- Urinary tract infections - where do they come from?
- Symptoms of lower urinary tract infection
- Urinary tract infections in children
Urinary tract infections - where do they come from? Urinary tract infections are usually caused by the intestinal bacteria Escherichia coli. The bacteria, which reach the bladder through the urethra into the bladder, attach themselves through thread-like structures to the bladder wall and begin to multiply. Inflammation of the bladder (cystitis) and urethritis (urethritis) are the most common urinary tract infections in women.
Urinary tract infections
The concept of “Urinary Tract Infections” (UTI) unites a group of inflammatory diseases of the urinary system, which develop when an infectious pathogen enters the body.
The organs of the urinary system include:
- kidneys - a paired organ responsible for filtering blood and producing urine;
- ureters - hollow tubes through which urine flows into the bladder;
- the bladder is a hollow organ, a smooth muscle reservoir in which urine accumulates;
- The urethra (or urethra) is a tubular organ that removes urine from the body.
Despite the fact that the urinary tract is normally sterile, any organ can be susceptible to the development of an infectious process. A special feature is that in most cases, inflammation is transmitted between organs along the ascending (from the urethra up to the kidneys) or descending pathway (from infected kidneys to the bladder).
Causes of UTI
Causes of urinary tract infection:
- Urodynamic disturbances (vesicoureteral reflux, obstructive uropathy, neurogenic bladder dysfunction).
- The severity of the pathogenic properties of microorganisms (certain serotypes, the ability of E. coli to adhere to the uroepithelium, the ability of Proteus to secrete urease, etc.).
- Features of the patient's immune response (decreased cell-mediated immunity under the influence of factors produced by macrophages and neutrophils, insufficient production of antibodies).
- Metabolic disorders (diabetes mellitus, hyperuraturia, hyperoxalaturia, nephrocalcinosis, urolithiasis).
- Vascular changes in renal tissue (vasoconstriction, ischemia).
- Instrumental manipulation of the urinary tract.
Classification of the disease
There are several classifications of infectious diseases of the urinary system.
By localization:
- upper urinary tract infections, these include inflammation of the kidneys (pyelonephritis), ureters;
- lower urinary tract - bladder (cystitis) and urethra (urethritis).
According to the nature of the disease:
- Uncomplicated . They occur without structural changes in the tissues of the urinary apparatus, in the absence of obstructive uropathy or other concomitant diseases.
- Complicated . They occur against the background of difficulty urinating, when using instrumental methods of examination or treatment (catheterization).
Depending on the location of infection by the pathogen:
- Hospital . Also known as hospital-acquired or nosocomial. They develop when an infectious pathogen enters the body while in a medical institution.
- Out-of-hospital . They develop in an outpatient setting under circumstances favorable for infection.
According to the nature of symptoms:
- Clinically significant infections . They are characterized by obvious, often intense symptoms.
- Asymptomatic infections. The clinical picture is weak, the symptoms slightly worsen the patient’s quality of life.
What symptoms accompany the disease?
There are a number of signs that are characteristic only of genitourinary tract infections. Each disease will progress differently, but if the patient exhibits the following symptoms, this indicates one of the pathologies:
- specific and excessive discharge;
- problems with urination;
- neoplasms in the form of condylomas and papillomas;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- tingling, itching and burning;
- discomfort in the genitourinary tract;
- rash or redness on the genitals.
Factors contributing to the development of the disease
Urinary tract infections are widespread diseases and are among the top five most common infectious diseases. Here are some signs:
- Failure to comply with personal hygiene rules . The perineal area is anatomically designed in such a way that pathogenic pathogens can migrate across the skin from the anus or vagina (in women). Ignoring hygiene rules and unclean hands when urinating can lead to microbial contamination.
- Hypothermia . A cold of the ureter is one of the main enemies of the entire urinary system.
- Decreased immunity . This condition is typical for older people, patients suffering from immunodeficiency and severe chronic diseases.
- Presence of other infectious diseases . For example, the causative agent of sore throat, streptococcus, can cause severe pyelonephritis if it enters the kidneys with blood.
- Inpatient treatment or surgery . In the case of resuscitation or intensive care, it becomes necessary to catheterize the bladder, which violates the sterility of the urinary system and opens the gates of infection.
- Anomalies in the development of the organs of the urinary system. Pathologists can diagnose the disease while the child is still pregnant.
- Obstructive uropathy is difficulty in excreting urine due to urolithiasis, prostatitis or other reasons.
- Unprotected sexual contacts . Some sexually transmitted infections can reproduce in the urinary system and can cause urethritis or cystitis.
The course of UTI is characterized by a number of features depending on the gender and age of the patient:
- Women suffer from infectious diseases of the urinary system much more often than men. This is explained by the proximity of the urethra, vagina and anus, which contributes to the spread of pathogenic microflora. Also, the length of the urethra in women is much shorter than in men, because microorganisms, if treatment is not started in a timely manner, easily reach the bladder, provoking the development of cystitis.
- Men get UTIs less often than women. Due to physiological characteristics, the urethra in men is much longer than in women. Therefore, infectious pathogens reach the bladder or kidneys with less frequency. But the course of the disease is almost always more severe, with intense pain, a high risk of complications such as prostatitis, etc.
In the age group from 20 to 50 years, women are more likely to experience UTI problems. But in the category after 50 years, the situation changes: at this age, the frequency of “male” diseases (prostatitis, adenoma) increases, which can cause complications and spread of infection to the organs of the urinary system.
Prevention of urinary tract infections
1) Importance in preventive measures is given to the timely sanitation of chronic foci of bacterial infection (tonsillitis, sinusitis, cholecystitis, dental caries and others), from which the infection can spread through the bloodstream and affect the urinary system. 2) Compliance with hygienic rules for caring for intimate areas, especially girls and women, pregnant women. 3) Avoid overwork and hypothermia. 4) Timely correction of changes in the human immune system. 5) Timely treatment of diseases of the urinary system (urolithiasis, prostatitis, developmental anomalies).
Infectious disease doctor N.I. Bykova
Pathogens and ways of their penetration into the body
Different types of microorganisms can provoke the appearance and development of inflammation in the organs of the urinary apparatus:
- bacteria (Escherichia coli, ureaplasma, gonococci, streptococci, Trichomonas, listeria, staphylococci);
- mushrooms (yeasts of the genus Candida);
- viruses (herpetic viruses, papillomaviruses, cytomegalovirus).
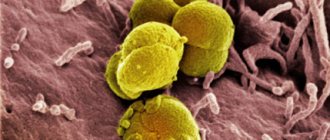
The most common causative agent of UTI is the gram-negative bacterium Escherichia coli (E. coli). This bacterium is classified as opportunistic and is a normal component of the intestinal microflora.
If hygiene procedures are neglected, improper washing of the perineum (from the anus forward), in case of a drop in the body's defenses (hypothermia, the presence of viral diseases), severe forms of dysbacteriosis, E. coli begin to actively multiply in the skin and can migrate to the urethral mucosa, developing which causes inflammation.
There are several possible ways of penetration and spread of pathogens in the urinary tract:
- Contact . Unprotected sexual intercourse (vaginal or anal), migration along the skin from the anus, catheterization, cystoscopy.
- Hemorrhagic and lymphogenous . Entry of the pathogen through the system of body fluids (from the blood or lymph) in the event of the presence of infectious foci in the body. For example, carious teeth, tonsillitis, sinusitis, pneumonia (against the background of an advanced viral infection, a pathogenic pathogen can penetrate the bladder mucosa - hemorrhagic cystitis develops).
- Descending . Movement of the pathogen from the kidneys through the ureters, bladder to the urethra.
- Rising . Infectious inflammation spreads from bottom to top: from the urethra to the kidneys.
Newborns are prone to developing UTIs due to possible birth defects, underdevelopment or late formation of some parts of the urinary system (urethral valves, ureteric orifice). The occurrence of infectious and inflammatory diseases is possible due to improper use of diapers.
For what reasons do women develop diseases of the genitourinary system?
Urogenital infections are now common diseases in men, women and children.
Diseases of the genitourinary system are transmitted sexually. The infection can be caused by viruses, bacteria, fungi, or parasites. “Hidden” infections are considered the most dangerous, since they occur unnoticed and appear at the most inopportune times. Today there is a large increase in urogenital infections, with a large percentage of young people among those affected.
More than half of those infected do not even know they have health problems.
Urogenital infections develop differently in men and women.
In men, the lower urinary tract is affected, resulting in pain and difficulty urinating. In men, inflammation of the genitourinary system is varied: inflammation of the urinary canal (urethritis) and inflammation of the prostate system (prostatitis). In most cases, men are carriers of diseases.
On the one hand, a woman has no risk of inflammation of the genitourinary system, but on the other hand, there is a high risk of urinary tract infection. The disease may occur without acute manifestations or in a chronic form. A woman is mainly susceptible to urethritis, cystitis (bladder) and pyelonephritis. The treatment takes place without the intervention of surgeons.
Cystitis in children occurs with painful and frequent urination, temperature and fever may rise. It occurs more often in girls. In children, this may occur due to frequent use of the pool, sauna, lack of personal hygiene, as well as the presence of chlamydia in their parents.
Signs of urethritis:
- Burning and pain when urinating, frequent urge;
- Copious discharge from the urethra, its sticking and redness;
- Absence of traces of a pathogen with a high concentration of leukocytes in the urine.
- Using special methods for a comprehensive diagnosis of diseases of the genitourinary system, E. coli, gonococcus or chlamydia can be detected.
- Inflammation can occur due to existing diseases (tonsillitis, periodontitis), as well as when an infection enters the urethra due to poor personal hygiene or sexual intercourse.
Signs of cystitis:
- Hypothermia of the body;
- Failure to maintain personal and intimate hygiene;
- Bladder problems (stones and tumors);
- Anomaly of the urinary system
Acute cystitis occurs differently in different people, lasting from two to ten days. Acute cystitis causes increased body temperature, weakness, and pain when urinating. It can develop into pyelonephritis; the tissues of the pelvis and kidneys become infected. In such a situation, hospitalization is necessary.
Chronic cystitis occurs in waves; exacerbations alternate with recessions of the disease. There is a regular constant urge to urinate and pain during this process.
The symptoms of chronic cystitis are constant, only the intensity of pain changes during the treatment process. Laboratory tests cannot detect pathogens in the urine of this chronic form of cystitis.
Tuberculous cystitis is the most dangerous.
Postcoital cystitis (cystitis after sex) - its mechanism lies in the anatomical feature of the female urethra. During sexual intercourse, vaginal mucus refluxes into the urethra and this causes irritation and inflammation. Constantly changing sexual partners further provokes the disease.
“Honeymoon cystitis” appears in a woman who, by the time she begins sexual activity, has disturbances in the vaginal microflora. Even thrush can cause acute cystitis in a woman.
- Developmental disorders of the genitourinary system
- Congenital anomalies
- Diseases (diabetes mellitus, urolithiasis, multiple sclerosis, spinal cord damage, weakened immunity, etc.
) - Sex life
- Gynecological surgeries
- Old age
- Pregnancy
- Foreign bodies in the genitourinary canals.
It can also be the result of severe stress and negative environmental influences.
Before starting treatment, a comprehensive diagnosis is prescribed. The patient must undergo all the necessary tests and only then the doctor makes an accurate diagnosis. In most cases, drug treatment is prescribed. For each type of genitourinary canal disease, treatment is carried out according to a specific scheme. It is not recommended to use traditional medicine for treatment.
- Antibiotics - Furadonin, Furagin, Furazolidone, Palin, Azithromycin.
- Second-line drugs are antibiotics prescribed in a hospital. These include aminoglycosides. These agents have a powerful antimicrobial effect, and some of them have a large list of contraindications. More often, doctors recommend Amikacin.
- Herbs and remedies made from them, used along with antibiotics and other tablets. They are called uroantiseptics of plant origin. It is better to take them to prevent the development of exacerbations and during periods of possible deterioration in health.
- Immunomodulators are used to treat the genitourinary system in women and men.
They improve and accelerate the effect of the main medicine for genitourinary infections.
Vitaferon can be used as such a drug. This is a universal, safe remedy for strengthening the immune system and treating infectious, viral, fungal, and bacterial diseases.
Vitaferon can be taken by adults, children and even pregnant women due to its composition. Ascorbic acid enhances the effect of interferon, and the active substance interferon alpha-2b has antiviral, antibacterial and immunostimulating properties. The drug Vitaferon does not cause side effects.
Release form: suppositories. The doctor prescribes an appointment, depending on the patient’s condition and the course of the disease.
Treatment for this type of disease is almost the same in both sexes. Only during pregnancy and lactation, the doctor can prescribe treatment with Amoxiciln and herbal medicines.
In modern medicine, there is more than one way to normalize the functioning of the genitourinary system by treating kidney and bladder diseases of varying complexity. The attending physician tries to prescribe antibacterial therapy, immunostimulating and phytomedicines, for a speedy recovery of the patient.
The most common cause of pathology of the genitourinary system in the fairer sex is infection with harmful bacteria. This includes fungi, parasites or viruses. At the same time, signs of a disease of the genitourinary system in a woman may be different.
When diagnosing, it is very important to understand which of the pathogens provoked the disease. Here you can note the most common cause of infection. This happens through the anus. Intestinal bacteria enter the vagina, then the urethra and infect the entire system, these can be:
- streptococci;
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa;
- enterococci.
Infectious diseases of the genitourinary system in women can also be provoked by frequent visits to public toilets, swimming in a dirty pond, or by neglecting all the rules of personal hygiene. It is also necessary to constantly monitor the general state of the immune system. If it weakens, the vagina will be the most vulnerable place for bacteria to grow.
For example, thrush develops as a result of the activity of the Candida fungus. If you ignore the deviation, the inflammatory process can spread to other organs of the system. At the first curd discharge, you should consult a doctor and determine the nature of its origin.
Provoking factors for the activation and propagation of infections:
- Untreated chronic diseases.
- Failure to comply with personal hygiene rules.
- Abuse of bad habits such as smoking and drinking alcohol in excessive quantities.
- Poor nutrition.
- Frequent sexual intercourse with different partners and without the use of contraceptives.
- Long-term treatment with certain drugs that suppress the immune system.
Manifestation of symptoms
Clinical manifestations of UTI can appear already at the initial stage of the disease. But the process of infectious inflammation can also be asymptomatic for a long time.
A urinary tract infection can present with various symptoms:
- pain in the pelvic area, lower back, side;
- itching in the urethra;
- burning sensation, pain, difficulty urinating;
- increased urge to urinate;
- uncharacteristic liquid discharge from the bladder (clear, serous, greenish-purulent);
- hyperthermia, chills, fever;
- change in odor and color of urine.
In children, especially younger children, the symptoms of UTIs may be even more vague than in adults.
Children under 1.5-2 years old cannot indicate the location of pain, they become more tearful and restless.
Parents may notice an increase in urination, traces of unusually colored urine on the diaper, and an increase in body temperature.
Characteristic symptoms
Often, genitourinary tract infections are accompanied by painful urination.
Diseases of the genitourinary tract are characterized by certain symptoms. In inflammatory processes, diagnosis is necessary. All diseases progress differently, but the main manifestations are:
- pain;
- discomfort and anxiety that disturb the genitourinary tract;
- itching, burning and tingling;
- discharge;
- problematic urination;
- rashes on the genitals;
- neoplasms (papillomas and condylomas).
Diagnostic methods
A preliminary diagnosis is made after an analysis of the patient’s complaints by a therapist or urologist. To confirm the diagnosis and draw up a set of treatment measures, the following are prescribed:
- general clinical analysis of blood and urine;
- biochemical analysis of blood and urine (metabolic indicators such as urea, creatinine, and some enzymes characterize kidney activity);
- bacteriological culture of urine or PCR analysis (to determine the nature of the causative agent of the disease);
- instrumental research methods (cystoscopy, biopsy, urography, X-ray contrast studies, ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder).
Timely and comprehensive diagnosis makes it possible to identify the disease at an early stage and prevent the spread of the inflammatory process.
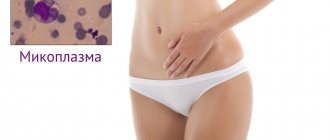
Signs of mycoplasmosis
Women often suffer from this deviation due to weakening of the protective functions of their body. The pathology is localized in the cervix, urethra or vagina. Infection with mycoplasmosis most often occurs during sex if the couple does not use contraceptives. Over time, a woman will develop symptoms such as:
- burning and itching sensation in the external genitalia;
- pain in the lower back or lower abdomen;
- discomfort and pain during sexual intercourse;
- specific vaginal discharge in the form of mucus.
Methods of therapy
The main goal of therapeutic measures for urinary tract infections is to suppress the infectious-inflammatory process and eliminate the pathogen. In the treatment of UTIs, drugs from different groups of antibacterial agents are used:
- Sulfonamide drugs . This group includes Etazol, Urosulfan, and combination drugs (Biseptol). The use of sulfonamides shows high efficiency; they are excreted in the urine, showing high clinical concentrations in the urinary system, and have low toxicity to the kidneys.
- Nitrofuran derivatives. Furazolidone, Negram, Nevigramon, Furagin are used orally, Furacilin solutions are used for washing. Nitrofurans are widely used in the treatment of UTIs, especially if the microorganisms are resistant to other antibacterial drugs. They are active against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, blocking their cellular respiration. However, in the treatment of chronic, sluggish forms, nitrofurans show weaker effectiveness.
- Antibiotics . This group of drugs is the drug of choice when a doctor draws up a treatment program. It may take 3-7 days from the moment samples are submitted for analysis until results are obtained identifying the pathogen. In order not to waste time, the doctor prescribes a broad-spectrum antibiotic. Fluoroquinolones are most often used to treat UTIs. Drugs in this group include Norfloxacin (Nomitsin), Ofloxacin (Oflobak, Zanotsin), Ciprofloxacin. In addition, penicillins (Augmentin), tetrazincines (Doxycycline), and cephalosporins of the second and third generations (Ceftriaxone, Cefixime) are prescribed for the treatment of UTIs.
To prevent the development of fungal infections, antimycotic agents (Fluconazole) are added.
As part of the treatment complex, antispasmodic drugs are prescribed (to restore urinary function), non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and combination drugs of herbal origin (Canephron).
Kidney herbal preparations, teas, and cranberry juice are widely used. Additionally, physical therapy sessions may be prescribed.
During treatment, it is necessary to follow a diet with limited consumption of sour, spicy, salty foods, alcoholic and carbonated drinks, coffee and chocolate. These foods, by changing the pH of urine, can cause irritation of the mucous membrane of the urinary system.
What diet should you follow to prevent infectious diseases?
One of the preventive measures is proper diet. To prevent genitourinary tract infections in women, it is necessary to stop consuming foods that contain oxalic acid or purines. It is also best to reduce the salt dosages commonly used.
Before breakfast, it is recommended to drink 1-2 glasses of plain water; this should become a daily procedure. It is better to eat food in small quantities, more than 4 times a day. There are diets No. 6 and 7. The first is created to reduce the amount of uric acid and salts that are formed as a result of the activity of harmful organisms.
Diet No. 7 can help cope with unstable blood pressure and swelling. Here it is necessary to drink water in moderation and exclude foods such as cereals, salt and other plant foods. With diet No. 6, the patient needs, on the contrary, to drink a lot of water and consume more fruits and dairy products.
Drinking plenty of fluids and eating right is the key to the health of the whole body.
Diet is also disease prevention. It is important to exclude foods that contain purines and oxalic acid. Also limit your salt intake. Make it a habit to drink water on an empty stomach in the morning; only after this small procedure can you eat. Eat small meals 5-6 times a day. Usually, for diseases of the genitourinary system, diets No. 6 and 7 are used.
The main objectives of diet No. 6 are to reduce the amount of uric acid and salts formed in the body. You need to consume more liquid, vegetables and fruits, as well as dairy products. And diet No. 7 is aimed at removing metabolic products from the body, combating swelling and unstable blood pressure. Here, on the contrary, liquid intake is limited, and cereals and salts, mainly plant foods, are excluded.
Consequences of the disease
Urinary tract infections, affecting the mucous membrane, can cause serious consequences for the entire body. Pain and frequent urge to urinate greatly impair the patient’s quality of life.
If treatment is incorrectly selected or the doctor’s orders are not followed, the UTI returns again, causing severe relapses.
Against the background of progressive pyelonephritis, renal failure, deformation of the ureters (prolapse of the kidney), and impaired urine excretion (reflux) may develop. Having a UTI while carrying a child can cause spontaneous abortion at any stage.
How does urethritis manifest?
Inflammatory processes that occur in the urethra are called urethritis. This pathology is not the most dangerous disease and cannot bring big problems to a woman. But this does not mean that it can be ignored and left unattended.
The deviation manifests itself through the following symptoms:
- pain, as well as a sensation of itching and burning when urinating, including during menstruation;
- a slight admixture of pus in urine;
- swelling rarely occurs;
- redness of the outer part of the genital organ.
According to some signs, urethritis can be confused with cystitis, so independent treatment is often useless. To completely get rid of the disease, it is necessary to correctly diagnose it by consulting a doctor and using the medications prescribed by him.
Preventive measures
Preventive measures to prevent UTIs consist of lifestyle adjustments and following certain rules:
- timely treatment of infectious foci in the body;
- compliance with hygiene standards;
- prevent hypothermia of the body;
- empty your bladder on time;
- using condoms during sexual intercourse.
Urinary tract infections are not a strict indication for hospitalization of the patient; outpatient treatment shows high effectiveness if timely consultation with a doctor.
But by not following medical prescriptions and ignoring the symptoms of the disease, you can cause the disease to spread to neighboring organs and provoke the transition of a UTI to a chronic form.
Glomerulonephritis
Glomerulonephritis is one of the most dangerous diseases of the genitourinary system in women. The concept of pathology means that the patient will suffer from streptococcal infection. The disease manifests itself through symptoms such as:
- edema;
- general weakness;
- shortness of breath;
- change in urine color due to blood.
All signs are general; if the form of the disease is acute, high blood pressure and oligonuria may be added, that is, small doses when urinating. Chronic glomerulonephritis usually shows no symptoms at all, especially in remission.
How to treat?
Diseases of the female genitourinary system are most often associated with inflammatory processes. Therefore, to suppress pathogens, you should take an antibacterial drug . However, only a doctor can prescribe an antibiotic based on tests and identification of the pathogen.
The course of antibiotics should be completed completely, otherwise untreated diseases may become chronic.
In addition, along with antibacterial tablets, the doctor may prescribe immunostimulating agents .
Treatment of neoplasms (fibroids, cysts) may be limited to taking hormonal medications , or may lead to surgery.
In addition to drug treatment, you can, with the consent of your doctor, resort to traditional medicine. For this, herbal mixtures and berries are used as decoctions (chamomile, blueberries, leeks, dill seeds, steelberry roots). In addition to herbal decoctions, a decoction of viburnum with honey is used for inflammation of the urinary tract.
List of modern broad-spectrum antibiotics in suppositories
Rectal and vaginal administration, to the same extent as injection, reduces the load on the organs of the digestive tract. Some patients are confused by this release form. Meanwhile, antibiotics for genitourinary infections in children in the form of rectal suppositories are among the best. Depending on the chosen dosage, they can be used in children, adolescents and adults. When treating urogenital infections in women, vaginal suppositories with antibiotic action can be used.
If we talk about specific suppositories, it is worth noting such suppositories as:
- "Indomethacin" in the form of rectal suppositories;
- "Methyluracil" in the form of vaginal suppositories;
- "Terzhinan";
- "Pimafucin";
- Diclofenac suppositories - can be used both rectally and vaginally.
Antibiotic drugs for cystitis and kidney inflammation
Cystitis most often inevitably leads to pyelonephritis. And the reason lies in the fact that women, for one reason or another, put off visiting a doctor and try to be treated with folk remedies or homeopathy. As a result, the infection rises through the ureters and chronic pyelonephritis (inflammation of the kidneys and pelvis) develops. This is a very serious condition that after several years (and in some patients even faster) leads to the development of chronic renal failure. And this disease is already fatal and requires either a donor kidney transplant or attending hemodialysis procedures for the rest of your life.
The most effective antibiotics for pyelonephritis and cystitis:
- "Cefotaxime";
- "Amoxicillin";
- "Lincomycin";
- "Augmentin".
The patient cannot prescribe these antibiotics on his own, since if the type of bacteria that caused pyelonephritis is outside the “action zone” of the drug, then the therapy will be in vain. Only after passing tests and drawing up a complete clinical picture of the disease is it permissible to prescribe treatment.
Symptoms of chlamydia
Chlamydia can be considered one of the most secretive pathologies of the genitourinary tract in patients, as it can occur without showing any signs. But if they appear, special attention should be paid to the following:
- vaginal discharge with an unusual odor and an admixture of pus;
- fever up to 38 degrees and general weakness;
- itching;
- pain in the external and internal organs of the genitourinary system.
If any of the symptoms make themselves felt, you must visit a gynecologist on the same day. Next, you will need to undergo a series of studies, which will determine the nature of the deviations. It is extremely undesirable to ignore these manifestations of pathology, since they can also affect other diseases that are no less dangerous for women.
Trichomoniasis
One of the most common sexually transmitted diseases that can be transmitted to a sexual partner is trichomoniasis. In women, this disease causes damage to the vagina. Trichomoniasis can also be contracted through household contact.
Symptoms of the disease:
- pain during sexual intercourse and urination;
- yellowish discharge with an unpleasant odor;
- swelling and redness of the external genitalia.
To treat this disease, as well as other sexually transmitted or infectious diseases of the genitourinary system, antibiotics are used.
Methods for preventing the inflammatory process
The prescribed treatment must be completed. Many women stop taking medications immediately after relief occurs, not wanting to overload the body with unnecessary chemicals.
However, you should know that the timing and dosage of the drugs are designed to completely extinguish the inflammatory process. Early refusal of treatment is fraught with the return of the disease.
In addition, women need to remember that after treatment for inflammation of the genitourinary system, extreme caution must be exercised. Prevention measures:
- Dress according to the season - overheating is also not good for the body. You should especially be wary of hypothermia. You need to wear warm boots, trousers, tights, preventing freezing.
- It is better to choose linen from natural fabrics. When wearing short skirts, it is better to choose closed panties rather than thongs. It is easy to catch an infection in public transport, a park, or a university. In addition, narrow strips injure the mucous membranes, opening the path to infection.
- When wearing pads, you should follow the rules for changing them. No matter how much manufacturers guarantee their antibacterial properties and convince them that they “breathe,” microbes multiply very quickly in them.
- Cleanliness is the key to health. It is necessary to observe hygiene requirements and wash regularly. Do not use other people's towels, washcloths, or clothes.
A good way of prevention is walking, exercising without fanaticism, light sports, and an active lifestyle. The overall tone of the body promotes good blood circulation, improved metabolic processes and resistance against infection. Then you won’t have to deal with inflammation of the genitourinary system and take antibiotics.
Diseases of the genitourinary system are diagnosed more often in women than in men (due to the anatomical features of the body). The list of diseases includes pathologies of the kidneys, bladder, ureters, fallopian tubes, ovaries, uterus, vagina and urethra.
All diseases are conventionally divided into those caused by infections (viruses, fungi, bacteria, parasites), as well as non-infectious types. Treatment is prescribed based on the results of the examination.
Infectious diseases of the urinary tract and reproductive system are characterized by the fact that inflammatory processes develop some time after infection. It depends on how the infection entered the organ. These diseases have common symptoms:
- problems with urination - you have to visit the toilet often, or, conversely, the urge is false;
- discomfort, pain, acute pain, burning and itching when emptying the bladder;
- swelling;
- dizziness, headaches;
- aching or pulling pain in the lower back, groin;
- sleep problems;
- increased body temperature;
- vaginal discharge;
- the presence of impurities in the urine;
- rash on the external genitalia.
The following infectious diseases of the genitourinary system are distinguished:
Name of the disease
Characteristic
This is an inflammation of the bladder. It is usually caused by E. coli. Cystitis is often a consequence of unprotected sexual intercourse if the woman’s partner was a carrier of any bacterial infections.
The symptoms of the disease are as follows:
- impurities in urine;
- burning during urination;
- pain in the lumbar region;
- general deterioration of condition
This is kidney inflammation. It is usually caused by bacteria. It can develop against the background of other diseases.
- discomfort and heaviness in the lower back;
- stomach ache;
- frequent urination;
- increased blood pressure and body temperature
Diagnosis methods
If you suspect the development of the disease, you must contact a general practitioner, who will issue a referral to a urologist or nephrologist. Patients with urinary tract infections have characteristic external signs that are noticeable to an experienced doctor:
- bags under the lower eyelids;
- swelling of the eyelids, cheeks, puffiness of the lower half of the body;
- gray-yellow complexion;
- burst capillaries of the eyeballs.
Photo gallery: manifestations of external symptoms of pathologies
Swelling of the face forms after sleep
Bags under the eyes in patients with urinary tract infections appear in 2–3 weeks
Broken capillaries are associated with changes in blood pressure
Differential diagnosis of diseases is carried out on the basis of leading and clinical syndromes. To obtain the most complete information about the disease, doctors prescribe various laboratory and instrumental tests.
Taking urine tests requires compliance with some mandatory rules to ensure maximum accuracy of the result. One of my patients gave urine during menstruation, which was strictly prohibited. In the analysis, laboratory technicians saw a large number of red blood cells, which are typical for an acute inflammatory process - pyelonephritis. The patient was treated with antibiotics, which negatively affected the state of her intestinal microflora. After clarifying the situation, the patient had to take probiotics to normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
What studies are used to confirm the diagnosis:
- A general urine analysis characterizes its physical properties and cellular composition. For infectious pathologies, an increase in the level of protein, leukocytes and erythrocytes is typical. This causes the urine to become cloudy and change its color from straw yellow to red, brown or purple.
Blood in urine is typical for inflammation
- The study of urine according to Zimnitsky allows you to determine the concentration ability of the kidneys. Every 3 hours the patient must urinate in special labeled jars. In inflammatory diseases, a decrease in urine density is observed.
- Ultrasound examination of the urinary system can detect structural and functional changes. In the pictures you can see dilated and deformed pelvis and ureters, an increase in the thickness of the bladder wall.
- Urography is the introduction of a contrast agent into the patient’s body, as well as the subsequent creation of X-ray images. The drug allows you to determine narrowings and filling defects in any part of the urogenital tract, which helps to suspect a particular pathology.
The picture shows how the passage of contrast is disrupted
What medications will you need to take?
Even such strong remedies as antibiotics will not cope with the infection alone. To defeat the disease, you will have to take other pills for genitourinary tract infections:
- herbal uroanoseptics:
Canephron is an effective remedy based on natural ingredients, produces an antimicrobial effect, eliminates inflammation;
Phytolysin. Clears the urinary tract of pathological agents, stops the inflammatory process. Contains mint, orange, pine, sage oils, vanillin;
Cyston. Eliminates pathogenic microorganisms and removes their waste products.
- anti-inflammatory - Paracetamol, Ibuprofen, Nimesulide, Tsefekon, Baralgin, Ketanov;
- antispasmodics - Papaverine with No-shpa, Bencyclane with Drotaverine.
- diuretics - Hypothiazide, Diuver, Furosemide, Aldactone.
Important! To prevent diuretics from causing major kidney problems and other complications, at the same time it is necessary to insure yourself with saline solutions, potassium, and calcium.
- multivitamins – Ascorutin, Aerovit, Milgamma, Tetrafolevit.
In the treatment of such female ailments, ladies have a special “demand” for suppositories: Vitaferon, Indomethacin, Voltaren.
List of effective broad-spectrum antibiotics in ampoules
The injectable form of antibiotics for infections of the genitourinary system in women and men has proven to be safe in comparison with tablet preparations. When administered intramuscularly or intravenously, the drug enters almost immediately directly into the blood. Tablets are almost always very aggressive towards the mucous membrane of the esophagus and stomach (which is why they are usually advised to be taken after meals). Injection administration does not have these disadvantages. Rarely anyone knows how to give themselves injections, so such products are used mainly only in hospital settings. In addition, for self-administration of injections, the sterility of the room is very important.
- "Cefoperazone" belongs to the group of cephalosporins. the drug is produced only in the form of ampoules for injection, which should be administered once or twice a day, depending on the pathology. "Cefoperazone" is used for infectious inflammation in the respiratory, urinary tract, and for dermatological pathologies. It has proven its effectiveness as an antibiotic for infections of the genitourinary system in men and women. In some cases, use in the case of gynecological infectious inflammation is justified.
- "Lincomycin" is a universal antibiotic. For genitourinary infections, the latest generation can be used both intravenously and intramuscularly. It is often prescribed for the treatment of the development of infectious pathologies after abdominal operations. The exact dosage and frequency of administration is determined only by the attending physician.