Causes of cystitis
To prevent cystitis, you need to understand why it starts.
This pathology is based on an inflammatory process, which is infectious or non-infectious in nature. Infectious cystitis occurs due to the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the bladder. By multiplying in it, they provoke the development of the disease. There are a number of reasons for this:
- The presence of acute or chronic inflammation of the genital organs in women. Even ordinary vaginal candidiasis or thrush can cause cystitis. Sexually transmitted diseases also lead to its development.
- Hypothermia. Each organism has its own opportunistic microflora, which, in normal health, does not cause any pathological processes. Once a person gets cold, his immunity decreases. As a result, opportunistic microorganisms acquire negative properties, which causes the development of the disease.
- Bacteria can enter the bladder from foci of inflammation located in other parts of the body. In this case, the route of infection is hematogenous or lymphogenous.
- There is a special type of this disease, which is popularly called “honeymoon cystitis.” It occurs after unprotected sexual intercourse, especially if it occurs for the first time in both partners. Also, having sex during menstruation predisposes to the development of this pathology.
- Cystitis is often one of the first signs of an “interesting situation.” In pregnant women, under the influence of hormones, the immune system is suppressed. This is how nature intended, because initially the unborn child is foreign genetic material for the mother’s body.
- Taking medications that suppress ovulation or emergency contraception. This leads to disruption of the natural hormonal levels of the female body. The result of this is a decrease in the activity of the immune system and increased susceptibility to various infections.
Non-infectious cystitis develops due to exposure to unfavorable factors on the body. This also causes the development of an inflammatory process in the bladder. These include:
- Urolithiasis disease. Stones located in the lumen of the bladder have an irritating effect on its intima. Over time, this leads to the development of inflammation in it.
- Radiation therapy for malignant neoplasms or taking antitumor drugs. These aggressive types of exposure have a destructive effect not only on the tissue affected by metastases, but also on the mucous membranes of all organs.
- Abuse of alcohol, fatty and spicy foods.
- Traumatic damage to the intima of the bladder during endoscopic manipulations or diagnostic procedures.
- Prostatic hypertrophy in older men. An enlarged prostate prevents the free passage of urine, causing it to stagnate in the bladder. With prolonged contact with his intima, urine has an irritating effect on it.
- Menopause period in women. At this stage of life, the function of the reproductive organs fades and hormonal levels change. Under the influence of hormones, atrophic processes are triggered in the female body, especially in the mucous membranes.
The following causes of the disease are identified:
- Infections. A common cause of cystitis are representatives of gram-negative flora (80%) - Escherichia coli, Proteus, Enterococcus, Klebsiella. About 20% are gram-positive microflora (staphylococcus, streptococcus), ureaplasma, chlamydia, fungi, viruses, helminths, zoonotic infection. The most common method of infection is ascending. This occurs when bacteria enters the genitals or anus and travels through the urethra into the urinary organs. A contributing factor may be a decrease in immunity due to hypothermia of the patient's body. This route of transmission of infection is observed in 86% of cases. Less common is the so-called descending route - penetration of infection through the blood or lymphatic tract. This occurs when there is any focus of chronic infection in the body (caries, sore throat). Cystitis during pregnancy occurs in the presence of microorganisms and decreased immunity due to changes in hormonal levels.
- Taking medications. Sometimes patients suffering from chronic diseases of the musculoskeletal system or cancer are forced to take cytostatics. Such drugs cause inflammation in the genitourinary organs as a side effect. This is caused by the release of acrolein during the metabolism of the drug, which has an irritating effect on the mucous membranes. In this case, medicinal cystitis develops.
- Allergic reaction. The development of acute cystitis is due to the individual characteristics of the body - a reaction to certain allergens that cause inflammation in the bladder. Subsequent knowledge of how the disease manifests itself will help avoid the development of the inflammatory process.
In 80% of cases, E. coli (Escherichia coli) is the cause of cystitis.
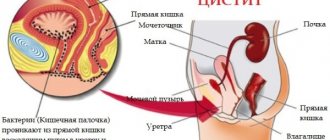
In women, cystitis develops much more often, which is due to anatomical features. The urethra is very close to the entrance to the vagina, and the anus is also located nearby. If the rules of intimate hygiene are not followed, E. coli can easily penetrate the urinary tract.
Development of cystitis in women.
Cystitis occurs 4 times more often in women than in men.
The main cause of the disease is a bacterial infection.
Sometimes non-infectious (aseptic) cystitis occurs. This condition develops when the mucous membrane is damaged by instruments during medical research, by stones during urolithiasis, or by the introduction of various chemicals into the organ. Radiation and chemotherapy can also cause inflammation in the bladder. It should be borne in mind that such cystitis quickly becomes infectious due to the attachment of microorganisms.
Manifestation of the disease
Signs that indicate acute cystitis in women:
- A sharp increase in the number of visits to the toilet.
- High temperature due to poor health.
- Urinary incontinence, especially at night.
Along with the listed symptoms, aching pain occurs in the pubic area and lower abdomen. If acute cystitis in women was caused by inflammatory processes in the urinary canal, then in this case it will manifest itself as itching and burning, especially when going to the toilet.
Prevention of tetanus in wounds
You should also pay attention to the color of urine - when cystitis manifests itself, it becomes cloudy from blood impurities. This is especially pronounced in acute hemorrhagic cystitis.
In this case, regardless of the form of the disease, it is important to complete the entire course of treatment measures. By the way, even a full course of medication does not guarantee a complete cure for cystitis if there are no symptoms. Accordingly, treatment must be completed until the inflammatory process is completely relieved in order to avoid subsequent relapse and the need for surgical intervention.
How to treat cystitis?
Every person should know how cystitis begins, so that if alarming symptoms appear, consult a doctor. This seemingly harmless disease can cause more serious health problems. Therefore, it should be treated by a specialist.
At the initial stage of the disease, you can go to a local clinic at your place of residence, see a local therapist, who will refer you for the necessary examinations, and then, based on their results, prescribe appropriate therapy. In case of severe cystitis or when complications develop, treatment is carried out by a urologist in a hospital setting.
Alternative medicine offers a considerable arsenal of remedies that are effective in the fight against cystitis. To get rid of the disease, it is recommended to take a decoction of dill seeds or parsley leaves, an infusion of chamomile flowers and lingonberry leaves. Warm baths with natural antiseptics - chamomile, calendula - help well. If the patient does not feel better within 24 hours of treatment with folk remedies, you should consult a doctor.
In the absence of adequate treatment, acute cystitis becomes chronic, which relapses several times a year. Possible upward spread of infection to the kidneys, which leads to the development of acute pyelonephritis.
We suggest you read: Urine smells when you have cystitis - Without cystitis
With the prolonged presence of stones in the bladder, bedsores form on its intima, which leads to damage to the deeper layers of its wall. Due to constant contact with urine, which is an aggressive environment, ulcerative defects occur. Over time, they may perforate and develop urinary peritonitis, which often leads to the death of patients.
Clinical symptoms of the disease last about a week, reducing the patient’s capacity and activity for 3-4 days.
Typically, symptoms of acute cystitis in a woman appear after suffering from hypothermia, after menstruation, sexual intercourse, or defloration. Risk factors in premenopausal women include a history of acute cystitis in the past and sexual activity. In women who do not have sexual intercourse, the disease rarely develops.
Cystitis develops less frequently in men, and the symptoms do not differ from the classic ones. The first signs of cystitis appear 2-3 days after sexual intercourse, and the risk of its occurrence increases when using spermicides.
As the disease develops, the following symptoms are observed:
- Urge for frequent imperative urination, during which pain, pain and burning occur in the urethra. Urination in small portions with a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder.
- Pain and discomfort. The first and most common symptom of cystitis. Patients complain of unpleasant painful sensations in the perineum and lower abdomen. The intensity varies. Sometimes the disease is asymptomatic - on average in 10% of cases, and patients do not attach any importance to this. This leads to chronicity of the process and the development of complications. Patients may also complain of slight pain in the lower abdomen with radiation to the back, which causes difficulties in diagnosis.
- Burning, itching. It is the most characteristic symptom of the disease.
- Fever, headache, malaise, increased fatigue, decreased performance.
- The appearance of blood in the urine is hematuria. Depending on the amount of urine, the color of urine can range from pale pink to brick. The presence of blood indicates a viral etiology of the disease. In severe cases of the disease, sharp pain occurs when urinating and the release of droplets of blood at the end of urination.
- The urine of patients with cystitis has a characteristic cloudy color and an unpleasant odor.
- When palpated in the suprapubic region, patients complain of pain.
The most common symptom of cystitis is pain in the perineum and lower abdomen.
Pathogenesis of cystitis in women.
Pathogenesis of cystitis in men.
Pain and frequent urination are symptoms of cystitis.
If acute cystitis is not treated, or when therapy for the disease is incomplete, the process becomes chronic. During periods of remission there are no manifestations of cystitis, but during exacerbations the same symptoms occur as in acute pathology.
To improve well-being and relieve pain, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. For example, diclofenac, nurofen, ketorol are used.
Antispasmodics can also be prescribed to reduce discomfort. Such means include no-spa.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NCjmNsrqrlI
The main reason for the development of cystitis is the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the bladder cavity. The causative agent of the disease can be bacteria, viruses, fungi and even protozoa. Most often, cystitis of a bacterial nature is observed, when the causative agent is Escherichia coli.
The most common types of cystitis in women are defloration and associated with sexual intercourse.
In addition to pathogenic bacteria, the following factors can cause cystitis:
- taking certain medications, such as Ifosfamide or Cyclophosphamide;
- ionizing radiation, which is used in the treatment of cancer;
- a foreign body, which can be a urethral catheter;
- exposure to chemicals that are part of personal care products;
- other diseases of the genitourinary system, for example, urolithiasis, prostatitis;
- damage to the spinal column, etc.
In some cases, it is not possible to determine the cause of the disease, so this cystitis is called interstitial.
There are also a number of factors that contribute to the development of the inflammatory process in the bladder, which include the following:
- local or general hypothermia of the body;
- stagnation of urine in the bladder;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- unbalanced and unhealthy diet (eating large amounts of hot and spicy foods);
- pregnancy;
- childbirth;
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- wearing tight or synthetic underwear and clothing;
- sexual infections;
- surgical interventions and invasive research methods on the organs of the reproductive and urinary systems.
The first signs of cystitis in women may be as follows:
- frequent urge to urinate;
- feeling of bladder fullness;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- pain and burning along the urethra after urination;
- the appearance of pathological impurities in the urine (mucus, blood, pus).
In severe cases, the clinical picture of cystitis can be supplemented by symptoms of general intoxication of the body, namely: increased body temperature, general weakness, chills, excessive sweating, etc.
If you are concerned about the above symptoms, do not under any circumstances engage in self-diagnosis or self-medication, as this does not always bring the expected result.
A urologist diagnoses and treats cystitis. Only a specialist knows how to properly treat this disease in order to avoid chronicity of the inflammatory process and not cause harm to health.
Therefore, if you experience at least one of the above signs of cystitis, contact your nearest clinic for an appointment with a urologist. The doctor, after conducting a comprehensive examination of the body, will make an accurate diagnosis and select the most effective treatment regimen for you.
Treatment of cystitis is mainly carried out on an outpatient basis under the guidance of a urologist. Indications for hospitalization of patients may be severe intoxication syndrome, spread of the inflammatory process to the kidneys, or cystitis in pregnant women.
You can treat cystitis at home only after consulting a urologist, since all drugs have side effects, and folk remedies are not effective enough to cope with bacterial inflammation.
An experienced specialist can cure acute cystitis quickly, in about 2-3 days, but the fight against chronic inflammation of the bladder can take several weeks.
Before treating chronic cystitis, it is necessary to find out the cause, because only by eliminating it can a positive effect of therapy be achieved.
When treating cystitis, specialists are guided by the following principles:
- bed or semi-bed rest throughout the entire period of acute symptoms of the disease;
- therapeutic nutrition. The diet for cystitis should be dairy-vegetable, that is, fermented milk products, vegetables and fruits should predominate in the patient’s daily diet. Fried, hot, salty and spicy foods, as well as alcoholic drinks are strictly prohibited;
- antibacterial therapy. Antibiotics are prescribed first with a broad spectrum of action, and after obtaining the results of urine culture and antibiogram. An antimicrobial drug is used, to which the causative agent of cystitis is sensitive;
- analgesic therapy. For severe pain in the bladder, patients are prescribed painkillers and antispasmodics;
- installation of antiseptics in the bladder;
- phytotherapy. Diuretic herbs and herbs are used. Let's look at it in more detail below;
- physiotherapeutic treatment (electrophoresis, phonophoresis, inductothermy, UHF and others).
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Uro-Vax for cystitis: features of using the drug
There are also cases when chronic cystitis in women has to be treated using surgical methods. Surgery is necessary if the outflow of urine from the bladder is impaired by a stone, tumor or foreign body. Also, surgical intervention is indispensable when the walls of the bladder become wrinkled, when an antiseptic solution is injected into it under general anesthesia to straighten it.
Antibiotics occupy a central place in the treatment of acute and chronic cystitis. The selection of an antibacterial drug should be done exclusively by a specialist, since self-medication can lead to irreversible health consequences.
Let's look at the most effective antibiotics used for cystitis in women.
Nitroxoline
https://youtu.be/C_6QsDiDH5c
Nitroxoline is a derivative of eight-hydroxyquinoline and belongs to the oxyquinolones. The drug is active against most gram-positive and gram-negative microbes, as well as some fungi, in particular candida.
Nitroxoline is indicated for cystitis, urethritis and pyelonephritis.
Scheme and doses: 2 tablets (100 mg) 4 times a day with meals for 14-21 days.
Treatment of acute inflammation
Getting rid of only the painful and inconvenient symptoms of a disease is not an effective treatment. It is necessary to take a comprehensive approach to the problem, eliminate the causes of the disease, stop the inflammatory process, and prevent the emergence of new lesions.
Medications
The following remedies will help relieve inflammation and pain in acute cystitis:
- Products that have an antibacterial effect. These are antibiotics of various spectrums of action, for example, the penicillin series, the fluoroquinolone group. Drugs are selected specifically for the type of infection or concomitant disease. Additionally, studies can be carried out to determine the susceptibility of bacteria to a particular active component. They must be taken as a course; even after visible improvements, the scheme does not need to be interrupted. Prescribed exclusively by a doctor.
- Antispasmodics. Since the symptoms of acute cystitis include pain and cramps, it is antispasmodics that help relieve discomfort and facilitate urination.
- NSAIDs or non-steroidal drugs . Their purpose is explained by the need to stop the inflammatory process, relieve the main symptoms, but not eliminate the cause. You can only take NSAIDs for a certain period, since long courses can have a negative effect on the body.
- Steroid hormones or corticosteroids . The drugs are used only for the eosinophilic form of the pathology, which is quite rare and associated with a change in the size of the bladder, namely its reduction.
- Herbal medicines . Herbal medicines may be recommended as an addition to the main treatment. Their natural composition helps as a diuretic and anti-inflammatory agent. There are ready-made urological herbal mixtures and preparations made from herbal ingredients.
It is important to drink enough liquid, at least 2 liters per day.
In addition to taking basic medications, physiotherapeutic procedures or direct effects on the bladder can help in the fight against cystitis.
Physiotherapy
After the acute painful stage of bladder inflammation has been relieved, physiotherapeutic measures are recommended for effective treatment. It can be:
- hardware ultrasonic influences;
- electrophoresis;
- magnetic therapy;
- influence of electromagnetic fields.
Physiotherapy is carried out only as prescribed by the attending physician with a preliminary analysis of possible contraindications.
Phytotherapy
The use of herbal components is encouraged for diseases of the bladder and kidneys, but subject to proper use. Decoctions are good at stimulating urination, which is necessary in inflammatory processes to prevent stagnation of urine.
The fees are prepared independently and purchased ready-made. Preparations that combine natural ingredients, additionally enriched with vitamins and other active ingredients are considered universal.
In urology, herbs such as lingonberry leaves, chamomile, tansy, St. John's wort, cross, oak bark, licorice, bearberry, string, birch buds, horsetail are often used.
Diet
Proper nutrition will help speed up recovery and reduce the likelihood of inflammation reoccurring. Spicy and fried foods, alcohol, coffee are canceled, it is better to give up fast food, smoked meats and other well-known junk food. You need to increase your diet with plant-based and natural products.
Provoking factors
There are predisposing factors, the presence of which increases the likelihood of developing the disease. The bladder mucosa has effective mechanisms that prevent infection from entering it. A decrease in local immune defense is facilitated by:
- Hormonal disorders.
- Hypothermia.
- Hypovitaminosis.
- Accompanying illnesses.
- Postponed surgeries.
- Chronic constipation.
- Prolonged sitting.
- General immunodeficiency.
Impaired urine flow is another factor that often provokes the occurrence of cystitis. This may be caused by:
- Prostatic hyperplasia (adenoma).
- Weakness of contractile activity of the muscular layer of the bladder.
- Disturbances in the regulation of the act of urination on the part of the nervous system.
- Narrowing of the lumen of the urethra (urethra), which, for example, is often noted after sexually transmitted diseases.
Prostate adenoma interferes with the flow of urine.
Also provoking factors for the development of cystitis are:
- Sex with a lot of partners. Frequent changes and unprotected sex lead to cystitis. True, this is the best case scenario. More often, acute cystitis becomes a manifestation of one of the sexually transmitted infections.
- Changes in blood circulation in the pelvic area, which is caused by wearing tight underwear, tights, and sedentary work. Leads to favorable conditions for the proliferation of microbes and promotes the inflammatory process.
- Chronic kidney disease. Their presence contributes to the disease and leads to a decrease in immunity.
- Intestinal diseases. In this case, pathogenic microflora is activated, which penetrates the urinary tract.
- Nutritional – errors in the diet cause irritation in the bladder mucosa and symptoms of cystitis appear.
- Changes in hormonal levels during diabetes, menopause, obesity. It leads to a decrease in immune status, and against this background it is easier for microbes to penetrate the mucous membrane and cause inflammation.
- Contraception with spermicides, use of contraceptive diaphragms.
- Gynecological diseases that change the normal microflora of the vagina.
Unprotected sex provokes the appearance of cystitis.
The causes of the inflammatory process in the bladder are associated with a decrease in the body's defense reactions. With a good immune status, pathogens, once in the bladder, are not able to gain a foothold on the urinary mucosa and are washed out of it along with urine.
The following factors can provoke a decrease in local immunity and the development of infection:
- instrumental interventions on the bladder;
- infections transmitted from partner to partner;
- injury to the urethra during coitus (sex);
- hormonal changes (menopause, menstruation, pregnancy);
- long inability to urinate;
- sudden change in climatic conditions, hypothermia.
The causes of the disease may lie in the presence of genitourinary diseases (urolithiasis, urethritis, pyelonephritis, etc.) or diabetes. With these pathologies, local immunity is weakened, which contributes to the development of infection if the pathogen penetrates into the urinary organ.
Acute cystitis is provoked by Escherichia coli, which accounts for about 80% of cases. Other opportunistic microorganisms that live in the intestines, including Klebsiella and Proteus, can also cause exacerbation. Less commonly, herpes viruses, chlamydia, trichomonas, mycoplasma and Candida fungi contribute to the disease.
Acute cystitis in children
Cystitis can occur in children of almost any age, but most often this disease is detected in girls 5-6 years old. The main reason for the development of an acute inflammatory process in the bladder is the anatomical features of the structure of the genitourinary system, weak local protection of the mucous membrane of the bladder, and the lack of endocrine function of the ovaries. In addition, a prerequisite for the development of cystitis in girls is improper washing of the external genitalia, when E. coli gets from the anus to the urethra. To avoid the development of cystitis in girls, the mother must either wash her daughter herself or teach her to do it correctly - from front to back.
Frequent viral infections and weakened immunity create excellent conditions for the proliferation of pathogenic microflora in the body and the development of cystitis.
Classification of cystitis
By etiology:
- Infectious (indicating the pathogen).
- Non-infectious (chemical, medicinal, allergic, food).
With the flow:
- Spicy.
- Chronic (duration more than 3 months).
According to the presence of complications:
- Uncomplicated - develops with unchanged urinary tract, without concomitant diseases and provoking factors. About half of patients are subsequently diagnosed with an occult kidney infection.
- Complicated – occurs against the background of functional and organic changes in the bladder, the presence of concomitant diseases of the internal organs, after instrumental research methods. Complicated conditions also include old age, hospital infection, and pregnancy.
Pathogenesis of cystitis.
Possible complications and prevention
Lack of treatment for cystitis leads to the appearance of a chronic form, which takes longer and more difficult to get rid of. In particularly advanced cases, the kidneys become infected, disruptions occur in their functioning, pyelonephritis and other serious pathologies develop.
There are certain rules to prevent the occurrence of acute cystitis. These include the following recommendations:
- proper intimate hygiene using appropriate cosmetics;
- regular emptying of the bladder and bowels;
- avoiding hypothermia of the body, in particular the pelvic organs;
- protected sex with an unverified partner;
- If symptoms appear, even minor ones, get tested and consult with a therapist, urologist or gynecologist.
Any disease, including acute cystitis, is easier to cure if measures are taken in the initial stages. There is no need to ignore discomfort and unusual conditions; you should seek advice from a specialist as soon as possible.
What tests are performed for cystitis?
To confirm cystitis, the specialist must prescribe the following tests to the patient:
- general urine analysis;
- urine analysis according to Nechiporenko;
- bacteriological examination of urine;
- cystoscopy;
- ultrasound examination of the bladder and abdominal organs, including the kidneys.
In urine with cystitis, you can find a large number of white blood cells, bladder epithelium, as well as bacteria that caused this disease.
Urine culture allows you to determine which microbe caused cystitis and which antibacterial drug it is sensitive to and which it is resistant to, which greatly facilitates the selection of an effective treatment regimen.
Protein in the urine during cystitis, regardless of its quantity, should in no case go unnoticed, since its appearance may be a sign of impaired kidney function.
Cystoscopy is an endoscopic examination of the bladder, which is performed using a special device - a cystoscope. A cystoscope is a metal tube equipped with a video camera and a set of instruments, which is inserted through the urethra into the bladder. Using this study, you can carefully examine the bladder mucosa, take material for histological analysis, and, if necessary, perform a minor operation, for example, remove a polyp.
An ultrasound examination of the bladder and kidneys is carried out to assess the condition of the organ itself and surrounding tissues.
Diagnostics
The first symptoms of cystitis force the patient to seek medical help. To confirm the diagnosis of “bladder inflammation” and receive treatment, you need to contact a nephrologist, urologist, or gynecologist. The doctor will collect the necessary medical history and ask what medications the patient is taking, whether he has had unprotected sexual intercourse, stressful situations, and what concomitant diseases he has.
Laboratory and instrumental studies for cystitis:
- General urine analysis;
- General blood analysis;
- Bacteriological culture of urine to identify the causative agent of infection;
- Ultrasound of the bladder to study organic changes in the structures of the affected organ;
- Urethroscopy and cystoscopy.
Obtaining the result of a bacteriological examination of urine may take several weeks, but based on the results, the attending physician, knowing the causative agent, will be able to quickly cure cystitis and accurately select an antibiotic. Cystoscopy is not performed in acute forms of the disease, although it is an exclusively informative study.
Cystitis during pregnancy
During pregnancy, immunity decreases, which becomes one of the risk factors for acute cystitis. This condition is an adaptive reaction of the body to pregnancy and prevents embryo rejection. Because of this, the microorganism, entering the bladder, quickly causes an inflammatory process.
Cystitis can develop in early pregnancy, but the disease has the same symptoms as in the classic development of the disease. The pathology should be differentiated from frequent urination, which occurs in a pregnant woman due to an enlarged uterus and compression of the bladder. In this case, the woman does not experience the discomfort and unpleasant sensations that are characteristic of cystitis. After 3 months, the uterus lifts up and stops putting pressure on the bladder - everything returns to normal and the symptoms disappear.
Pregnancy is a risk factor for cystitis.
Symptoms of cystitis in children are varied and include:
- General symptoms are fever, chills, intoxication, dyspeptic symptoms.
- Pain syndrome is the appearance of pain in the lower abdomen, in the side, in the urethral canal when urinating.
- Dysuric disorders - leakage, urinary incontinence day and night, not previously encountered, imperative urges, frequent urination.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Nematodes (roundworms) - structure, classification, infection
Clinical manifestations vary depending on the age of the child. In young children, general symptoms predominate. There are no specific ones and children at this age cannot always indicate the complaints that bother them.
In older children, the general condition is slightly disturbed, as a result of which there are no signs of intoxication or fever. Here dysuric disorders and pain syndrome come to the fore.
Which doctor should I contact?
Since cystitis refers to diseases of the urinary system, a specialized doctor is a urologist, and it is he who should be contacted if you notice characteristic signs of inflammation.
For some reason, it is generally accepted that a urologist is a male doctor, so women are embarrassed to contact him.
Meanwhile, this is just a myth, and due to prejudice, the patient may receive illiterate advice, and improper treatment will lead to the disease becoming chronic.
Unfortunately, not all clinics can boast of having a urologist; in this case, you will have to either go to a private clinic or ask your local physician for a referral to another hospital.
Regimen for the treatment of cystitis
Treatment of cystitis at home includes following the following recommendations. You need to adhere to bed rest. You should only go to a warm toilet so as not to aggravate the disease. During treatment of cystitis, it is necessary to avoid sexual intercourse.
The following foods should be avoided in your diet:
- Fat.
- Too spicy.
- Salty.
- Alcohol.
- Carbonated drinks.
The consumption of these products has an irritating effect on the walls of the bladder. During the period of illness, it is important to drink more fluid, up to 2 liters per day.
For example, for cystitis, cranberry juice is recommended. It allows the body to quickly cope with the manifestations of the disease, and its use makes urine less suitable for the proliferation of microorganisms. It is best to choose freshly squeezed juice, and you should not use a packaged drink. You can make your own cranberry juice.
Cranberry juice is useful for cystitis.
Lingonberry is another berry, the use of which is useful for bladder inflammation. The active substances it contains have a disinfecting effect. In order to prepare a healthy drink, you need to pour a tablespoon of berries with a glass of boiling water and let the product brew.
These products are used at home by women and men. They help reduce the severity of cystitis symptoms and enhance the effect of other tablets.
Canephron.
Applicable:
- Monurel.
- Canephron.
- Phytolysin.
Monurel contains dry cranberry extract and vitamin C. This product prevents the active proliferation of microorganisms on the bladder mucosa and prevents relapses of chronic cystitis.
Canephron is available in the form of a solution and tablets for oral administration. The product contains centaury herb, rosemary leaves and medicinal lovage roots. The active components of the drug have anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects. The drug has a diuretic effect and eliminates spasm of the urinary tract.
Phytolysin is a paste from which a suspension is prepared for oral administration. This herbal medicine exerts its effect due to the presence in the composition:
- Sage, Peppermint, Scotch Pine and Orange oils.
- Herbs include bird's-eye knotweed, horsetail and goldenrod.
- Roots of lovage and parsley.
- Onion peels.
- Wheatgrass rhizome.
- Fenugreek seeds.
- Birch leaves.
Phytolysin.
Phytolysin has a diuretic and antispasmodic effect, and also helps to loosen kidney stones.
Treatment of cystitis is usually carried out on an outpatient basis, is comprehensive and includes taking antibacterial drugs, painkillers and antispasmodics. Adequate therapy along with diet will help avoid complications and achieve a quick cure.
Types of disease
Pathological processes on the bladder mucosa can occur in different ways, which will subsequently affect the principles of treatment. The classification includes a number of signs according to which acute cystitis is divided into the following types:
- Catarrhal . More often, the initial stage of the disease, when inflammation is localized in the upper part of the tissues, has not yet penetrated deep into the mucous membrane of the bladder. There is swelling of the affected areas and redness due to vasodilation.
- Hemorrhagic . The stage of continued development of catarrhal cystitis is characterized by deeper tissue damage, affecting the vascular plexuses. Blood appears in the urine, anemia may develop, and blood clots can be seen in the urine.
- Granular and bullous cystitis . The stage is one of the most dangerous, as it represents the pathology in an advanced form, with the infection penetrating even deeper, to the muscle fibers. The tissues of the bladder begin to receive less nutrition, metabolic reactions in them are disrupted, and the likelihood of cell death and the formation of necrotic formations increases.
- Encrusting . A type of bladder inflammation in which hard crystalline salt fragments form on the bladder mucosa, injuring the tissue and leading to further inflammation.
- Primary and secondary . This classification is used to divide the disease according to the type of occurrence. Primary cystitis is characterized by the independent development of inflammation, and secondary cystitis appears as a result of pre-existing dysfunction of organs or individual tissues of the genitourinary system.
- Focal or diffuse . This division is based on the localization of the problem area. In the focal form, a single focus of inflammation is diagnosed, and in the diffuse form, damage to almost the entire mucous membrane of the organ is observed.
Dividing the disease into certain categories helps to connect the overall picture of the disease and prescribe the optimal course of treatment.
Herbal medicines for the treatment of cystitis
Cystitis and urethritis in women can also be treated with herbal remedies, which are not inferior in effectiveness to synthetic analogues. Let's look at them.
Canephron N
Canephron is available in the form of tablets or drops, which consist of rosemary leaves, lovage and yarrow roots.
Canephron effectively eliminates pain in the urethra and reduces the severity of the inflammatory process in the bladder. It can also be used to prevent exacerbations of cystitis.
Scheme and doses: adult women are prescribed two tablets or 50 drops three times a day before meals.
Cost: 410-480 rubles.
Monurel
Monurel is an extract of cranberry fruits combined with ascorbic acid. The drug has antimicrobial, diuretic, and immunostimulating properties.
Monurel is used both for the treatment and prevention of exacerbations of cystitis.
Scheme and doses: 1 tablet before bedtime for 30 days.
Cost: 470 rubles.
Cyston
Cyston is a medicine that consists of more than ten plant components. The drug has anti-inflammatory, analgesic, antimicrobial and diuretic properties. Cyston also dissolves stones in the urinary tract and prevents their formation.
Regimen and doses: two tablets twice a day for 2-3 weeks.
Cost: 380 rubles.