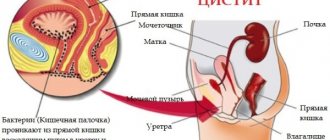
Antibiotics for cystitis
Just a few 30-40 years ago, cystitis did not require taking antibacterial drugs; a woman only had to take phytotherapeutic drugs for some time, follow the rules of personal hygiene, a certain diet, and the disease would recede.
Things have changed dramatically these days. Infectious agents have become immune to naturally occurring antibacterial substances. Now treatment is not possible without antibiotics. Moreover, now cystitis almost always becomes chronic.
Modern antibiotics, especially when it comes to broad-spectrum tablets for cystitis, cause many side effects and have many contraindications. Therefore, their uncontrolled use is unacceptable. Before you start taking medications, you need to conduct a urine test to identify the specific pathogen and determine its sensitivity to antibiotics. Only after this a specific antibacterial drug is selected. In severe, advanced cases (when granulations develop in the bladder and other complications), the doctor prescribes collargol installations.
To determine the effectiveness of the treatment, after finishing taking antibiotics, the urine is re-cultured on nutrient media.
Some drugs that are used to treat cystitis:
- McMirror1. Macmiror, an antimicrobial drug, nitrofuran, which has a wider spectrum of action than other nitrofuran drugs used in the treatment of urinary tract infections, has proven itself well in the treatment of cystitis. Quick elimination of the causative agent of the inflammatory process from the surface of the mucous membrane of the bladder allows you to quickly alleviate the unpleasant symptoms of cystitis. The main thing is to follow the dosage regimen and course of therapy.
- Nolicin, as well as nolicin analogues - Norbactin, Normax. It is a broad-spectrum antibacterial drug. It is prescribed only in cases where taking other antibiotics has shown to be ineffective, because it is a reserve drug. This means that infectious agents have not yet developed resistance to it. The active substance, norfloxacin, belongs to the group of fluoroquinolones. Other drugs from the fluoroquinolone group have also proven their effectiveness: Ciprofloxacin, Ofloxacin. The price of Nolitsin is affordable and is about 100 rubles.
- Monural. Perhaps the most popular drug against urinary tract infections. It is prescribed even for unconfirmed cystitis (without urine test results). Monural is prescribed as a therapeutic agent for acute cystitis. In the chronic form of the disease, this remedy is ineffective, because It is impossible to cure chronic cystitis with a single course of antibiotics. Monural is a strong uroantiseptic. Approximate price: 350 rubles.
- Palin. Used to treat urinary tract infections. The antibiotic belongs to the quinolone group of drugs. One of the main active ingredients is pipemidic acid. Used to treat cystitis, infectious pyelonephritis with ascending infection. Price - about 200 rubles.
- Nitroxoline. The drug belongs to the hydroxyquinoline group of antibiotics. It is used not only for cystitis, but also for other infectious lesions of the excretory system.
- Nevigramon. The main active ingredient is nalidixic acid. The drug is used to treat urinary tract infections and is highly effective. The price is quite high, about 2000 rubles.
- Furagin. Both Furagin itself and its analogue, Furamag, are used. It is used in case of proven sensitivity of the cystitis pathogen to Furagin. The cost of the drug is about 100-200 rubles.
- Furadonin. The basis of the drug is nitrofuran, which has antimicrobial properties. It has a relatively low price - about 50 rubles.
- Rulid. A powerful antibacterial drug with a broad spectrum of action. Belongs to drugs from the macrolide group. It is an antibacterial agent of semi-synthetic nature. It has many side effects, so it can only be prescribed by a specialist. Price - about 800 rubles.
McMirror
Pharmacotherapeutic group: antimicrobial and antiprotozoal agent - nitrofuran.
Directions for use and dosage: The drug is taken orally following the recommendations:
- Vaginal infections:
- Adults: 1 tablet 3 times a day after meals for 7 days (both sexual partners should take the drug).
- Children: recommended dose of 10 mg/kg body weight daily for 10 days. The recommended dose should be taken in two divided doses.
- Urinary tract infections:
- Adults: depending on the severity of the disease, 1-2 tablets 3 times a day for 7-14 days.
- Children: recommended dose of 30-60 mg/kg body weight. The recommended dose should be taken in two divided doses.
- Intestinal amoebiasis:
- Adults: 2 tablets 2-3 times a day for 10 days.
- Children: recommended dose of 10 mg/kg body weight 3 times a day.
- Giardiasis:
- Adults: 2 tablets 2-3 times a day for 7 days.
- Children: recommended dose of 15 mg/kg body weight 2 times a day for 7 days.
- Inflammatory diseases of the upper gastrointestinal tract associated with Helicobacter pylori:
- Adults: 2 tablets 2-3 times a day for 7 days.
- Children: recommended dose of 15 mg/kg body weight 2 times a day for 7 days.
On the recommendation of a doctor, the course of treatment for urinary tract infections can be extended or repeated.
Side effect:
- Dyspeptic disorders: nausea, vomiting, bitterness in the mouth, diarrhea, heartburn.
- Allergic reactions: skin rash, itching.
Contraindications:
- Hypersensitivity to the active substance or any component of the drug.
- Sucrose/isomaltose deficiency, fructose intolerance, glucose-galactose malabsorption.
Nolitsin
Nolitsin tablets belong to the pharmacological group of antibiotics and exhibit antimicrobial effects on bacteria and pathogenic microorganisms. The drug is used for the treatment of inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system: cystitis, urethritis, acute and chronic pyelonephritis and prevention of relapses.
Dosage: the drug is administered orally.
- Infectious cystitis (acute uncomplicated) – 0.4 g 2 times a day, for a course of 3-5 days;
- Prevention of relapses of urinary tract infections, if exacerbations occur at least 3-4 times a year - 0.2 g once at night for 6-24 months.
Side effects from the digestive system:
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Bitterness in the mouth;
- Lack of appetite;
- Diarrhea;
- Pain in the epigastric region;
- Enterocolitis pseudomembranous;
- Elevated levels of AST, ALT.
Side effects from the genitourinary system:
- Polyuria;
- Crystalluria;
- Glomerulonephritis;
- Hypercreatininemia;
- Dysuria;
- Albuminuria;
- Bleeding from the urethra.
Possible complications: hallucinations, headache, rapid heartbeat, insomnia, fainting, swelling, urticaria, erythema maligna, itching. Rarely: photophobia, arthralgia, candidiasis, chemosis, candidiasis.
Absolute contraindications:
- Pregnancy,
- Childhood,
- Fluoroquinolone intolerance
- Congenital deficiency of the enzyme glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase.
Relative contraindications:
- Cerebrovascular accidents;
- Allergy to acetylsalicylic acid;
- Epilepsy,
- Atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels.
In case of liver failure, Nolitsin is used with extreme caution. During treatment, it is recommended to avoid sunlight and physical activity.
Monural
The drug Monural belongs to the pharmacological group of antibiotics and has a broad spectrum antimicrobial and bactericidal effect. Monural is used for the treatment of acute and recurrent bacterial cystitis, urethritis, bacteriuria, pyelonephritis, as well as for the prevention of UTIs after operations and diagnostic studies of the urethra. The drug is considered one of the most effective remedies for the treatment of cystitis and is approved for use during pregnancy.
Dosage for cystitis:
- Adults – 3 g once, possibly repeating a day later at the same dose;
- Children over 5 years old – 2 g of the drug diluted in water, once, it is prohibited to take it again.
The best time to take it is in the evening before bed, no earlier than 2 hours after eating. You should empty your bladder before use.
Side effects:
- Hypersensitivity, manifested by itching and skin rashes;
- Diarrhea;
- Heartburn;
- Nausea and vomiting.
Contraindications:
- Children under 5 years of age;
- Severe form of renal failure;
- Hypersensitivity.
During lactation, it is recommended to stop breastfeeding during treatment with the drug.
Palin
The drug Palin is an antibiotic from the quinolone group, used for the treatment of acute and chronic cystitis, urethritis, pyelonephritis, prostatitis, as well as for the prevention of infections in urology and gynecology after instrumental diagnosis.
Dosage:
- Treatment of genitourinary system infections - 0.2 g before meals, every morning and evening, the duration of the course of treatment is determined according to individual indications.
Side effects:
- From the nervous system - occasionally headache, depression, confusion, visual disturbances, agitation, sensory disturbances, tremors of the limbs, extremely rarely - grand mal seizures.
- From the digestive system - diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, pain in the epigastric region, and occasionally - colitis, accompanied by severe diarrhea.
- From the hematopoietic system - anemia, eosinophilia, thrombocytopenia in patients with renal failure.
- Allergic skin manifestations;
- Photosensitivity.
Contraindications:
- Pregnancy and lactation;
- Liver failure, cirrhosis;
- Acute renal failure;
- Intolerance to individual components of the drug;
- Children's age up to 14 years.
Driving is not recommended during treatment with the drug.
Nitroxoline
Nitroxoline tablets are a drug with an antibacterial effect from the group of antibiotics. It is used to treat urinary tract infections - cystitis, pyelonephritis, urethritis, epididymitis, prostate adenoma or carcinoma, as well as to prevent infection during surgery, cytoscopy and catheterization.
Dosage:
- Treatment for adults - 0.1 g 4 times a day, the course of treatment is 2-3 weeks;
- Prevention of complications - 0.1 g 4 times a day, the course of treatment is 2-3 weeks.
Nitroxoline tablets are taken after meals.
Side effects:
- Digestive system - nausea, vomiting, appetite disturbances, rarely liver failure;
- Nervous system – ataxia, headache, polyneuropathy, paresthesia, optic neuritis (with long-term use);
- Allergic itching, skin rash.
Contraindications:
- Lactation and pregnancy;
- Quinoline intolerance;
- Cataract;
- Neuritis;
- Deficiency of the enzyme glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase;
- Cataract;
- Renal failure accompanied by anuria, oligoanuria;
- Severe liver failure.
Nevigramon
Nevigramon capsules are antibacterial agents and exhibit a bacteriostatic effect. The drug is used to treat genitourinary tract infections (cystitis, urethritis, pyelonephritis, prostatitis), gastrointestinal diseases (cholecystitis), as well as for the prevention of postoperative complications.
Dosage:
- Adults at the beginning of treatment - 2 capsules (1 g) 4 times a day an hour before meals, the course lasts 7 days;
- Adults after a week of treatment – 1 capsule (0.5 g) 4 times a day;
- Children under 12 years of age – 0.05 g per 1 kg of body weight, the dose is divided into 3-4 doses.
Side effects:
- Nervous system – dizziness, headache, weakness, drowsiness, toxic psychosis, increased intracranial pressure, convulsions;
- Visual impairment – distortion of light perception, diplopia, decreased vision;
- Digestive system – nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, stomach pain;
- Allergic manifestations - Quincke's edema, anaphylactic shock, paresthesia, urticaria, skin rashes, itching;
- Arthralgia.
Contraindications:
- Allergy to the components of the drug;
- Children under 12 years of age;
- Epilepsy, porphyria;
- Parkinson's disease;
- Pregnancy in the 1st trimester, lactation;
- Severe liver and kidney failure;
- Severe atherosclerosis.
During treatment with the drug, it is not recommended to drive a car or be exposed to sunlight.
Furagin
Furangin tablets belong to the group of nitrofurans, they exhibit an antimicrobial effect. It is used to treat infections of the genitourinary system (cystitis, prostatitis, urethritis, pyelonephritis), to prevent complications after surgery.
Dosage:
- Adult patients - 2 tablets 4 times a day in the acute phase of the disease, 2 tablets 3 times a day - during continued treatment;
- Children - 5-7 mg/kg of weight with standard therapy, 1-2 mg/kg of weight with long-term treatment;
- For preventive purposes - 1 tablet morning and evening.
Side effects:
- Digestive system - nausea and vomiting, epigastric pain, loss of appetite, diarrhea.
- Nervous system – drowsiness, damage to peripheral nerves, blurred vision, dizziness;
- Manifestations of allergies – rash, itchy skin;
- Fever, hyperthermia.
Contraindications:
- Pregnancy and lactation;
- Intolerance to drugs of the nitrofurin group;
- Newborn age (up to 1 week);
- Lack of the enzyme glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase;
- Damage to peripheral nerves.
During treatment with Furagin, it is recommended to follow a protein diet.
Furadonin
The antimicrobial drug Furadonin belongs to the group of nitrofurans and is used to treat urinary tract infections (cystitis, urethritis, pyelonephritis, pyelitis), to prevent infection during urological diagnostics and surgical interventions.
Dosage:
- For adult patients - 0.1-0.15 g 3-4 times / day, course of treatment for 7-10 days in the acute period, for the prevention of relapses - 1-2 mg per kg of weight;
- For children – 5-7 mg per 1 kg of child’s weight in the acute period of the disease, 1 mg per 1 kg of child’s weight with long-term use for preventive purposes.
The drug has an exceptionally bitter taste, it is taken after meals with plenty of liquid, and is accompanied by a protein diet.
Side effects:
- From the digestive system - nausea and vomiting, anorexia, pain in the epigastric region, occasionally hepatitis, diarrhea, jaundice;
- From the respiratory system - cough, chest pain, asthma attacks if there is a history of asthma, pulmonary infiltrates.
- From the nervous system – drowsiness, headache, dizziness;
- On the part of the hematopoietic system - disorders of the blood formula;
- On the part of the skin – erythema, dermatitis;
- Allergic manifestations - rash, Quincke's edema, chills, anaphylaxis;
- Arthralgia, myalgia.
Contraindications:
- Hypersensitivity to the components of the drug;
- Lactation and pregnancy;
- Children's age up to 1 month.
- Kidney and heart failure;
- Liver cirrhosis, chronic hepatitis;
- Porphyria.
Rulid
The drug Rulid is an antibiotic from the macrolide group, exhibits broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity and has low toxicity. Rulid is used for infections of the genitourinary system (cystitis, urethritis, cervico-vaginitis), infections of the upper and lower respiratory tract (pneumonia, pharyngitis, sinusitis, bronchitis, tonsillitis, pharyngitis), infections of the skin and soft tissues.
Dosage:
- In adults – 0.15 g 2 times/day or 0.3 g once;
- In children over 4 years old – 0.15 g 2 times a day;
- For liver failure - 0.15 g once.
Side effects:
- Digestive system – diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, pain in the epigastric region;
- Anaphylactic reactions – swelling, bronchospasm, anaphylactic shock;
- Skin – hyperemia, rash, urticaria;
- Liver – acute hepatitis, increased enzymes AST, ALT;
- Pancreatitis;
- Nervous system - headache and dizziness, paresthesia;
- Slight disturbance of taste and smell.
Contraindications:
- Pregnancy and lactation;
- Children under 4 years of age;
- Hypersensitivity to macrolides;
- Taking ergotamine or dihydroergotamine due to the risk of limb necrosis.
Today, infectious agents have developed efficacy against a variety of antimicrobial drugs. The adaptation process continues rapidly and with prolonged use of one or another antibiotic, the infectious agent “gets used to” and “learns” to counteract it.
Therefore, you must be careful when taking antibiotics:
- Nitrofuran drugs (Furagin, Furadonin) are not effective enough, which is why they are more often prescribed for prevention.
- First generation cephalosporin drugs (cefradine, cephalexin, etc.) are characterized by low effectiveness.
- In 25-30% of cases, infectious agents (Escherichia coli) are insensitive to ampicillin.
- The effectiveness of Biseptol in the fight against E. coli, according to various estimates, ranges from 30 to 80%.
Review of antibiotics from the site “my family doctor”
Choice of treatment tactics
The effectiveness of treatment measures depends on how early the diagnosis is made. Determining the cause of the pathology (identifying the type of infection) also plays a significant role. With the development of chronic or acute forms of cystitis, medications may not have an effect, and the infection will progress further, causing diseases of the kidneys and genital organs.
The main task of specialists involved in patient therapy is to prevent the inflammatory process by destroying pathological microorganisms in the area of damage to the urinary mucosa.
The choice of medicine for cystitis is made exclusively by a doctor, taking into account the characteristics of the disease in women:
- type of infection;
- degree of development of the disease;
- individual characteristics of the body (age, gender, weight, etc.);
- presence of contraindications;
- tendency to exhibit adverse reactions.
An important point is to determine the reaction of pathological microorganisms to the composition of the drug. For this purpose, a special study is carried out to help determine the most suitable medication.
Herbal medicines for cystitis
In a complex of therapeutic and preventive measures for cystitis, natural remedies based on plant components, such as extracts of bearberry leaves, horsetail and cranberry fruits, are often used.
For example, the dietary supplement “UROPROFIT®”2, the components of which have antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and antispasmodic effects.**
The complex of biologically active substances included in the dietary supplement “UROPROFIT®” helps normalize urination, improves the functional state of the kidneys and urinary tract, and also reduces the risk of repeated exacerbations of chronic cystitis.**
In pharmacies you can find:
- Lingonberry leaves. Lingonberry leaf is used for all known diseases of the excretory system. It has pronounced anti-inflammatory, astringent and diuretic effects. The composition of lingonberry leaves includes substances that suppress the vital activity of Staphylococcus aureus. In combination with traditional drugs, it has a beneficial effect on the immune system and also increases the effectiveness of antibiotics. It is better to purchase it in the form of crushed raw materials and brew it yourself. Filter bags have lower efficiency. The cost is about 50 rubles.
- Cyston. Includes many extracts of various plants. Thanks to its constituent substances, it has anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial and diuretic effects. Increases the effectiveness of traditional drugs. By itself, it is effective only with long-term use. The cost is about 300 rubles.
- Canephron. Canephron is used as an additional remedy for acute cystitis, as well as for the prevention of exacerbations of chronic cystitis. Has an analgesic effect. The cost is about 300 rubles.
- Monurel. Not to be confused with Monural - this is an antibiotic. Monurel is a herbal medicine based on cranberry extract. It has a complex effect, relieves pain, fights infectious agents, and eliminates inflammation. Since the cranberry contained in Monurel (in the form of an extract) is harmless, the product is also recommended as a measure to prevent exacerbation of chronic cystitis. The cost is about 500 rubles.
- Phytolysin paste. It is based on orange, sage and pine oils. It has a complex effect, fighting all manifestations of cystitis, from inflammation to pain, including eliminating the source of development of the disease. The average price is 230 rubles.
Causes
Quick treatment of cystitis is possible only when the causes of the disease are established. Doctors identify the following reasons:
- infectious diseases of the genitourinary system;
- E. coli or staphylococcus;
- systematic hypothermia;
- diabetes;
- impaired blood circulation in the pelvic organs;
- consequences of surgery or injury;
- menopause.
Sometimes the disease can develop during pregnancy, when women's hormonal levels and microflora of the mucous membranes of the genitourinary system change.
When should you see a doctor?
Timely consultation with a doctor helps reduce the risk of developing negative health consequences, which can be serious in advanced and chronic cystitis.
To prevent such situations, there are signs in which you should definitely consult a doctor:
- pain during urination, burning, itching of the genitals;
- frequent but unsuccessful urge to empty the bladder;
- bloody or very cloudy urine;
- an increase in temperature above 38 degrees together with the above symptoms;
Taking painkillers helps reduce the signs of cystitis, but does not cure or stop the inflammation process.
Only a doctor can prescribe effective treatment for cystitis after carrying out diagnostic measures, and it is highly undesirable to delay visiting a doctor.