Inflammatory processes occurring in the ovaries pose a serious danger to women's health. Medical statistics are disappointing: up to 20% of women who have had inflammation suffer from infertility. In addition to infertility, patients also experience other problems that lead to disruption of their general condition. Often the inflammatory process in the ovaries spreads to the fallopian tubes and uterus.
CAUSES OF THE DISEASE
The main causes of inflammation of the ovaries and appendages are microbes. They enter the body due to non-compliance with hygiene standards and during sexual intercourse. Inflammation can also be caused by:
- childbirth, abortion, surgery;
- infectious diseases;
- weakened immune system;
- overwork and stress.
The causative agents are pathogenic organisms: chlamydia, gonococci, staphylococci, streptococci and a number of others.
SYMPTOMS AND TREATMENT
The first signal of possible inflammation of the ovaries is pain. In most cases, it is not sharp, pulling, and does not cause serious problems. But if painful sensations appear in the lower abdomen, then it is better not to delay a visit to the gynecologist. Painful menstruation is also one of the signs of inflammation occurring in the ovaries. Inflammatory processes can also be judged by the presence of copious discharge (often with an unpleasant odor) from the vagina. In advanced cases, the temperature rises and chills appear. If a woman observes at least one of these signs, then she urgently needs the help of a doctor.
A particular danger of inflammatory processes in the ovaries lies in the fact that in the absence of treatment, the pain gradually subsides and pronounced symptoms disappear. But this is not at all a sign of a woman’s recovery. On the contrary, the disease goes “deeper”, affecting the tubes, the uterus, and becomes chronic. Treatment consists of prescribing anti-inflammatory drugs, as well as vitamin and strengthening complexes. If the inflammation is complicated and affects the fallopian tubes, then surgical (laparoscopic) intervention is advisable.
BE PREGNANT OR TREAT?
Inflammation of the ovaries, especially chronic ones, leads to irreversible consequences in the form of tissue degeneration. It is difficult to get pregnant during inflammation, due to a woman’s hormonal imbalance and the process of egg maturation. However, if the egg has nevertheless matured and fertilization has occurred, then the joy may be overshadowed by a possible ectopic pregnancy, pathologies in the development of the fetus, as well as a miscarriage. Therefore, when diagnosing ovarian inflammation, first of all, you need to think about your own treatment, and not about conceiving a child. With modern diagnostic and treatment methods, the disease is easy to diagnose and achieve complete recovery. To do this, you only need to seek medical help in time.
The most amazing part of a woman's body is her reproductive system. After all, it is in it that a new life and its development begin. Pregnancy for an expectant mother is a new stage in life. It is not surprising that almost every woman strives to become a mother and is preparing for such a long-awaited event. There are no special difficulties if the girl is physiologically healthy. But sometimes there are cases when the female genital organs malfunction and reproductive function is disrupted. One of these common problems is adnexitis (inflammation of the ovaries). When making this diagnosis, a woman has a reasonable question - is it possible to get pregnant with inflammation of the ovaries? Let's talk about this in more detail.
What is ovarian inflammation
A disease accompanied by inflammation in the female appendages is called adnexitis. Like any other inflammatory process, this disorder can be acute or chronic. Pathology occurs against the background of the formation of a focus of infection with reduced immunity.
The clinical picture depends on the cause of the inflammatory process, its form and stage of development. Before making a diagnosis, diagnostics are carried out, which includes laboratory research methods, gynecological examination and ultrasound. This disease has many serious complications, especially if the inflammation of the ovaries becomes chronic with the formation of adhesions.
How to recognize the disease during pregnancy?
It is quite easy for a gynecologist to detect an inflammatory process in the cervix. First, the doctor conducts a conversation with the patient, learns about her complaints, and studies the medical history. Then she performs a gynecological examination using a speculum.
The doctor can see signs of inflammation of the cervix of the reproductive organ, and also detect discharge with pus in the woman’s vagina. If cervicitis occurs in a chronic form, then the symptoms will not appear so clearly.
During a gynecological examination, the doctor must take a smear. This is necessary in order to determine the type of pathogen and prescribe the correct treatment. In addition to the routine examination, the gynecologist recommends additional tests. These include laboratory tests of blood, urine, and ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs.
The result of the smear examination will show not only the pathogen, but also the number of leukocytes. If it is higher than normal, then this indicates the development of an acute inflammatory process. If, on the contrary, there are few of these components, then we are talking about a chronic type of pathology.
Based on the results of all the diagnostic measures the woman has undergone, the attending physician can make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment. The prognosis is quite favorable; getting rid of cervicitis is not particularly difficult if the woman strictly follows all the recommendations of specialists.
Is it possible to get pregnant with adnexitis?
No doctor can say with 100% certainty and guarantee that pregnancy will occur. Even if, during delayed ovulation, which is a consequence of inflammation, fertilization of the egg occurs, then, according to physiological norms, the fertilized egg must move towards the uterine cavity in order to attach to the wall there and begin its development. It is at this stage that a failure in this system may occur, the cause of which is obstruction of the fallopian tubes.
Also, pathogenic microorganisms can become a provocateur, causing disruption of the functioning of the egg and preventing its movement to the uterus. In such a case, there is a high risk of developing an ectopic pregnancy. Due to the unfavorable conditions created, the fertilized egg simply does not have time to reach the uterine cavity and attaches to the wall of the ovary or fallopian tube. Naturally, in such conditions the child cannot develop and the pregnancy is terminated.
Whether pregnancy occurs or not in this case depends on many factors. Here you should take into account the woman’s age and her physiological characteristics. The general state of health and the presence of complications arising from ovarian inflammation are also taken into account. In any case, before conceiving a child, it is necessary to undergo a full course of examination and, if pathology is present, it is better to cure all lesions, and only then begin to plan the birth of a child.
Is it possible to get pregnant?
Unilateral or bilateral adnexitis is an inflammatory process caused by the activity of pathogenic microorganisms or bacteria, and is expressed in an inflammatory process localized on the ovary and fallopian tube (with a bilateral course - on both pairs of organs, with a unilateral course - only on one). Thus, strictly speaking, mechanically this process does not affect conception in any way, but there are a number of features:
- This is pronounced swelling of the fallopian tube and its inflammation. As a result of this pathological process, the lumen of the fallopian tube becomes minimal. This significantly increases the likelihood of developing an ectopic pregnancy;
- In addition, with salpingoophoritis, blood circulation in the pelvic organs, including the uterus and its endometrium, is significantly impaired, as a result of which conception is difficult because the embryo does not receive enough nutrition. And even if pregnancy occurs with adnexitis, it can become frozen in the very early stages for this reason. Naturally, this will lead to miscarriage at such an early stage that the patient may not know about it;
- Pregnancy may not occur for another reason - this is a changed, swollen mucous membrane of the inner layer of the uterus - the endometrium. During the inflammatory process, it also becomes partially drawn into it. The embryo often cannot attach to such a changed endometrium.
There are other factors that significantly interfere with conception with this diagnosis.
For salpingoophoritis
However, the likelihood of conception varies depending on the form of the disease. As mentioned above, unilateral or bilateral adnexitis is distinguished. Moreover, each of these varieties can occur in a chronic or acute course.
The probability of conception with a unilateral process is higher than with a bilateral one. This is due to the fact that at least one tube remains more or less passable, and also because the changes in the endometrium are not so pronounced and the hypertonicity is not so strong. Simply put, the inflammatory process is exactly two times less pronounced than with a bilateral one.
Bilateral adnexitis leads to such severe disturbances of the mucous membrane and blood circulation in the pelvic organs that pregnancy is very unlikely.
Is it possible to get pregnant with chronic adnexitis? In this case, the likelihood of conception is highest. If in an acute course the pathological changes are expressed very significantly and interfere with conception, then in a chronic case they are expressed quite insignificantly, which sometimes does not interfere with not only getting pregnant, but also carrying the fetus normally. However, since immunity drops significantly during pregnancy, it must be remembered that in this situation, chronic left-sided adnexitis can develop into acute, which is extremely undesirable, as it can cause inflammation to spread to the fetus, missed pregnancy, etc.
Expectant mothers should pay attention to the fact that although conception is possible, planning a replenishment with this disease is impossible. First it needs to be cured. This is due to the fact that the process has a very negative effect on the fetus and the course of pregnancy, as well as the birth process, which will be discussed below.
After salpingoophoritis
Pregnancy after salpingoophoritis is possible. Moreover, as mentioned above, it is advisable to plan replenishment strictly after the ort of this pathology has been cured. Unilateral and bilateral salpingoophoritis after treatment ideally leaves no signs behind and does not in any way affect the likelihood of conception. But in reality, in most cases the situation is different.
The inflammatory process leads to the development of adhesions in the fallopian tubes. Adhesions in the tubes prevent eggs from leaving them into the uterine cavity, where conception should occur. This can lead to the development of an ectopic pregnancy, as well as prevent conception altogether, leading to infertility. From the description it is clear that a bilateral process in this case poses a greater danger in terms of the development of infertility than a unilateral process, in which at least one fallopian tube remains healthy.
Although such complications are quite common, they are nevertheless relatively favorable, since they are easy to correct. During a low-traumatic laparoscopic intervention, it is possible to dissect adhesions and restore tubal patency.
How does ovarian inflammation affect pregnancy?
If pregnancy does occur with such a serious pathological disorder, there is a high risk of premature birth, miscarriage and uterine bleeding. This is due to the fact that during pregnancy the inflammatory process reduces the protective functions of the uterus and damages its internal tissues. Under such conditions, the fetus can be most actively attacked by viruses and bacteria. In addition, the mother's excited immune system can create additional difficulties.
Bleeding can occur due to the attachment of the fertilized egg to the lower part of the uterus, and with inflammation of the ovaries, the fertilized egg tends to attach itself to this part of the organ. It can also be noted that this pathology provokes the production of antibodies, which can result in the development of thrombohemorrhagic syndrome. The danger of such a violation is expressed in the formation of a large number of blood clots and premature placental abruption.
Adnexitis causes the following pathological conditions during pregnancy:
- fetal infection;
- premature birth;
- miscarriage;
- hydatidiform mole;
- frozen pregnancy.
In the chronic course of the disease, hormonal disruptions occur, as a result of which the development of the fetus is disrupted and the most serious complication is infertility.
Before planning a pregnancy, you need to consult a gynecologist, take tests and smears to identify the presence of an inflammatory process. If the test results reveal that a pathological disorder is present, the doctor will prescribe a course of conservative therapy.
Further, after completing the course, diagnostics are carried out again and, if everything is in order, the woman first needs to completely restore her reproductive function and ensure its physiological functioning. To do this, a sleep and rest schedule is observed, and hormonal levels are adjusted by taking medications. You also need to normalize your metabolism and strengthen your immune system.
To prevent the occurrence of such a pathological disorder, you need to especially carefully monitor your health and not expose yourself to unfavorable factors. And if a disease occurs, do not despair. Modern medical methods make it possible to cure the inflammatory process in a fairly short period and give a chance for the birth of a healthy child.
Inflammation of the appendages or adnexitis is a fairly common disease among the female population. It can affect women of absolutely any age - those who are in menopause or even those who have not been sexually active.
Inflammatory diseases of the genital organs
Inflammatory diseases of the genital organs include: colpitis - inflammation of the vagina;
cervicitis - inflammation of the cervix; salpingoophoritis, or adnexitis, is inflammation of the appendages (ovaries and fallopian tubes); endomyometritis is a chronic inflammation of the inner layer of the uterus. The leaders among these diseases are chronic salpingoophoritis and endomyometritis. The main cause of their occurrence is sexually transmitted infections: trichomoniasis, mycoplasmosis, chlamydia, etc. As the name of this group of infections suggests, the pathogen enters a woman’s body mainly through sexual contact with an infected person.
Long-term inflammation of the fallopian tubes and ovaries leads to the development of dense connective tissue that replaces dead cells. As a result, the already very thin lumen of the tube (only 1-2 mm in diameter) can easily be “overgrown” with connective tissue, and the tube will become impassable for the egg.
Under such conditions, the meeting of sperm and egg does not occur, and therefore fertilization is impossible. In addition, in the process of inflammation, the cells lining the inner surface of the fallopian tubes are also affected.
They promote the movement of the egg through the tube; in addition, many microorganisms, such as chlamydia and mycoplasma, can penetrate these cells and disrupt their functioning with their vital activity.
Whether a woman had inflammation of the appendages before pregnancy can be judged by the results of tests performed before pregnancy, as well as by the presence of the following complaints: moderate, periodic, dull, nagging, aching pain in the lower abdomen, aggravated by cooling, as well as menstrual irregularities, which becomes unstable - with delays, intermenstrual discharge.
Pain is usually felt in the lower abdomen, in the groin areas, in the sacral area, and in the vagina. Often its intensity does not correspond to the nature of changes in the genital organs, i.e. inflammatory changes in organs can be minimal or as a result of treatment they can be eliminated, and pain, as a residual phenomenon, persists for a long time.
This condition can last a long time, without a clearly defined beginning and end of the disease. Signs of chronic inflammation of the uterine appendages and the uterus itself include pathological discharge from the genital tract - more or less abundant, sometimes with an unpleasant odor.
Inflammatory processes in the ovaries can lead to disruption of their functioning, while ovulation—the release of an egg from the ovary—does not occur at all (in this case, pregnancy is impossible) or occurs late.
So, if normally ovulation occurs in the middle of the cycle, then with chronic salpingoophoritis, as a result of a disruption in the production of ovarian hormones, it occurs later than expected, almost before menstruation.
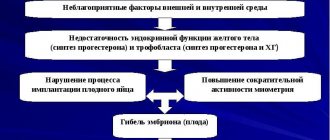
In place of the egg after ovulation, a special gland is formed - the corpus luteum. This gland produces the hormones progesterones, which ensure the onset of pregnancy and are the main supporting factor in the first trimester.
In chronic salpingoophoritis, ovulation occurs untimely, and the corpus luteum does not work fully, producing an insufficient amount of progesterone. This factor often causes the threat of termination of pregnancy in the first trimester.
As already mentioned, the main cause of ectopic pregnancy is also the inflammatory process. As a result, connective tissue grows and the lumen of the fallopian tubes narrows. In addition, the work of the cilia of the ciliated epithelium, the cells that cover the inside of the fallopian tubes and promote the advancement of the egg into the uterine cavity, is disrupted.
It must be said that during an ectopic pregnancy, the pregnancy test is often positive, and the woman may experience the same subjective sensations as during intrauterine pregnancy (nausea, dizziness, etc.).
The inflammatory process can manifest its negative impact at different stages of pregnancy.
Thus, damage to the inner layers of the uterus leads to a change in the defense system inside the uterus. The inner layer of the uterus, trying to protect itself from aggressive factors (microbes, viruses that cause inflammation), perceives the embryo as a foreign agent, and the embryo is rejected and miscarried.
If, nevertheless, the fertilized egg manages to attach, then in most cases this occurs in the lower parts of the uterus, that is, a low attachment or placenta previa is formed. These conditions, in turn, serve as risk factors for bleeding during pregnancy.
A chronic inflammatory process can lead to a change in the antigenic structure of infected endometrial cells: the body begins to produce antibodies to its own cells, that is, the cells of its own body are destroyed.
This process is the most common cause of the development of disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome. One of the symptoms of this complication is the formation of thrombosis. During pregnancy, the occurrence of microthrombosis in the placental area leads to placental abruption, intrauterine growth restriction, and the development of gestosis - a pregnancy complication, often manifested by the appearance of protein in the urine, edema, and increased blood pressure.
In conditions of chronic inflammation of the genital organs during pregnancy, a malfunction occurs in the immune system, which serves to recognize and remove foreign substances from the body. Blood cells involved in the immune response have a toxic effect on the development of the embryo and the formation of the placenta.
All of the listed disorders in the body that occur during the inflammatory process of the genitals can lead to the following pathologies:
- anembryonia, i.e. absence of an embryo in the fertilized egg;
- non-developing, or frozen, pregnancy (in this case the death of the embryo occurs);
- spontaneous miscarriages at various stages of pregnancy;
- premature birth;
- intrauterine fetal death;
- infection of the fetus.
Intrauterine infection is possible if the inflammatory process is activated during pregnancy. In the early stages of pregnancy, intrauterine infection can lead to the formation of various fetal malformations, and in later stages - to fetal growth restriction syndrome.
Such a baby adapts less well after birth and sometimes requires additional treatment. Therefore, newborns whose mothers suffered from chronic inflammatory diseases of the genitals, especially sexually transmitted diseases, undergo additional testing for these infections.
During childbirth
Inflammatory diseases of various parts of the reproductive system can also have a negative impact on the course of labor. One of the most common complications during childbirth is premature or early rupture of amniotic fluid.
Most microorganisms have a set of special enzymes that can affect the membranes and lead to untimely release of amniotic fluid. If normally the water pours out when the contractions are already in full swing, the cervix is completely or almost completely open, then in the presence of inflammatory lesions the water can pour out before the contractions begin.
In this case, the development of weakness of labor is possible; in addition, a long anhydrous period is a predisposing factor for infection of the uterus and membranes. Polyhydramnios, which often accompanies inflammation of the appendages in women, also leads to the development of primary or secondary weakness of labor.
In this situation, the uterus is overstretched and cannot contract well during childbirth. Prolonged labor against the background of prematurely discharged amniotic fluid, as well as the need to use birth stimulants when labor weakness develops, ultimately negatively affects the condition of the newborn.
After childbirth
The inflammatory process of the genital organs does not go away without leaving a trace even in the postpartum period. The likelihood of developing postpartum endomyometritis increases, which is manifested by insufficient contraction of the uterus, increased temperature, the appearance of pain in the lower abdomen, increased bleeding, and the appearance of characteristic foul-smelling discharge. This condition requires hospital treatment.
Thus, the chronic inflammatory process, which most often occurs in a latent form, leads to pronounced changes in the immune system, the hemostasis system (blood coagulation system) and to serious complications during pregnancy, childbirth and the postpartum period.
While carrying a baby, all women who suffered from inflammatory diseases of the genital organs before pregnancy are examined to exclude infections, including sexually transmitted ones. If certain pathogens are identified, appropriate treatment is carried out.
All women suffering from chronic inflammatory gynecological diseases are given treatment aimed at preventing oxygen deficiency (hypoxia) of the fetus and are prescribed drugs that improve blood circulation in the placenta.
Every woman should approach pregnancy planning with special responsibility. Examination before pregnancy and elimination of foci of inflammation will help to avoid complications during pregnancy, childbirth and the postpartum period.
Marina Vasilyeva obstetrician-gynecologist, maternity hospital No. 4, Ph.D., Moscow
A little about the structure
Inflammation of the appendages and uterus is also called inflammatory disease of the female pelvic organs. This includes not only inflammation of the uterus, but also processes occurring in the abdominal cavity or subcutaneous fat. Inflammatory diseases include:
- Myometritis – inflammation of the uterine myometrium;
- Endometrium - inflammation of the uterine mucosa;
- Endomyometritis is a combination of the first two diseases;
- Salpingitis is an inflammatory process in the fallopian tube;
- Pelvioperitonitis – inflammation of the peritoneum;
- Salpingo-ophritis, also known as adnexitis, is a simultaneous inflammation of the ovary and fallopian tube; a distinction is made between unilateral and bilateral adnexitis.
The inflammatory process can be sluggish or pronounced, but in any case it affects the menstrual cycle and reproductive health of a woman. Let's consider for what reasons a focus of inflammation appears and whether it is possible to get pregnant with inflammation of the appendages.
Indications for Pap test
When to do a smear for cytology:
- with diagnosed infertility;
- when planning pregnancy;
- in case of menstrual irregularities, for example, an atrophic type of cytology smear will indicate hormonal changes in the body against the background of menopause;
- if oral contraception is used;
- with genital herpes;
- for obesity;
- if human papillomavirus is detected in the body;
- if a woman is promiscuous;
- in preparation for installation of the IUD.
This research is not always possible.
A smear for cytology is not taken:
- during menstruation, because red blood cells may be erroneously detected in a cytology smear;
- with acute inflammatory process in the genital area;
- with heavy vaginal discharge and severe itching.
READ MORE: What is metaplastic epithelium of the cervix
Pregnancy cannot be a contraindication to the procedure. There is no point in taking this test for women who are not sexually active (virgins).
A smear for cervical cytology is prescribed to all women over 18 years of age during a routine examination by a gynecologist once a year. Also, indications for the analysis include: menstruation disorders, the presence of papilloma virus and genital herpes, free sexual intercourse, infertility, the use of hormonal contraceptives, the installation of an intrauterine device, planning pregnancy.
Infectious diseases are also often a reason to take a smear for cytology. What the result shows can only be determined by a specialist.
Causes of inflammation
One of the main reasons is infection. This could be E. coli coming from the intestines, or other infections and fungi. Most often this occurs due to the fault of chlamydia, streptococci, staphylococci, mycoplasmas, enterococci, and herpes virus. There may be combinations of several anaerobes.
Sometimes the inflammatory process develops for other reasons, including:
- Depression and stress that weaken the immune system;
- Hormonal imbalances;
- Menstrual irregularities;
- Irregular sex life;
- Frequent change of sexual partners.
All these reasons are interconnected. If an infection occurs, a woman feels discomfort, possibly itching and irritation of the genitals. Accordingly, in this state the desire for sexual intimacy is significantly reduced. At the same time, prolonged abstinence from sexual intercourse reduces blood flow to the pelvic organs, causing stagnation.
In addition to this, hormonal levels are disrupted, as a result of which the follicles do not develop fully, and cysts with immature eggs are formed. This condition can result in a chronic, severe course of the disease and the need for surgical intervention.
Manifestation in women
One of the most common diseases of the female reproductive system is inflammation of the ovaries (adnexitis). This gynecological ailment occurs in more than 65 percent of patients visiting antenatal clinics.
Frequently changing sexual partners, early onset of sexual activity and the hidden development of inflammatory processes are factors that lead to the formation of chronic ovarian diseases. According to statistics, about 80 percent of patients with similar problems are nulliparous women whose age does not exceed 25 years.
We recommend you find out:Cold ovaries treatment
and rehabilitation
A woman who suffers from ovarian inflammation will usually notice some changes. She experiences:
- dull aching pain in the groin;
- discomfort in the lower abdomen;
- pain before and during menstruation, with colds;
- painful sexual intercourse;
- disruption of the menstrual cycle;
- disturbances in ovarian function;
- infertility.
Symptoms
In the early stages, symptoms may resemble heavy periods. There is a viscous, aching pain in the pelvic area, weakness, and a possible increase in body temperature to 37-37.5 ° C. In addition, a bilateral inflammatory process manifests itself:
- Spread of pain to the legs and lower back;
- Brown vaginal discharge;
- Sharp pain when examined by a gynecologist;
- Pain during sexual intercourse;
- Minor bleeding in the middle of the cycle;
- Delay of menstruation by more than a week.
If these manifestations are detected, an immediate examination and consultation with a gynecologist is required. The sooner inflammation is detected, the easier and faster it can be gotten rid of.
Inflammation of the appendages during pregnancy: symptoms and diagnosis
Salpino-oophoritis during pregnancy is characterized by the following symptoms:
- pain in the lower abdomen and sacrum,
- increased pain when going to the toilet,
- increase in body temperature,
- intoxication of the body,
- nausea,
- vomit,
- headache,
- gastrointestinal disorders.
Advice! If pain appears in the lower abdomen during sexual intercourse or there is a decrease in libido, it is recommended to consult a doctor.
Miscarriage during inflammation of the ovary during pregnancy occurs after conception after 2 - 2.5 months. Chronic adnexitis provokes regressive pregnancy. When the embryo dies and the egg does not exfoliate.
Bloody discharge occurs only two weeks after the death of the embryo. They may be scarce. Toxicosis and signs of the presence of an embryo in the body disappear:
- swelling of the mammary glands,
- drowsiness,
- changes in vaginal secretion.
Chronic adnexitis can be diagnosed by the following signs:
- delayed fetal development,
- high water,
- premature birth,
- placental insufficiency.
The gynecologist diagnoses the disease during an examination. When palpating the area of the appendages and ovaries, he will pay attention to the patient’s painful sensations.
An ultrasound examination of the ovaries confirms the diagnosis. The ovaries and fallopian tubes increase in size during illness. It is possible that adhesions are forming in the ovaries. Using an ultrasound, the doctor will determine the presence of inflammatory processes.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is prescribed by the attending physician, having carefully studied the clinical picture of the disease. Ultrasound is prescribed to determine the size of the uterus and appendages. The condition of the uterus is assessed by examination.
A mandatory diagnostic procedure is the collection of secretions from the cervical, urethral and cervical canals - this helps to determine the causative agent of the infection.
In addition, the doctor may require an examination of the sexual partner of the sick person, since many infectious diseases are asymptomatic in men, unlike women.
Pregnancy
Is it possible to get pregnant with adnexitis and where to start planning a pregnancy? Experts say that there is indeed a chance to get pregnant, but the inflammatory process can seriously affect the course of pregnancy. With a high degree of probability, such a pregnancy will end in miscarriage, threatening the woman’s life.
To plan a healthy pregnancy, your doctor will prescribe medications, including oral pills and vaginal suppositories. If you seek help in a timely manner, inflammation can be cured fairly quickly, within two to three weeks. In addition, antimycotic therapy is prescribed if the cause of inflammation is fungal colonies, as well as antiviral therapy if the cause is a viral disease.
At the same time, the question of whether it is possible to get pregnant after inflammation of the appendages is considered closed - the inflammation is relieved, the appendages restore their function and within several cycles their complete restoration and conception of a child becomes possible.
Treatment of inflammation
Treatment tactics are chosen by the attending physician and depend on the form of the disease and the cause of its occurrence. Acute forms are usually treated in a hospital with antibiotics.
In severe cases, surgical intervention, such as laparoscopic debridement, may be necessary. It allows you to remove accumulated suppuration, dissect adhesions, irrigate the uterus with saline solution with an antibiotic, and remove adhesions of the fallopian tubes to prevent blocking their lumen.
Treatment is a complex undertaking that requires detoxification of the body through intravenous therapy and physiotherapy. The procedures include physiotherapy, mud therapy, autoplasmotherapy, autohemotherapy, and gynecological massage.
Complications
If treatment is untimely or completely absent, quite serious complications are possible, affecting not only the reproductive organs. There is a high probability of developing primary and secondary infertility.
The appearance of adhesions between the fallopian tubes and the ovaries block the lumen of the tubes and prevent sperm from entering the cavity for fertilization. There is also too great a risk of ectopic pregnancy due to the fact that the egg cannot leave the fallopian tube due to the adhesion.
Even with successful fertilization and the birth of the fetus in the uterus, the pregnant body with salpingoophritis will reject the fetus, and blood circulation between the uterus and placenta will be disrupted. Possible infection of the fetus, premature birth and spontaneous miscarriage.
You can plan a healthy pregnancy only when inflammation therapy is completed. At the same time, treatment is continued even when the inflammatory process has disappeared, to prevent relapse. In most cases, therapy continues until the moment the child is conceived.
Prevention
To avoid recurrence of inflammation of the appendages, you should have an active sex life with one partner and beware of unprotected sexual intercourse. Hypothermia must be avoided, and any infections or viruses that appear, even those not affecting the reproductive organs, must be eliminated effectively and as quickly as possible.
Women planning a second pregnancy after a cesarean section or natural birth must undergo an ultrasound of the pelvic organs to exclude the presence of adhesions and inflammatory foci.
The inflammatory process in a woman can develop in both the external and internal genital organs.
Unfortunately, some diseases caused by inflammation make it impossible to achieve or carry a normal pregnancy. In this article we will look not only at the main inflammatory gynecological diseases, but also determine whether it is possible to get pregnant with endometritis and other “female” ailments.
Inflammatory diseases of the external genitalia of women include:
- vaginitis;
- vulvitis;
- bartholinitis.
Inflammatory diseases of the female internal genital organs (pelvic organs) include:
- endometritis (inflammatory process in the uterine cavity);
- salpingitis (inflammatory process in the fallopian tubes);
- cervicitis (inflammatory process in the cervix);
- adnexitis (salpingoophoritis - inflammatory process in the uterine appendages);
- oophoritis (inflammation of the ovaries);
- pelvioperitonitis (inflammatory process in the pelvic peritoneum).
According to statistics, inflammatory diseases of the female genital organs are in first place among all gynecological ailments.
Pap smear during pregnancy
A smear for cytology during pregnancy is taken at least 3 times - this can be done either in the gynecologist’s office or in a private laboratory - for example, in Invitro using liquid cytology.
The study is important for monitoring the vaginal microflora of the expectant mother. If there is the slightest suspicion that a woman’s genital tract is infected, a cytological examination is performed additionally. Read more about taking a smear during pregnancy →
The result of a smear on flora above type 2 purity during pregnancy means an inflammatory process in the woman’s genital tract. In this case, the expectant mother may complain of itching and burning in the external genital area, as well as a change in the smell and color of vaginal discharge.
Many women wonder whether it is possible to get pregnant if they are diagnosed with cervicitis.
In most cases, the cervical canal retains its patency and does not create obstacles to the penetration of sperm. Thus, pregnancy can occur naturally.
If, during the process of inflammation, adhesions or scars have formed, or the walls of the cervical canal have become much thicker and denser, this creates an obstacle to natural fertilization and the woman is diagnosed with infertility.
In this case, it is possible to restore the patient’s ability to conceive through surgery, restoring the patency of the cervix, or using in vitro fertilization (IVF).
When planning a pregnancy, it is better to contact a gynecologist in advance to identify possible pathologies. If inflammation is detected when a woman is already pregnant, the doctor prescribes comprehensive treatment, taking into account the contraindications characteristic of this female condition.
At the slightest suspicion of the presence of infections and fungi harmful to the fetus, cytology is often used. The inflammatory type of smear makes it possible to diagnose pathological processes if a woman complains of burning and itching of the external genitalia, changes in the color and smell of discharge.
To analyze the state of the vaginal microflora in pregnant women, cytology smears are done at least three times. If necessary, your doctor may order additional PAP tests.
READ MORE: Is it possible to take cytology during menstruation?
A Pap test for pregnant women is performed using conventional technology.
Symptoms
The main symptoms of inflammation of the genital organs are pain in the lower abdomen, the presence of pathological discharge from the vagina, as well as swelling of the tissues.
The inflammatory process of the female genital organs can have an acute and chronic course. Acute inflammation has pronounced symptoms - severe pain in the lower abdomen, a rise in body temperature, as well as a general reaction of the body. A chronic inflammatory process can develop as a consequence of acute inflammation, but it can also begin immediately without a preliminary acute phase. Chronic inflammatory process of the female genital organs often occurs asymptomatically or with mild symptoms; exacerbations alternate with short-term improvements. If treatment for acute inflammation is not started in time, then over time it will develop into a chronic form.
It should be noted that recently, asymptomatic gynecological diseases, including sexually transmitted diseases, have become increasingly common. Moreover, even pathological vaginal discharge does not always occur with such diseases. Without special tests, it is difficult to distinguish them from the norm.
With the hidden course of female diseases, there is no pain in the abdomen, bleeding, irregularities in the menstrual cycle and other symptoms. For this reason, every woman needs to undergo a preventive examination with a gynecologist at least twice a year. Constant monitoring will allow early detection and treatment of the inflammatory process.
Inflammatory processes of the female genital organs often provoke disorders of sexual and reproductive functions, involving secondary cardiovascular, nervous, endocrine, and other systems of the woman’s body in this pathological process. As a result of inflammatory diseases, a woman may develop a severe adhesive process in the fallopian tubes, which is the cause of tubal infertility.
Let's look at the possibility of the occurrence and development of pregnancy due to various inflammations.
Purpose of the analysis
What does a smear reveal for flora and cytology? Its main purpose is to detect pathological changes in tissues, which can later transform into a cancerous tumor.
If a cytology smear from the cervix is taken regularly, then negative indicators can be identified at an early stage - for example, an inflammatory disease, which can be cured in a short time with appropriate therapy and prevent further complications.
What does a cytology smear show? The results of the study can be both positive and negative.
Positive can be "bad", "abnormal", "atypical" or mean "dysplasia". It is clear that a bad cytology smear is not the norm, that is, there are inflammatory changes in the mucosa, and atypical pathological cells are detected in the smear, which should not be there.
A negative smear is considered normal. This means that the cervix is healthy, the cellular structure of the epithelium is not changed, and the microflora does not contain pathogenic microbes.
In order to prevent and prevent the development of dangerous diseases, cytology of a smear from the cervical canal is done for every woman. This analysis allows us to identify abnormalities in the cellular structure of the cervix that cause the development of cancer.
To avoid possible pathologies, all women should regularly visit a gynecologist. If changes occur, they are recorded at an early stage, when the disease is treatable and full recovery is still possible.
READ MORE: Cytology analysis in gynecology, what is it
In addition to cellular pathologies, a cytology smear allows you to evaluate the mucous membrane and determine the presence of harmful microorganisms in the vagina. The PAP test does not determine the exact data of these parameters, so in such cases it is necessary to use additional methods of analysis.
Can you get pregnant if you have ovarian inflammation?
Ovarian inflammation, especially its chronic form, is fraught with irreversible consequences, including infertility and ectopic pregnancy. It is very difficult to get pregnant with oophoritis, since hormonal levels and the process of egg maturation are disrupted. As a result, pregnancy in the presence of ovarian inflammation can be accompanied by disturbances in the development of the fetus, as well as miscarriage, which can occur at any stage of pregnancy.
So, when thinking about pregnancy with ovarian inflammation, you need to immediately think about the possible consequences.
Treatment
It is difficult to treat the condition during pregnancy, especially in the early and middle stages, since the use of antibiotics is contraindicated during this period. Namely, taking them is the main way to treat the condition. Pregnant women can be prescribed immune drugs, which can sometimes suppress the process or transfer it to a chronic stage. However, this happens quite rarely.
Therefore, in most cases, broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed, such as amoxicillin, metronidazole, etc. They are quite effective, but can have a negative effect on the fetus. Therefore, it is better to plan a replenishment after adnexitis.
Chronic endometritis: is it possible to get pregnant?
Chronic endometritis often becomes a serious obstacle to pregnancy and the birth of a child.
The fact is that the inflamed endometrial membranes are not ready for implantation of a fertilized egg into the uterus. Therefore, with chronic endometritis, the following are usually observed:
- absolute infertility;
- inability to carry a pregnancy to term (2 or more miscarriages or missed pregnancies in a row);
- lack of IVF success.
The chances of a successful pregnancy and subsequent pregnancy are greatly increased after adequate treatment of chronic endometritis.
Modern medicine offers many ways to treat inflammation of the female organs, which normalize the functioning of the entire reproductive system, allowing a woman to conceive and successfully bear an absolutely healthy child. Indeed, today, thanks to assisted reproductive technologies, you can even get pregnant without fallopian tubes! You should not rely on chance and, dreaming of pregnancy, you should definitely consult with specialists.
In medicine, inflammation of the ovaries and fallopian tubes is called adnexitis or salpingoophoritis. Is it possible to get pregnant if the ovaries and fallopian tubes are inflamed?
This question interests many women of childbearing age, since these pathologies are quite common.
The likelihood of pregnancy with adnexitis depends on several factors:
- the stage at which the disease is;
- the presence of any complications and concomitant diseases;
- patient's age;
- physiological characteristics of a woman’s body.
Modern gynecology has a separate direction, which is based on the treatment of the ovaries and restoration of the functionality of the female reproductive system, so that the expectant mother can normally bear and safely give birth to a child.
If the connective tissue during inflammation of the ovaries does not have rough scars that prevent the normal passage of an unfertilized egg through the fallopian tubes, nothing interferes with the occurrence of pregnancy.
However, harmful bacteria that appear as a result of the inflammatory process can create dysfunction of the egg, and it will not be able to move to the uterus.
When the tubes become completely obstructed, infertility occurs.
If the egg is stuck in the fallopian tube and an active sperm gets close to it, pregnancy can occur directly in the tube. This condition is pathological and is called “ectopic pregnancy”.
There is only one treatment for ectopic pregnancy - an operation in which the fertilized egg is removed along with part of the tube. And if you can imagine, then in case of an ectopic pregnancy, surgical intervention is necessary.
Adnexitis is also characterized by the fact that ovulation occurs at a slow pace, and the female body experiences a deficiency of progesterone.
Fertilization may occur, but there is a risk of pregnancy termination in the early stages.
Consequences of the disease for pregnant women
Is it possible to get pregnant with cervicitis? It's possible, but it's not worth it. When a pregnant woman experiences cervicitis of the cervix, there is a high probability of spontaneous abortion in the early stages. There is also a danger that the fetus can become infected in utero, and labor can begin ahead of schedule.
After birth, a child may acquire purulent-septic lesions of the skin and internal organs due to an infection that has entered the baby’s body.
If pathogenic microorganisms enter during the first stages of pregnancy, placental insufficiency may develop and problems may arise with the formation of the child’s organs. This can lead to freezing and miscarriage of the fetus.
If cervical pathology appears in late pregnancy, then the baby may have developmental delays, as well as the formation of serious infectious pathologies.
Other possible dangers and complications
Adnexitis during pregnancy can cause damage to the uterine cavity, which will lead to its vulnerability to all kinds of viral infections.
Even a fertilized egg in such a situation will be perceived by the uterus as a foreign object that it must expel.
- With inflammation of the ovaries, a fertilized egg can attach to the lower part of the uterine cavity. In this case, the woman will most likely experience bleeding.
- Adnexitis during pregnancy can cause a woman’s body to begin to produce antibodies.
- Thrombohemorrhagic syndrome may develop, the danger of which is thrombosis and placental abruption.
Inflammation of the ovaries in a pregnant woman can lead to the following pathological processes:
- Miscarriage.
- Fading pregnancy.
- Fertilized egg without embryo.
- Fetal infection.
- Premature delivery.
If adnexitis becomes chronic, a hormonal imbalance may occur in the female body with all the ensuing consequences.
What can cause adnexitis and how to treat it
Most often, the virus that provokes inflammation of the appendages enters a woman’s body during sexual intercourse, although failure to comply with basic rules of individual hygiene plays a huge role in this regard.
Other, no less common, causes of adnexitis are artificial abortions, diseases of an infectious or inflammatory nature.
Poor immunity, stress and nervous tension, and hypothermia play an important role.
Bacteria that provoke adnexitis:
- chlamydia;
- mycoplasma;
- gonococci;
- streptococci;
- staphylococci.
To diagnose the possibility of pregnancy, doctors use ultrasound, take cultures from the vagina, and study blood and urine tests.
In order for a woman to have the opportunity to become pregnant and bear a child after suffering inflammation of the appendages, she must take all measures to restore her hormonal levels, strengthen the immune system and normalize metabolism.
Before a planned conception, a woman must undergo a course of anti-inflammatory and hormonal therapy. Pregnancy should occur no earlier than six months after complete recovery.