.
Folded tongue
Quite deep and noticeable longitudinal and transverse grooves are formed on the back of the organ. Most often this is a congenital phenomenon, but there are cases when the pathology becomes a consequence of injuries, burns and infections. Symptomatic treatment of the folded form of glossitis is prescribed in the presence of severe discomfort, burning sensation, pain and breathing problems. In this case, antiseptic rinse solutions are prescribed, for example, Chlorhexidine, as well as anti-allergenic drugs if acute symptoms were provoked by an allergic reaction. During therapy you will have to give up salty and spicy foods.
This pathology is treated when causing inconvenience
Catarrhal type of disease
The development of the pathological process is accompanied by the formation of swelling, redness of individual parts of the organ, and the appearance of a dense white coating over the entire surface of the back. The cause of the problem may be a thermal or chemical burn or mechanical injury. As part of therapy, rinses with antiseptic and anti-inflammatory solutions are prescribed, nutrition is adjusted and vitamin complexes are prescribed.
Some problems can be solved by rinsing
Candidal glossitis
The distinctive symptoms of this pathology are a thick cheesy plaque and bad breath. In this case, patients usually do not experience significant discomfort or pain. Candidiasis infection, caused by too intense proliferation of yeast-like fungi Candida, can be triggered by an imbalance of microflora in the oral cavity after long-term drug therapy, taking antibiotics or insufficient hygiene.
Therapy in this case is aimed at restoring the balance of microflora. To do this, a complete sanitation of the oral cavity is carried out, antifungal drugs are prescribed, such as Nystatin or Fluconazole, and vitamin complexes are recommended to strengthen the immune system.
Diamond shape
The epithelial layer noticeably thickens and becomes thicker, taking on the shape of a diamond or rectangle, and a characteristic plaque appears. This type of illness usually indicates a malfunction of the gastrointestinal tract. Since most often this is only a symptom and not an independent disease, treatment should be aimed at eradicating the source of the problem, and rinsing with antiseptics and anti-inflammatory solutions is usually prescribed to relieve symptoms. If the patient complains of pain, painkillers are prescribed.
Purulent-phlegmous type of pathology
The lesion spreads to the deeper layers of the epithelium and may affect adjacent areas of the oral cavity. This is one of the most severe forms, during the development of which the patient’s temperature rises and all signs of intoxication of the body are noted. In such a situation, antibiotics are usually prescribed: Doxycycline, Ceftriaxone, Rocephin and others. In particularly severe clinical cases, surgical removal of the purulent neoplasm is performed, followed by monitoring the patient’s condition during the rehabilitation period.
Gunter's glossitis
This form develops against the background of serious pathological conditions associated with the functioning of the hematopoietic system. The disease is considered a frequent companion to anemia. In this case, the surface of the organ becomes unnaturally smooth and acquires an overly bright red or crimson color. It is necessary to treat first of all the anemia or pathology that has become the root cause of such symptoms. Vitamin B12 is often prescribed as part of therapy.
The photo shows Gunter's glossitis
"Hairy" tongue
Due to the thickening and keratinization of the filiform papillae covering the back of the tongue, the surface of the organ acquires a dark brown or even black color, its texture becomes rough, visually reminiscent of hard stubble. This type of pathology has been studied much less than others. Until now, experts cannot establish the exact prerequisites for its formation. Possible causes include genetic predisposition, infections, taking powerful medications and bad habits.
This pathology is eliminated surgically
To eliminate the defect, it is usually necessary to surgically remove the hypertrophied filiform papillae, after which antiseptic treatment of the oral cavity and anti-inflammatory therapy are prescribed.
Drug treatment of inflammation
If symptoms of glossitis appear, treatment cannot be delayed and must be carried out under the strict supervision of a therapist. If necessary, your doctor may advise you to consult a dentist. He will also advise you on how to treat glossitis.
Experts usually recommend rinsing with antiseptic solutions: furatsilin, chlorhexidine, miramistin. Treatment of tongue glossitis in children often includes nystanine. According to the instructions, children under 1 year of age should be given 1 tablet per day. From 1 to 3 years – maximum 3 tablets. From 3 to 15 years – no more than 5.
When the tongue becomes inflamed, compresses of ointments with an analgesic and healing effect will help. For example, Kamistad, lidocaine, Solcoserine. If the causes are established and treatment with the above medications does not help, doctors prescribe antibiotics: doxycycline, suprax, rocephin, tetracycline. Read more in the article: “How to treat glossitis.”
Irrigation of the damaged area with medicine
When treating glossitis with medications, it is recommended to take medications to maintain immunity. Vitamin complexes containing large amounts of microelements are suitable. Medicines that stimulate the body’s general immunity are also prescribed.