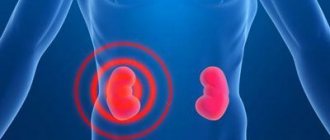
Kidney diseases often affect the functioning of the entire body, because the main task of this organ is to remove toxic metabolic products that can negatively affect vital processes. You can read more about the functions of the kidneys in the human body here.
The kidneys are a paired organ through which blood passes every second through the glomerular apparatus. It is in it that it is “cleaned” from all toxins and unnecessary components. If the filtration process is disrupted, then toxins do not completely enter the urine, but spread through the bloodstream through the vascular bed, reaching the tissues of the brain, heart, etc.
You can learn more about the structure of the kidneys from this article.
Kidney diseases occupy one of the leading positions among all pathological processes encountered in medical practice. Most often, the clinical picture of these diseases is quite vivid, especially if both organs are affected at once.
Symptoms of kidney disease can occur in patients of any age and gender. They are widespread throughout the world, therefore they are a pressing problem in modern medicine. The characteristics of kidney disease in men are described here.
Types of kidney diseases
There is no uniform classification of kidney diseases. In medicine, a simplified version of the types of diseases is used, which helps in diagnosis and selection of effective treatment. Highlight:
After pilonephritis
- Glomerulopathies are pathological processes affecting the glomerular apparatus of the kidneys. In turn, glomerulopathies can be of non-inflammatory and inflammatory origin, acquired and congenital. The most famous disease from this group is glomerulonephritis; amyloidosis and membranous nephropathy are less common.
- Tubulopathies are diseases that develop as a result of damage to the tubular structures of the kidneys. Tubulopathies include necrotizing nephrosis and Fanconi syndrome.
- Diseases arising as a result of damage to the stromal structures of the organ. First of all, it is pyelonephritis.
- Pathologies arising from pathological processes in large and small vessels of the kidneys - aneurysms, atherosclerosis, embolism.
- Anomalies of kidney development - aplasia, organ duplication, hypoplasia, dystopia. Signs of congenital kidney defects in most cases are detected in early childhood.
- Kidney injuries . A bruise can cause rupture of the kidney capsule, and in severe cases it causes complete proliferation of the organ structure.
- Neoplasms . Kidney tumors can be either benign or malignant.
Kidney diseases have both general and specific symptoms.
Pyelonephritis
Pyelonephritis refers to an inflammatory disease that extends to the calyx, renal pelvis and renal parenchyma. Due to its anatomical features, this disease is more often detected in women than in men. Inflammation is caused by microorganisms that are found in the body of every person, as well as microflora that come from the external environment. The causative agents of the disease include:
- Proteus;
- staphylococci;
- streptococci;
- coli.
In some cases, the disease manifests itself as a result of the action of several pathogens. In this case, the progression of pyelonephritis occurs due to a violation of the outflow of urine from the kidneys. Also, the reason may lie in the disruption of blood flow and lymph circulation; against this background, a pathogen can enter the body and easily infect the organ.
There are 3 forms of pyelonephritis:
- spicy;
- subacute;
- recurrent.
The acute form occurs due to disruption of the immune system, hypothermia and after some instrumental research methods. The chronic form becomes a consequence of an acute inflammatory process of the kidneys.
A specialist makes a diagnosis based on the results of ultrasound, x-rays and other diagnostic methods. Therapy involves the prescription of antibiotics that have a broad effect. After carrying out the necessary diagnostics and identifying the sensitivity of microorganisms, the patient is prescribed antibiotics that have a targeted effect. It is recommended to use general strengthening medications in combination.
General symptoms of kidney pathologies
Signs of kidney disease vary in intensity. Typically, patients note the particular severity of one or two symptoms; other manifestations of the disease are less disturbing.
Pain
torsion of the renal pedicles
Kidney damage is indicated by pain localized in the side or lumbar region. Acute sharp pain is characteristic of an attack of urolithiasis and occurs as a result of blockage of the urinary tract by a stone. Painful sensations during an attack spread to the ureter, so pain is felt both in the abdominal cavity and in the groin. Intense pain is caused by torsion of the kidney pedicle, which is possible if the organ is vagal. In patients with nephroptosis, low back pain may be triggered by heavy lifting or excessive physical activity. Inflammatory processes lead to swelling of the kidney tissue, resulting in dull, aching pain and, above all, they are characteristic of pyelonephritis. With cancer, severe pain occurs in the last stages of the malignant process.
Dysuria
This term refers to a pathological urination disorder.
Dysuria is one of the very first signs of most renal pathologies.
With pyelonephritis, the frequency of urination increases, and urine discharge can be painful. Urinary retention and nocturia (frequent urination at night) occur with glomerulonephritis. The term polyuria refers to an increase in the amount of urine to two or more liters. Anuria (acute urinary retention) is determined in case of renal failure, blockage of the urinary tract by a stone, in patients with interstitial nephritis. In some diseases, the color of urine also changes. Cloudy urine indicates the presence of protein or pus; red urine (mixed with blood) may occur in the acute stage of pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis.
Temperature increase
A rise in temperature indicates inflammatory processes in the kidney tissues. With pyelonephritis in the acute stage, the temperature can remain at 38-39 degrees for several days. Temperature may also indicate a carbuncle and kidney abscess; with these pathologies, higher numbers are recorded on the thermometer.
Hypertension
When the vessels of the glomeruli are damaged or with congenital anomalies of their development, spasm of the arteries occurs, which provokes a rise in blood pressure. A sharp rise in pressure may also indicate torsion of the renal pedicle
Nausea with vomiting
These symptoms may accompany pyelonephritis, renal failure, and malignant processes in the kidney tissue.
Edema
They are divided into nephrotic and nephritic. Nephritic ones occur when blood pressure rises, against the background of which the liquid part of the blood enters the intercellular space. The location of nephritic edema is the area under the eyes and eyelids, most often forming in the afternoon. They can be easily removed with folk remedies and mild diuretics. Nephrotic edema is the result of an imbalance in protein fractions, affecting the facial area, then moving to the lower back and lower extremities. In advanced cases, fluid accumulates in the pericardial sac, peritoneum, and pleural cavity. Nephrotic edema takes a long time to grow, it is dense and quite difficult to eliminate. Similar changes are recorded in chronic renal failure and glomerulonephritis.
Skin changes
Pale skin indicates anemia, which often occurs in patients with glomerulonephritis. Dry skin and itching occur due to the accumulation of nitrogenous waste in chronic renal failure.
It is imperative to consult a doctor to identify the cause of deterioration in health if you experience:
- Edema.
- Change in urine color.
- Dysuria.
- Pressure surges.
- Temperature.
- Lower back pain.
Kidney diseases can also manifest as weakness, loss of appetite, decreased ability to work, and increased irritability.
Nephroptosis
Also wandering, drooping kidney. It is not infectious in nature. It is characterized by displacement of an organ from its usual place. Normally, during breathing and physical activity, displacement occurs to the height of one vertebra. The presence of the disease is indicated by the fact that in a person in an upright position the size of the displacement exceeds 2 cm, and when breathing 3-5 cm. More often it is right-sided. The causes of nephroptosis are physiological, acquired:
- mechanical damage;
- hard physical labor;
- frequent dieting, weight gain or loss;
- pregnancy and childbirth;
- bearing a large fetus.
It appears more often in women. There are 3 stages of nephroptosis:
- The first one does not have any clear symptoms. The doctor prescribes sanatorium treatment, wearing a corset, physical therapy, massage or increased nutrition for low weight.
- In the second stage, the pain becomes stronger. The organ goes down 2 vertebrae.
- At the last stage, displacement occurs by 3 vertebrae. Nephropexy is performed. The kidney is fixed back into its anatomical location.
Surgery also occurs at the second stage. After surgery, prolonged bed rest is required.
Signs of kidney pathologies in women
Diseases of the urinary system and in particular the kidneys, especially those of an inflammatory nature, are more common in women. This is primarily due to the anatomical features of the urinary organs - in women, the urethra is short, which increases the risk of infection first entering the bladder, and then along the ascending path into the kidney tissue. The likelihood of developing kidney pathologies also increases during the period of bearing a child - the growing uterus puts pressure on the urinary structures, changing their location, and thus creating suitable conditions for the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms.
Signs of kidney disease in women are pronounced, so representatives of the fair sex are more likely than men to consult a doctor in a timely manner.
Young girls and women are most often diagnosed with:
- Pyelonephritis.
- Nephrolithiasis.
- Nephropathy of pregnancy.
- Kidney failure.
- Hydronephrosis.
- Polycystic disease.
- Nephroptosis.
The first signs of kidney disease in women are:
- Swelling of the face and lower extremities, which goes away in the evening.
- Weakness.
- Headache.
- Changes in the color and volume of urine.
- Dryness of the skin and mucous membranes of the mouth.
- Blood pressure fluctuations.
- Pain localized in the lower back and abdomen.
Women with symptoms of renal pathologies must undergo a gynecological examination. It is necessary to exclude inflammation of the appendages, ectopic pregnancy, and ovarian apoplexy.
Prevention
Treatment of renal diseases involves a complex of measures from conservative therapy to surgical intervention.
A common feature of both treatment and prevention of kidney diseases is minimizing the load on the urinary system. In this regard, the following recommendations are proposed:
- eliminate a sedentary lifestyle to prevent urine stagnation;
- adherence to a therapeutic diet, the main feature of which is a decrease in the amount of protein foods, an increase in the amount of fiber, and drinking plenty of fluids;
- decoctions and teas from medicinal plants can cleanse the body of toxins.
If kidney problems are detected, you should immediately review your lifestyle and diet.
Signs of kidney pathologies in men
- Symptoms and signs of kidney disease in men are not as pronounced as in women. The erased nature of the first manifestations of diseases leads to the fact that pathologies are detected at later stages, which accordingly complicates their treatment. Men are more likely to have urolithiasis and hydronephrosis; boys are more likely to have glomerulonephritis than girls. The first signs of kidney disease in men: Swelling of the face and limbs.
- Increased blood pressure.
- Pain in the lumbar region.
- Decreased urine output.
- General lethargy.
Renal pathologies in men must be differentiated from prostate diseases, especially in old age.
Hydronephrosis
With this disease, the organ cavities expand.
Often the cause of expansion is a violation of the outflow of urine. Manifestations of hydronephrosis can be congenital or acquired. Congenital occurs due to certain anomalies in the human structure. Acquired pathology results from urolithiasis, tumors, and impaired urine outflow.
For a long period, such a disease does not manifest itself in the form of pronounced symptoms. Only if there are stones or infection in the kidneys can a disease be suspected. There may be minor pain in the lumbar region. Often the only noticeable symptom of kidney disease is blood in the urine.
Causes of kidney diseases
The main factors that provoke kidney disease include:
- Exposure to infectious microorganisms - bacteria, parasites, viruses.
- Autoimmune processes leading to the production of antibodies against one's own cells.
- Exchange disorders.
- Exposure to toxins, poisons.
- Pathological disorders of venous or arterial blood flow.
- Organ injury.
- Congenital malformations.
In women, polycystic kidney disease often occurs together with an ovarian cyst. Inflammation of the organ can be provoked by medical manipulation - transvaginal ultrasound, catheterization. The risk of developing kidney disease in women increases with age, especially during menopause. Kidney prolapse can be caused by sudden weight loss.
In men, inflammatory infectious processes in the kidneys are more often associated with injuries, hypothermia, and poisoning. Alcohol abuse can also provoke the development of the disease.
Nutritional rules for patients with kidney pathologies
The special diet of patients with kidney disease plays an important role in the success of treatment. First of all, the patient needs to limit the consumption of protein foods. But it should be remembered that proteins cannot be completely excluded, since protein compounds are key links in the construction of all tissues of the body.
The diet for patients with kidney pathologies includes the complete exclusion of fatty and fried foods, processed foods, smoked foods, coffee, carbonated drinks, alcohol, etc. You should eat 4-5 times a day in small portions. It is better to eat boiled, baked or, best of all, steamed foods.
The diet for patients with renal pathologies includes the complete exclusion of fatty and fried foods, processed foods and smoked foods.
Many patients mistakenly limit the amount of fluid they drink, but this should not be done. The liquid helps remove pathogenic microorganisms from the urinary system. It is believed that you should drink at least two liters of water per day. In fact, you need to drink as much as you want and follow your usual drinking regimen. The exception is patients with renal failure - this diagnosis requires limiting the amount of fluid consumed.
Treatment
Treatment of kidney diseases is selected depending on the established diagnosis. During the acute stage of the process, several groups of medications are often prescribed. The main goal of therapy is to reduce the symptoms of diseases and restore organ function.
Medications used:
- Antibiotics. Their use is necessary for inflammatory processes.
- Uroseptics.
- Painkillers and antispasmodics.
- Diuretic medications.
- Medicines that promote the resorption and removal of stones.
In case of severe kidney damage, a course of hormonal medications may be prescribed. The only treatment option for urolithiasis or neoplasms can sometimes be surgery. In case of chronic renal failure in the last stages, dialysis is prescribed.
Traditional methods of treatment should be used only in conjunction with a course of therapy prescribed by a doctor. Many herbal remedies help improve the excretory capacity of the organ, reduce symptoms, and promote the dissolution of stones.
But grandmother’s recipes alone cannot be used, since delaying contacting a doctor can lead to partial death of organ tissue, which is considered an irreversible process.
Diagnostics
Modern medicine has many ways to identify any kidney disease. Comprehensive diagnostics is extremely important, which includes:
- lab tests;
- Dopplerography of blood vessels;
- Ultrasound;
- nephroscintigraphy;
- biopsy;
- CT and MRI.
Kidneys can be treated after an accurate diagnosis has been made. Therapy is prescribed by the attending physician, taking into account associated symptoms and contraindications.
How to cure kidneys
In the relapse stage, the patient’s treatment begins with an updated diet and mandatory intake of medications from different pharmacological groups. The patient needs to reduce the load on the affected organ, and it is important to find out what causes the characteristic pain and what the diagnosis is called. After diagnosing kidney diseases, conservative treatment begins, which provides an integrated approach to the health problem:
- dietary nutrition;
- medications;
- gentle regime;
- phytotherapy.
DETAILS: What they are faced with in the urology department
If you find out the specific name of kidney disease, this is already a significant step towards a speedy recovery. When a pathogenic infection becomes the main pathogenic factor, it is clearly impossible to do without taking antibiotics to exterminate the pathogenic flora. This may include intravenous injections or oral antibiotics. This is how doctors act for pyelonephritis; in other clinical situations, the recommendations are as follows:
- diuretics: Canephron, Nephrosten, Veroshpiron, Furosemide, Aldactone;
- antispasmodic drugs: No-spa, Drotaverine, Scopolamine, Mebeverine, Atropine sulfate, Metacin chlorosil, Papaverine, Halidor;
- herbal medicines: Cyston, Fitolysin, Cystenal, Rowatinex, Canephron;
- antihypertensive drugs: Clonidine, Pentamin, Clonidine, Reserpine, Gemiton;
- uroseptics: Furadonin, Nolitsin, Nitroxoline and Furagin.
Kidney disorders and pregnancy
Do expectant mothers have kidney pain? The condition of pregnancy in women deserves special mention, since it is an increased risk for the kidneys. The female body at this time, in fact, works with double load, this also applies to the urinary system. Carrying a child rebuilds the metabolism of the expectant mother, especially in terms of the exchange of phosphorus and calcium and some acids. The action of the hormone progestron has a dilating effect on the ureters and renal pelvis; their tone decreases, and urine becomes more concentrated as its outflow worsens. In addition, a woman becomes more vulnerable to infections due to decreased immunity.
Pregnant women may have pain in their organs due to:
- uroliths;
- glomerulo- and pyelonephritis.
Any signs of kidney problems, such as back pain in the kidney area. Situations where the left kidney hurts or the organ on the right is affected will definitely become a reason for the expectant mother to contact an obstetrician-gynecologist in order to identify a possible pathology and take timely measures.
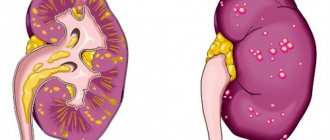
Polycystic
Polycystic disease affects both kidneys at once and consists of the formation of cysts in the parenchyma ranging in size from a pinhead to a large cherry.
Pathological formations grow and lead to kidney failure. The hereditary disease can manifest itself in newborns or in people over 30 years of age, and is treated with both conservative and surgical methods.
Kidney diseases and conditions
Any disease that affects the blood vessels, including diabetes, high blood pressure (hypertension), and atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries), can impair the kidneys' ability to filter blood and regulate fluids in the body.
Disease and infection in other parts of the body can also cause kidney problems. Because kidney damage can be life-threatening, disorders and diseases that can affect the kidney deserve immediate attention.
Kidney disease often does not cause any symptoms until an advanced stage and can lead to end-stage renal failure, which is fatal to a person unless a dialysis machine is used or a kidney transplant is performed.
There are more than 100 disorders, diseases and conditions that can lead to progressive kidney destruction. Some of the most common problems are described in the article listed below. Warning signs that should not be ignored are also listed in the next Symptoms section.
Urinary tract obstruction
The urinary tract may become partially blocked (for example, due to kidney stones, a tumor, an enlarged uterus during pregnancy, or an enlarged prostate gland).
High blood pressure can lead to infection and kidney damage. With a kidney stone, the blockage is often painful. Other obstructions may not cause any symptoms and are only detected if blood and urine tests are abnormal or imaging tests such as X-rays or ultrasound detect it.
Urinary tract infection
Infections – Urinary tract infections, such as cystitis (bladder infection), can lead to more serious infections further down the urinary tract.
Symptoms include fever, frequent urination, a sudden and urgent need to urinate, and pain or a burning sensation during urination. There is often pressure or pain in the lower abdomen or back. Sometimes the urine has a strong and unpleasant odor.
Pyelonephritis is the name for infection of the kidney tissue; most often this is the result of cystitis that has spread to the kidney. Obstruction in the urinary tract can make kidney infection more likely.
What examinations need to be completed?
Tests performed on samples of your blood and urine are the first step in investigating kidney problems. These types of studies can show how well the kidneys remove excess fluid and waste. imaging techniques may be used if changes in the shape or size of the kidneys, bladder, or urinary tract are suspected . A sample of kidney tissue, a biopsy , sometimes helps diagnose the specific cause of the problem.
Tests commonly used for screening and diagnosis. There are several testing methods that are commonly used by health care professionals to detect kidney or urinary tract problems. The blood sample may be analyzed for creatinine (and estimated glomerular filtration rate [eGFR]) and urea.
The level of these wastes in the blood increases as kidney filtration decreases. Abnormal results are usually the first sign of kidney disease.
A urine sample is usually also tested and analyzed (urinalysis) as part of routine screening. This battery of tests looks for signs of kidney and urinary disease, such as red blood cells, white blood cells, and protein in the urine.
If you have diabetes or high blood pressure, you should have your GFR and urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio checked annually to detect kidney disease in its early stages. If you are a current smoker, obese, have cardiovascular disease, a family history of chronic kidney disease, and you are age 35 or older, you should have your urine creatinine ratio
If you have symptoms suggestive of infection, a urine culture can confirm the presence of a bacterial infection.
Tests to monitor kidney function - If you have been diagnosed with kidney disease, your doctor will ask you to have laboratory tests to help monitor your kidney function. Levels of urea, creatinine and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) in the blood are measured from time to time to see if kidney disease is worsening.
How to recognize pain?
The localization of pain is absolutely important, since it is not always easy to determine what exactly is hurting. The localization of pain most often occurs on one side of the body. In this case, the pain is located slightly below the ribs, and in some cases it can even radiate to other areas:
- on the side of the abdomen, and sometimes it touches the groin;
- along the entire path of urination;
- pain can affect the genitals;
- in rare cases, the pain reaches the thigh, or rather their inner surface.
The characteristics of pain are quite unique and often have a paroxysmal nature and are accompanied by an acute type of sensation:
- In the presence of urolithiasis, when pathological changes affect the outflow of urine, an increase in peristaltic function is observed, as well as spasmodic phenomena in the ureter. In this case, the release of a pointed stone injures the urine outflow tract and affects the nerve endings. Pain can be observed in the groin area, along the entire urinary tract, as well as in the genitals.
- If pain is caused by inflammatory reactions in the organ itself, then the manifestations are somewhat different - the kidneys expand, their volume increases, and swelling in the kidneys is also observed. In this case, stretching is observed in the renal capsule, and it contains a large number of nerve endings. When the membrane stretches and the endings become irritated, severe pain occurs.
Nephropathy in pregnancy
The disease manifests itself in late pregnancy with impaired function of blood vessels and kidney capacity. Given the danger to the normal development of the fetus, even a mild form of nephropathy in pregnant women is treated in a hospital setting.
Drug therapy consists of taking medications that reduce the risk of blood clots, normalize blood pressure, relieve arterial spasm, and diuretics. The diet is aimed at restoring lost proteins, while reducing the consumption of salt and animal fats to a minimum. Late toxicosis can lead to renal or heart failure, retinal and placental detachment, and internal bleeding.
Glomerulonephritis
This is a bilateral kidney lesion that affects the glomeruli. The most common cause of the disease is streptococci. The glomerulus is an extremely important part of the excretory system, as it filters blood. If it is affected, then the corresponding processes in the kidneys are disrupted.
The kidneys become unable to remove toxic waste products and begin to miss some beneficial substances. The causes of glomerulonephritis are:
- infectious diseases, especially those associated with the pathogenic activity of streptococci;
- intoxication (alcohol, mercury, drugs and certain medications);
- systemic pathologies;
- Alport syndrome;
- Fabry syndrome.
The main signs of this disease are an increase in blood pressure and a decrease in the daily amount of urine. Laboratory examinations detect protein in the blood, red blood cells in the urine, and deviations in biochemical analysis (changes in the ratio of certain proteins).
If such unfavorable symptoms appear, you should consult a specialist. If the clinical picture of glomerulonephritis is very pronounced, bed rest is prescribed. Antibiotics and immunosuppressants are prescribed among the medications. Active symptomatic treatment is indicated.
Diet
Diet for kidney inflammation is one of the main conditions for recovery. If the patient does not experience edema, then he is advised to drink plenty of fluids. The main principle of the diet is to reduce the load on the diseased organ as much as possible. Therefore, the diet must include fruits, vegetables, and cereals. You should not consume fried, spicy, meat products, or salt.
simptomer.ru
Inflammatory kidney damage is called the general term nephritis (from the Greek nefros - kidney, and -it - inflammation), and usually has several variants of the course of the disease:
- acute diffuse nature of kidney inflammation;
- chronic version of kidney inflammation;
- focal spread of inflammation in the kidneys.
The formation of inflammation in the kidneys is a very serious pathological condition, characterized by unbearable pain and other unpleasant manifestations of the disease.
The types of nephritis include the most common acute and chronic pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, pyonephrosis (a purulent focus in the kidney tissue), and tuberculous kidney disease.
Pyelonephritis is an inflammatory reaction in the pyelocaliceal zone and the parenchyma of the renal organs.
Glomerulonephritis is a bilateral renal inflammation caused by a violation of the structure and function of glomeruli (glomeruli of the kidneys, through which fluid must be filtered from the bloodstream).
Pyonephrosis is the final purulent-destructive degree of specific and nonspecific pyelonephritis.
Tuberculosis of the kidneys is an infectious inflammatory process in the kidney tissues, provoked by a specific pathogen: Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Koch bacillus).
All types of nephritis are quite serious and require specialized treatment.
First aid for kidney pain
If your kidneys start to hurt, the first thing you need is rest. You need to lie down in a comfortable position. You can take a painkiller if the pain is unbearable and call a doctor.
When your kidneys hurt, you can temporarily relieve the sensation with a heating pad or a hot bath. This effect relieves muscle tension.
Warm compresses should not be used if you have heart problems.
The main medicine for kidney pain is a spasm reliever. Baralgin or Maxigan will do. They do not get rid of the cause, but they facilitate the course - they remove spasms, relieve pain, and relax the muscles. If this medicine is not available, No-shpa or Drotaverine will do.
As first aid, fruit drinks with a diuretic effect (cranberries, lingonberries) and warm tea with lemon are given. Measure your temperature and blood pressure regularly.
If your kidneys start hurting on the street, you need to sit on a bench or lean against a wall and call an ambulance.
You should call a doctor if your kidneys still hurt a lot after taking medications, if your urine is dark red, or if you have hypertension. Regular swelling of the legs should be alarming.
Cyst formation in an organ
A cyst is a benign fluid-filled formation on the body of the kidney. Multiple neoplasms are polycystic. For a long time, cysts may not show their presence in any way. The only way to detect them is to perform an ultrasound examination.
If the cyst does not exceed 5 cm in diameter and does not impede blood circulation and the process of urination, it is not touched at all, only observed regularly. If unpleasant symptoms such as bleeding and pain appear, indicating an increase in the size of the cyst or its rupture, urgent surgical intervention is recommended.
Drug therapy
Drug therapy for renal pathologies is carried out using drugs from various groups, which usually take the form of tablets or injection solutions:
- general antibiotics;
- antimicrobials and uroantiseptics;
- antispasmodics and analgesics;
- diuretics;
- medications to dissolve stones and normalize metabolic processes;
- herbal preparations, which contain only natural ingredients of plant origin, etc.
Kidney failure
One of the most serious kidney diseases. It is expressed in the complete or partial loss of the kidneys’ ability to remove urine from the body and along with it all harmful metabolic products. An important symptom is a small volume of urine when urinating or its complete absence. The causes may be chronic diseases, infections, internal injuries of the hematopoietic system, blockage of the ureter, etc.
In most cases, with a timely and competent approach, the disease can be completely cured. In addition to a course of drug therapy, a strict diet with low protein and salt levels is indicated.
More severe forms of kidney failure can result in kidney loss or death. In this case, only an organ transplant or constant hemodialysis can help.