Among urological pathologies, urethritis in men is often encountered; symptoms and treatment are determined by a urologist. In males, this pathology is diagnosed much more often, and it occurs in a more severe form. The urethra is the lower part of the human urinary tract. The urethra ends at the external urethra. In men, this canal is narrower and longer. This is a favorable factor for the proliferation of microbes and the development of inflammation. What are the causes, symptoms and treatment of urethritis in men?
Urethritis - what is it?
Urethritis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the urethra. In the vast majority of cases, it is an infectious pathology caused by the colonization and active development of bacteria, viruses or fungi. The process can also occur without clinical symptoms. In this case, the patient remains a carrier and spreads pathogens through sexual or household contact with other people.
The relevance of urethritis is caused by the frequency of its occurrence. In the structure of pathologies of the male urinary system, it confidently takes first place. According to statistics from the World Health Organization, every year at least 75, and other pathogens - more than 150 million men fall ill with gonorrhea. The largest number of patients is observed in countries where there are problems with the use of barrier contraceptives and personal hygiene.
Official statistics in Russia state that the main causes of urethritis in men (gonorrhea, chlamydia, trichomoniasis and candidiasis) are diagnosed in a total of 262 new patients per 100 thousand population per year. This number does not include patients who do not seek medical care.
Treatment with folk remedies
Folk remedies for the treatment of urethritis in men are used in addition to drug treatment. In acute cases, herbs are used in a monthly course, and in chronic cases, the course is extended to a year, but with mandatory breaks. The plants used must have antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and diuretic effects. The following recipes have proven to be most effective:
- Herb tea. To prepare tea, just one tablespoon of raw material (currant leaf, lingonberry leaf, or linden blossom) brewed in a thermos with a glass of boiling water for 20 - 30 minutes is enough. Drink 30 - 40 minutes before meals.
- Parsley infusion. For preparation in 500 ml. water at room temperature, add a tablespoon of fresh parsley and leave to steep for 7 hours. Take 100 ml. every three hours.
- Infusion of parsley seeds. To prepare, pour 1 teaspoon of seeds into a liter of cold water and leave to steep for 8 – 10 hours. Strain and take three tablespoons every three hours.
- Wheatgrass infusion. You need to add 2 heaped tablespoons of crushed raw materials to a glass (250 ml) of cold water and leave for 12 hours. Then strain and re-pour the wheatgrass with a glass of boiling water for 10 minutes. Mix both strained infusions and 100 ml each. taken three times a day.
- Herbal collection. Take 20 grams of elderberry inflorescences, chamomile inflorescences, St. John's wort, and 10 grams of cornflower and calendula. A tablespoon of the prepared mixture is brewed with a glass (250 ml) of boiling water, after forty minutes, filtered and drunk at night.
- Cranberry juice. Mash 500 grams of berries and squeeze out the juice. Pour the cake with two liters of water and bring to a boil. Strain and add the strained juice, and you can sweeten it a little with honey or sugar. Take at least a liter per day.
- Fresh and brewed blackcurrants It is better to eat currants separately from meals. For brewing, take both fresh and dried berries. Brew one tablespoon of fresh currants with a glass of boiling water and leave for 20 minutes. It is better to brew dry berries in a thermos; a teaspoon of dried berries is enough for a glass of boiling water.
- Baths of brewed chamomile are also used to wash the genitals. Chamomile is a good antiseptic and has an anti-inflammatory effect.
- Treatment with a decoction of oak bark is also used in the form of baths. To do this, pour one teaspoon of crushed bark into a thermos with a glass of boiling water and leave for at least three hours. Use the warm, strained infusion for five-minute baths of the genitals three times a day. The duration of the course is three days. You should abstain from sexual intercourse during treatment.
There are many ways to treat urethritis with folk remedies, but before use, medical consultation is necessary.
The first signs of urethritis in men
Since there are many pathogens that can cause the development of urethritis in men, the clinical picture of the disease varies significantly. However, there are several common features:
- Between infection and the onset of the disease usually ranges from 2 to 60 days (prodromal period).
- The first symptom is discomfort, aching or burning pain during urination.
- With urethritis, dysuric syndrome often develops. Due to pain, the bladder is not completely emptied, so the urge often increases, both during the day and at night. The urine stream may become smaller.
- Changes in the color and clarity of urine are almost always observed. It may contain purulent, cheese-like, mucous or even bloody impurities.
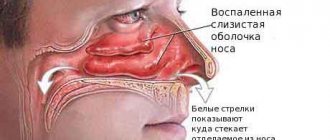
- Upon visual examination, the hyperemic mucous membrane of the external opening of the urethra draws attention. The surrounding tissues may be swollen and have an elevated temperature.
- With a pronounced inflammatory process, the patient’s general well-being may deteriorate, body temperature may increase (up to 38-39°C), and performance may decrease.
Symptoms and signs of urethral inflammation
The first symptoms of urethritis in a man appear, depending on the incubation period of the pathogen, from several hours (allergic) to several years (tuberculosis). The most typical of all types of urethritis are the following symptoms:
- Burning, itching, pain when urinating.
- Purulent discharge.
- Frequent urination.
Hyperemia or high temperature with urethritis, as a rule, is not observed. The discharge depends on the pathogen and is of a different nature. This is often a green or white discharge with an unpleasant odor that appears in the morning and forms yellow crusts on the penis. With inflammation of the urethra, redness and sticking of the external opening, pain in the lower abdomen, and cloudy urine may be observed.
Symptoms of urethritis by type and nature of the course
Acute form
Urethritis always begins with the acute phase of the disease, regardless of the type of pathogen.
With gonorrhea, pain dominates during urination or ejaculation. In the initial portion of urine, grayish-yellow discharge (pus, mucus and white blood cells) appears. Body temperature may rise.
The prodromal period of chlamydia lasts 2-4 weeks. Discharge from the urethra is predominantly mucous or mucopurulent in moderate quantities. The pain syndrome is moderate, the general condition rarely worsens. Often accompanied by acute prostatitis.
With mycoplasma or ureaplasma urethritis, the asymptomatic period can last up to 60-70 days. It is possible that the temperature may rise to subfebrile levels (37-38°C) with dyspnea and itching.
If the cause of inflammation is the herpes virus, then symptoms appear 3-8 days after sex. Areas of redness, ulcers and blisters appear on the mucous membrane of the urethra, outer flesh, and penis, which cause severe itching. Regional lymph nodes also enlarge and the temperature rises.
Staphylococcal and streptococcal acute urethritis is characterized by the detection of large purulent discharge from the urethra. At the same time, the patient’s well-being sharply deteriorates - hyperthermia and intoxication increase. If treatment is not timely, septic complications occur.
The candidal form of the disease is characterized by a pronounced burning sensation and cheese-like discharge. A white coating appears on the mucous membranes of the penis, which is easily removed with mechanical pressure.
Chronic form
The chronic form of the disease is characterized by relapses of symptoms and long periods without any complaints. Patients are concerned about:
- periodic itching in the urethral area
- discomfort during sexual intercourse, especially during ejaculation;
- the presence of mucus or pus in the semen;
- frequent urge to urinate (especially at night, which can lead to sleep disturbances);
- discharge of pus or mucus from the urethra (mainly in the morning).
The severity of symptoms in the chronic course is much less pronounced. The patient's general condition does not worsen. An exacerbation on its own after 7-14 days can go into long-term remission, when the disease can be diagnosed only by bacteriological examination. Most often it turns into chronic cystitis and urethritis if they are caused by gonococci, chlamydia, mycoplasma, E. coli, and the patient has not sought qualified medical help.
Prognosis, complications
With timely and adequate treatment, acute urethritis can be successfully cured. Otherwise, it will become chronic. There is also a risk of the following complications:
- prostatitis;
- cystitis;
- pyelonephritis;
- sexual dysfunction;
- infertility;
- vesiculitis;
- orchitis;
- epididymitis;
- colliculitis;
- balanoposthitis.
Causes of the disease
Almost always, urethritis is an infectious inflammatory process. This implies that the pathological pathogen most often enters the urethra from the outside or from other affected tissues of the patient’s body. The most common cause of infection is unprotected sexual intercourse (about 85%). There is also a household route of infection, when infection occurs through the use of shared personal hygiene products or laundry.
If we are talking about the migration of infection within the body, then 2 mechanisms of its spread dominate:
- hematogenous - from inflamed tissues the pathogen enters the bloodstream and then settles on the urethral mucosa;
- descending – from higher located organs of the genitourinary system along with urine or sperm.
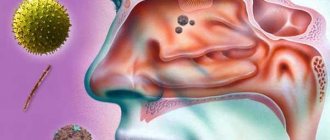
The most common causative agents of infectious urethritis are:
- Gonococcus is a paired gram-negative bacterium that can infect the mucous membranes of the urinary system, rectum, eyes and oral cavity.
- Urogenital Trichomonas is a single-celled organism that colonizes only the mucous membrane of the genital organs.
- Chlamydia is a bacterium that is an intracellular parasite of the epithelium of the urethra. May provoke the development of autoimmune reactions (Reiter's syndrome).
- Ureaplasma and mycoplasma are small types of bacteria that parasitize inside the epithelium of the urinary tract.
- Escherichia coli is a gram-negative bacterium that is normally found in the digestive system. Capable of colonizing and destroying the urethral epithelium.
- Streptococci and staphylococci are groups of gram-positive bacteria that can cause purulent inflammation with severe intoxication.
- Candida is a conditionally pathogenic fungus. Activated when the reactivity of the immune system decreases.
- Genital herpes virus. Affects the skin, as well as the mucous membranes of the urinary organs.
In less than 1% of patients, non-infectious urethritis is observed. During diagnostics, it is not possible to isolate the pathological pathogen. It is believed that the reasons for its development are:
- exposure to ionized radiation (during radiation therapy);
- allergic reactions to topical use of ointments;
- traumatization of the urethra by the introduction of foreign objects into it;
- thermal or chemical damage due to self-washing of the urethra with solutions or antiseptics.
Risk factors for developing urethritis
The conducted studies made it possible to identify factors that may contribute to the development of urethritis:
- urological surgery;
- abnormalities in the development of the urethra;
- placement of a catheter in the bladder (longer than 48 hours);
- obstruction of the urethra with partial or complete disruption of its patency (urolithiasis, oncological processes);
- diabetes mellitus, if therapy fails to normalize blood glucose levels
- sexual intercourse with frequent changes of partners;
- diseases and abnormalities of connective tissue development;
- end-stage renal failure;
- hormonal disorders;
- the need for long-term use of drugs that suppress the immune system;
- oncological pathologies, regardless of their location.
Prevention
In most cases, urethritis is caused by various bacteria and is transmitted during sexual intercourse. As a preventive measure, it is necessary to maintain personal hygiene, be selective in intimate relationships, and use condoms. Proper nutrition is important.
It is necessary to exclude salty, spicy and fatty foods, and alcoholic drinks. When you have the urge to go to the toilet, you should empty your bladder immediately. Check with a urologist annually to avoid hypothermia.
Urethritis is a serious disease that can lead to serious complications, including infertility and cancer. Self-medication is not allowed, as it is necessary to know the cause of the disease and the type of pathogen. Uncontrolled use of antibiotics can lead to worsening of the condition.
Watch the video:
Kinds
In clinical practice, several classifications of urethritis are used. It is called primary if the infection occurred from the outside (after contact with a sick person). The secondary form of the disease occurs if the primary source of infection is in the patient’s body (the genitourinary system, pelvic organs and any other location). It usually develops against the background of immunosuppression (taking cytostatics, courses of radiation therapy, hematological pathologies, HIV, congenital diseases of the immune system).
Depending on the pathogen that caused the disease, nonspecific and specific forms are distinguished. Nonspecific urethritis is caused by microorganisms that are conditionally pathogenic flora, and they can be isolated from healthy patients (streptococci, staphylococci, Escherichia coli, Proteus, Candida).
Specific urethritis is caused by pathogenic pathogens that are transmitted primarily sexually (chlamydia, trochomonas, gonococcus, ureaplasma, mycoplasma).
Separately, non-infectious urethritis is distinguished, which occurs due to irritation or damage to the mucous membrane (allergic reagents, drugs, ionizing radiation). But in half the cases it turns into a bacterial form.
Depending on the duration of urethritis, it is divided into 2 large groups:
- acute form – the disease lasts up to 3 months;
- chronic – symptoms of urethritis bother the patient (possibly with periods of remission and relapse) for more than 3 months.
Diagnosis of pathology
A man suffering from severe pain must undergo a complete hardware examination. Ultrasound diagnostics allows you to examine the pelvic organs and determine the cause of pain. On the screen, a specialist can note the presence of compactions in tissues, changes in the shape of an organ, or the presence of stones in the bladder.
If no cause is identified, the patient is sent for magnetic resonance imaging. The device allows you to view internal organs in a three-dimensional image. The MRI method reveals pathology.
A man needs to undergo an unpleasant procedure - taking a smear from the urethral canal. Patients experiencing pain are usually afraid of this procedure, but it is necessary. The collected smear is sent to the laboratory for testing. Specialists isolate microorganisms from the sample. The bacteria are placed in a special cup, where they actively multiply. The grown bacteria are exposed to antibiotic substances. This method allows you to determine the type of microbe that caused the pain and the drug that can destroy it.
To make a diagnosis, you need to take a detailed blood test. The qualitative and quantitative content of red blood cells, leukocytes and unusual cells is determined in the patient’s blood. If the erythrocyte sedimentation rate is increased and a large number of red blood cells are detected, this indicates the presence of an inflammatory process in a man. Some patients have pathogenic cells in their blood. Such cells cause viral diseases in the human body. The AIDS and HIV viruses are very dangerous.
After a complete examination, the results are transferred to the attending physician. Using them, he makes a diagnosis and prescribes treatment.
Cystitis
Cystitis is often the cause of pain in the urethra. The disease occurs due to various colds. The process of inflammation begins to develop in the bladder and moves into the urethral canal. With cystitis, urination becomes difficult. The person begins to go to the toilet frequently. Urine is released in droplets, the bladder does not empty completely. If the patient is diagnosed with cystitis, then treatment is carried out with the help of medications.
Medicines for the treatment of cystitis include three pharmacological groups:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs;
- Antibiotic drugs;
- Diuretics.
Cystitis can have two main forms. The disease occurs in chronic or acute form. Chronic cystitis occurs unnoticed by the patient; the symptom is a rare cutting pain in the urethral canal. The treatment is long-term. In the first stages, painkillers are added to therapy. The acute form of cystitis is accompanied by constant cutting pain and fever. Some men experience a rise in body temperature. Treatment of acute pathology must be carried out in a hospital setting under medical supervision.
Urethritis
Pathology occurs due to bacteria unusual for the urethra. It is often possible to detect the presence of staphylococcus in the microflora. The bacterium causes inflammation along the entire length of the urinary tract. Treatment includes antibiotic and antimicrobial drugs.
The usual treatment regimen is carried out for 5–7 days. The patient is prescribed an antimicrobial drug, metronidazole, and antibiotics. Antibiotic drugs are selected based on the sensitivity of microorganisms. Staphylococcus is not immediately treatable. In this case, levofloxacin is more effective. The drug has high absorption and rapid action. The action of the substance is to disrupt the integrity of the membranes of pathogenic cells. A destroyed cell wall leads to its death.
Urethritis causes nagging pain in the groin and penis. The pain is concentrated in the urethral ring and the sphincter of the bladder.
Diagnostics
If symptoms of pathology occur, a man should consult a urologist. He begins the examination by collecting anamnesis. The doctor asks questions regarding complaints, the presence of other diseases of the urinary system, sex life, medications that the patient constantly takes, personal hygiene, bad habits and previous surgical interventions and procedures.
Then the inspection takes place. The patient takes off his clothes, and the urologist examines the genital area and pays attention to changes in the mucous membranes, the presence of pathological discharge or tissue swelling.
To confirm the diagnosis and verify the pathogen that caused the pathology, before starting antibacterial therapy, it is necessary to collect secretions from the urethra. The material is sent to a bacteriological laboratory, where microscopy is performed, as well as inoculation on life-giving media. In case of chronicity of the process or relapse, determination of sensitivity to antibacterial drugs is also indicated in order to select the most effective treatment strategy.
Collection from men should occur no earlier than 2 hours after the last urination. To carry out the manipulation, you must use a sterile swab.
In addition, all patients are advised to:
- general blood test with leukocyte formula (possible leukocytosis, neutrophilia, increased ESR);
- Ultrasound of the bladder with determination of residual urine, prostate gland and kidneys - to exclude damage to these organs.
When the inflammatory process spreads to other organs, the patient is advised to donate blood for antibodies to the most common pathogens.
How is urethritis treated?
The prognosis for the course of urethritis in men depends on the correctness of the diagnosis; the faster the cause of inflammation is identified and treatment is applied, the higher the likelihood of a speedy recovery, avoiding complications and relapses. To achieve the effectiveness of treatment, it is necessary to go through several stages:
Diagnosis of the disease
The genital organs are examined, and the symptoms that appear are also noted. Painful urination and urethral discharge are considered more common characteristic symptoms.
In order to identify the causative agent of the disease, the following tests are necessary:
- Blood analysis. Necessary for identifying and identifying sexually transmitted infections.
- Analysis of urine. Determines the general condition of the body and the presence of an infectious process.
- Analysis of a smear from the urethra is needed to determine the microflora and type of microorganisms that caused inflammation.
Treatment methods for urethritis
To recover from this disease, it is necessary to stop the spreading infection in the body, removing the source of inflammation. It is also important to restore the functionality of the urethra. The prescription of treatment is dictated by the form of the disease.
For infectious urethritis, they undergo a course of antibacterial therapy (Azithromycin, Metronidazole, Doxycycline, Ceftriaxone); for urethritis of a non-infectious nature (allergic, traumatic, congestive), the cause of inflammation is eliminated. In the case of allergic urethritis, antihistamines (Suprastin, Tavegil) are used. In case of traumatic urethritis , surgical intervention is possible; injecting uroseptic drugs directly into the urethra aimed at restoring the urethral mucosa is also effective. To get rid of congestive urethritis , it is necessary to increase physical activity, which will eliminate blood stagnation in the pelvis. Drugs are also used to eliminate venous insufficiency (Eskuzan, Venza).
Don’t forget about restoring the microflora after antibacterial therapy; probiotics (Linex, Bifidumbacterin) will help with this. Also, for a speedy recovery, you should take immunomodulators (Cycloferon, Uro-Vakson).
The diet should be adjusted by reducing the consumption of foods that irritate the urethral mucosa (sour, hot, spicy foods and also foods with preservatives).
Repeated examination
At the final stage, it is necessary to re-examine and take tests to exclude the presence of the disease in the body.
The course of treatment for urethritis lasts from two weeks to a month, it all depends on the severity of the disease and compliance with the prescribed therapy. Urethritis very rarely requires hospital treatment, so at home an important role is played by the correct use of prescribed medications, refusal of sexual intercourse and diet.
Treatment of urethritis
Modern treatment of inflammation of the urethra is based on the principles of evidence-based medicine. This means that the positive effect of any drug must be confirmed in independent studies. Only after this a new technique or medication is recommended by international and national recommendations of urologists. Next, the role of the most popular drugs in the treatment of urethritis will be considered.
Antibacterial therapy
Since in the vast majority of cases urethritis is caused by bacterial flora, the basis of treatment is the prescription of antibacterial drugs. The most commonly used are cephalosporins, macrolides, fluoroquinolones, protected penicillins, and tetracyclines.
Cephalosporins
This is a group of antibiotics with a bactericidal effect and a wide spectrum of action. Most often prescribed for gonorrhea, or if the patient has staphylococcal, streptococcal flora or E. coli. The mechanism of action is a violation of the integrity of the cell membrane, which leads to the death of the microorganism.
The most commonly prescribed drugs are ceftriaxone, cefotaxime or cefoperazone. The course of treatment with drugs is 3-14 days.
Macrolides
Combines a group of antibacterial drugs for the treatment of urethritis (azithromycin, clarithromycin, erythromycin, spiromycin, josamycin) with a bacteriostatic effect. When used in urine, they create a high therapeutic concentration, which is why they are widely prescribed in urology. Macrolides are effective against chlamydia, damage by E. coli, staphylococci, streptococci, mycoplasma or ureaplasma.
All drugs are available in tablets and taken orally 1-2 times a day. They are prescribed for 3-10 days.
Fluoroquinolones
A group of nalidixic acid compounds with a bactericidal mechanism of action (inhibition of the bacterial DNA gyrase enzyme). They are excreted from the body in the urine, therefore they effectively treat inflammation of the urethra, which is caused by chlamydia, gonococcus, E. coli, and staphylococci.
In urological practice, levofloxacin, ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin, and ofloxacin are used. Duration of therapy is 3-7 days.
Tetracyclines
These are bacteriostatic antimicrobial agents with a broad spectrum of action. Tetracyclines inhibit the synthesis of protein molecules in the cells of pathogenic pathogens, thereby preventing their further reproduction. For urethritis, they are prescribed if mycoplasma or ureaplasma is isolated.
The only drug that is actively used is doxycycline. It is prescribed in the form of capsules of 100 mg for 5-10 days.
Synthetic penicillins
Despite the increase in microflora resistance to penicillins, they continue to be used for the treatment of urological pathologies. They retain their effect against nonspecific bacterial pathogens - staphylococci, streptococci or Escherichia coli.
Amoxicillin is used in combination with clavulanic acid. For adult patients, it is prescribed 875/125 mg 2 times a day for 5-14 days.
Polyene antibiotics
Despite the name of the group, it combines powerful antifungal drugs. They are used for candidiasis of the urethra. The mechanism of action is connection with the styrene group of the cell membrane and disruption of ion transport through it, which leads to the death of the pathogen. Nystatin is most often prescribed, but natamycin and amphotericin B are also used. In tablet form, the drugs are used for generalized fungal processes affecting internal organs.
Antiseptics
Uroseptic drugs are used in clinical practice if the process is caused by nonspecific flora - Escherichia coli, staphylococci, Proteus. But their use is rational only if there is no intoxication or increase in body temperature.
Fosfomycin is the most commonly prescribed antiseptic. This drug, in addition to its wide spectrum of action and good tolerability, also prevents the adhesion of bacteria to the mucous membrane of the urinary tract. For nonspecific urethritis, it is enough to take 3 g once.
The second popular antiseptic is nitrofurantoin from the nitrofuran group. It has a bacteriostatic effect and blocks various enzymes in microbial cells. For treatment, it is prescribed 100 mg 2 times a day for 5-7 days.
Candles and ointments
To treat fungal urethritis, ointments and suppositories with nystatitis or flucocazole are used. When used topically, these drugs do not penetrate the epithelium well, so they practically do not enter the systemic circulation. Due to this, they have a low incidence of side effects.
For nonspecific urethritis, it is possible to use Levomekol ointment. It contains chloramphenicol, an antibacterial agent that acts on staphylococci, streptococci and E. coli. The drug also promotes faster regeneration of the epithelium.
With chlamydia, Reiter's syndrome often develops, an autoimmune process that affects large joints. For its treatment, gels and ointments based on non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (diclofenac, ketoprofen, ibuprofen) or glucocorticosteroids (dexamethasone) for local use are prescribed.
Immunomodulators
In domestic medicine, immunomodulators are widely used to treat chronic urethritis in men. It is believed that this group of medications affects certain groups of neutrophils and leukocytes, activating their activity, and also has an antioxidant effect. The most popular among them are “Polyoxidonium” and “Galavit”.
However, this group of drugs has no proven effect. All available research was carried out either by the manufacturer or by domestic scientists who are financially dependent on it. There is also a lack of information about them in international peer-reviewed journals. That is why they are not included in recommendations for the treatment of urethritis, and are not recommended for use in this disease.
Vitamins
In recent decades, attitudes towards vitamins have also changed. Previously, they were prescribed for chronic inflammatory processes to strengthen the body. But a significant number of studies have emerged showing that this can lead to hypervitaminosis. It is often accompanied by neurological symptoms, visual and hearing impairment, dyspeptic symptoms and skin rashes. Therefore, vitamins should be prescribed only in the presence of proven hypovitaminosis, and they should not be taken routinely by patients with chronic urethritis.
Folk remedies
Many plants contain anti-inflammatory substances that can reduce the severity of pain and inflammation in pathologies of the genitourinary system in men. They can be used as a complement to traditional treatment. The most common recipes are as follows:
- Parsley infusion. Bring about 1 liter of table water to a boil and add 2 teaspoons of dried parsley leaves, then leave for 45-60 minutes in a cool place. Drink a glass after meals.
- Infusion of cornflowers. Pour 200 ml of boiling water over a teaspoon of plant leaves and leave for an hour. Then it can be taken 1 tablespoon before meals 3 times a day.
- Currant tea. Throw 3 tablespoons of leaves into 1.5 liters of hot water and bring to a boil. After half an hour you can drink 1 glass.
Traditional methods include hirudotherapy (the use of leeches). However, its clinical effect is questionable.
Additional treatments
After diagnosis, the patient is given certain recommendations regarding lifestyle and nutrition. Until complete recovery, the patient is prohibited from any sexual contact (even using a condom). This will avoid infecting new people. It is also necessary to maintain personal hygiene. Towels, linen, soap must be strictly individual. Do not reach into the urethra with unprotected hands.
The diet for urethritis must be balanced and contain a sufficient amount of nutrients and vitamins. It is important that the patient drinks at least 1.5-2 liters of fluid per day (if he does not have kidney or heart failure).
Physical therapy for urethritis has limited use. It has not been proven that it improves the course or promotes recovery. Modern recommendations also do not recommend homeopathic remedies.
Principles of patient treatment
In men, symptoms and treatment are determined by a doctor. Experienced doctors know how to treat this urological pathology.
For urethritis, treatment has the following objectives:
- relieving inflammation;
- elimination of pain, itching and burning;
- destruction of the infectious agent;
- prevention of complications.
Therapy can be carried out at home. This is possible in the absence of complications. The regimen and therapy are selected by the doctor individually, depending on the causative agent of the disease. Etiotropic treatment of urethritis may include the use of antibiotics, antiprotozoal drugs with antibacterial action, antiviral or antifungal agents.
Auxiliary methods for treating urethritis at home include the use of local antiseptics (Miramistin, Dioxidin, Collargol, silver nitrate), physiotherapy, and diet. Physiotherapeutic methods include electrophoresis, UHF therapy, and magnetic therapy. Physiotherapy is carried out for chronic inflammation or acute inflammation during the recovery period. In the acute phase of the disease, physiotherapy is contraindicated.
During treatment you should not have sexual intercourse. Treatment of traumatic urethritis may require surgery. The congestive (stagnant) type of inflammation requires normalization of lifestyle (increasing physical activity, limiting time spent working at the computer and watching TV). An allergic form of inflammation of the urethra requires the use of antihistamines.
Complications of urethritis
The main complications of urethritis occur with a long course of the disease. The most commonly observed undesirable conditions are:
- Spread of the infectious process throughout the genitourinary system involving the prostate gland (prostatitis), bladder (cystitis), kidneys (pyelonephritis), epididymis (epididymitis), testicles (orchitis).
- Septic complications in streptococcal and staphylococcal infections. Development of sepsis and/or lesions in other organs.
- Degenerative changes in the urethra with its narrowing.
- Reiter's syndrome is a reactive inflammation of the joints, skin, and conjunctiva of the eyes.
- Obstructive form of infertility due to gonorrhea. It develops as a consequence of sclerosis of the vas deferens, and is a serious problem in andrology.
Prevention of urethritis
Urethritis is a preventable disease. To do this, a man must have an understanding of intimate and sexual hygiene, lead a healthy lifestyle and not neglect visiting a doctor.
It is especially important to observe the following rules:
- Never take antibiotics unless prescribed by a doctor. The same applies to antifungal and antiviral agents.
- Avoid casual sex, do not practice sexual deviations, and do not perform self-catheterization.
- Do not use other people's towels, hygiene items, or underwear.
- Wash yourself promptly and regularly, especially after visiting the toilet or having sexual intercourse. Change your underwear on time.
- Do not drink alcohol, do not smoke. Spend more time outdoors, take walks.
A man who takes care of his health is less likely to encounter diseases. It is especially important to consult a doctor if signs of inflammation appear in the genitourinary system - pain in the penis, burning, difficulty urinating, poor potency. It is important to start treating diseases as early as possible, then it will be possible to avoid such complications as urethritis in men.
Forecast
Urethritis is a benign disease. With proper treatment and timely use of antibacterial drugs, a man recovers completely in 98% of cases. The problem of correct selection of antibiotics arose due to the increase in antibiotic resistance (especially in gonococci, chlamydia and staphylococci). Therefore, all patients who seek medical help undergo a collection of urethral secretions with bacteriological examination.
There are factors that can contribute to the chronicity of the disease:
- interrupted course of treatment (immediately after symptoms disappear);
- diabetes;
- congenital malformations of the urinary system;
- diseases of the immune system;
- uncompensated concomitant diseases.
Prevention methods
You can reduce the likelihood of sexually transmitted infections by eliminating promiscuous sex with casual partners and using barrier contraceptives.
Natural latex condoms are effective as contraceptives, but do not prevent sexually transmitted diseases. Before sexual intercourse, you should avoid the use of alcohol and drugs. This preserves the protective functions of the immune system and increases the likelihood of correct condom use. It is also not recommended to have sex for a week after treatment.
Cutting pain for urethritis
Pain and pain when urinating in women occurs due to inflammation of the urinary canal. Urethritis can be non-infectious or infectious. When an infection is introduced, the causative agents are usually gonococci and cocci, E. coli, chlamydia, fungi and mycoplasmas.
More on the topic: How is vesicoureteral reflux treated?
Urethritis can be primary, or a consequence, secondary. If a primary type of urethritis is diagnosed, this is an independent pathology, since the secondary one always accompanies other diseases, for example, vesiculitis, prostatitis or cystitis.
The urethra in women has a short and wide structure, which is not unfavorable conditions for the growth of bacteria and microorganisms. There are many bends in the male urethra, where there is a physiological accumulation of microorganisms that begin to reproduce during stagnation.
The most common causes of urethritis are:
- infection through sexual contact without barrier contraception;
- violation of hygiene rules for intimate areas;
- during catheterization;
- in case of irritation of the mucous membranes of the genital organs with hygiene products in the form of gels and soaps;
- entry of microbes and pathogenic microorganisms from neighboring organs.
Symptoms of urethritis in the acute stage are manifested in painful excretion of urine. The disease is also characterized by a reddened and inflamed urethral canal on the outside, discharge of pus along with urine (pyuria), a burning sensation when urinating in women and itching. Pus or mucous secretion may also be released from the external urethra. If inflammation closes the lumen, urinary incontinence is present.
Urethritis in pregnant women
All infections that enter the body of a woman carrying a child affect the fetus and its development. The degree of risk depends on the type of disease and type of infection. The most dangerous form during pregnancy is urethritis caused by chlamydia or ureaplasma. They cross the placenta and infect the fetus.
During pregnancy, the symptoms of urethritis do not differ from those in non-pregnant patients. The peculiarity lies in the implicit expression of the manifestations of the disease, when a woman ignores the pain sensation due to the peculiarity of her condition. An examination by a gynecologist immediately reveals urethritis, especially with complaints of itching and a slight burning sensation during urination.
Outside the urethra during urination, women secrete fluid, the type of which depends on the pathogen that provokes the disease. The manifestation of the symptom is very similar to cystitis, not only during pregnancy, but for expectant mothers there is a particular health threat.
Cravings when urinating during pregnancy are especially unpleasant. Infections are very difficult to treat, since it is important not to harm the health of the mother and to prevent pathologies in the child. During childbirth, you can also infect the baby, who will develop conjunctivitis or pneumonia.
Treatment is required in any case, since neglect of the disease leads to its complication and transition to a pathology of the urinary system. Less dangerous during pregnancy is non-infectious urethritis, which is treated with gentle herbal-based medications, which is safe for the health of both the mother and the developing fetus.
Therapeutic measures
Treatment of the disease in most cases is carried out using drug therapy. If the patient experiences severe pain, the use of antispasmodics is recommended.
If a symptom occurs due to a bacterial infection, the use of antibiotics and antimicrobial drugs is recommended.
Treatment of the pathological condition is carried out using antifungal medications.
To improve the performance of the immune system, patients are prescribed immunomodulators. Thanks to these drugs, the body's resistance significantly increases. Patients are recommended to take herbal teas that have an anti-inflammatory effect.
Important! During the treatment period, patients are not recommended to consume large amounts of liquid.
However, for certain diseases, experts advise compliance with the drinking regime. This aspect must be clarified with your doctor. To avoid stagnation of urine, timely emptying of the bladder is recommended. During the treatment of pathology, it is necessary to prevent colds. The patient is advised to exclude the possibility of hypothermia.
If the disease occurs against the background of an infection, the patient is recommended to take antibiotics - Normax, Nolitsin, Furadonin.
At the same time, it is recommended to use antispasmodics - No-shpy, Papaverine.
It is necessary to use drugs that are of plant origin - Phytolysin, Cyston, Canephron.
If the pathological process occurs in the acute phase, then the patient should be treated with bed rest.
When body temperature rises, it is necessary to take antipyretic medications: Nurofen, Paracetamol and others. In advanced cases, the bladder is washed.
Causes of the disease
Primary urethritis, according to statistics, more often appears in women after sexual intercourse. The entrance to the female urethra is located between the clitoris and the vestibule of the vagina.
During intercourse, the microflora of the vagina is introduced into its mouth. Due to the anatomical features, the lumen of the female urethra is wide, which facilitates easy penetration of microbes.
Nonspecific urethritis in men also almost always appears after sexual intercourse. A prerequisite for this is the presence of the pathogen in the woman’s genitals.
Remember! Using a condom will reliably protect you from sexually transmitted infections.
Another cause of primary inflammation may be medical intervention. If sterility was not observed when inserting a cystoscope or catheter, there is a high probability of infection.
The likelihood of infection also increases with prolonged catheterization of the bladder.
Somewhat less frequently, inflammation appears as a result of infectious diseases at distant locations. Cases have been described when, after severe follicular tonsillitis, a patient developed urethritis.
Chronic inflammation of the prostate or seminal vesicles can also lead to this complication.
Cases have also been described where inflammation of the urethra was the result of an allergic reaction without the participation of pathogens.
A decrease in the body's defenses contributes to the occurrence of an infectious process in the genitourinary system. Weakening of the immune system due to vitamin deficiency, poor nutrition, HIV infection, and bad habits dramatically increases the risk of microbial invasion.
Long-term treatment with corticosteroids and immunosuppressants also leads to a decrease in resistance to infections.
Candidal urethritis often begins during long-term antibiotic therapy. The result is sometimes a disruption of the natural balance of microflora. With the complete destruction of bacteria, rapid proliferation of fungi occurs.
Classification
According to the type of course, this disease is divided into primary and secondary urethritis. In the first case, it begins directly in the lumen of the organ.
However, the disease can also develop due to an inflammatory process in another part of the body. The cause of the secondary form of inflammation of the urethra can be:
- pyelonephritis;
- chronic prostatitis;
- inflammation in the seminal vesicles;
- cystitis;
- diseases of the pelvic organs;
- distant foci of chronic infection.
Based on the type of agent that caused the process, nonspecific urethritis is divided into:
- bacterial;
- viral;
- trichomonas;
- candidomycotic;
- traumatic;
- allergic.
When the mucous membrane is exposed to bacteria, pathology is most often provoked by microbes of the coccus group and Escherichia coli.
Trichomonas and candidomycotic forms of the disease mainly develop as a result of sexual infection.
Treatment
Treatment will be completely different for each diagnosis. In general, various diseases are stopped due to the use of antibacterial drugs and medications for viral and fungal infections. Therapy is also used to remove toxins from the body. There are a number of other pathologies, the treatment of which consists of surgical intervention. These can be benign or malignant tumors or stones in the canal.
Be sure to drink plenty of fluids, but only with the permission of your doctor. This is necessary in order to remove toxic substances from the body that bring negative effects.
It is prohibited to drink drinks containing gases, alcohol, or coffee. It is better to include tea from various medicinal herbs, compotes and natural juices in your diet. If you experience pain in the urethra after urinating, you should urgently go to a medical facility. If left untreated, the outcome will be extremely unfavorable.
What else can cause pain in the urethra?
Pain in the urinary tract is often provoked by diseases of non-infectious etiology. These include tumors, lice pubis, urolithiasis and gout. Also, the reasons are often irritation from the chemical components of powders, lubricants in condoms, and alkaline soap.
Cramps can be allergic in nature and often spread to various organs of the genitourinary system, especially with renal colic. The patient will not confuse the appearance of renal colic with anything else, since the intense pain syndrome is very sharp and sudden, radiating to the groin and external genitalia. Such colic indicates the development of urolithiasis.
Pain is often caused by formations in the urethra or bladder. Stones and sand, together with the current of urine, carry away small fragments, which, with their sharp edges, can damage the membranes of the urinary tract mucosa. Sometimes there is blood when urinating in men.
Urolithiasis develops when the metabolism is disturbed, especially if there are other inflammatory diseases of the urological sphere, injuries, harmful environmental conditions during work, as well as an improper diet or gout. If the lower third of the ureter is clogged with stones, the symptoms will resemble acute urethritis or cystitis.
More on the topic: Why are urates in urine dangerous?
Other predisposing factors
Pain can be caused by non-infectious diseases. These include urolithiasis, tumors, gout, and lice pubis. The reason may lie in chemical irritants (use of alkaline soap, powder, lubricated condoms). The pain may be allergic in nature. The pain can be radiating. This is often observed with renal colic. With it, patients feel a sharp, acute pain that radiates to the groin area and genitals. Renal colic is one of the manifestations of urolithiasis.
Pain can be caused by stones in the bladder or urethra. Small particles (stones, sand) can be carried away with the urine current. All this can injure the urethral mucosa. The development of urolithiasis is based on metabolic disorders. Predisposing factors include poor nutrition, the presence of inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary organs, injuries, gout, and harmful working conditions. In case of blockage of the lower third of the ureter, the symptoms of the disease will resemble those of acute cystitis and urethritis.
Diagnostic methods
Signs of inflammation and symptoms accompanying urethritis unmistakably indicate this disease. To confirm the diagnosis, laboratory tests of urethral discharge are studied.
The disease is confirmed by the preliminary detection of microorganisms that cause infectious urological pathology.
Subsequently, the secretions are inoculated onto special nutrient media. At the same time, it is possible to establish the sensitivity of the pathogen to certain types of antibiotics.
When visually examining the initial portions of urine under a microscope at low magnification, multiple purulent threads are visible.
In cases of suspected trichomoniasis, it is recommended to examine fresh discharge immediately after collecting the material. The smears are not recorded.
The pathogens are clearly visible on glass preparations. They look like epithelial cells. Meanwhile, in native smears their organelles in the form of flagella are clearly visible.
Concept and features
Chronic urethritis implies that the patient periodically experiences the influence of this disease . This may be due to a cold, exposure to other external factors, and so on.
The disease itself, urethritis, is a special type of inflammatory process that is present in the area of the urethra. This disease is infectious and can be transmitted sexually. It occurs in exactly the same way in both men and women.
Chronic urethritis periodically wakes up, causing inconvenience to its owner.
The most common is gonococcal acute urethritis , otherwise it is called chronic or gonorrhea.
This disease is widespread in men and can be transmitted sexually, as well as through traditional oral and anal sex. You can also become infected with a similar disease through household means.
The incubation period of such a disease can be from 3 to 5 days, and you can observe the first symptoms within the first day after the disease.
Non-gonococcal urethritis occurs in 40% of cases. The reason for the appearance of such a disease in the body is infection with chlamydia. This form of the disease is called chronic chlamydial urethritis.
Often, the cause may be ureaplasmosis or sexually transmitted diseases . This disease manifests itself somewhat later than the gonococcal form. You will be able to see the first signs of the disease a few weeks after the infection has settled in your body.
On our website you can learn about the following types of urethritis:
- nonspecific;
- non-infectious;
- spicy;
- gonorrheal and non-gonorrheal;
- bacterial;
- trichomonas;
- chlamydial;
- candida;
- allergic.
The main differences between urethritis and cystitis are described here.
Preventive actions
It is necessary to identify symptoms of urethritis in men and begin treatment as early as possible. This is the only way to guarantee a complete cure. But it is much easier to prevent the disease.
To do this, you must adhere to the basic rules of prevention:
- Carefully monitor compliance with personal hygiene standards. Avoid wearing underwear made of synthetic materials. In such underwear, skin breathing becomes difficult, and it is possible to create a greenhouse effect, which promotes the rapid proliferation of pathogenic microflora. It is better to give preference to panties made from good quality cotton fabric.
- The use of other people's hygiene items, such as towels or bed linen, is strictly prohibited. Transmission of infection is possible through them.
- Avoid promiscuous sex. It is much more pleasant and safer to have one sexual partner. When in contact with potential carriers of infection, you can protect yourself by using a condom. But such protection does not give 100% results.
- Get medical examinations regularly. Urethritis in the early stages can occur in a latent form. It can only be detected through laboratory diagnostics. It is enough to be examined once every six months. Visit a urologist even if you have no prerequisites for developing sexually transmitted diseases.
- If an infection is detected, treatment should be timely and complete. Untreated diseases can cause serious complications.
- Protect yourself from hypothermia and overheating.
- Excessive physical activity, as well as injuries to the genital organs, can also increase the likelihood of rapid development of infection. Try to maintain a proper daily routine and avoid dangerous situations.
- Eat right, exercise and give up bad habits. Monitor the state of your immune system. Eat more fresh vegetables, berries and fruits. Drink more pure mineral water.
Following these recommendations will help reduce the likelihood of developing the disease. Remember that it is easier to prevent any disease than to treat it for a long time and painfully.
Now you know whether it is possible to cope with urethritis. This disease is fraught with negative health consequences. Therefore, it is extremely important to contact a specialist when you notice the first alarming symptoms. This will help maintain men's health and reproductive function.
Cravings with cystitis
Problems with urination in all patients indicate, first of all, a disease of the bladder. The most common is its damage by inflammatory processes. Cystitis in acute forms most often affects women, whose bodies enter pathogenic microorganisms through the urethra, lymph flow or bloodstream. The most common causative agent of the disease is Escherichia coli.
Inflammation of the walls and mucous membranes in the bladder appears due to the following factors:
More on the topic: Methods of treating tuberculosis of the genitourinary system
| № | Helpful information |
| 1 | infectious diseases of the urinary organs in the chronic stage |
| 2 | prolonged hypothermia |
| 3 | failure of the bladder to produce mucopolysaccharides |
| 4 | disruption of the body's hormonal levels |
| 5 | problems with nervous system function |
| 6 | when performing manipulations with the introduction of a catheter or cystoscope |
| 7 | poisoning of the body with substances containing harmful toxins and chemical components |
| 8 | circulation problems |
| 9 | frequent colds and viral diseases |
| 10 | patient's physical inactivity |
In young patients, cystitis in the acute stage occurs when the rules of hygiene of intimate areas are not observed. This disease causes pain when urinating in men, as well as pollakiuria. In some patients, the frequency reaches 25-30 times a day. Many people note constant discomfort, pain above the pubis, usually at the end of urine output. The sphincter often spasms, which causes the flow to stop and severe pain.