Local immunity in children develops slowly and over a long period of time, so they are more susceptible to bacterial infections. The chances of developing streptoderma are further increased due to the inability to comply with all necessary hygiene rules and frequent minor skin injuries.
Risk factors
The main reason that provokes the development of streptoderma in a child is decreased immunity. Children often experience decreased protective function of the body and skin. The disease often manifests itself in infants and children who learn about the world by putting otherworldly objects in their mouths.
The first factor is streptococcus
Streptococcus is a pathogenic microorganism and can be found in the body of every person. The pathogen lives on the mucous membranes, skin, and digestive tract. Often, against the background of such a lesion, a staphylococcal infection develops.
Often the cause of the dry form of streptoderma in children is Staphylococcus aureus.
The second factor is skin damage
As long as the protective barrier of the skin and mucous membranes is strong, streptococcus and other microorganisms do not affect health. If the protective functions are lost or the skin is damaged, infection easily develops.
Often observed with the following lesions:
- wounds, insect bites, scratching allergic rashes;
- the presence of microtraumas that are not noticeable to the human eye without a special examination.
Streptococcal infection, which is activated on the affected skin in children, causes severe inflammation.
Streptoderma - causes
For the pathology in question to occur, three factors must be present:
- Weakened immunity.
Chronic diseases, viral infections, helminthiasis, intoxication and other problems can reduce the activity of the defense system. - Damage to the skin or mucous membrane.
Small wounds, abrasions, microtraumas and scratches serve as “entry gates” for pathogenic microorganisms. - Source of bacteria.
Streptococcus lives constantly on the skin, as well as on the mucous epithelium. If microbes enter damaged areas, they become active and multiply quickly, provoking an inflammatory process.
Is streptoderma contagious?
In addition to self-infection with its own bacteria, a child can also become ill as a result of external contacts. The answer to the question of whether streptoderma is contagious in children is positive. The described pathogenic microorganisms remain stable in the environment. They often get on the skin from household items (towels, dishes) and soft toys. Streptoderma is transmitted similarly in children through contact with an apparently healthy carrier of microbes. The most dangerous is considered to be infection from a patient with any pathologies caused by the specified pathogen.
Why do relapses and persistent streptoderma occur in children?
Severe, persistent condition and relapses occur in the presence of predisposing factors:
- prematurely born children;
- the presence of anemia, helminthiasis, infectious diseases;
- chronic skin diseases;
- allergic dermatitis;
- otitis, rhinitis;
- influence of external factors;
- lack of personal hygiene, lack of proper child care;
- prolonged contact of damaged skin with water.
Often, in order to avoid a chronic condition with streptoderma, it is recommended to apply ointment in a timely manner for the treatment of children.
Possible complications
With effective treatment, the child's symptoms disappear within a week.
With reduced immunity and the presence of chronic pathologies, some complications may occur:
- damage to internal organs,
- allergic dermatitis,
- scars and scars after ulcers,
- blood poisoning or sepsis,
- autoimmune pathologies,
- purulent lymphadenitis or lymphangitis,
- glomerulonephritis,
- erysipelas.
Each of these pathologies is quite dangerous and requires treatment. The insidiousness of streptoderma lies in the fact that it can leave scars on the skin. In order to prevent their formation, you must be careful with the bubbles, never burst them, and use wound-healing medications.
Symptoms and forms of the disease
Symptoms characteristic of streptoderma in children:
- a red pink spot that quickly enlarges;
- deterioration of health;
- intoxication;
- frequent headaches;
- muscle pain;
- digestive disorders;
- enlargement and inflammation of the lymph nodes at the site of infection;
- temperature increase.
Streptococcal impetigo
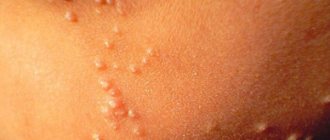
This type of streptoderma is more common than others. Single elements of a rash appear on the child’s skin, which are most often localized on the skin of the face, feet and sometimes appear on the nose. This species does not penetrate deep tissues.
Characteristic features:
- the skin initially turns red , and then a bubble appears, inside of which there is a cloudy or clear liquid;
- after filling with liquid, the bubble opens and dries out, and a crust appears in this place;
- the crust flies off , and a dark pink spot forms in its place;
- each bubble develops within 7 days.
In order to start treatment on time, you need to know what it is and promptly identify streptococcal streptoderma in children. If you start treatment when the first symptom appears, new blisters will not appear.
Bullous impetigo
The disease is severe and requires immediate treatment.
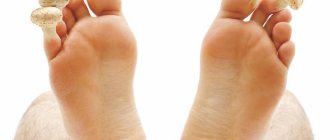
- affects the skin of the hands and feet;
- the blisters are large and accompanied by severe inflammation;
- your health worsens, your body temperature rises;
- deviations from the norm are observed in the analyses;
- the blisters are filled with purulent fluid; after opening, erosions appear.
It is not easy to cure such streptoderma in a child, but the disease can be avoided without consequences if treatment is started on time.
Slit impetigo
This type of disease often affects the face in the mouth area:
- lesions in the corners of the lips, which are often called jams;
- rarely may spread to the corners of the eyes and wings of the nose;
- Initially, one bubble appears, which goes away with timely treatment;
- rarely becomes chronic.
This type of streptococcal infection is often observed on the skin in children who attend kindergarten and are in a group with other patients.
Erythemato-squamous streptoderma
Characteristic signs of this form of the disease:
- the dry form occurs on the face and very rarely spreads to the body;
- with this streptoderma, it is not weeping elements that appear, but pink spots with scales;
- The disease is contagious and therefore requires intensive treatment.
Dr. Komoravsky says that this type of streptoderma in children is quite common and can develop in a child of any age.
Tourniol - superficial panaritium
In most cases, it occurs against the background of streptococcal impetigo. In this case, the infection develops on damaged skin around the nails. The reason lies in the intense scratching of the blisters that appear on the face. Therefore, you need to explain to children that touching the rash is prohibited.
The skin becomes very inflamed, swelling and pain appear. Erosions form on the affected area. In severe cases, rejection of the nail plate occurs.
Streptococcal diaper rash
Affects the skin behind the ears. It occurs as a secondary infection against the background of allergic and atopic dermatitis and diaper rash. The bubbles can merge with each other, and cracks appear at the site of opening. Difficult to treat.
At home, it is important to maintain good hygiene.
Streptococcal ecthyma vulgaris
Affects deep tissues and provokes the development of ulcers.
- blisters appear on the buttocks and legs;
- occurs as a result of infectious diseases that reduce immunity - chickenpox, measles, intestinal infection, influenza;
- may be a consequence of complications of diabetes mellitus , blood diseases, vitamin deficiency.
The disease is protracted. The patient's health worsens and body temperature rises. The main condition for recovery is intensive therapy.
Streptoderma - complications
In most cases, the child tolerates the disease normally without dangerous consequences. With weak immunity, streptoderma in children occurs in the form of vulgar ecthyma. This type of pathology is difficult to treat, but it can be treated with strong antibiotics. It is extremely rare that streptococcal pyoderma provokes the following complications:
- scarlet fever;
- guttate psoriasis;
- septicemia;
- glomerulonephritis;
- microbial eczema;
- transition of the disease to a chronic form.
Diagnosis of streptoderma
Only a dermatologist can diagnose the disease after a thorough examination. Sometimes a visual inspection is sufficient. To confirm the diagnosis, the affected skin is scraped and sent for microflora culture.
At the same time, it is recommended to conduct an antibiotic resistance test. Then the therapy will be successful and will quickly show positive results.
Additionally, the following studies are prescribed:
- blood analysis;
- general urine analysis;
- feces on worm eggs;
- blood test for HIV.
After receiving the results, the doctor makes an accurate diagnosis.
Stages of the disease
IT IS IMPORTANT TO KNOW!
There are three stages. At the initial, bullous stage of streptoderma, the appearance of purulent blisters is observed in the lesion. Further in the photo you can see deep skin lesions and ulcers, which dry out after some time. The third stage, and with it the chronic form of the disease, develops due to lack or improper treatment.
Similarities and differences between streptoderma and other diseases
All skin diseases may at some stage resemble streptoderma. The initial signs of streptoderma can mislead even an experienced dermatologist. Therefore, its characteristic symptoms are in children, but require a full examination.
Pyoderma
In fact, streptoderma is a subtype of pyoderma. This name has any disease that is accompanied by purulent inflammation of the skin. A significant difference is that streptococcus provokes the development of special blisters.
When a staphylococcal infection is attached, the elements of the rash may fill with cloudy liquid.
The attending physician may have doubts during a visual examination, but clinical studies will confirm the diagnosis and determine how to treat streptoderma in specific children, depending on the results.
Herpes
Seizures can also be a sign of streptoderma, so they are often confused with herpes. The difference is the rapid opening of the bubbles, and in their place cracks appear in the corners of the mouth. With herpes, the blisters last for a long time, and then there is no trace left in their place.
Streptococcal skin infections in children begin to itch after blisters appear. With herpes, itchy skin occurs long before the rash appears. Unlike this virus, streptococci rarely cause fever in this form of the disease.
Candidiasis of the corners of the mouth
With this disease, deep cracks are observed. Characteristic signs of thrush appear on the mucous membranes. The rash is small, white and cannot be transmitted to a healthy person. Streptoderma in children is contagious and can easily be transmitted to a healthy child.
Chicken pox
With chickenpox, the rash usually begins to affect the scalp and face. Therefore, initially it can be confused with another disease. But the rapid spread of bubbles throughout the body should leave no doubt.
Komarovsky claims that in most cases, chickenpox is accompanied by a strong increase in body temperature. Treatment of streptoderma in children lasts about a week, and chickenpox goes away completely after 21 days.
Allergic rash
An allergic rash, which is accompanied by the appearance of blisters with a clear liquid, has almost identical symptoms to streptoderma. The child complains of severe itching and discomfort. The difference between allergies is that when pressure is applied, the rash turns pale.
Syphilitic rash
With syphilis, the rash may be atypical. Sometimes it appears as papules in the corners of the mouth. With such a rash, the circle of the rash is characterized by severe inflammation. It extends not only to the mucous membranes.
Forms of the disease have several stages of development. A child can become infected with syphilis through contact with a sick person and through household items.
What is streptoderma and how dangerous the disease is for children
Streptoderma is a dangerous infectious disease. More often this disease is detected in children. For the development of the disease, two factors must be present: the presence of streptococcus and damaged skin with weakened immunity.
Like any other infectious disease, streptoderma is dangerous due to its complications. Pathogenic microorganisms from the source of infection can penetrate other organs, thereby causing inflammatory processes.
Penetrating into the sinuses, streptococci provoke the development of a pathology such as sinusitis. When microorganisms enter the hearing organs, they cause otitis media, and when they enter the cranial cavity, they cause meningitis and meningoencephalitis. If left untreated, damage to the deep layers of the epidermis and the formation of microbial eczema or non-healing ulcers may occur.
Treatment of streptoderma in children
There are universal recipes for treating streptoderma in children, but any doctor selects therapy individually, taking into account the form and stage of development of the disease. Without timely and correct treatment, the disease can cause serious complications.
Hygiene rules
In the treatment of streptoderma, it is very important to follow basic hygiene rules:
- It is forbidden to wet the affected areas of the skin with water for 3-5 days, as it can cause the spread of infection;
- wipe the rash with a damp towel or napkins (it is recommended to use chamomile decoction);
- it is necessary to monitor the child’s actions so that he does not scratch the blisters (antihistamines are additionally prescribed for this);
- the child must have personal household items and utensils;
- during illness, soft toys should be removed , and the rest should be washed regularly;
- all skin injuries (cuts, scratches) should be immediately treated with antiseptics;
- the room in which the child is located must be kept clean;
- iron the child's clothes
Hygiene and treatment of streptoderma are interconnected. With proper care, the symptoms of the disease can be significantly reduced.
Local treatment
Modern means for local therapy - antiseptics and antibiotic ointments are effective and easy to use. The doctor selects an ointment for streptoderma for the treatment of children individually.
- Zinc. This ointment is highly effective and low cost. It is used to eliminate various types of rashes. It disinfects, eliminates inflammation and promotes rapid recovery. The effectiveness of treating streptoderma in children with this ointment is confirmed by Komarovsky himself. Approximate price – 40 rubles.
- Antimicrobial ointment Baneocin. This product is a combination product. Produces antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects. Has a detrimental effect on streptococci. Therefore, ointments of this type are effectively taken for streptoderma in children. Treatment with drugs in this category is mandatory. Approximate price – 300 rub.
- Syntomycin ointment. A well-known antimicrobial and antibacterial agent. Effectively helps with purulent inflammatory processes of the skin and streptococcal infections. Approximate price – 90 rub.
- Pyolysin is an ointment for external use. The product has antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and immunostimulating effects. Promotes rapid skin regeneration. Approximate price – 2300 rub.
- Tetracycline ointment. The drug is a local antibiotic. Used to treat purulent infectious skin diseases. Approximate price – 50 rub.
- Antimicrobial drug Bactroban. An antibiotic that is destructive to pathogenic microorganisms. Helps prevent the development of contagious infections. Approximate price – 1300 rub.
- Fusiderm is a bactericidal ointment. Helps with dry and other forms of streptoderma. Approximate price – 1400 rub.
- Salicylic ointment. Produces moderate antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effects. Quickly dries the rash and speeds up the recovery process of the affected areas. Approximate price – 30 rubles.
- Ichthyol is a remedy for the effective elimination of streptoderma in children. Treatment with the drug in the vast majority of cases shows positive results. Approximate price – 50 rub.
- Levomekol ointment. The combined drug has anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial and regenerating effects. Eliminates general symptoms of the disease. Approximate price – 120 rubles.
Why does streptoderma need to be treated with ointment?
In case of single elements of the rash or minor skin damage by infection, urgent local treatment is necessary. It will help prevent the spread of the disease and the development of complications. At the same time, it is important to understand how to treat streptoderma in childhood, so as not to harm the baby.
An antibiotic-based ointment produces a pronounced local effect and, if selected correctly, prevents the spread of infection.
Antiseptics
Effective antiseptics:
- aqueous solution of brilliant green;
- hydrogen peroxide;
- chlorhexidine;
- fucorcin;
- salicylic alcohol (no more than 2%).
Antiseptics are applied to the area around the lesion. To do this, you can use a cotton swab or swab. The procedure is repeated 3-4 times a day for drying and disinfection. Pediatricians advise the person who will be treating the skin to adhere to more careful hygiene rules.
Systemic treatment of streptoderma with antibiotics
To treat streptoderma in children, tablets and ointments with penicillin antibiotics are used. Treatment with other types of antibiotics is possible if you have an allergic reaction to penicillin.
- penicillin series of antibiotics - Amoxicillin, Flemoxin solutab, Amoxiclav;
- cephalosporins – Suprax, Ciprofloxacin;
- macrolides – Erythromycin, Sumamed.
Such drugs are taken strictly as prescribed by the doctor.
Folk recipes
At home, treatment of streptoderma in children with folk remedies is not the most effective. Some recipes can be used in additional therapy to drug treatment. The child is also prescribed vitamin nutrition and diet.
Some folk tricks:
- fresh juices – increase immunity;
- fruits, vegetables - help the body overcome infection;
- berries, dried fruits, legumes – antioxidants necessary for health;
- tea tree oil – has an antiseptic effect;
- Olive oil – helps eliminate discomfort in the presence of scales and moisturizes the skin.
With complex therapy, a quick recovery can be achieved.
Traditional medicine against streptoderma
Such drugs can be added to an intensive care regimen only with the participation of a specialist and the absence of an allergic reaction to herbal components. An integrated approach to the problem is necessary to speed up the result, since the patient voluntarily scratches the foci of pathology, causing an infection with subsequent suppuration of the dermis. Traditional medicine against streptoderma will suggest several effective recipes that cleanse the skin, make it even, smooth and healthy.
- 2 tbsp. l. Steam dried chamomile flowers in a glass of boiling water. Infuse the steep broth, cool and strain. Use to treat ulcers for 6-7 days. Using the same principle, you can prepare a decoction of oak bark, which also has an antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effect.
- Grind calendula flowers and dry them on the windowsill. 2 tbsp. l. pour the raw material with medical alcohol in the same volume and leave for a week. Use to regularly lubricate painful ulcers. If you use tartar juice, it is better to treat the foci of streptoderma with a concentrated composition.
- Prepare a medicinal decoction from walnuts: chop the walnut and pour boiling water over it in a ratio of 1 tbsp. l. raw materials per glass of boiling water. Take 0.5 cups orally before meals, already cooled and infused, at the first signs of streptoderma. Every day it is recommended to prepare a fresh portion of the medicine.
- In concentrated form, you can use garlic juice and black pepper. Squeeze out the garlic pulp and grind it with the same amount of ground black pepper. Mix and apply to inflamed sores up to 3 times a day. Be careful not to burn the skin with the concentrate.
- Elderberry decoction has bactericidal properties; according to the recipe, only 1 tbsp. l. raw materials need to be boiled and infused in a glass of milk. Cool for two hours, and after straining, use the chosen treatment method at home as a lotion for streptoderma.
Hydrogen peroxide and potassium permanganate
In one container you need to prepare a solution of potassium permanganate of a pale pink color, in the second - a 4% composition of hydrogen peroxide. Do not mix these ingredients with each other, but use hydrogen peroxide and potassium permanganate alternately. First, treat the wounds with peroxide, and then with a pink anti-inflammatory composition. The procedure should be carried out up to 4 times a day until the unpleasant symptoms of streptoderma are finally eliminated from the life of the clinical patient.
Pomegranate juice
Combine pomegranate juice with natural honey in equal proportions. Grind the medicine thoroughly and store in the refrigerator. For treatment at home, a few drops are enough to apply the composition to the source of pathology and rub it well. Carry out the procedure three times a day until the signs of streptoderma and visible problems with the dermis completely disappear.
Prevention
The main rule of prevention is to isolate a sick child from healthy ones. The optimal quarantine time is 10 days.
Simple recommendations will help reduce the risk of infection:
- compliance with hygiene rules;
- strengthening the immune system;
- proper nutrition;
- moderate physical activity;
- regular walks in the fresh air.
When itching occurs, it is important to ensure that the child does not scratch the blisters. This accelerates and spreads infection.
Diagnostics
The disease in the photo bears a strong resemblance to a number of other diseases. For example, it is very difficult to distinguish streptoderma from herpes from a photo or appearance. The method of bacteriological culture of scrapings helps the doctor clarify the nature of the skin rash and help make a diagnosis of streptoderma.
How to treat with folk remedies?
To speed up recovery, auxiliary treatment with folk remedies is allowed for streptoderma in adults. These include:
- overheating of the skin and increased sweating should be avoided;
- following a diet that excludes sweet, fatty, and spicy foods from the diet;
- clothing should be made from “breathable”, natural materials;
- dressings soaked in herbal decoctions that have drying properties and are not allergens: chamomile and oak bark;
- Since you cannot shower or bathe during illness, it is recommended to wipe healthy skin with napkins soaked in chamomile decoction.
Any treatment, even with the most proven methods, must be accompanied by permission and supervision of a doctor. Otherwise, complications may arise that are difficult to correct.
View photos
[collapse]
Which doctor should I contact?
At the first signs of streptoderma, consult a dermatologist. Contact the doctors of the Botkin.pro medical video consultation service. See how our doctors answer patient questions. service doctors for free, without leaving this page, or here. Consult your favorite doctor.
What it is
Streptoderma refers to a number of infectious skin lesions that are caused by streptococcus. Symptoms are observed only on the skin surface; the sebaceous glands and hair follicles are not susceptible to infection. The main signs appear on the face of children, less often of adults, the characteristic area is the area around the mouth.
In order to quickly get rid of streptoderma, it is important to know how it begins, how and with what to treat it, and whether it is possible to treat it with ointments at home. We will consider these and other questions below.
Streptoderma is classified as pyoderma, meaning a purulent lesion in the epidermis. The pathology is caused by streptococcus; it begins with rash symptoms that look like large and small blisters, ranging in size from a millimeter to 2-4 cm.
What is streptococcus? This is an anaerobic bacterium, capable of life in an oxygen environment and without oxygen. There are a number of varieties of streptococci belonging to groups A, B, C, D, etc. Streptoderma is caused by representatives of group A.
Children suffer from streptoderma more often than adults. This is due to more delicate skin and unprepared immunity. Also, the disease can suddenly begin in women during moments of hormonal disruption, for example, during menopause, or in men and women who are elderly, since by this time a person has accumulated a significant baggage of chronic diseases, skin tone decreases, etc.
The effectiveness of treatment is largely determined by age. It is easier to treat children, since a young body has a faster metabolism. In an elderly adult, streptoderma often becomes chronic, difficult to treat.
Streptococcal infection is the cause of rheumatism
The cause of the development of the disease is beta hemolytic streptococci of group A. They are capable of producing enzymes that have a cardiotoxic effect, and some strains of them are capable of causing an autoimmune response, which leads to the development of systemic inflammation of the connective tissue in the body of a patient with damage:
- membranes of the heart (rheumomyocarditis, rheumatic carditis),
- joints (rheumopolyarthritis),
- small cerebral vessels (rheumorrhea),
- skin (ring-shaped and nodular erythema, rheumatic nodules),
- pleura (rheumopleuritis), liver (rheumatic hepatitis),
- kidneys (rheumatic nephritis).
The disease is most often registered in children 5 - 15 years old.
Rice. 5. Heart damage due to rheumatism. The cause of the disease is streptococcal infection.
Rice. 6. Consequences of rheumatism suffered in childhood.
Prevention of streptoderma
To avoid streptoderma, follow the recommendations:
- observe the rules of personal hygiene, especially when in crowded places: wash your hands more often, use individual underwear, a towel, etc.;
- avoid close contact with people suffering from streptoderma;
- treat chronic skin diseases in a timely manner;
- maintain normal blood sugar levels;
- do not abuse alcohol;
- avoid stress;
- strengthen your immune system, take multivitamins in spring and autumn;
- lead a healthy lifestyle.
Streptococci - the cause of erysipelas
Erysipelas (translated from French as red) is an infectious skin disease caused by group A beta hemolytic streptococcus (GABHS). With erysipelas, a limited area of the skin and tissue is affected.
Streptococcal infection penetrates through wounds and abrasions, diaper rash and cracks, psoriatic, herpetic and other skin lesions. The pathogen multiplies in the lymphatic skin capillaries. Toxins of the pathogen cause serous, often serous-purulent inflammation, which is complicated by the destruction (necrosis) of soft tissues. Autoimmune complexes contribute to the development of hemorrhagic syndrome, as evidenced by the appearance of erythema (redness), swelling and blisters with serous-hemorrhagic contents.
With erysipelas, the lower extremities are more often affected, and less often the upper extremities. The skin of the face is even less commonly affected.
The disease develops quickly, rapidly, with pronounced symptoms of intoxication. Pain, redness and swelling are the main symptoms of erysipelas.
In case of classic erysipelas, microbiological examination is not carried out. Antibiotics of the penicillin group are the drugs of choice in the treatment of the disease.
Rice. 7. The photo shows erysipelas in a child.
Rice. 8. The photo shows a mug. The cause is streptococcal infection. A hyperemic, raised lesion is visible on the skin of the face. Its surface is shiny and tense.
Rice. 9. The photo shows a mug. Phlegmonous-necrotic form of the disease.
Rice. 10. The photo shows erysipelas (phlegmonous-necrotic form). Streptococci are the culprits of the disease.
Rice. 11. The photo shows erysipelas (gangrenous form of the disease). The culprit of the disease is streptococcus.
Questions from patients - answers from Botkin.pro doctors:
Dry streptoderma in an adult
A pink scaly spot on the forearm, the doctor diagnosed dry streptoderma. The doctor also said that it is not particularly contagious, but it is better not to come into contact with the affected area... I read on the Internet that it is very contagious, where is the truth? How to behave so as not to infect anyone, especially a small child? Can the stain be covered with a band-aid? If your hand is in a sweater, is it possible to become infected through the fabric?
Kadaner Evgeniy IlyichDermatovenereologist (Dermatologist)
Sign up for a video consultation
Write to the doctor
Good afternoon 1. The truth is that atypical (including dry) streptoderma is a diagnosis that is more microbiological (laboratory confirmed) than clinical (based on examination). Infectiousness depends on the properties of the identified pathogen strain. But opinions may differ. 2. Until the diagnosis is finally established, there is no need for isolation 3. The stain cannot be sealed with a plaster due to the fact that most of the microbes that cause pyoderma are anaerobes (they feel comfortable without access to oxygen) 4. It is necessary to treat the jacket with disinfectants after using it as a barrier .
Traditional methods
To combat streptoderma, it is recommended to use camel thorns. You need to make lotions from the infusion of this herb and apply them to the affected areas of the skin. The duration of one procedure is one hour, then the lotion must be removed from the skin, but washing the body is not recommended. The herbal infusion should be concentrated.
Alder cones are no less effective in treating streptoderma (it is best to use brown cones rather than green ones). From these cones you need to make a strong decoction and soak the affected areas of the skin in it. The procedure must be carried out at least two to three times a day until complete healing.
( 1 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5)
Symptoms
The causative agent of the disease determines the specific clinical picture. However, in general, the symptoms of streptoderma are more or less similar. The cause is often minor damage - for example, scratches in children or shaving in young men. Symptoms include:
- Two to three days before the appearance of the rash, a person subjectively feels pain at the site of the future lesion. The inflammatory process still remains in the inner layers of the epidermis.
- Next, blisters or redness appear. Zaeda or classic impetigo gives dry red crusts (“lichen”). The size of the rashes varies from 3-5 mm to large ones, more than 2 cm in severe forms of the disease.
- The blisters inside are filled with purulent-serous contents.
- In children, the symptoms of streptoderma in the form of skin manifestations are accompanied by manifestations of general intoxication - lethargy, low-grade fever, and perhaps poor appetite.
- Subjectively, a person feels pain and sometimes itching in the affected areas.
Without treatment, the lesions tend to grow. If the course of the disease is unfavorable, complications are possible: the infection goes deeper, forming boils and abscesses up to general sepsis. Therefore, timely treatment of streptoderma plays an important role. The disease can also take a chronic form with the formation of permanent foci of proliferation of pathogenic microflora. Therapy against the disease will avoid this development.
How is the infection transmitted?
In this case, the infection is transmitted through direct contact, as well as through shared objects. Most often, outbreaks of the disease occur in public institutions such as kindergartens and nurseries, in which a large number of children are in close contact with each other. And if to all this is added the neglect of sanitary and hygienic standards on the part of the educational staff, then the disease can affect the entire group of children at once. Adults become infected with streptoderma from their children or through their toys.
Kinds
Doctors classify diseases depending on their location and mode of occurrence. All types can appear equally in children and adults, but it must be remembered that children are more susceptible to the disease and tolerate it more severely. The main types are:
- Classic impetigo - also known as "lichen". Appears on the face, as a rule, in very young children. This is an abortive form, that is, it does not require complex treatment and goes away quite quickly. Streptococcal lesions of this type develop most often.
- Ring-shaped streptoderma - characterized by the appearance of rashes, bullous-type blisters, small and dense in appearance, filled with ichor inside. This form is prone to growing and expanding its range.
- Syphiloid impetigo is a disease of newborns that develops in the first months of life. The rash occurs on the thighs and buttocks. The affected areas form characteristic chancre, indeed similar to the early stages of syphilis.
- Bullous impetigo is a relatively rare, but severe and dangerous form of the disease, manifests itself in the form of large papules - from 2 cm, filled with purulent-serous contents. These bubbles are also called conflicts. Over time, the papules open, leaving behind characteristic oily crusts. This form can cause deep scars and peeling nails.
- Seizure or slit-like impertigo is a symptom of not only physiological, but often also psychological problems. This condition is associated with the habit of licking or chewing the lips, which causes crusts to form at the corners of the mouth.
- The vegetative or chronic form of impertigo is associated with constant rashes that appear for no specific reason. The lesions are painful, erosive, and leave scars. Treatment of streptoderma should be aimed at overall improvement of the body's condition.
A separate form is Bockhart's impetigo or ostiofolliculitis. This type of disease is considered specific to men; it most often affects adolescents due to hyperactivity of the sweat and sebaceous glands, as well as excess hormones. In boys and young men, the areas of beard and mustache growth on the face are affected; Bockhart's impetigo may initially occur due to the use of insufficiently clean razors or shaving brushes. It is necessary to distinguish this disease from ordinary juvenile acne, since streptoderma leaves deep scars in the form of potholes.
Symptoms of streptoderma
The onset of streptoderma in adults is usually acute. Often the disease occurs against the background of various infectious pathologies, for example, ARVI, which is caused by a decrease not only in the general immune properties of the body, but also in local skin protective factors.
Developing symptoms (see photo) can be observed on the face, as well as on the lower extremities, upper extremities, thighs, and buttocks. The main clinical signs are the formation of rashes and the presence of itching. Rashes, as a rule, are represented by small blisters on reddened skin, which are filled with transparent or cloudy contents. Characterized by rapid growth along the periphery and a fairly active increase in the number of rashes, their spread to other parts of the body.
In a fairly short time, the bubbles burst and yellowish crusts quickly form in their place. With timely diagnosis, proper care and treatment, the disease quickly regresses. However, if left untreated, the infection can become long-lasting and recurrent. Rashes are often accompanied by symptoms of discomfort and even pain, such as when a seizure forms (damage to the corners of the mouth), as well as when deep layers of skin are involved.
Symptoms such as high fever, swollen lymph nodes, and weakness rarely accompany superficial forms of streptoderma in adults. These signs may simply be symptoms of a current ARVI.
How can children become infected with streptoderma?
- May be on the baby’s skin;
- From toys, dishes, bed linen and towels;
- From a carrier of streptococci, who himself may be healthy;
- From someone who is already sick with diseases caused by streptococcus.
Most often, streptoderma affects children who have weak immunity , chronic skin diseases , otitis or rhinitis . Streptoderma can occur with burns and frostbite. The likelihood of this disease is also high if the baby is poorly cared for.