Hydrocephalus is broadly defined as any increase in the volume of cerebrospinal fluid (cerebrospinal fluid or cerebrospinal fluid) in the skull, including cerebral edema, and narrowly defined as enlargement of the ventricle, which causes accelerated growth of the head and requires surgical intervention. The International Working Group on Hydrocephalus describes the condition as active distension of the ventricular system as a result of inadequate passage of cerebrospinal fluid from the site of secretion (in the ventricles of the brain) to the site of absorption into the circulatory system. This definition includes the concept of hydrocephalus as a progressive process.
What is hydrocephalus in newborns
Hydrocephalus of the brain in newborns is a serious disease associated with a malformation of organ tissue when fluid accumulates inside its ventricles. It is not removed from the baby’s skull and is not absorbed into the bloodstream. As a result of this process, the division of brain cells and the formation of new tissues are disrupted.
The subarchanoid space is filled with cerebrospinal fluid. A sick child diagnosed with this pathology is called hydrocephalus.
Hydrocephalus of the brain in newborns is also called hydrocephalus of the brain. This is impaired circulation of cerebrospinal fluid.
If medical or surgical treatment measures are not taken in a timely manner, the newborn will face death or lifelong disability with impaired brain development, which will entail dysfunction of the musculoskeletal system and internal organs.
Symptoms
Symptoms of hydrocephalus depend on the age of the child. In newborns, the following signs can be identified:
- Very large head for its age (see photo)
- Head circumference is growing rapidly
- Too prominent forehead
- The fontanelles are enlarged and protruding
- The veins on the head are swollen
- Eyeball displacement (eye rolling)
- Developmental delays, mental and neurological disorders
- Frequent limb cramps
- The child often spits up profusely, is capricious, and cries.
The symptoms of children over 1 year of age are almost the same, but in addition, a venous network appears on the baby’s face, the child is far behind his peers in development.
Complains of headaches, nausea, fontanelles do not heal until age 3, urinary incontinence, blurred vision, etc.
What to do if there is Staphylococcus aureus in the baby’s stool?
To prevent trouble from taking you by surprise, read how to treat conjunctivitis in a child.
Causes of hydrocephalus
There is an exhaustive list of causative factors that can cause such a serious disease in newborns.
Hydrocephalus may occur in the following cases:
- while passing through the birth canal, the child received a traumatic brain injury , which was not detected by medical personnel and led to the development of complications;
- a woman carrying a child has suffered an infectious disease, microorganisms of which have crossed the placental barrier, penetrated the fetus and provoked irreversible changes in brain tissue (for example, cytomegalovirus infection, syphilis, rubella);
- tumor neoplasms in the brain that disrupt the normal functioning of the ventricles of the organ (can have both benign and cancer etiologies with formation during the period of intrauterine development of the fetus);
- increased intracranial pressure , which led to the occurrence of hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome (most often occurs in cases where a pregnant woman abused alcohol, used drugs and tobacco products);
- underdevelopment of the ducts in the ventricles of the brain, through which the outflow of fluid must be ensured;
- congenital presence of a disease such as Chiari syndrome, when the size of the brain is several times smaller than the internal volume of the skull, which causes an imbalance of intracranial pressure;
- a genetic anomaly associated with chromosomal abnormalities (also found in newborn children in whose family there were similar cases of the birth of newborns with hydrocele);
- intoxication of the child’s body during intrauterine development, which arose in connection with the initial poisoning of a pregnant woman (the toxic effects of toxic substances can be caused by poor-quality food, chemicals, salts of heavy metals, alcohol and other pathogenic factors);
- meningitis, which caused hydrocephalus of the brain in a newborn, as a complication of an inflammatory process of an infectious nature (typical for diseases that occur in the first days after the birth of a child, when the protective function of his immune system is not yet strong enough to withstand such dangerous bacterial agents).
Hydrocephalus of the brain in newborns is a fairly rare disease, which accounts for 0.12% of the total number of congenital malformations.
This also applies to those forms of cerebral hydrocele that were acquired in the first days of a child’s life as a result of an inflammatory process of an infectious nature, trauma, or improperly organized treatment of concomitant pathologies.
Causes of pathology
The causes of hydrocephalus in the first months of life are pathologies of pregnancy, disruption of the formation of the fetal nervous system.
The main causes of hydrocephalus of the brain are congenital and acquired.
Congenital hydrocephalus occurs due to:
- severe infections suffered during pregnancy;
- disturbances in the formation of normal brain development;
- disorders of the synthesis, outflow and absorption of cerebrospinal fluid.
Purchased:
- birth injuries;
- prematurity;
- a consequence of operations on brain structures;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- tumors;
- infectious diseases involving the meninges (meningitis, meningoencephalitis).
At an older age, hydrocephalus can develop on the basis of pathologies that have developed during life. These include injuries, brain tumors, and consequences of infectious diseases. Whatever the causes of the pathology, treatment should begin immediately after it has been diagnosed.
https://youtu.be/x3_SjKq5oHI
Forms of the disease
To make an accurate diagnosis, which includes a list of specific symptoms and a general clinical picture of the course of the disease, hydrocephalus of the brain in newborns is classified into separate forms.
They are as follows:
- open - the ducts inside the ventricles of the organ are completely open, and some of them are even in an overly dilated state, but absorption of cerebrospinal fluid does not occur;
- closed - there is no physiological communication between the ventricles of the brain and other tissues of the organ, which is caused by congenital anomalies, a genetic disorder, adhesions in the canals that were caused by an acute inflammatory process;
- external - excess fluid begins to accumulate exclusively in the subarachnoid space;
- internal - the exact opposite of the external form of hydrocephalus, is characterized by the formation of cerebrospinal fluid inside the ventricles of the brain, and excess fluid does not accumulate in the cavity of the cranium;
- mixed - the rarest form of hydrocephalus in newborns, which is difficult to treat traditionally, as it is characterized by the simultaneous appearance of cerebrospinal fluid inside the ventricles of the brain and the subarachnoid space (this type of pathology is also distinguished by large volumes of fluid, since it is simultaneously distributed throughout all segments of the skull);
- chronic - the disease is sluggish in nature, manifests itself periodically as the body’s reaction to the influence of one or several pathological factors at once (constant contact with toxic chemicals, untreated infection, traumatic brain injury that did not receive timely treatment);
- acute - develops dynamically, and the child’s health condition deteriorates rapidly, completely stopping the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid from the ventricles of the brain and intracranial space (this form of hydrocephalus requires urgent treatment using surgery to prevent extensive cerebral edema);
- occlusive - appears as a consequence of blockage of the ventricular ducts, which is caused by the formation of a foreign obstacle in the form of a tumor, hematoma, blood clots after a stroke or traumatic brain injury (the occlusive form of hydrocephalus in newborns always has an exclusively internal manifestation).
Hydrocephalus of the brain in newborns, regardless of the form of its development, requires a comprehensive examination of the child’s entire body and establishing the cause that caused the pathology of this organ. This will guarantee successful treatment with minimal risk of relapse of the disease.
Causes of water in a child's head
Hydrocephalus in newborns is often a congenital pathology. In three out of four cases, the cause is infectious diseases of the central nervous system that developed in utero. Every third newborn suffers from dropsy due to a head injury during childbirth. In children of different age categories, the causes of the development of the disease may differ:
| Age | Reasons for the development of hydrocephalus in a child | ||
| Often | Rarely | Very rarely | |
| Intrauterine development |
|
|
|
| Baby |
|
|
|
| Over one year old |
|
|
|
Infections, defects, anomalies and oncological formations
Dropsy can be caused by a huge number of reasons. It is noteworthy that some of them may be common to all patients, while others occur only in a certain age category. Infectious causes include:
- rubella;
- cytomegalovirus infection provoked by herpes virus type 1 or 2;
- toxoplasmosis;
- mumps or mumps;
- meningitis and meningoencephalitis, provoked by bacteria and viruses: Haemophilus influenzae, pneumococcus, herpes viruses, meningococcus.
Hydrocephalus in a child of tumor origin is provoked by papillomas, carcinomas, tumors of the cerebral ventricles or skull bones, oncological diseases of the spinal cord, cancer with metastases to the brain. Among the defects leading to the development of dropsy are:
- Dandy-Walker syndrome is a pathology of the development of the cerebellum and subarachnoid spaces. It is characterized by excessive expansion of the fourth ventricle of the posterior cranial fossa and underdevelopment of the middle lobe of the cerebellar vermis.
- Arnold-Chiari syndrome is an anomaly in which the contents of the posterior fossa of the skull descend into the foramen magnum.
- Arachnoid cysts, congenital or acquired after meningitis, surgery, Marfan syndrome.
- Narrowing of the cerebrospinal fluid channels of the brain.
- Congenital underdevelopment of the cerebral veins or openings through which cerebrospinal fluid flows from the aqueduct into the subarachnoid space.
Main signs and symptoms in newborns
Hydrocephalus of the brain in newborns has a main and additional signs indicating the progress of the disease. The basic symptom of the disease is a rapid increase in the circumference of the skull, which can be easily noticed visually without the use of instrumental diagnostic methods.
Additional signs of hydrocephalus in newborns are the following pathological conditions of the body:
- the child behaves restlessly, the head spontaneously throws itself beyond the shoulder line (it becomes extremely difficult to hold the head of a sick child, it requires great physical effort);
- the eyeballs shift to the lower part of the orbits, the child progresses to a severe form of strabismus (attempts to restore the normal position of the eyeballs will not bring a positive effect until the balance of cerebrospinal fluid in the skull and ventricles of the brain is normalized);
- the fontanelle of the newborn is in an inflamed and swollen state, traces of redness of the skin surface appear;
- the baby refuses to eat, or vomits after 1-2 minutes. after feeding;
- convulsions appear, which are expressed in writhing of the body, spasm of the muscle fibers of the lower extremities and the child’s lack of response to external stimuli.
Hydrocephalus of the brain in newborns, which occurs in severe form, can cause dangerous symptoms such as decreased visual acuity and partial hearing loss. The severity of the signs of the disease directly depends on the volume of accumulated fluid, as well as the timeliness of the treatment started.
Diagnostics
To confirm hydrocephalus in a newborn, the doctor will prescribe the following examination methods:
- monthly measurement of head circumference - by applying a centimeter tape;
- fundus examination – in case of swelling of the optic disc in newborns, fluctuations in intracranial pressure should be excluded;
- radiography of skull structures - examination of sutures, bone density;
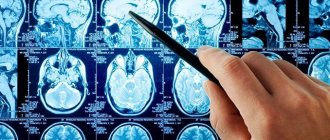
- magnetic resonance or computed tomography – the most accurate diagnosis of hydrocephalus, its causes and consequences for the newborn;
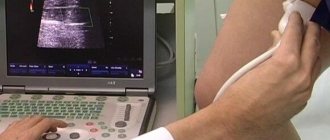
- In babies under one year old, neurosonography or ultrasound of the skull is often used - examination through a fontanel that has not yet become overgrown, which is completely safe for the baby.
The specialist evaluates all the information from instrumental diagnostic methods, and then compares it with complaints and the results of a neurological examination of the newborn. In this case, it is possible to correctly carry out differential diagnosis and select effective treatment. Since various diseases in infants can provoke increased secretion of cerebrospinal fluid, with hydrocephalus the symptoms and information from instrumental studies do not always coincide.
Diagnosis
A newborn with signs of hydrocephalus of the brain is examined, starting with the collection of information, which includes the time of the appearance of the first symptoms of the disease, and the establishment of causal factors that influenced the occurrence of the pathology.
Then the attending physician prescribes the following types of diagnostic tests for the child:
- examination by a neurologist - allows you to detect intracranial hypertension, which is a characteristic sign of hydrocephalus in newborns, as well as track reflex reactions to external stimuli;
- echoencephalography is an analogue of the screening method, as it makes it possible to establish a violation of the location of cerebral tissues, the appearance of increased intracranial pressure, and excessive expansion of the walls of the ventricles of the brain;
- neuroimaging - in infants it is performed through the fontanel using the neurosonography method (the location of the excess amount of fluid is determined, and the preliminary volume of cerebrospinal fluid is established);
- MRI of the brain is the most innovative and effective method for studying this organ, which is affected by hydrocephalus (the attending physician receives comprehensive information about the structure of tissues, ventricular ducts, as well as foreign tumors that impede the stable outflow of cerebrospinal fluid).
Analysis of urine, capillary and venous blood is carried out in a standard manner and is necessary so that the doctor has a general idea of the child’s health, the course of biochemical reactions in the body, the absence or presence of inflammatory processes, pathogens of viral and bacterial microorganisms.
The baby is also examined by a pediatric ophthalmologist and otolaryngologist to exclude complications that reduce the functionality of the organ of vision and hearing.
Attention to all factors
To minimize the consequences of hydrocephalus in a child, at the first suspicion of the disease, you should show the baby to a qualified doctor for an accurate diagnosis. The choice of the correct therapeutic approach is possible only if it is possible to establish the cause that provoked the disturbance in the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid. The doctor evaluates the pressure and determines where the substance accumulates. It must be remembered that in some cases the onset of the disease is hidden. In order to notice that something is wrong in time, it is necessary to regularly undergo scheduled medical examinations with him from the very birth of the baby. If dropsy is detected in the primary stages, the disease can be successfully cured completely. Sometimes specific medications are enough. In more advanced cases, the only option is urgent surgery. They choose what to do in a particular case based on the examination. The decision is made by a council of doctors with the participation of a neurosurgeon and neurologist. If a compensatory condition is established, the slightest delay in surgical intervention can already cause death. Adequacy and timeliness of medical care are the main points that make it possible to save a life and restore health to a baby.
Unfortunately, it is not always possible to notice the first signs of hydrocephalus in children in time, since the disease can be hidden at first. This is explained by its features. Hydrocephalus is caused by an imbalance in the production and absorption of cerebrospinal fluid by the cells of the body. The human brain is a complex structured object, supplied with nutritional components through blood vessels. Brain tissue is elastic and dense, but the organ has cavities - the cerebral ventricles. The inner surface of these elements is covered with a vascular network that forms cerebrospinal fluid. The substance washes the spinal cord, penetrates between the meninges, where it is absorbed in the subarachnoid space. There are also vessels capable of absorbing fluid in the spinal column. The cerebrospinal fluid flows through the cranial venous sinuses designated for this purpose. Liquid is absorbed here only at the correct pressure levels, when there is a difference in this indicator in different tissues. If intracranial pressure is higher than sinus pressure, cerebrospinal fluid enters here. When the balance of fluid absorption and production is disturbed, dropsy develops.
Drug therapy
Treatment of cerebral hydrocele in newborns with the help of pharmaceutical drugs has an extremely low therapeutic effect. This is due to the fact that not all types of medications are approved for use on infants.
Drug therapy can be used in the presence of hydrocephalus of the initial form of development, which is not characterized by a large number of complications or rapid dynamics of progression.
In this case, the following drugs are used:
- Actovegin is administered intravenously once a day with an initial dosage of 5 ml (depending on the weight of the newborn and the number of months, the dose can be adjusted by the attending physician to decrease or increase);
- Vasobral - a medicinal solution is used, which is added from a pipette to the formula or expressed breast milk, and then given to the newborn (recommended dosage 2-4 ml 2 times a day);
- Potassium aspartate is a medicinal solution for the symptomatic treatment of hydrocephalus in newborns, which ensures the removal of excess fluid outside the body through the kidneys (effective only if the retention of cerebrospinal fluid inside the ventricles is not associated with blockage of the ducts by tumor growths, hematomas or adhesions);
- Diacarb is a tablet drug that is prescribed based on the ratio of 10 mg/1 kg of the newborn’s weight (so that the child can take the tablet, it is crushed to a powder, mixed with food and fed).
Drug treatment of cerebral hydrocephalus in newborns is individual. The selection of a drug, the duration of therapy and the determination of the dosage of the drug are influenced by factors such as the weight of the baby, the presence of concomitant diseases, complications caused by dropsy, and the body’s response to the treatment process.
Other types of medications may be used at the doctor's discretion.
How is hydrocephalus formed?
Hydrocephalus occurs when the balance between the production of cerebrospinal fluid and its absorption is disrupted. Let's explain what this means.
The brain is a solid, richly supplied structure with dense elastic properties, in which there are several cavities. They are called the ventricles of the brain. They are lined with a kind of “moss” of vessels, and it is this (this is called “plexuses”) that is responsible for the formation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
The ventricles communicate with each other, and the cerebrospinal fluid leaves the brain substance through them. Next, he needs to wash the spinal cord and get into the gap between the middle and inner membranes, which cover both the spinal cord and the brain. In this gap (it is called the subarachnoid space), which is found both in the cranial cavity and in the spine, there are vessels that absorb cerebrospinal fluid, which by this time already contains metabolites that have been processed and released by the brain structures.
Next, the cerebrospinal fluid must enter the special veins that exist in the cranial cavity. They are called venous sinuses and their peculiarity is that they do not collapse, having a special attachment to the cranial bones. The absorption of cerebrospinal fluid into the venous sinuses depends on the difference in pressure: the pressure in the sinuses must be lower than the intracranial pressure.
Liquor performs the following functions:
- being an incompressible fluid, it protects the brain from injury;
- removes certain substances from both parts of the central nervous system;
- maintains constant intracranial pressure;
- ensures balance between the water-electrolyte composition of the circulatory system and this fluid;
- oscillatory movements of the cerebrospinal fluid affect the autonomic nervous system.
Cerebrospinal fluid is produced continuously. Depending on age, it is synthesized from 40 to 150 ml per day (for comparison, in adults - up to 1.5 l/day). This fluid contains some leukocytes in the form of lymphocytes, a certain amount of protein, and electrolytes. The level of gases and sugar correlates with that contained in the blood: for example, the glucose content in the cerebrospinal fluid should be half as much as in the blood.
If a violation occurs:
- formation of cerebrospinal fluid (its excess is synthesized);
- its absorption;
- flow of cerebrospinal fluid along the designated paths,
hydrocephalus develops. Depending on the level at which the disorder occurs, as well as the pressure that is created in the cranial cavity, there is a classification of the disease, which we will consider below. Doctors use it to guide the treatment of pathology.
When the balance between the formation and absorption of cerebrospinal fluid is disturbed, or its circulation suffers, then in order to achieve this absorption at all, the cerebrospinal fluid must be “pushed” into the vessels that utilize it, that is, intracranial pressure must be increased. This leads to expansion of the liquor spaces. The volume of the skull can only be changed in infants in the first months of life (as long as there are fontanelles and the interosseous sutures have not fused), therefore the expansion of the spaces where the cerebrospinal fluid circulates forces the brain to decrease in size.
Hydrocephalus is water on the brain. In the process of brain activity, metabolic processes occur. For their implementation, liquid is required. It contains essential nutrients. It circulates inside the skull, washing the brain, and is constantly renewed.
The liquid is called cerebrospinal fluid. The child's volume is 50 ml. In adults, this figure is 3 times higher (120-150). It is constantly updated. In infants - 8 times a day, in adults - 3. The hematopoietic system, spinal cord and brain are involved in production. In the brain, the ventricles are responsible for the renewal function. The veins in the parietal region are responsible for absorption.
Liquor nourishes and protects the brain from mechanical shocks and injuries, and creates the necessary microenvironment. It maintains the pressure necessary for life, which ranges from 70 to 180 mm Hg. Art. If changes occur in the body, circulation is disrupted and fluid is poorly absorbed. The amount of liquid increases. Hydrocephalus in a child occurs from an excess of cerebrospinal fluid in the skull.
Surgical intervention
Surgery is the most common treatment for hydrocephalus in infants. Timely surgical intervention makes it possible to eliminate excess cerebrospinal fluid, improve the child’s quality of life, or completely restore brain health.
The following methods of surgical treatment are distinguished:
- external drainage - used only in extreme cases, the operation is characterized by the removal of a drainage system from the cavity of the cranium, through which the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid is forcibly carried out;
- neuroendoscopy is an advanced method of treating hydrocephalus, aimed at restoring the ducts in the brain tissue through which cerebrospinal fluid will be drained from the ventricles into the cisterns of the brain;
- bypass surgery is considered the most primitive method of surgical therapy and is carried out in surgical departments of hospitals that do not have the opportunity to use advanced technologies and modern medical equipment (the child undergoes craniotomy, a catheter is inserted into the brain and the ventricle is bypassed to remove stagnant fluid).
The only drawback of the surgical method of treating pathology is the high probability of infection and the development of complications regarding the centers of the brain responsible for the functioning of internal organs, the functionality of the musculoskeletal system, psycho-emotional reactions, and the thought process.
https://youtu.be/I-Utgsk4OiU
Treatment
Hydrocephalus, or hydrocephalus, is most often treated with surgical placement of a shunt system. This system redirects the flow of cerebrospinal fluid from the central nervous system to another part of the body, where it can be absorbed through the blood circulation. Only a limited number of patients are treated with an alternative procedure called endoscopic third ventriculostomy. In this procedure, a small hole is made in the floor of the third ventricle to allow CSF to bypass the obstruction and direct flow to the site of resorption around the surface of the brain.
Therapeutic treatment
Drug treatment for hydrocephalus is used to delay surgical intervention in premature infants with posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus (in the absence of acute hydrocephalus). Normal absorption of cerebrospinal fluid may resume spontaneously during this interim period.
Drugs that affect the dynamics of cerebrospinal fluid through the following mechanisms:
- decreased secretion of cerebrospinal fluid by the choroid plexus - acetazolamide and furosemide;
- increased reabsorption of cerebrospinal fluid - isosorbide (efficacy is questionable).
Therapies designed to alter blood flow or pulsatility, reduce inflammation, reduce oxidative damage, or protect neurons have so far had limited success. Therapeutic treatment is not effective for long-term treatment of chronic hydrocephalus. This may cause metabolic consequences and should therefore only be used as a temporary measure.
Surgical intervention
Most surgeons use systems called shunts to direct fluid from the ventricles to other areas of the body, such as the abdomen, chest cavity, or heart. Each has its own advantages and disadvantages, but the most popular among neurosurgeons performing pediatric surgeries is the abdominal area. Here, the cerebrospinal fluid is absorbed from the surface of the intestines and returned to the bloodstream along with the vital salts and other products it contains.
There are many different bypass systems on the market. The simplest form of a shunt is an inert plastic tube about 3 millimeters thick that allows fluid to flow through it in one direction. There is a valve system that also regulates the flow volume. The shunt is placed into the brain by drilling a small hole in the skull; a reservoir or “bubble” can be felt through the scalp after the procedure is completed. This reservoir allows samples of cerebrospinal fluid to be taken using a tiny needle to test function or infection.
For some types of hydrocephalus, endoscopic third ventriculostomy is preferable to shunt placement. The surgery involves creating a tiny hole inside the ventricle to restore normal blood flow. The neurosurgeon guides the endoscope and microinstruments into the ventricle and makes a small hole. Cauterization of the choroid plexus can be performed during ventriculostomy, reducing the production of cerebrospinal fluid.
Folk remedies
The use of folk remedies in the treatment of such a serious disease as hydrocephalus in newborns has not been scientifically confirmed.
But still, the following homemade medicine recipes are used in everyday life:
- decoction of the roots of calamus - 40-50 g of rhizomes, cleaned of dirt, washed, then pour 200 ml of water and boil for the next 20 minutes. (the newborn is given 1 tablespoon of medicine 2 times a day 30 minutes before meals);
- milk with lemon balm - you will need to take 5 leaves of the medicinal plant, wash them thoroughly under running water, mash until the juice appears, and then pour in pre-expressed breast milk or nutritional mixture (the folk remedy is infused for 40 minutes, the lemon balm leaves are removed, and then feeding is carried out baby milk, which contains beneficial substances of a medicinal plant that can remove cerebrospinal fluid from the ventricles);
- cornflower tincture - you will need to take 1 tsp. dried flowers of this plant, pour 150 ml of boiling water over them and let it brew for 15 minutes. (give the child 1 tsp 3 times a day before feeding).
It is important to remember that traditional medicine strongly does not recommend the use of folk recipes in the fight against hydrocephalus of the brain in newborns. This is associated with a high probability of deterioration in the child’s well-being, complications and even death.
Prevention
In order to minimize the chance of developing hydrocephalus, follow these rules:
- Protect your child from head injuries in every possible way: wear helmets for rollerblading/scooter/bicycle skating, carry him in a car seat, and do not walk in places where there is a danger of injury.
- During pregnancy, a woman should be examined for the TORCH complex of infections, followed by consultation with an infectious disease specialist.
- If ARVI, rubella or any other disease occurs during pregnancy, additionally undergo an ultrasound scan of the fetus and consult with a medical geneticist and infectious disease specialist about the further management of the period of gestation.
- It is imperative to undergo routine examinations by a neurologist, ultrasound or MRI if the child was born premature.
- The previous rule applies to conditions after meningitis, meningoncephalitis, intracranial hemorrhages, and head injuries. Do not neglect visiting a doctor.
- Protect your baby from head injuries.
- During the period of bearing a child, it is necessary to undergo examination for TORCH - infections.
- If during pregnancy the expectant mother becomes infected, for example, with rubella or she gets sick with ARVI, then it is recommended to undergo an additional ultrasound examination and also visit an infectious disease specialist and a geneticist.
It is important to visit a neurologist, MRI or ultrasound if your baby was born prematurely or if he suffered an intracranial hemorrhage, meningoencephalitis, head injury or meningitis.
Now you know what hydrocephalus is in a child and the symptoms of the disease. Remember that by following simple preventive measures, you can prevent the development of pathology. The task of parents is to notice the disturbance in the baby’s body in time and take him to a doctor’s appointment in a timely manner.
Prognosis and consequences of pathology
The consequences of cerebral hydrocephalus in newborns directly depend on how promptly the presence of the pathology was identified and adequate treatment was initiated. A child who has received qualified medical care using medications or surgery subsequently develops without pathological disorders.
Only a minor speech impediment is possible. In case of infection of the shunt, drainage catheter or wound surface of the wound after neuroendoscopy, the development of the clinical picture is difficult to predict. There is a high probability of disability, epileptic seizures or death.
Article design: Oleg Lozinsky
https://youtu.be/kR5lJHsejRQ
How is the disease diagnosed?
A preliminary diagnosis of “hypertensive hydrocephalic syndrome” is made by neonatologists at the maternity hospital. For older children, they have neurologists. Then a comprehensive diagnostic examination is carried out to confirm or refute the diagnosis. In addition to monthly head circumference measurements, the following advanced diagnostic methods are used:
- neurosonography;
- MRI or CT scan of the brain;
- examination by an ophthalmologist of the fundus.
Neurosonography is widely used up to 2 years of age, while the main fontanel is not yet closed. It is used to diagnose the presence of cystic formations, tumors and hematomas.
But a more accurate picture, of course, is provided by an MRI study. Although the examination is quite expensive, this modern diagnostic method makes it possible to see the root of the problem as accurately as possible, which is fundamentally important for further treatment, which in many cases involves surgical intervention.
Diagnostic methods
Even with a pronounced clinical picture of the disease, before making a diagnosis it is necessary to conduct research in a medical institution. A small patient will need to consult a neurologist who will check reflexes and muscle tone. In case of hydrocephalus in children, a congestive disc is detected on the optic nerve. Therefore, they must be examined by an ophthalmologist. Also, if dropsy is suspected in a newborn, then measurements of the chest and head are taken. MRI allows detection of hemorrhages and neoplasms. This type of examination is used to determine the amount of fluid accumulated in the ducts.
In order to study the structure of the brain in detail, it is necessary to perform an ultrasound. A specialist will be able to examine changes in the gray matter through an open fontanel.
Other symptoms of hydrocephalus
https://youtu.be/AwwQtFITb9A
- Veins of large vessels are visible on the frontal, occipital and temporal areas of the head, the scalp is thin and shiny.
- Children with this disease are more tearful and sleep worse than healthy babies, they begin to hold their heads later, and do not smile for a long time.
- The fontanelle, which has not yet had time to overgrow by this time, pulsates and rises above the surrounding bones of the skull.
- The eyes seem deep-set, squint, drooping eyelids, and inability to keep the gaze on one point may develop.
- The knees are bent and difficult to straighten.
- Weak appetite and frequent regurgitation.
- Indifferent behavior of the baby.
- Trembling of limbs.
With intensive progression of the disease, more dangerous manifestations may develop:
- convulsions;
- drowsiness;
- loss of accumulated movement skills and basic communication;
- vomit;
- crying, in which the pitch and sound of the voice does not change.
If such alarming signals appear, this indicates a sharp deterioration in the condition. Therefore, parents are urgently obliged to show their baby to doctors.
Forecasts
The prognosis is influenced by timely diagnosis and therapeutic treatment. A child with such a diagnosis will be healthy and develop well. If therapy was carried out late in infancy, this subsequently affects his mental and physical development.
There are no universal prognoses for hydrocephalus in children. Everything is individual, and there are as many forecasts as there are patients themselves. The most positive prognosis is given with great caution to children with communicating hydrocephalus. With occlusive dropsy, cure without consequences does not happen so often.
Congenital hydrocephalus, if detected in time, is faster and easier to treat than an acquired disease. Hydrocephalus of the first degree is less likely to leave irreversible consequences than extensive and severe cerebral hydrocephalus. The prognosis is more positive the earlier doctors identified the disease and the sooner medical assistance was provided.
Unfortunately, a large number of children who have suffered severe forms of hydrocephalus subsequently develop debility, mental retardation, and mental and personality disorders. Among the lesions of the nervous system, the leading ones are cerebral palsy, as well as lack of coordination of movements.
Children whose parents treat diligently and consciously live much longer than abandoned children with congenital hydrocephalus. Dropsy of the brain is curable. Only the consequences of the disease can be total.
How long and how a child with hydrocephalus will live depends on the cause and type of the disease, as well as the time during which the diagnosis was made. Communicating forms of hydrocephalus have a more favorable prognosis, and congenital, timely diagnosed pathology is easier than acquired.
If treatment is started on time and adequate surgery is chosen, the child’s life continues, but its quality may suffer when various restrictions appear associated with impaired speech, vision, movement, hearing or coordination.
The prognosis for hydrocephalus depends on how quickly and promptly the diagnosis is made and treatment is started. Children with hydrocephalus can live a normal life, although they may face some problems with the maintenance of their shunts. If treatment of the disease in an infant is not started in a timely manner, then its development threatens the child with developmental delays, speech impairment, as well as irreversible changes in the brain leading to disability.
Symptoms
The manifestation of hydrocele is different in newborns and children over two years of age. In order not to miss the symptoms of the disease, you need to know what hydrocele looks like in newborns. The problem can be identified by the fact that the child’s condition is deteriorating and there is a slowdown in development. An open fontanel and soft bones of the skull create favorable conditions for the accumulation of additional fluid in the head. Therefore, the main sign of hydrocephalus in newborns is considered to be an increase in head circumference.
We recommend further reading: Causes of bags under the eyes in a one-year-old child and methods of treating red eyes
The diagnosis can be confirmed by other symptoms: loss of appetite, disturbed sleep, the baby does not hold his head up at the right time. Drooping eyelids and squinting may also be observed. But you shouldn’t wait for the child’s condition to worsen. Any of the listed symptoms is a reason for urgent hospitalization. Because the disease can only be treated in a hospital.
In older children, the pathology has different symptoms. Patients in this age category complain of poor sleep, nightmares, and headaches. Parents may notice that the child has poor coordination, he walks on tiptoes, irritability, and apathy have appeared.
Can dropsy be prevented?
The development of hydrocephalus cannot be prevented.
However, you can reduce its risk in a child using the following measures:
- regular visits to the doctor during pregnancy;
- prevention of infectious diseases;
- preventing injury and using protective equipment (eg helmet).
After a diagnosis of hydrocele in a baby or older child is made, many parents wonder what it is. Hydrocephalus is a condition in which excess fluid accumulates in the brain. You need to remember that the sooner you consult a doctor and carry out the correct treatment, the better the results.
Symptomatic manifestations
Signs of pathological changes can be detected during the prenatal period. The main symptom is a significant increase in head size. If intrauterine hydrocephalus is diagnosed, a woman can give birth exclusively by cesarean section. This will avoid compression of the skull, and, therefore, prevent the development of other pathologies of the central nervous system, which are subsequently almost impossible to eliminate.
The main symptomatic manifestations also include:
- prolonged closure of the “fontanelle”;
- bulge/disproportionate increase in the forehead area;
- bulging and increasing size of the fontanelle;
- uncontrolled eye movement (nystagmus), divergent strabismus;
- overhanging brow ridges;
- disturbance of visual activity;
- change in the appearance of the skin, mainly its pallor;
- increased heart rate;
- chin trembling;
- involuntary twitching of limbs;
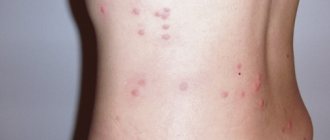
- transillumination of the venous network on the forehead, temples, and back of the head;
- frequent regurgitation;
- excessive tearfulness, capriciousness;
- general restless state of the child, sleep disorder and subsequent developmental delay.
In older children, a venous network appears in the facial area, an increase in the size of the fontanel, which prevents the possibility of its overgrowing, an increase in muscle tone in the limbs, and insufficient mental and physical development of the baby.
As for patients older than 2 years, the disease, as a rule, is severe. The general condition often worsens due to damage to the structural elements of the brain. Symptoms that appear during this period: a significant increase in head size, morning headaches, nosebleeds, attacks of nausea, vomiting, poor coordination of movements, enuresis.
Therapy methods
If microdropsy or the initial stage of its development is detected, complex treatment is prescribed. In the latter case, the doctor’s task is to compensate for the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid by taking diuretics. In the absence of a therapeutic effect, surgical treatment is indicated.
It is possible to cure a child suffering from a mild form of the disease if intracranial pressure is promptly reduced, while simultaneously accelerating and improving the removal of fluid. For this, taking diuretics and potassium supplements is indicated. Open hydrocephalus of a non-progressive nature is treated on an outpatient basis.
The pathological condition should be treated according to the following scheme:
- Diacarb. A drug with a weak diuretic effect helps block the enzyme that is responsible for the production of cerebrospinal fluid. At the same time, the drug relieves swelling, stopping an acute attack of glaucoma, reducing intracranial pressure.
- Asparkam. The medication restores electrolyte balance, supporting cardiac activity. Prescribed in combination with Diacarb.
If a small patient has significantly increased intracranial pressure, then conservative treatment is carried out in a hospital. The child is prescribed medications that remove fluid from the skull. Effective diuretics include osmotic and saline preparations.
They allow you to remove excess fluid through the kidneys. The drug of the first group is prescribed based on the results of laboratory tests related to osmolar plasma. Mannitol is an effective diuretic.
Saline medications (Lasix, Furosemide) remove excess fluid by blocking the absorption of sodium and chlorine ions in the kidneys. It is recommended to drink them in combination with potassium supplements.
If hydrocephalus progresses and the prescribed drug treatment is ineffective, surgery is necessary. The open form of the disease requires lumbar or ventricular puncture. If necessary, external drainage is carried out. It will temporarily reduce the level of intracranial pressure.
If a closed form of dropsy is detected, coagulation is prescribed. In the latter case, the synthesis of cerebrospinal fluid is suppressed. With the help of ventriculostomy, the natural circulation of fluid is restored and new pathways for its outflow are created. To ensure the outflow of water to other body systems, shunting is indicated.
https://youtu.be/bRtZs7jNkCk
Types of hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus can be congenital or acquired. Congenital hydrocele is already present in newborn babies at the time of birth. Acquired hydrocephalus develops during childbirth or after some time; it can occur at any age.
Hydrocephalus is also divided into communicating (open) and non-communicating (closed or occlusive). Hydrocele occurs when the flow of cerebrospinal fluid is blocked after it leaves the ventricles. With closed hydrocele of the head, its outflow is blocked inside the ventricular system.
How does the disease manifest?
In children under 2 years of age
In children under 2 years of age, the presence of the first signs will indicate the presence of hydrocephalus. This:
- deterioration of appetite and sleep;
- refusal of breastfeeding;
- moodiness, nervousness;
- decreased vision, squint, rolling of the eyeball;
- thin, shiny skin of the head with pronounced blood vessels;
- abnormal size of the skull;
- convulsions;
- muscle weakness;
- difficulty holding the head;
- growth retardation.
An experienced doctor will be able to identify dropsy based on the presence of minor symptoms. For minor problems, medication treatment is sufficient. For more severe symptoms, surgery is necessary.
It happens that the disease begins later. The symptoms are characterized by intracranial pressure. The child has:
- severe pain in the head;
- vomit;
- violation of movement coordination;
- fatigue and drowsiness;
- nervousness;
- vision loss and blindness.
School-age children do not adapt well to a group, have difficulty understanding the program, study poorly, and lose their memory. They suffer from nervous disorders. The causes may be various types of lesions:
- tumors;
- meningitis;
- aneurysm;
- renal failure;
- heart and vascular disease;
- hypertension;
- skull injuries.
Signs of hydrocephalus differ between children under 2 years of age and older children.
In children under 2 years of age
At this age, congenital hydrocephalus usually appears. This pathology is severe, the child’s condition quickly deteriorates, and damage to brain structures develops. In some cases, hydrocephalus is a consequence of meningitis or encephalitis, then it has a chronic course.
The peculiarity of the course of the disease in children of this age is due to the fact that the bones of the skull at this age are not yet tightly fused and can move relative to each other, making it possible for additional volume to appear in the skull for an increased amount of fluid. Therefore, the main symptom is an enlargement of the head, which progresses: more than 1.5 cm per month for at least 3 months in a row and more than 9 mm from 3 to 12 months of life.
A child is normally born with a head circumference that is 1-2 cm larger than the chest circumference; by 6 months the ratio should change. If the head remains larger than the chest, it may indicate hydrocephalus.
| Child's age | Normal head circumference, cm |
| Up to 29 days of life | 34-35 |
| 1 month | 36-37 |
| 2 months | 38-39 |
| 3 months | 40-41 |
| 6 months | 43-44 |
| 9 months | 45-46 |
| 12 months | 46-47 |
| 24 months | 48-49 |
| 3 years | 49 |
Other symptoms will be:
- blue-green veins are visible on the frontal, temporal and occipital parts of the head;
- the child is capricious, whiny, sleeps poorly;
- the baby is not gaining weight well;
- after 3 months he begins to hold his head up;
- does not know how to smile;
- begins to sit up late, crawl, walk;
- the skin on the head becomes thin and shiny;
- a pliable place at the top of the head - the fontanel - protrudes above the bones of the skull and pulsates;
- forehead increased in size;
- the pupil cannot stay in one place when fixing the gaze - it will make wide or small fluctuations up and down or left and right;
- the brow ridges hang over the facial skull, making the eyes appear deep-set;
- divergent strabismus is noted;
- frequent regurgitation during feeding;
- throwing back the head;
- it is difficult to straighten your legs, they are bent at the knee joints;
- drooping eyelids;
- when blinking or looking down, a white stripe of sclera appears between the upper eyelid and the upper edge of the iris;
- the child eats little by little, sucks sluggishly, reluctantly.
With rapid progression, which requires immediate hospitalization in a children's multidisciplinary hospital, where there are departments of neurology and neurosurgery, the following signs appear:
- convulsions;
- vomiting;
- crying on one note;
- drowsiness;
- previously acquired skills (sitting, walking, tracking toys) are lost;
- the impossibility (complete or partial) of independent movements in the limbs may develop.
Comprehensive examination
The initial examination of the patient is carried out by a neonatologist. He studies the anamnesis and symptoms. To make an accurate diagnosis, screening tests are prescribed:
- Ultrasound of the skull. Using the technique, congenital pathological conditions are identified. Screening is prescribed for infants in the first months of life.
- CT. The structure of gray matter is studied. CT scan reveals tumors and inflammatory foci.
- MRI. Used to detect hemorrhage and cysts. Using MRI, the doctor receives information about the current condition and structure of blood vessels.
If the diagnosis is confirmed, a consultation with a pediatric ophthalmologist is scheduled. The specialist must determine the primary symptoms of optic nerve atrophy. For this purpose, ophthalmoscopy is performed. Additional neurological diagnostic techniques include EEG and echoencephalography. Based on the data obtained, doctors make a prognosis and decide whether the patient is curable or not.
https://youtu.be/YFSnxFmRmqI
What leads to illness
To understand why the problem appeared and the reasons for the occurrence of dropsy in a newborn, it is necessary to evaluate the situation from different angles.
Among all the existing causes, the main provoking factor is considered to be infection of the fetus from the mother. Hydrocephalus also develops as a result of birth injuries to the head. Sometimes the cause of the disease is associated with genetic defects and pathologies of the nervous system.
Fetal hydrocephalus leads to the fact that due to the strong enlargement of the head, the baby cannot be born like other children. If a woman does not have a caesarean section on time, the baby will be born with pathologies or die.
The main causes of cerebral hydrocele after birth include:
- intrauterine infection;
- underdevelopment of blood vessels;
- developmental pathology;
- birth injuries.
Concussions, hemorrhages, papillomas, and meningiomas can also provoke the development of childhood dropsy.
Diseases such as rubella, herpes, mumps or toxoplasmosis suffered by a pregnant woman, as well as her habits (alcoholism, drug addiction and smoking) lead to hydrocephalus.