Unfortunately, today there are girls, and even women, who believe that gonorrhea is a “purely male” disease, since a guy “drips from the end.” From here a mind-blowing conclusion is drawn - since there is no “end” for women, this disease is not dangerous: so, you can take a pill, and everything will go away.
In fact, everything is much more tragic. And, above all, illness is the “tip of the iceberg.” We will talk about gonococcal infection.
What it is? Gonorrhea is one of the manifestations of gonococcal infection, the most common in the acute form, and is localized in the genitourinary system. Gonorrhea is caused by gonococci, and manifests itself as urethritis, cervicitis, and vulvovaginitis in women, which will be discussed below.
In general, gonococci cause severe inflammation and swelling in the rectum, mouth and eyes. In addition to the “classical” places, acute gonorrhea affects the Bartholin glands, ovaries and uterus, and cicatricial changes in the fallopian tubes occur.
- This is one of the most common sexually transmitted diseases.
About the causative agent of gonorrhea
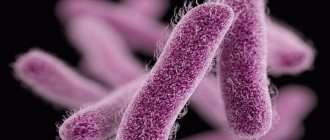
Gonococci are gram-negative bacteria with a round shape. They have a slightly bumpy surface. Often found in pairs. Pathogens are found in large numbers in leukocytes, which are captured and destroyed. Bacteria are clearly visible under a microscope when
Gonococci are not stable in the external environment. They quickly die under the influence of light rays, disinfectant solutions and heat. Certain strains of the pathogen exhibit the ability to become resistant to penicillin.
Rice. 2. Gonococci (Neisseria gonorrhoeae).
Causes of discharge
Gonorrhea discharge is formed due to the active proliferation of gonococci. As a result, a viscous liquid is released, which consists of:
- living and dead microorganisms;
- waste products of gonococci;
- exfoliated epithelial cells;
- in some cases blood.
During the formation process, some components decompose. This is accompanied by the release of gas in a small amount. But it creates an unpleasant odor to the discharge.
Transmission routes
- The main route of transmission is sexual, when pathogens are transmitted during unprotected vaginal or anal intercourse. 20 - 50% become infected with gonorrhea during a single unprotected traditional sexual intercourse. Much less - during oral intercourse.
- During perverted sexual intercourse, gonorrheal inflammation develops in the rectum, pharynx and tonsils. The disease can be transmitted through vibrators and sex toys of an infected person.
- The disease is transmitted from a sick mother to the newborn during childbirth. Gonorrheal conjunctivitis of a newborn occurs with the formation of ulcers that heal with a scar. The disease is complicated by blindness.
- Very rarely, the source of infection for little girls is the personal belongings of a mother with gonorrhea.
- Due to the instability of bacteria in the external environment, the disease is not transmitted through kisses, personal belongings of the patient, cutlery, toilets and in swimming pools.
Characteristic symptoms
Symptoms are different in men and women, due to their physiological characteristics. It may also differ depending on the location of the disease.
Among women
The manifestations of gonorrhea are different and depend on the location of the infection and the concomitant disease.
- Vaginitis. Gonococci are localized in the vagina. Manifestations of the disease include: itching, burning, pain when urinating, pain and discomfort in the lower abdomen, which intensify during menstruation, menstrual periods become more abundant, and discomfort during sexual intercourse. Vaginal discharge is white-yellow in color and has an unpleasant, putrid odor.
- Proctitis. Localization of gonococci in the rectum. Occurs in cases where anal sex is practiced. There is severe itching and burning in the anal area, discomfort during defecation, blood streaks in the stool, and mucopurulent discharge.
- Pharyngitis. Gonococci are localized in the nasopharynx and oral cavity. Infection can occur through oral sex, kissing an infected person, or using their brush, dishes, or cutlery. There is the formation of ulcers on the gums and other mucous membranes of the mouth and throat, enlarged lymph nodes, sore throat, swelling of the tonsils, and increased salivation.
- Conjunctivitis. Localization of gonococci in the eye area. Severe swelling of the eyelids, clouding of the cornea, hyperemia (overflow of blood vessels) of the mucous surfaces appears. In more severe forms, a decrease in visual acuity is observed.
Itching, burning in the lower abdomen - symptoms of vaginitis
If these symptoms do not recognize gonorrhea, which is initially in an acute form, then it becomes chronic. This takes approximately 1.5-2 months. The chronic form is most often asymptomatic; in rare cases, small purulent discharge from the urethra is noted in the morning.
In men
In men, gonorrhea manifests itself quite quickly. Clinical signs are pronounced and cause severe discomfort to the patient. But with different localization and concomitant diseases, symptoms may also vary.
- Urethritis. Localization of gonococci is the urinary tract. When they pass into the posterior part of the urethra, urocystitis is established. In this case, there is swelling of the head of the penis, redness of the skin of the affected organ, pain when emptying the bladder, and possible traces of blood. The discharge is yellowish in color. When a chlamydial infection occurs, the patient's condition worsens.
- Proctitis. Gonococci are found in the rectum. The symptoms correspond to an inflammatory process, there is severe itching, a rash in the anal area, and bleeding is possible.
- Arthritis. Damage to joints by gonococci is a very rare occurrence. Most often it occurs among representatives of non-traditional sexual orientation who practice frequent anal sex. The infection is localized in the ankle and knee joints. When there is swelling and pain at the site of inflammation. To detect the problem, a synovial fluid analysis is performed.
- Pharyngitis. In the nasopharynx area, redness of the mucous membranes is visible, the lymph nodes are enlarged, and rashes in the form of ulcers in the mouth and throat are possible.
Itching in the ball hole is a symptom of proctitis
Most often, men are affected by purulent urethritis. If timely measures are not taken, it goes into the chronic stage. It will take about 2 months to develop. It is practically asymptomatic.
How the disease develops
The latent (incubation) period for gonorrhea ranges from 2 to 5 days for men and from 5 to 10 days (and even 30 days) for women. During this time, gonococci enter from the mucous layer into the submucosal layer, causing its destruction. From there, the infection spreads through the lymphatic tract and enters the blood. Spreading retrogradely, gonococci penetrate through the fallopian tubes into the ovaries, causing their inflammation (adnexitis) and into the abdominal cavity.
With sharply reduced immunity, gonococci can spread through the bloodstream and cause sepsis and damage to certain organs - joints, mucous membrane of the eyes, skin, heart and membranes of the brain.
Video: what is gonorrhea
The incubation period of a sexually transmitted disease lasts from 3 to 5 days, sometimes it is 2 or more weeks. Then the symptoms of gonorrhea come. If you suspect infection, get tested. The doctor prescribes antibiotic treatment, the course is 1-2 days for acute forms and 5-7 for chronic ones. Find out from the video why Bicillin 5 is considered an effective cure for gonorrhea. You will understand why during the treatment process the patient is monitored and how his body reacts to the use of the drug. If there is no positive result, then the antibiotic is changed.
How it manifests itself
Gonorrhea - definition, causes, routes of infection, incubation period
Signs and symptoms of gonorrhea in women
Symptoms of gonorrhea with damage to the cervical canal
In 90% of cases, women are diagnosed with damage to the cervical canal, which is manifested by inflammation and purulent discharge with an unpleasant odor. Pain occurs during intercourse, and bleeding may occur after intercourse.
Symptoms of gonorrhea in the urethra
In 70% of cases, damage to the urethra is detected, which is manifested by purulent discharge from the urethra, frequent urge and terminal pain.
Symptoms of gonorrhea with damage to the small glands of the vestibule and the excretory duct of the large gland of the vestibule
When the small glands of the vestibule and the excretory duct of the large gland of the vestibule are affected, purulent or mucopurulent discharge is noted.
Symptoms of gonorrhea in the rectum
In 40% of cases, gonorrheal inflammation of the rectum is detected, in which redness of the perianal area and the appearance of wounds, rashes, blisters and warts are noted. The disease is manifested by discharge from the rectum, itching, urge and bleeding after defecation. Anoscopy reveals mucosal hyperemia, pinpoint hemorrhages and purulent exudate.
Throat damage due to gonorrhea
In 10% of cases with gonorrhea, throat damage is recorded. The disease is asymptomatic. Sometimes redness of the pharynx with purulent exudate and enlargement of regional lymph nodes are recorded.
Symptoms of gonorrhea when the appendages are affected
When the appendages are affected, pain in the lower abdomen is noted, and palpation reveals enlarged, dense and painful formations.
Pelvic inflammatory disease due to gonorrhea
Pelvic inflammatory disease may be accompanied by high fever, pain, vomiting, vaginal bleeding and painful intercourse.
The asymptomatic and low-symptomatic course of gonorrhea in women leads to late seeking medical help and, as a rule, during the development of complications of the disease, and the woman herself becomes a spreader of the infection for a long time.
Rice. 3. The photo shows gonorrhea in women. Inflammation of the cervical canal and purulent discharge are the main signs of the disease.
Rice. 4. In the photo, a woman has gonorrhea. Purulent discharge with an unpleasant odor is the main sign of the disease.
Prevention
Gonorrhea is a typical infectious disease that is sexually transmitted. But you can reduce the risk of its development to completely insignificant numbers. Prevention of gonorrhea is aimed at strengthening general immunity, preventing contact with the pathogen and normalizing the vaginal microflora. To avoid developing gonorrhea, follow a few simple rules:
- Avoid casual sex. Fidelity and abstinence are the basic principles of preserving a woman’s health. With a large number of irregular intimate contacts with different partners, the risk of contracting gonorrhea and other dangerous infections increases several times.
- When having sex with an untested partner, use a barrier method of contraception. Condoms can protect against most infections, including gonorrhea: the causative agent of the disease does not penetrate through the pores of latex.
You can buy condoms at any pharmacy
- Douche and rinse the vagina with Miramistin solution immediately after unprotected sexual intercourse with an untested partner. This drug helps neutralize the pathogenic effect of gonococcus and causes its death. For the procedure, it is recommended to use a special small vaginal syringe. Remember that such actions are effective only in the first few minutes after the end of sexual intercourse.
- Perform hygiene procedures every evening. The health of the genitourinary tract largely depends on the presence of beneficial bacteria that perform a protective function. If you do not change your underwear every day and bed linen once a week, there is a high probability of the death of beneficial microflora and the proliferation of harmful ones, which helps create a better environment for the development of gonorrhea. To maintain optimal balance, it is recommended to use intimate hygiene products.
Intimate hygiene soap does not disturb the fragile environment of beneficial vaginal microorganisms
- Before planning a pregnancy and if any doubtful symptoms appear, be sure to consult a gynecologist. Keep in mind that a truly reliable diagnosis can only be made by an appropriately qualified doctor.
- Regularly undergo preventive medical examinations and tests. Smears are used for timely diagnosis of many genital diseases. Every woman should be examined by a gynecologist once every six months to determine primary and secondary ailments.
- Play sports. With a sedentary and inactive lifestyle, discomfort in the pelvic area quite often occurs. These are stagnant phenomena associated with insufficient blood circulation throughout the body. Unfortunately, they make a woman more vulnerable to the action of pathogenic microorganisms. To avoid such complications, do a light warm-up (no more than fifteen minutes) during each working day. The general condition of the immune system is beneficially affected by visiting the pool or gym, doing yoga, dancing or jogging in the fresh air.
Yoga helps eliminate blood stagnation in the body
- Treat chronic diseases. The body is an interconnected system in which one pathological process can give impetus to the development of another. That is why doctors recommend getting rid of the problem immediately, even if it does not cause significant inconvenience and does not interfere with the quality of life. Remember that a healthy and strong body has a much lower risk of acquiring a chronic illness.
Complications
Pelvic organ damage
When infection penetrates the fallopian tubes and ovaries, chronic adnexitis develops. The disease is accompanied by the development of a large number of scars, which leads to the development of ectopic pregnancy, obstruction of the fallopian tubes and infertility.
With gonorrhea, purulent discharge often affects the skin. Purulent inflammation of the Bartholin glands and bladder develops. When infection penetrates the tissue, parametritis develops.
Lesions of other organs
When the infection spreads through the blood, joints, eyes, and meninges can be affected. But these complications are extremely rare.
Rice. 5. The photo shows gonorrheal arthritis.
Rice. 6. The photo shows gonorrheal conjunctivitis. The disease is accompanied by profuse suppuration.
Rice. 7. Damage to the skin due to gonorrhea.
Gonococcal conjunctivitis
Gonococcal eye infection can occur at any age and occurs as inflammation of the iris (iridocyclitis) or conjunctiva (conjunctivitis).
Most often this is associated with infection through dirty hands, as well as through shared use of hygiene items, including towels. Separately, blenorrhea (gonococcal ophthalmia) of newborns is distinguished when a child becomes infected while passing through the mother’s birth canal.
Symptoms:
- Severe swelling of the eyelids (they become swollen).
- Photophobia is increased sensitivity to bright light.
- Purulent discharge, which usually accumulates in the corners of the eye, on the eyelashes.
- Redness of the conjunctiva, increased bleeding.
In advanced cases, corneal ulcers appear, perforation occurs, and blindness develops.
Transmission of gonorrhea to newborns and children
Gonorrheal conjunctivitis of newborns
During childbirth, the causative agent of gonorrhea can be transmitted to the newborn and infect the mucous membrane of the eyes, which leads to the formation of ulcers, which subsequently heal with a scar.
Gonorrheal lesions of little girls
Very rarely, the source of infection for little girls is the personal belongings of a sick mother.
Rice. 8. The photo shows gonorrheal conjunctivitis of a newborn. The disease occurs with the formation of ulcers that heal with a scar. The disease is complicated by blindness.
Special forms of gonorrhea (extragenital)
Let's consider forms of gonorrhea that do not affect the urethra and genital apparatus.
Gonorrheal proctitis
It develops, as a rule, in women, secondarily: when pus leaks from the genital tract or during rectal sexual contact.
Discharge from the anus with proctitis of gonorrheal etiology is also purulent and can be detected in the stool.
Upon examination, fissures in the anus, severe redness and swelling of the anal area are revealed.
In the chronic form of gonorrhea, genital warts can grow rapidly.
Oropharyngeal form of gonorrhea
There is no discharge from the mouth with oropharyngeal gonorrhea.
As a rule, the patient's complaints are limited only to pain and sore throat.
Sometimes the tonsils and lymph nodes become inflamed.
However, in 70-80% of cases it is asymptomatic.
Ophthalmogonorrhea (gonorrheal conjunctivitis)
Discharge from the eyes with gonorrheal conjunctivitis is manifested by severe suppuration.
The eyelids swell and the patient develops photophobia.
The conjunctiva is red, rough, and bleeds easily.
The most severe complications of ophthalmogonorrhea are damage to the cornea, the formation of ulcers and possible perforation.
Diagnostics
Gonorrhea in women is easily diagnosed. A sample for research can be a smear from the pharynx of the cervix, rectum and throat.
Direct bacterioscopy is the simplest, fastest, most sensitive and specific method for detecting gonococci in the test material. Its sensitivity is 90%.
Inoculation of biological material on nutrient media has 95% sensitivity.
The PCR (polymerase chain reaction) technique is highly sensitive and specific and is comparable to that of culture.
Testing for gonorrhea should be carried out as soon as possible, as the disease can lead to serious health problems for a woman.
Rice. 9. The photo shows the preparation of a smear for examination.
Rice. 10. The photo shows gonococci (smear of pus). Microscopy view (methylene blue staining on the left and Gram staining on the right).
Features and characteristics of the disease
Gonorrhea is caused by pathological microorganisms – gonococci. In men, the urinary system is damaged. In women, the urinary and reproductive systems become infected. Infection of other organs is also possible. A diagnosis can only be made after a thorough examination.
The disease most often affects sexually active people who do not like to protect themselves with condoms. Moreover, infection in this way occurs only in half of the men who had sexual contact with an infected partner. In women, this figure is much higher and reaches almost 100%.
Infection through household means is also possible, but such cases are very rare, since gonococci require a moist environment in which they develop. But when using personal hygiene products and other things of an infected person, you can “catch” this disease.
Treatment
Currently, pathogen strains that exhibit resistance to penicillin, tetracyclines and ciprofloxacin are widespread.
Strains resistant to fluoroquinolones are widespread in Asian countries.
In the heterosexual part of the population, 1/3 of cases of disease are combined with chlamydial infection, so treatment of gonorrhea in women in this case is carried out with two antibiotics.
In case of uncomplicated course of the disease, a single dose of ciprofloxacin (Tsiprolet) is recommended. If the disease is detected in a pregnant woman, treatment is carried out with third-generation cephalosporins or spectinomycin.
With adequate treatment, the patient's condition improves within a few days. Do not self-medicate. Only a doctor will prescribe the correct treatment and determine the fact of cure. Self-medication leads to the development of resistant strains of the pathogen and the transition of the disease to a chronic form.
Incubation period
Discharge does not appear immediately after infection. This requires some time - an incubation period. During this period, the pathogen, gonococcus, multiplies in the body, accumulating in various tissues.
The first signs of the inflammatory process appear after 5-7 days. Most often it depends on gender, but other factors also play a role.
In men, discharge is detected 3-4 days after infection. For women, this period is slightly longer - 6-7 days. In addition, they may not experience other clinical manifestations. This situation is typical for 50% of infected patients.
When does pathological secretion appear?
A certain amount of time must pass from the moment of infection for the first symptoms to appear. Most often, the incubation period is from three to seven days, but with stronger immunity, signs appear only after a few weeks (maximum a month).
It is important to note that the time at which pathological secretion occurs will directly depend on the woman’s immunity level. In a weakened body, the infection develops and spreads faster.
As for the late onset of symptoms, the reason may lie not only in good immunity. It is possible that the woman attempted to self-treat another infection by taking antibiotics. In this case, the first symptoms may simply not be noticed.
When does gonorrhea discharge disappear during treatment?
With timely diagnosis and treatment, the acute form of gonorrhea can be cured fairly quickly. After taking medications prescribed by a doctor once or twice, the symptoms of discharge in men disappear after 3-5 days, and in women after 1-3 days.
In advanced forms of the disease, when the infection affects not only the mucous membranes of the urethra and vagina, but also internal organs, treatment may take 7-10 days. In this case, the discharge stops after 5-15 days.
Important! The cessation of discharge does not mean that the infection is suppressed and completely destroyed. Recovery is recorded if a repeat test does not reveal gonorrhea.
What is the disease?
Gonorrhea is a fairly common sexually transmitted disease. Can be transmitted through sexual, oral and household contact. The causative agent of gonorrhea is a pathogenic gonococcus. It can penetrate the genitourinary system, and then enter the uterus, as well as other organs.
With this disease, it is important to organize timely treatment to avoid serious complications and unpleasant health consequences. But the fact is that symptoms may not appear for a long time. In this case, the woman does not even suspect that she is a carrier of the gonorrheal pathogen.
Doctors believe that practically the first manifestation of the problem is pathological secretion, which may resemble candidiasis in its symptoms.
Yellow
Like cottage cheese
In this case, the woman tries to take antifungal drugs on her own, but such treatment does not affect the pathogenic gonococcus.
For gonorrheal vulvovaginitis
The inflammatory process affects:
- lower genitalia,
- vagina,
- external os of the urethra,
- labia
Among the main symptoms it is worth highlighting:
- yellowish discharge that resembles cream in consistency;
- itching sensation in the perineal area;
- Quite often, blood is released along with secretion;
- Excessive blood overflow in the vessels is often observed;
- pain not associated with menstruation in the lower abdomen;
- nausea and vomiting (rare);
- painful sensations during sex.
Thick purulent
Yellow
What STIs and STDs have discharge similar to gonorrhea?
Patients complain of the presence of discharge in most sexually transmitted diseases:
- chlamydia;
- trichomonas infection;
- candidiasis (thrush);
- ureaplasmosis;
- mycoplasmosis.
Discharge in women can provoke the development of bacterial vaginosis (violation of the ratio of normal and opportunistic vaginal microflora).
One of the significant reasons for this symptomatology in representatives of both sexes is nonspecific bacterial microflora (staphylococci, E. coli, etc.).
Why is there no discharge in chronic gonorrhea?
Gonorrhea becomes chronic after 2 months, provided that treatment is ineffective or absent. Over this period of time, the symptoms become attenuated.
You may notice faint discharge or its absence. The disease did not disappear, but acquired a chronic form, where the cause is a decrease in the severity of the immune response. It is during this period that the inflammatory process can affect various organs of the genitourinary system (in men - the prostate, in women - the uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries).
Discharge after completion of therapy
In some cases, after completing the course of therapy, the discharge does not stop. There are many reasons for this. The main ones include:
- ineffectiveness of treatment;
- relapse of gonorrhea;
- combination with other urethrogenital diseases that were not affected by this type of therapy.
Treatment failure most often occurs due to the patient's failure to comply with the doctor's instructions. But in some cases, the cause is antibiotic resistance of gonococci.
In cases of combination of gonorrhea with trichomoniasis, the gonococci are protected by the Trichomonas membrane from the effects of medications. During treatment, the protection is destroyed, trichomoniasis is cured, but the gonococci remain unharmed. This causes the gonorrhea to recur.
In addition, after treatment for gonorrhea, other diseases may remain: chlamydia, ureaplasmosis, etc.
In order to find out the cause of the discharge, tests are prescribed for the most common infections, and not just for gonorrhea.
In order to find out whether the disease is completely cured, control tests are carried out 2 weeks after therapy, which show whether a second course of treatment is required.
Gonorrheal discharge from the genital tract
In the acute course of the disease, that is, after primary infection, discharge from the genital tract has the following symptoms:
- the color of the discharge is yellowish, sometimes with a light green tint, cloudy;
- density and structure - at first liquid, then with a tendency to thicken, sometimes with the inclusion of thicker flakes or lumps of yellow-green color;
- impurities - at the acute stage without impurities, with progression streaks of blood are visible;
- smell - unpleasant putrid-purulent, fishy or with notes of musty blood.
In addition to the characteristic discharge with an odor, gonorrhea is accompanied by additional symptoms: burning and pain during urination (typical when the urethra is affected by an infection), acute pain during sex (the symptom appears when the mucous membranes of the genital tract are affected), nagging pain in the lower abdomen and lower back (this phenomenon observed when the infection spreads to the bladder, uterus, gonads).
What tests require discharge for gonorrhea?
Even knowing the full picture of the presence of gonorrhea in the patient’s body, the doctor is in any case obliged to confirm the diagnosis through tests. For this infection, the clinical material is pathological discharge from the urethra in men and the vagina in women. They play a major role in the following studies:
- smear microscopy - during diagnosis, the doctor examines the discharge under a microscope, as a result of which he can visualize the causative agents of the disease;
- bacteriological culture - during the study, the resulting material is placed in a Petri dish in a nutrient composition and placed in suitable conditions, as a result of which the bacteria multiply, allowing the doctor to assess their activity and sensitivity to antibiotics;
- PCR is the most informative, but also expensive analysis, which allows you to isolate pathogen DNA even from a small amount of biological material.
Top article: It hurts to pee after a urethral smear
Microscopic analysis is considered the most informative and accessible. It is suitable for urgent diagnosis in women and men with symptoms of gonorrhea (discharge) in the acute stage. To diagnose chronic forms of the disease, culture and PCR are more often used.