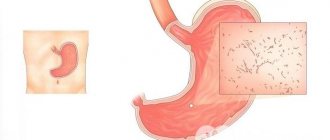
Diverticulosis of the sigmoid colon is a disorder when seals, called hernias, appear on the walls of the intestinal tract. These growths are called diverticula. They can remain in the intestines for many years, but do not show symptoms at all.
If an infection enters the intestinal tract, the diverticula become inflamed—diverticulitis. Formations come in different sizes. It all depends on the stages of formation of the disease. The pathological process is localized in the sigmoid colon - a section of the large intestine. The disease shakes sigma itself. During an exacerbation, the quality of life worsens. Let's analyze the issue of diverticulosis of the sigmoid colon, information about symptoms, treatment of the disease.
Expert opinion
Sevastyanov Roman
General practitioner, hepatologist, gastroenterologist, highest qualification category. Site Expert
Previously, we talked about 5 symptoms of polyps in the intestines, we recommend that you read this information at this link.
Causes of pathology
There are several circumstances under which people develop sigmoid diverticulosis. Let's look at the reasons in more detail:
- Age. When the muscles of the intestinal walls become weak, the process of destruction of the digestive organs begins.
- Weak connective tissues. This phenomenon can be observed at birth or after a failure in the formation of collagen fibers.
- Intestinal motility problems. With high pressure in the cavity of the intestinal tract, the fibers of the walls are weakened, and characteristic compactions appear.
- Muscle spasm. This activates contraction of intestinal vessels and disruption of blood circulation. As a result, the area near the vessels atrophies, and stretch marks appear. As a result, diverticula grow inside the intestinal tract.
- Hereditary character. The threat of getting sick increases a couple of times when elderly family members have difficulties with diverticula.
- Nutrition. Many studies have proven that in African countries, where people have been eating plant foods for a long time, they suffer from diverticulosis much less often than in the West, where meat foods predominate in the diet.
Diverticular disease of the colon
The disease is a neoplasm on the walls of the sigmoid colon in the form of diverticula. The latter look like thinned areas of the mucous membrane that protrude on the surface of the organ. Diverticula of the sigmoid colon can also be congenital due to a developmental defect. The acquired form is more often diagnosed in the older generation, and equally in males and females. The formation of such protrusions is diverticulosis, and their inflammation due to pathogenic bacteria leads to diverticulitis.
- How to stop bleeding from hemorrhoids - a scheme for effective treatment with hemostatic drugs
- Intestinal disease: symptoms and treatment
- Causes of mucus in the stool of an adult - diagnosis and treatment methods
Causes of diverticulitis
The following factors cause the development of diverticulitis of the sigmoid colon:
- Age over 50 years . During the natural aging process, the condition of the intestinal walls deteriorates, which leads to their weakening.
- Genetic predisposition . Those who have a family history of diverticulitis are more likely to develop it.
- Nutrition . The predominance of plant foods in the diet increases the risk of sigmoid diverticulitis.
- Chronic constipation . A condition characterized by increased pressure in the sigmoid colon, which provokes protrusions.
Symptoms of inflammation of the sigmoid colon
Diverticulitis of the sigmoid colon is characterized by an insidious course. In some patients, the symptoms appear very clearly, accompanied even by cramping pain. Diverticulosis of the sigmoid colon in the inflammation stage has other symptoms:
- aching pain on the lower left side of the abdomen;
- unstable stool with frequent constipation;
- bloating with a bias towards the left side;
- heaviness in the abdomen, which goes away only after bowel movements;
- in more severe forms – nausea and vomiting;
- the presence of blood in the stool;
- heat;
- general malaise.
Stages, signs and possible complications
Table of stages of the disease.
| Stages | Description |
| Disease without symptoms | Often the patient does not know about the presence of the disease and only after a random examination for another reason does the doctor discover the pathology. |
| Acute diverticulosis | Distinctive symptoms are spasms of the walls of the sigmoid colon. |
| Complicated disease | The last stage of the disease, which is characterized by a dangerous health condition. Requires immediate medical attention. |
| Diverticulitis | It is formed as diverticula are filled with feces, which creates a suitable environment for the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms. |
| Peri-intestinal infiltrate | In this case we are talking about inflammation of the peritoneum. |
| Intestinal fistula | Spontaneous detection of an abscess is typical, which leads to the formation of fistulas. With this form, surgery is necessary. Intraintestinal hemorrhage. It occurs due to damage to the intestinal mucosa due to the influence of hardened feces. |
| Diverticulum perforation | When perforation affects the peritoneal area, there is a high probability of peritonitis. |
To notice the disease in its premature stages and begin treatment, you should know the symptoms in full. Let's analyze the signs of the disease:
- Abdominal pain is the main and first criterion for the formation of the disease. It is often missed by doctors, because in the initial stages the pain is not severe and disappears after defecation. Such unhealthy feelings are considered as poor nutrition, short-term disorders.
- As the painful course develops, the pain intensifies, becomes dull or pulling, and is expressed in the form of attacks. The main thing is to focus on the fact that unhealthy feelings are localized closer to the navel on its lower side. After eating, the pain worsens, which should alert you.
- In some cases, unhealthy feelings radiate to the right side of the abdominal cavity. Therefore, pain is often confused with exacerbation of appendicitis.
- The pain disappears after the gas subsides.
- There is also heaviness in the abdomen and bloating.
- Frequent constipation with pain. After constipation, diarrhea begins (lots of mucus).
If you experience regular constipation and pain, even minor ones, you need to visit a doctor.
Treatment
With diverticulosis, it is important to normalize stool and intestinal motility. The patient is prescribed a strict diet with a lot of fiber, prebiotics for microflora, laxatives, antispasmodics, remedies for diarrhea and flatulence. Diverticulitis is treated on an outpatient basis with regular monitoring by a specialist.
Diet
In the initial stages of the disease, diet is the main component of treatment. It prolongs the uncomplicated period and prevents the development of the disease. An individual diet should be prepared by a gastroenterologist. After studying the clinical picture, he will write out recommendations.
Those suffering from diverticulosis are advised to consume foods with a lot of fiber, lactic acid drinks, and plenty of fluids. Fractional meals are of particular importance. The menu should not contain sweet, spicy, salty dishes. Strong tea and coffee, sweet flour products and alcohol are prohibited.
Drug therapy
In case of complications, antibiotics and hemostatic drugs are prescribed. To eliminate the symptoms of intoxication, enemas and infusion therapy are used. In severe cases, frozen plasma is used.
High-quality therapy alleviates the condition, eliminates most symptoms, and prevents complications.
Surgical intervention
Surgical treatment is prescribed in the most severe cases:
- Damage to diverticula.
- Internal flow.
- Peritonitis.
- Abscess.
- Tumor growths.
- Fistulas.
During the operation, it is not the growths that are removed, but part of the damaged organ - the segmental intestine is removed. First, the affected segment is cut out, and then the continuity of the entire intestine is restored by stitching together the healthy parts of the organ. The size of the removed segment depends on the severity of the disease. Surgery for diverticulitis is inevitable, but it does not go away without leaving a trace, and the patient will have to carefully monitor his diet throughout his life.
Diagnostics
Since the disease does not initially show symptoms, doctors use certain examination methods. Diagnosis of diverticulosis of the sigmoid colon is as follows:
- X-ray examination of the intestinal tract with a barium mixture. As a result, the diverticula become filled and visible;
- Irigoscopy - study to examine the mucous membrane of the sigmoid colon;
- Colonoscopy is a process similar to the previous examination, only the mucous membrane of the large intestinal tract is examined.
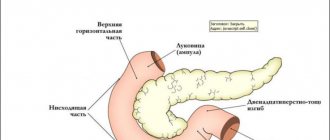
What is the sigmoid colon
The name of the sigmoid colon, one of the sections of the large intestine, is directly related to its shape, similar to the Greek Latin letter “sigma”. It begins in the upper part of the small pelvis with a slope to the left side of the abdomen. Then the sigmoid section passes into the rectum, and its bends can reach the right hypochondrium. The organ itself is completely covered by the mesentery, which consists of a large number of vessels and nerves.
Drugs
Treatment with antibiotics and anti-inflammatory substances is justified for diverticulitis. Conservative therapy, in addition to antibacterial agents, for inflammation, looks like this:
- substances to improve intestinal motility;
- antispasmodics;
- laxatives;
- vitamin complexes;
- medications for hemoglobin growth.
In case of complications in the hospital, medications are administered intravenously, which increases the effectiveness of treatment. Nutrition is administered parenterally, which makes it possible to “rest” the gastrointestinal tract.
Early stage sigmoid diverticulosis can be treated with medication. The main medications on the list are:
| Alpha Normix | An antibiotic belonging to the broad-range group. Presented in the treatment of infectious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, diverticulosis of the sigmoid colon. Recommendations for use prescribe a dosage of 200 mg for adults and children over the age of twelve years. Reception is carried out every 8 hours. The duration of therapy does not exceed 7 days. The medicine can be taken in a repeated course, but only after a break of a month. Price from 650 rubles. |
| Amoxiclav | Belongs to the group of penicillins. Prescribed for inflammation of the urinary tract, problems with the gastrointestinal mucosa. The dosage is 1 pill. The break between doses is also 8 hours. The dosage is prescribed for adults and children over twelve years of age. Cost from 200 rubles. |
| No-Shpa | Shows a calming effect on spasms of the smooth muscles of the digestive organs. The dosage for an adult is from 120 to 240 mg throughout the day. The drug can be divided into 3 doses. Cost from 50 rubles. |
| Buscopan | Prescribed to relieve spasm of the muscles of internal organs, reduces the secretion of the digestive glands. The instructions for use indicate a dosage of 1-2 pills after meals. Take up to 5 times within 24 hours. Cost from 330 rubles. |
| Duphalac | The drug belongs to the laxative group and is sold in syrup form. Helps with long-term constipation. According to the instructions, you can take from 15 to 45 ml. The medicine does not need to be diluted. Cost from 290 rubles. |
| Domperidone | An antiemetic drug that eliminates the feeling of nausea. The drug alleviates dyspeptic symptoms associated with decreased gastric emptying. Adults and children over five years of age are prescribed 10 mg three times within 24 hours, thirty minutes before meals. |
| Linex | A complex remedy that belongs to the group of drugs that normalize intestinal microflora. Prescribed when the composition of the normal intestinal flora changes. A child over twelve years old and an adult are prescribed two capsules per day. Cost from 250 rubles. |
Some recipes useful for diverticulosis
Add 1 tablespoon of bran to 200 ml of kefir or yogurt (any fermented milk product will do) and leave for 30 minutes to swell. Kefir with bran can be consumed instead of breakfast.
Gradually, the amount of bran is increased to 3 tablespoons, and at the same time, be sure to pay attention to your well-being: replacing constipation with frequent loose stools is not the best result. The target stool is soft, shaped, which helps prevent intestinal trauma, relieve inflammation and flatulence.
A decoction of mint, chamomile and plantain seeds has good anti-inflammatory properties.
To prepare, you need to take vegetable raw materials in equal proportions (1 teaspoon each), add 250 ml of boiling water, leave for 1.5 hours. Take 1/2 cup 3 times a day on an empty stomach, 30 minutes before meals, the course of treatment is 10 days.
1 tablespoon of olive, flaxseed or vegetable oil mixed in a glass of kefir will help get rid of constipation; take the resulting product shortly before bed. This recipe can be used for a long time.
A decoction of flax seeds also has a laxative effect.
Example of a diet for 7 days
Many gastroenterologists believe that patients with diverticulosis need to follow a separate nutrition method - consume proteins separately from carbohydrates. The body acquires a maximum of nutrients, and the process of digesting food is facilitated. Taking into account the advice of nutritionists and doctors, below is a 7-day diet for patients with diverticulosis of the large intestinal tract. The menu for each day is presented below:
- Monday and Tuesday. It is preferable to eat liquid food (soups with vegetables), fruits, herbal tea.
- Wednesday. During the day - unload the body. You can drink kefir or eat only apples.
- Thursday. Fish day. You can use the broth with not very fatty river or sea fish.
- Friday. You can eat oatmeal or buckwheat porridge. For lunch you can eat boiled meat and pureed vegetables. It is preferable to eat an orange or banana for an afternoon snack. In the evening you can eat a few spoons of lean cottage cheese.
- Saturday. The day starts with a white omelet. A steamer is useful for cooking. It is preferable to season vegetable salad or porridge with vegetable oil. You can have yogurt for dinner.
- Sunday. You can make vegetable soup, bake fish, eat fruits, drink compote.
What are the types of diverticula?
Diverticular disease of the sigmoid colon is a special case of diverticulosis of the large intestine. A distinctive feature of the disease is the presence of diverticula, protrusions of the intestinal wall. They can be single or multiple, congenital and acquired. Depending on which structures of the intestinal wall are involved in the pathological process, true and false (complete and incomplete) diverticula are distinguished.
| True diverticulum | False diverticulum |
| The anatomical structure of the protrusion wall is similar to that of the intestinal wall, i.e., it includes the mucous membrane, submucosal layer, muscular and serous membranes. | The wall of the formation contains only the mucous membrane and submucosal layer. A false diverticulum that penetrates into the muscular lining of the intestine, but does not extend beyond its limits, is called incomplete. A false diverticulum extending beyond the intestinal wall is called complete. |
| It is a congenital anomaly. | It is an acquired pathological formation. |
| Emptying of the diverticulum is not impaired. | Emptying is difficult. |
| It is most often localized in the right parts of the colon. | It is most often localized in the left parts of the colon. |
In the vast majority of cases, diverticula are found in the left half of the colon (descending colon and sigmoid colon), which accounts for 90% of cases of diverticular disease. In 10% of patients, total damage to the large intestine is observed. The favorite localization of diverticula is the sigmoid colon (50–65% of cases).
General information
Diverticula of the sigmoid colon are one of the manifestations of diverticulosis of the large intestine, which is characterized by the presence of pathological protrusions in the walls of the sigmoid colon, resulting from degenerative processes, impaired motility and chronic constipation.
This is one of the most common diseases of the large intestine. Diverticulosis is diagnosed in almost every tenth resident of developed countries. Approximately one third of cases are due to sigmoid colon diverticula. Another 10-13% is occupied by combined pathology, when the process extends to both the sigmoid and descending colon. It should be noted that only 20% of patients ultimately develop symptoms; in all others, sigmoid diverticula are found incidentally or are not diagnosed intravitally. The problem is relevant for those countries where the diet is very low in high-fiber foods, and less relevant for countries in Africa, Asia and South America. Proctologists treat diverticulosis.
Diverticula of the sigmoid colon
Description of the disease and the causes of its occurrence
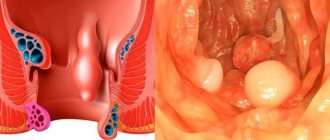
Diverticula are small pouches, protrusions in the wall of the intestine.
Diverticula are small pouches, protrusions in the wall of the intestine. Most often they form in the sigmoid colon, since it is curved and most vulnerable.
Diverticula of the sigmoid colon can be congenital or acquired. Congenital diverticula are formed in a child in the womb due to developmental disorders or unfavorable conditions.
Acquired diverticula appear over the course of life at any age due to poor nutrition, poor lifestyle, or congenital weakness of connective tissue.
If the diverticulum is not single, but there are many of them, this condition is called diverticular disease or diverticulosis. These bulges can collect stool as it moves through the intestines. Retention of feces in diverticula causes inflammation, which is called diverticulitis. Diverticula can vary in size. The larger the size of the diverticula, the higher the risk of complications.
The main cause of diverticula is degenerative changes in the wall of the colon, weakness of connective tissue and vascular changes. The cause of this condition may be other chronic diseases, age or poor lifestyle.
The formation of diverticula is directly affected by nutrition. Insufficient fiber and large amounts of carbohydrates lead to constipation. As a result, hardened feces stretch the intestinal walls, which leads to the appearance of diverticula. People with chronic constipation are at risk for diverticulosis.
Excess weight and lack of physical activity can also lead to the formation of diverticula. Both can cause constipation, hemorrhoids, and diverticulosis. It has been proven that among residents of Asian and African countries, where plant foods predominate, diverticulosis occurs much less frequently than among residents of Western countries.
Sigmoid colon diverticulum is not essentially a disease; it is a condition that is not always accompanied by any symptoms or complications. But if the lifestyle that led to the formation of diverticula remains the same, after a while the diverticulum will become larger, then they will begin to become inflamed and in 20% of cases will lead to complications.
Symptoms and treatment in adults
There are no clinical symptoms specific to this disease that would indicate only diverticulitis.
The diagnosis is established on the basis of complaints, anamnestic data, laboratory and instrumental research methods, as well as directly on the operating table.
Often, patients admitted for emergency surgery with a diagnosis of appendicitis actually have inflamed intestinal diverticula, their perforation with the development of peritonitis.
Nonspecific symptoms of the disease are:
The inflammatory process in the intestinal wall is always accompanied by pain; patients complain of moderate or severe pain in the lower abdomen, often on the left, which does not decrease after defecation.
Often there is a reflex tension of the abdominal muscles in the projection of inflammatory changes, pain increases when coughing, sneezing, after eating, and during physical activity.
Increased pain on palpation of the abdomen and reflex muscle tension are often mistaken for symptoms of appendicitis.
Stool instability manifests itself in alternating constipation and diarrhea. This change is due to irregular motor activity of the intestine, its excessive spasm and subsequent atony.
Inflammatory changes in the saccular branches can lead to erosion and ulceration of nearby vessels, which causes bleeding.
Blood streaks may be found in the stool, or hidden blood loss may be indicated by indirect symptoms: low hemoglobin, pale skin, increased weakness and fatigue.
Toxins and pyrogens formed as a result of inflammation cause intoxication of the body: the patient’s temperature rises, weakness and sweating develop, appetite is impaired, there may be a single vomiting, and nausea appears.
Changes occur in blood tests: ESR accelerates, the number of leukocytes and neutrophils increases. The appearance of these symptoms is evidence of a developing catastrophe in the abdominal cavity.
Such symptoms require urgent diagnosis and treatment; the patient should be hospitalized in the surgical department.
Diverticulosis and its types
To adequately assess the patient’s condition, proctologists have developed a classification of diverticular disease of the sigmoid colon. It has 3 main forms:
- Diverticulosis without pronounced symptoms.
- Diverticular disease with clinical signs.
- Advanced stage, accompanied by complications.
Asymptomatic course of the disease
Most cases of sigmoid colon diverticulosis are diagnosed incidentally when patients are being examined for other pathologies. A person sometimes feels a slight pain that radiates in the abdomen, specifically in the lower left part. The patient attributes this to poor quality food, because everything goes away after a bowel movement or with the release of gases. The doctor recommends following a diet for this form of diverticulosis, and in case of constipation, prescribes laxatives.
With clinical manifestations
A gradual worsening of the symptoms of such a pathology of the sigmoid colon if the doctor’s recommendations are not followed leads to more serious consequences. This is how diverticulitis develops, which can lead to complications of the disease. The severity of symptoms depends on the number of diverticula in the intestine, concomitant ailments and the age of the patient. The pain becomes more acute, becomes stronger after meals and spreads to the buttocks and even the lower back. This form of sigmoid colon diverticulitis requires medical or even surgical treatment.
Symptoms of the disease
Most often, with diverticula of the sigmoid colon there are no symptoms or patients simply do not attach any importance to them. Uncomplicated diverticulosis can manifest itself with signs that are familiar to almost everyone:
- periodic pain in the left iliac region (projection of the sigmoid colon), which weakens after bowel movement;
- the presence of mucus in the stool;
- feeling of fullness and discomfort in the lower abdomen on the left;
- constipation, which sometimes alternates with diarrhea.
If the sigmoid colon diverticulum becomes inflamed, the pain becomes more intense, cramping, or constant. Fever, general weakness and other signs of intoxication may appear.
Important: the symptoms of diverticulosis are similar to many intestinal diseases, and only a thorough examination can establish an accurate diagnosis. Therefore, if similar symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor.
Nutrition during exacerbation of diverticulosis
In case of acute symptoms or exacerbation, the diet is changed. Moderate pain allows the consumption of easily digestible foods. In such cases, the table is set according to model No. 4 (chronic colitis). Severe pain and bleeding may require complete rest of the gastrointestinal tract with fasting and intravenous feeding.
Exacerbations require you to exclude raw vegetables and fruits, and switch only to pureed baked versions. The peel needs to be removed to make it easier for the intestines. Berries only in the form of jelly, dried fruits - from compotes.
Soups are preferably in the form of purees, milk. The porridge is boiled well and made semi-liquid.
Fish, poultry, and meat are prepared by boiling or steaming in the form of cutlets and soufflés. Hard-boiled eggs are replaced with soft-boiled eggs. Omelettes are left.
Products and dishes at table No. 4
Among sweets during an exacerbation, small portions of honey, marshmallows and marshmallows without additives and chocolate are allowed.
It is good to drink bran or oatmeal jelly, rosehip decoction, chamomile or mint tea.
Traditional medicine tips
Centuries-old traditional medicine recipes will help avoid complications, and for some, even the disease itself. For this it is recommended to use:
- aloe juice;
- flax seeds;
- plantain seeds;
- herbal preparations;
- echinacea;
- dill;
- nettle;
- parsley;
- bran;
- honey;
- linseed oil.
Herbal decoctions. For their preparation, herbs are used that have a laxative, soothing, and wound-healing effect. To prepare the collection, take chamomile, plantain, yarrow, echinacea, nettle, mint, motherwort, and mix them in equal quantities in one container. For one dose, you need one tablespoon of this mixture, which is poured with a glass of boiling water, infused and drunk. For each meal you need to prepare a new portion.
Rose hip. Rosehip decoctions can strengthen the intestinal walls and improve blood circulation. But this is a drink that has a fixing effect. Therefore, doctors do not recommend drinking decoctions made only from rose hips. You can add hawthorn. To prepare such a vitamin drink, you must use a thermos. Place two tablespoons of fruit in a liter thermos and pour boiling water over it. It is better to prepare the decoction in the evening. In the morning you don’t have to strain, but divide the entire volume throughout the day and drink it in equal parts with the addition of honey.
It is recommended to drink 30 drops of aloe juice daily. You can add rosehip to the decoction if the juice is unpleasant, or dilute it with honey. There is no need to limit honey; it is a good option to completely replace sugar.
Bran. People with this diagnosis or those who want to avoid the disease should have bran in their diet constantly. This is the richest source of fiber, which is harmful to diverticula. The same can be applied to bran bread.
One tablespoon of bran is poured into a glass of low-fat kefir or milk, stirred and drunk morning and evening. This treatment is progressive: the daily dose of bran should be increased by one spoon. Increase consumption to 10 spoons, then reduce. You don’t have to take a break, but continue in the same order.
Oatmeal or flaxseed jelly. Mucus is very beneficial for the intestines, and you simply cannot find a richer source than oats and flax. These two components can be used separately, or you can make a mix of them. But first they are ground in a coffee grinder, diluted in hot milk or water.
To avoid causing diarrhea, it is better to use skim milk and dilute it with boiled water. Add two tablespoons of the dry mixture to a glass of hot liquid. After this, you need to cover, wrap and let it brew for half an hour. Can be accepted. It is advisable to take two glasses of jelly a day, prepare one in the morning before breakfast, the other in the evening an hour before bed.
Diagnostic methods
First of all, the doctor interviews the patient. Patient complaints may confirm suspicions of diverticular disease. Using palpation, the specialist identifies painful areas on the abdomen. Additionally, the doctor prescribes tests and instrumental examination.
- Blood tests are ordered.
- Irrigoscopy is performed. X-ray examination of the intestine using a contrast agent.
- CT scan.
- Sonography. The procedure helps to identify purulent abscesses and changes in the thickness of the intestinal walls.
- Colonoscopy.
Through angiography and scanning with technetium-labeled red blood cells, the doctor can identify the source of the bleeding. If the formation of a fistula in the bladder is suspected, the patient is prescribed cystoscopy.
Disease prevention
In most cases, the prognosis after treatment of this disease is favorable. But relapse is possible. Regular diet, consumption of foods rich in fiber, and physical activity almost completely eliminate this.
But people of older retirement age, due to their physical health, cannot always follow the recommendations given by their doctor. Therefore, they remain at risk and may experience complications:
- chronic diverticulosis;
- intestinal obstruction;
- diverticulum ruptures;
- intestinal bleeding;
- oncological degeneration of diverticula;
- bacterial infection.
Such complications do occur, but are extremely rare. Therefore, doctors strongly recommend not to forget about diets and regular examinations with a coloproctologist. Be sure to include fiber-rich foods in your diet. Physical activity is desirable, but whenever possible. If you were inactive in your youth, catch up in retirement. Be healthy!
Diverticulosis is a disease that affects hollow organs. It is characterized by the presence of several diverticula - pockets or sac-like protrusions of the wall. The most common diverticulum of the large intestine is diverticulosis of the sigmoid colon. This is due to the peculiarities of the structure and function of this section of the intestine.
Elderly people are more susceptible to the disease. Let's look at the main causes, symptoms and treatment methods for diverticular disease.
The importance of diet
The first assistant in pathology is called diet. It is noted that in countries with a predominant plant diet, diverticulosis is very rare. On this basis, experts reshape the patients’ nutritional regimens in the direction of increasing fiber.
It is fiber that helps improve intestinal permeability and cleanse the mucous walls. At the same time, the main symptoms of diverticulosis disappear - flatulence, constipation, bloating, bloating, nausea, rumbling sounds. Removing processed products from the body reduces toxic poisoning and relieves the body of the need to fight rotting inside.
In addition, stool disorders are an integral component of the disease. Patients often refuse food so as not to be “tied” to the bathroom. The body suffers from a lack of microelements and becomes dehydrated. A reasonable diet brings bowel movements back to normal without loss of nutritional value.
Products recommended for intestinal diverticula