Oncology of which organs is accompanied by ascites?
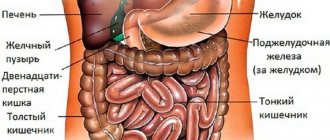
Ascites develops when cancer affects any organ near the abdominal cavity. The most common types of cancer that cause dropsy are:
- colon and rectum;
- ovaries in women – 50% of cases of ascites;
- mammary glands;
- liver – ascites manifests itself in 70% of cases;
- pancreas;
- stomach;
- organs in the pelvis.
The severity of ascites depends on the stage and whether the cancer is metastatic. Severe ascites leads to cardiac and pulmonary failure, which significantly impairs the patient’s quality of life and causes death. Manifestations of ascites are the same for women and men. In women, the likelihood is increased with ovarian cancer, in which pathology occurs in 50% of cases and often causes death in patients.
What types of cancer can cause ascites?
Most often, ascites develops with the following oncological diseases:
- ovarian cancer;
- liver cancer;
- pancreas cancer;
- stomach and intestinal cancer;
- uterine cancer;
- mammary cancer;
- non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, Burkitt's lymphoma.
Basic methods for diagnosing ascites:
- palpation and percussion of the abdomen to assess the total volume of fluid is not informative for transient ascites;
- periodic weighing of body weight will allow you to exclude or suspect hidden edema;
- Ultrasound diagnostics - allows you to detect excess fluid in the abdominal cavity, as well as check the condition of organs and their functioning;
- diagnostic laparocentesis - allows you to biopsy exudate and pump out excess fluid. It is considered the most informative method possible, because allows you to determine the composition of the exudate and determine the microflora in the abdominal cavity;
- X-rays and tomography reveal fluid when the body position changes.
Abdomen with ascites
Ascites in oncology occurs as a consequence of the pathology of any organ near the internal cavity of the abdomen. A process of release of liquid secretion into the abdominal area occurs if the tumor grows through the outer wall of the organ.
Complications accompany the following diseases:
- Malignant tumors in the uterus and ovaries. With this pathology, fluid accumulation may appear at an early stage if the tumor has already grown towards the peritoneum. Then the fluid is produced by the inflamed tissues located around the tumor. The volume of liquid is small and is partially eliminated from the body on its own. But in the terminal stage of a cancerous tumor, when metastases spread, ascites becomes full-fledged.
- Colon and rectal cancer. The main cause of fluid stagnation is metastasis of malignant cells into the lymphatic system. Metastases retain fluid in the lymph nodes, which leads to their expansion and the appearance of an inflammatory process. Lymph enters the abdominal cavity. In the circulatory system, there is a decrease in the volume of blood circulating in the vessels. To normalize blood flow, the kidneys remove less urine from the body. As a result, excess water again enters the lymph nodes, and from there into the abdominal cavity. The volume of moisture in the peritoneum increases, the cycle closes. This situation may develop until renal failure sets in or until an infection in the abdominal cavity causes peritonitis.
- Stomach tumors.
- Tumors in the mammary gland.
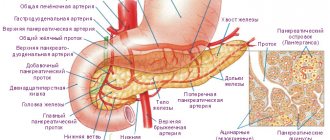
- Malignant process in the liver. The disease develops both with an oncological tumor of the liver and with a diagnosis of cirrhosis. In 70% of liver cancer cases, people suffer from dropsy. The complication develops in much the same way as with intestinal tumors. Liver pathology does not allow the organ to function normally. As a result of problems with the movement of blood through the liver, free fluid appears outside the walls of the blood vessels. Its excess must be eliminated through the lymph nodes. However, the system gradually fails, and stagnant lymph enters the peritoneum.
Ascites can also occur in newborns. Pathology occurs if hemolytic disease is diagnosed. Infants under one year of age suffer from pathology with diagnoses of malnutrition and congenital nephrotic syndrome.
Forecast
The prognosis for people diagnosed with abdominal ascites is unfavorable even in the absence of cancer.
When predicting survival, a number of factors are taken into account:
- Once the diagnosis has been made and treatment has begun, in the early stages of detecting a complication, one can hope for success. An important condition is successful therapy of the primary pathology.
- The stage of the pathology is the transient stage and responds well to drug treatment. When severe stage ascites is detected, the patient develops symptoms of insufficiency in the heart and lungs, which significantly reduces the likelihood of a favorable outcome.
- Prognosis of the primary disease - this factor remains the most important in the treatment of ascites. Even if therapy is effective, the patient may die from failure of major organs. For example, if ascites is diagnosed, accompanying cirrhosis of the liver, the survival rate of patients within five years from the date of diagnosis is no more than 20%. For cardiac dysfunction – no more than 10%
If dropsy occurs as an accompaniment of oncological pathology, the survival prognosis is complicated by the stage of cancer and the degree of pathology.
If ascites is detected in the early stages, therapy for a malignant tumor is successful.
When the process is neglected, there are no accurate statistics on the survival rate of patients with cancer combined with ascites. In this situation, it is difficult to determine the cause of the deterioration of the patient’s condition. It can be caused by either a primary disease or a secondary process.
Causes of ascites in oncology
The reasons for the development of ascites in oncology are different; the basis is an impaired water-salt balance in the body. The main reasons for the development of ascites in cancer:
- damage to lymphatic and blood vessels, their blockage, causing stagnation of venous blood, lymph entering the abdominal cavity;
- high permeability of the peritoneal vascular system due to the development of metastases;
- when the liver tumor is damaged, the level of albumin in the blood decreases and hepatomegaly develops;
- secretion of exudate by malignant tumors;
- involvement of the kidneys and adrenal glands in the process, which regulate the water-salt balance in the body;
- vein thrombosis, which impairs blood circulation;
- dysfunction of the thyroid gland;
- insufficient availability of nutrients caused by fasting;
- inflammatory processes in the abdomen of a non-infectious nature.
The risk of developing dropsy increases with factors such as alcoholism, hepatitis of all types, improper blood transfusions, drug use, high blood cholesterol and type 2 diabetes.
Causes
Ascites in oncology develops due to the destruction of lymph nodes. That is, lymphatic drainage is disrupted in a certain area. Also, during an illness, cancer cells spread throughout the organ, which aggravate the patient’s condition.
Pathology can provoke not only excessive accumulation of fluid in the cavity, but also an increase in intra-abdominal pressure, due to which the diaphragm moves into the chest.
In rare cases, the disease develops in the postoperative period. Sometimes a complication in the abdominal cavity develops due to a course of chemotherapy, during which intoxication of the body occurs.
In addition to these sources of the formation of the disease, doctors include several more etiological factors:
- dense placement of abdominal folds to each other;
- a large number of blood and lymphatic vessels;
- entry of atypical cells during surgery;
- tumor growth beyond the peritoneum.
Treatment of ascitic effusion
To remove fluid, drainage is installed, and it is necessary to identify the causes of the disease.
If such clinical symptoms are present, it is necessary to establish the primary focus. When a malignant neoplasm is identified, its treatment begins. For this purpose, chemotherapeutic drugs, represented by cytostatics and targeted drugs, are used. Irradiation of the cancerous tumor and metastases is also recommended. In severe cases, surgery is performed with partial or complete removal of the affected organ. All the measures described are an integral part of the complex therapy of ascites. Without them, removing fluid from the abdominal cavity will be pointless, since its volume will be renewed due to continued exudation. To reduce effusion, drains are placed in the abdomen. Through them, the exudate is drained into a container.
Symptoms of pathology
One of the direct symptoms of ascites is an increase in abdominal volume by two to three times.
Malignant ascites in cancer is accompanied by the following characteristic symptoms:
- Dyspnea. The volume of the abdomen increases, the fluid “props” the diaphragm from below, not allowing the lungs to expand fully.
- Cough. Triggered by congestion in the blood vessels and lung tissue. Secondary pneumonia may occur.
- Increase in size of the abdomen. Its diameter can double and even triple.
- Heart failure. It manifests itself as tachycardia and arrhythmia, in which the heart seems to flutter in the chest.
- Yellowness of the skin. Appears due to an increase in the concentration of bilirubin in the blood as a result of impaired liver function.
- Spider veins and pinpoint rash. Appear due to dysfunction of the blood coagulation system.
- Swelling in the lower extremities. They appear due to a decrease in blood oncotic pressure. This symptom occurs when plasma protein concentration decreases.
- Dyspepsia. Dyspeptic symptoms consist of a feeling of fullness in the epigastrium, belching of air or eaten food.
In theory, treatment of ascites should first of all be aimed at eliminating the primary cause - the growth of cancer cells. If it is possible to stop this process, then we can hope to restore the mechanism for removing excess fluid in a normal way.
But the practical use of chemotherapy only helps with intestinal tumors. If cancer cells spread to the liver, stomach, uterus or ovary, treatment does not work.
Why does cancer cause fluid to accumulate in the abdomen?
In liver cancer, the causes of ascites are the same as in cirrhosis (in fact, liver cancer in most cases develops against the background of cirrhosis): impaired blood outflow, increased pressure and congestion in the veins, impaired albumin synthesis and a decrease in oncotic pressure of the blood.
In case of malignant tumors of other organs (stomach, intestines, uterus, ovaries), ascites occurs due to damage to peritoneal cancer cells. Because of this, fluid absorption is impaired. If tumor cells invade the lymph nodes, ascites may occur due to impaired lymph flow.
How does it manifest?
Symptoms depend on the organ in which the malignant tumor grows. The complication appears over several months and is accompanied by symptoms:
- A pronounced sign of ascites is the growth of the abdomen. The symptom manifests itself gradually with an increase in fluid in the cavity. The patient feels fullness and heaviness in the abdomen, pain occurs, and belching appears.
- Patients with dropsy have swollen legs. In the first stages, the swelling goes away in a lying position, and later it constantly accompanies the patient. The swelling covers the entire leg and even extends to the genitals.
- Fluid in the abdominal cavity presses on the internal organs of the peritoneum, so the person feels short of breath.
During the examination, the doctor feels the abdomen and diagnoses its enlargement and protrusion of the navel.
If ascites accompanies ovarian cancer, women can sometimes confuse it with pregnancy, because menstruation stops with a tumor of the reproductive system.
Signs of ascites are secondary. The main disease is still cancer. Dropsy complicates the course of the primary pathology.
What it is
Ascites (dropsy) in medicine is a condition in which a certain amount of fluid accumulates in the abdominal cavity. This condition poses a danger to the patient's health.
The disease is classified as secondary, as it develops against the background of existing pathologies. Most often it is cancer. Ascites, especially in severe cases, is accompanied by displacement of internal organs. The heart muscle, rectum, diaphragm, and blood vessels change their position.
In patients, due to the accumulation of a large volume of fluid, inguinal, diaphragmatic and umbilical hernias develop.
Ascites is observed during the formation of a malignant tumor that affects the pancreas, liver, rectum, stomach, mammary glands, and large intestine. At the same time, the severity of the secondary disease does not depend on the primary and the presence of metastatic lesions.
On this topic
Life expectancy for stage 4 gastric cancer with metastases
- Yuri Pavlovich Danilov
- July 9, 2020
In patients, in addition to symptoms of malignant lesions, there is an increase in intra-abdominal pressure, which is accompanied by pronounced symptoms. Such changes cause respiratory and heart failure.
Cancer itself is not a cause of death, but patients die due to complications. The main one is dropsy.
Stages
Ascites has three stages that determine the severity of the course:
- Stage 1 – transient ascites – accumulation of exudate or transudate in the abdominal cavity of a small volume, no more than 400 ml, almost invisible in appearance, determined by ultrasound examination;
- Stage 2 – moderate ascites – the fluid reaches a volume of up to 5 liters, some mild symptoms are identified;
- Stage 3 – intense ascites – more than 20 liters of fluid accumulated in the abdominal cavity, which cannot be treated with medication. The patient suffers from heart and pulmonary failure. Manipulation is required to pump out excess liquid, because... the condition threatens the patient's life.
Symptoms of ascites depend on the stage of development of the underlying disease and how much fluid has collected in the abdominal cavity. The main sign of the pathological condition is a significant increase in abdominal volume. If the patient is standing, the abdomen has a saggy appearance. When the patient lies down, the appearance of the peritoneum changes significantly - it resembles that of a frog - flat in front, swollen on the sides. Added to these symptoms is a constant feeling of heaviness, fatigue, flatulence, belching, and pain.
According to patients, at the next stage of ascites development, swelling of the legs appears. They are initially present when the patient is in an upright position and disappear after a short rest. After some time, swelling remains on the body constantly, regardless of the patient’s posture. At the same time, they tend to rise upward.
Clinical picture
The presence of fluid in the peritoneum is accompanied by severe symptoms, which manifest themselves depending on the location of the primary lesion.
The main manifestation of the disease is an increase in the volume of the abdomen. This is due to the fact that fluid begins to accumulate in the abdominal cavity. Already at the 2nd degree he sags in a standing position. When a person lies down, the stomach looks like a “frog”. It manifests itself as bulging in the lateral sections.
In the early stages, heaviness, painful sensations appear, and a feeling of fullness occurs. Patients also complain of constant belching and flatulence.
Establishing diagnosis
Dropsy suggests the presence of an underlying cancer.
In addition to examining the enlarged abdomen, additional diagnostic methods are used:
- Ultrasound examination - using ultrasound, you can detect fluid at an early stage of pathology and determine changes in internal organs.
- X-ray.
- Tomography.
- A puncture of the peritoneal wall is also called laparocentesis. The procedure is aimed at pumping out fluid from the abdominal cavity and further examining it. A cell from the removed material is examined under a microscope to determine the presence of inflammation and assess the microflora in the abdominal cavity.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of ascites is based on clinical examination data. If necessary, instrumental tests are prescribed:
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- computed tomography;
- R-graphy (radiography) for differential diagnosis with other diseases;
- diagnostic puncture with cytological examination of the liquid contents of the stomach - unlike other diseases, cells with signs of malignancy will be found in the puncture.
Possible complications
Ascites aggravates the underlying cancer disease, and in addition provides additional complications:
- peritonitis – when an infection enters the abdominal cavity, the process is acute and requires immediate medical attention;
- intestinal obstruction;
- development of inguinal or umbilical hernias;
- heart and pulmonary failure;
- intestinal bleeding.
In the absence of proper and timely treatment of ascites, the following complications may develop:
- bacterial peritonitis (acute inflammation of the peritoneum);
- hemorrhoidal bleeding;
- hernias with possible pinching (inguinal, white line of the abdomen, umbilical);
- pleurisy;
- cardiac decompensation;
- intestinal obstruction.
There is a high probability of developing hepatorenal syndrome. It is accompanied by severe renal dysfunction in the absence of organic organ damage.
Preventive measures and prognosis
With such complications of malignant neoplasms, people do not live long if they are detected late and not treated. If the diagnosis is made in time and the correct medication regimen is prescribed, the prognosis improves. In order to prevent malignancy and its complications, the patient should be advised to eat a proper diet, moderate physical activity, and give up bad habits.
Prevention of ascites in oncology involves careful attention to one’s health on the part of patients. When malignant processes are detected in the body, the patient is obliged to adhere to all the doctor’s recommendations and promptly notify him of the slightest changes in well-being. The patient must undergo routine tests and not neglect the prescribed treatment.
All bad habits are prohibited - drinking alcohol, smoking. Patients with malignant tumors need to hang daily and monitor their body weight. With a rapid increase, one may suspect the development of edema or ascites, which requires immediate medical intervention.
Life expectancy with oncology and ascites for half of the patients does not exceed 2 years. Many patients face a more favorable prognosis. Longer life expectancy is possible in patients whose cancer is detected in the early stages.
The prognosis in the presence of malignant tumors and ascites depends on many factors:
- patient's age;
- presence of metastases;
- volume of fluid in the abdominal cavity;
- the presence of concomitant chronic diseases.
To prevent the accumulation of liquid secretions, you need to take time to prevent primary diseases that can cause dropsy. The list includes cancerous tumors of the reproductive system, as well as cirrhosis of the liver, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, and diseases of the cardiovascular system.
Normal metabolism in the body is possible if the organs work normally. It is necessary to monitor the health of the liver, pancreas, spleen, and kidneys, which are responsible for removing toxic substances.
Prevention measures include:
- Passing annual fluorography.
- Regular gynecological examinations for women.
- Periodic medical examination.
- Following the rules of a healthy lifestyle.
- Maintaining a balanced diet.
Therapy methods
Treatment of ascites in oncology is carried out regardless of the stage of its development. This condition reduces the effectiveness of cancer therapy and worsens the prognosis for the patient.
If there is a slight increase in the amount of fluid in the abdomen, the patient is prescribed a special diet. Nutrition for ascites implies a maximum reduction in salt. The diet of a sick person should contain foods rich in protein and potassium. Dietary food implies the presence in the menu of boiled lean meat, fish, baked potatoes, cottage cheese, spinach, carrots, and dried fruit compote.
If there is a large amount of fluid in the abdomen, diuretics (Veroshpiron, Diakarb) are prescribed. The dose and regimen of medications is calculated individually, taking into account the patient’s condition. During the course of treatment, it is assumed that no more than 500 ml of fluid will leave the patient’s body during the day. Otherwise, the likelihood of increasing signs of intoxication of the body increases.
With a rapid increase in the volume of fluid in the abdominal cavity, drug treatment is ineffective. In this case, a special operation is indicated - laparocentesis. To remove excess fluid, under local anesthesia, a puncture is made in the abdominal wall just below the navel, after which it is pumped out by gravity. In one procedure you can get rid of 10 liters of water. If the volume of fluid is greater, laparocentesis is repeated after a few days.
Some experts advise treating ascites using folk remedies. Doctors allow the use of diuretic medicinal herbs - milk thistle, birch buds, sage, oregano and others. But these plants should be used with caution after consultation with a specialist.
Survival and prognosis
Ascites occurs not only against the background of cancer, but is also associated with other pathologies and can occur with a benign tumor. At the same time, the prognosis for life is rarely favorable even if the underlying disease is not oncological. The stage of cancer is very important, because With early diagnosis, survival rates are higher.
At the initial stage, ascites responds well to conservative treatment; as the tense state increases, medications are useless; the situation depends on the possibility of surgical correction. At a progressive stage, the development of pathologies of the heart and lungs is unfavorable for the patient’s life.
The highest life expectancy is at stages 1 and 2 of cancer, when the therapy has a good effect. At stages 3 and 4, the cancer process is started, metastasis of the body occurs, if dropsy is added to the described condition, survival rate is reduced to zero. It is extremely difficult to diagnose why such sick people die from the underlying pathology or ascites.
Diseases associated with ascites
Sometimes, if the tumor or metastases affect the liver or biliary tract, the patient may develop jaundice. AST and ALT increase, and bilirubin levels can reach several hundred units. Outwardly, such a patient is easy to identify - he has yellow sclera of the eyes and skin. With this variant of the disease, the patient also receives intoxication of the body. Glucose droppers and the use of various sorbents help solve this problem. Instead of ineffective activated carbon, it is better to take Polysorb or Enterosgel. A good effect is also obtained from the use of membrane plasmaphoresis.
Prevention of ascites in oncology
Ascites is not an independent pathology, so the main preventive measures should be aimed at preventing the underlying disease. The reasons for the development of oncology have not yet been studied; the only preventive measure is to normalize the functioning of organs and metabolism. It is recommended to monitor the health of the pancreas, liver, spleen and kidneys, which are responsible for removing toxins from the body.
Standard prevention methods:
- annual fluorographic examination;
- for women, regular gynecological examinations;
- healthy, active lifestyle, walks in the fresh air;
- balanced diet;
- regular medical examination;
- rejection of bad habits.