Gonorrhea in women - what is it?
Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted sexually transmitted disease, popularly known as gonorrhea. The causative agent of the disease is gonococcus (Neisseria gonorrhoeae). This bacterium was named in honor of the scientist who discovered it, Neisser. If we turn to the Greek language, the term “gonorrhea” can be translated as “discharge of semen.”
Gonorrhea is a common disease. About 62 million people are infected with it every year. In 2000, 170,000 cases were recorded in Russia.
Gonorrhea is divided into acute, subacute and chronic. In the first two cases, the disease lasts no more than 2 months. In the chronic form of infection, the infection period is more than 2 months. In this case, gonorrhea can have a hidden, asymptomatic course.
The disease tends to spread in an ascending manner. Once in a woman's genital tract, gonococci lead to inflammation of the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, and pelvic peritoneum.
Causes of gonorrhea infection
Gonorrhea is transmitted sexually. Moreover, the type of sex does not matter. Infection occurs through genital-oral, traditional and anal contact. The infection can be transmitted even during petting.
Scientists do not rule out the possibility of infection through domestic means, but such a situation rarely occurs. The household route of transmission occurs when hygiene rules are violated, when using other people's towels, when wearing other people's underwear, etc.
Newborn babies can be infected with gonorrhea while passing through the birth canal of a sick mother.
Once in the external environment, gonococci lose their high ability to live. They die when heated to +55 °C and when exposed to ultraviolet rays.
Gonococcus, which lives in the mucous membranes of humans, is very contagious. Infection occurs in 70% of cases, even after a single sexual intercourse. As a “monoinfection,” gonorrhea is rare. In 80% of cases, a person is additionally infected with chlamydia and/or trichomonas.
There are women who are at increased risk for contracting gonorrhea:
- Sexual intercourse with different men.
- Women under 25 years of age.
- Women who have had gonorrhea before.
- Women with other sexually transmitted infections.
- Pregnant women.
- Women who lead an antisocial lifestyle abuse alcohol and drugs.
Infection of a woman is possible even when the disease in a man is practically asymptomatic, becoming chronic, because the gonococcal infection continues to be released from the genitourinary system. Even many years after suffering from acute gonorrhea, a man can infect his partner.
Basic diagnostic methods
Doctors diagnose “Acute gonorrhea” after receiving test results. To verify the presence of the disease, a dermatovenerologist examines the patient and listens to his complaints. The clinical picture is usually clear immediately; it differs from other infections, but the doctor has no right to make a diagnosis without examination results.
Attention: specialists strongly recommend that patients with severe manifestations of gonorrhoea come to their next appointment with a sexual partner.
The main diagnostic methods that are used when gonorrhea is suspected include:
- sowing;
- smear;
- provocation techniques;
- PCR.
To identify gonococcus in the fresh phase of infection, you do not need to undergo a comprehensive complex examination. As a rule, a smear test is sufficient. Bacterioscopic examination is accurate and simple.
The doctor takes samples of the discharge and sends them to the laboratory. The causative agent of acute gonorrhea is clearly visible under a microscope. If all the symptoms of gonorrhea are present, but bacterioscopic examination gives a negative result, they resort to provocative diagnostic methods. With the help of drugs or medical instruments, the “excretion” of the parasite is stimulated. After this, a smear is taken again. The doctor determines which provocation is suitable. This diagnostic technique is:
- mechanical - bougienage of the urethra with a metal tube;
- biological - administration of a gonococcal vaccine or “Pyrogenal” intramuscularly;
- chemical - treatment of the urethra with various solutions;
- alimentary – the patient’s intentional intake of alcoholic beverages, spicy or salty foods.
Many doctors combine several types of provocation. To confirm or refute gonorrhea, a referral for culture is given. Bacteriological research is included in the list of mandatory ones. However, it is carried out before prescribing drugs. This is dictated by the fact that any antibacterial agent suppresses the vital processes of parasites.
When will the first symptoms of gonorrhea appear?
After the infection enters the body, it takes from 3 days to 3 weeks. During this period, there may be no symptoms of the disease. Although most often gonorrhea makes itself felt 5 days after the infection occurs. The specific timing depends on the intensity of the immune system.
If the immune system is weak, then the first signs of the disease may appear as early as 1-2 days after the infection has occurred. A recent illness, steroid therapy, treatment of cancer, etc. can trigger a decline in defenses.
Late manifestation of gonorrhea symptoms is associated with good functioning of the immune system, or with the use of antibiotics during this period. A person can use them to treat other diseases. The drugs will dull the symptoms of gonorrhea, so the disease will manifest itself later.
Timing of the onset of the first symptoms after infection
The incubation period of infection lasts from 3 – 7 days to 2 – 3 weeks. Accordingly, the first signs of the disease, as a rule, appear after 5 days. The shortening or lengthening of the incubation period depends on the body’s defenses.
If the immune system is very weakened, then the first symptoms of the disease will appear within 24-48 hours (recently suffered a severe infectious disease, treatment with steroids, chemotherapy, etc.).
Late manifestation of gonorrhea is associated either with good immunity, or with taking antibiotics for other infections after infection, or with an attempt at self-medication. This, and not only, is due to the fact that the first symptoms of gonorrhea are almost invisible.
Symptoms of gonorrhea in women
Gonorrhea causes disorders in those organs that are affected by gonococci. During sexual intercourse, they penetrate from the urethra into the woman’s genital tract, colonizing the cervix. Then the infection rises higher, affecting the uterus itself, ovaries and appendages. Sometimes the peritoneum is involved in the inflammation process. The rectum and urethra may be affected. This happens during anal intercourse. Oral contact leads to the development of gonococcal pharyngitis.
The first symptom of gonorrhea is discharge. The leucorrhoea changes its natural color to yellow, it becomes thick, and an unpleasant odor begins to emanate from it. Often women perceive a change in the nature of discharge as candidiasis or nonspecific colpitis, so they are in no hurry to consult a doctor. Self-medication leads to the fact that the signs of the disease are suppressed, and it becomes chronic.
Gonococci can cause symptoms such as:
- Gonorrheal cervicitis. A woman experiences itching, burning and tickling in the perineal area. When examining the cervix, the doctor notices redness and swelling. A yellow leucorrhoea is released from the cervical canal, which stretches like a ribbon.
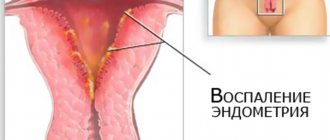
- Gonorrheal endometritis and salpingoophoritis. If gonorrhea is not stopped in time, it will lead to inflammation of the appendages and uterus. The woman begins to complain of abdominal pain, which is concentrated in the lower part. The pain can be sharp or nagging. At the same time, a change in the nature of the discharge occurs. They may contain pus and blood. Body temperature increases to 39 °C, general intoxication of the body increases, which is manifested by weakness, malaise, nausea and vomiting. Appetite disappears.
When the uterine mucosa is involved in the inflammatory process, a characteristic symptom of the disease is pain that occurs during intimacy.
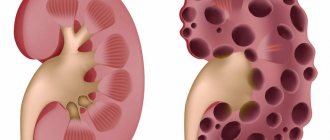
- Gonorrheal urethritis, cystitis and pyelonephritis. Gonorrheal urethritis develops when an infection affects the urethra. A woman complains of pain when emptying her bladder. The urethra itself becomes swollen and inflamed, and responds with pain to the touch. As the disease progresses, gonococci will invade new areas and lead to inflammation of the bladder and even the kidneys.
- Gonorrheal proctitis. This symptom is characterized by itching and burning in the anal area. The act of defecation becomes painful, and false urges to empty the bowel appear. In addition to feces, yellow mucus begins to be released from the anus, in which blood may be visible. The anus is red, and pus is visible in the folds of the anus.
- Gonorrheal pharyngitis. This disease may remain undetected for a long time, as it will masquerade as a sore throat. When swallowing food, a woman develops a sore throat, and the lymph nodes located under the jaw increase in size. Body temperature rises, but may remain at subfebrile levels. It often happens that gonococcal pharyngitis produces meager symptoms, which manifest themselves exclusively as a sore throat. During the examination, the doctor visualizes red tonsils, which will be covered with a yellow-gray coating.
How does urine change with gonorrhea? In acute gonorrhea, the infection is localized in the anterior urethra, so the first portion of urine will always be cloudy, and the second will be clear. If the infection spreads to the posterior urethra, then frequent urination and increasing pain at the end are added to the existing symptoms. The urine portion will be cloudy in both portions.
Symptoms of the chronic form
Symptoms of the chronic form of the disease are subtle. Sometimes they will be missing. The disease can be suspected by vaginal discharge, but it is most often insignificant. From time to time a woman experiences pain in the lower back and lower abdomen. However, it is difficult to associate such manifestations of gonorrhea with infection.
Chronic gonorrhea causes the menstrual cycle to be disrupted. This failure is caused by inflammation of the uterus. Bleeding can occur in the middle of the cycle; the periods themselves differ in duration and pain. During menstruation, symptoms of gonorrhea such as cervicitis, endometritis, urethritis may worsen.
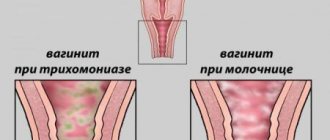
The vagina is not damaged by gonococci, since its mucous membrane is represented by squamous epithelium. While these pathogens prefer to reproduce in cylindrical cells. However, during pregnancy and in girls, symptoms of vulvovaginitis caused by gonococci may occur.
A woman does not find out about her infection immediately, but only after the incubation period, the duration of which usually ranges from 3-4 days to 2-3 weeks. It all depends on the properties of the pathogenic bacteria and the general condition of the patient’s body. Before the first symptoms appear, women most often feel quite healthy. 50-70% of patients do not experience any discomfort at all during the illness, and it is asymptomatic, due to which gonorrhea is diagnosed in a chronic form.
Chronic gonorrhea
Chronic gonorrhea occurs with an erased clinical picture, the symptoms are mild or unnoticeable at all. Among the symptoms characteristic of chronic gonorrhea, one can highlight only vaginal discharge, periodic lower back pain radiating to the leg and aching pain in the lower abdomen.
With chronic gonorrheal inflammation of the uterus, the menstrual cycle is disrupted. Intermenstrual bleeding occurs (see bleeding between periods), and the periods themselves become longer and more abundant. Menstruation can cause an exacerbation of infection (cervicitis, endometritis, adnexitis, urethritis).
Since gonococci prefer columnar epithelium, the vaginal mucosa, which is represented by squamous epithelium, is almost not affected. The only exceptions are girls and pregnant women with developed vulvovaginitis.
Complications of gonorrhea in women
Gonorrhea is a dangerous disease, as it can cause the following complications:
- Inflammation of the Bartholin glands, which are located near the entrance to the vagina.
- Female infertility, which will be caused by obstruction of the appendages, or a violation of the structure of the endometrium of the uterus.
- Decreased sexual desire.
- Complications of pregnancy and the period after childbirth. The likelihood of spontaneous early onset of labor, delayed fetal development, early breaking of water, and ectopic pregnancy increases. If a child is infected with gonococci, he may die in the first hours after birth, or even in the womb. The woman herself increases the likelihood of purulent complications and sepsis.
- The birth of a child with gonorrhea. The disease can cause conjunctivitis, otitis media, genital infections and even blood poisoning in the fetus.
- Spread of the pathogen throughout the body. The dermis, joints, kidneys, liver, heart, and brain may be affected.
- Conjunctivitis caused by gonococci. Infection occurs due to gross violation of hygiene rules.
Chronic gonorrhea in women often causes infertility, since inflammation leads to deformation of the fallopian tubes, the formation of adhesions, and infection (obliteration) of the tube lumen with connective tissue, thereby disrupting their patency. This pathology occurs in women in 8-20% of cases of chronic infection.
Practical experience: Tuboovarian complications in women with gonorrhea are not uncommon. During my night shift, a patient was admitted to the hospital with symptoms of body intoxication and complaints of severe abdominal pain. She also showed clear signs of pelvioperitonitis (irritation of the peritoneum). I have never seen such an advanced form of gonorrhea.
The patient was urgently sent for surgery, which lasted about 3 hours. All internal genital organs were surrounded by adhesions, and the appendages could not be visualized. The pus had already entered the peritoneal cavity, so it took some effort to remove it. The test results obtained after the operation revealed that the patient had gonorrhea. I have repeatedly operated on women with tubo-ovarian abscess, but I have never encountered such a severe course of the pathology.
To prevent all these undesirable consequences, women are recommended to undergo an examination at least once a year, and preferably more often, by a gynecologist in a district consultation, to use protective equipment during sexual intercourse, and to have a regular sexual partner.
Complications during pregnancy
Infection with gonorrhea is dangerous during pregnancy, since it develops very quickly due to good blood supply to the genitourinary organs and a decrease in the body's defenses. In addition, most often the disease is asymptomatic. If infection with gonococci occurs in the first trimester, this leads to spontaneous miscarriage due to the development of endometritis; at later stages, various complications and postpartum pathologies arise.
There is also a big risk:
- Early rupture of amniotic fluid,
- Premature birth,
- Infection of a child in utero or during its movement through the birth canal,
- Development of fetal pathology.
Intrauterine gonococcal infection is a huge problem for doctors and parents, since a newborn can develop sepsis, which poses a real threat to the baby’s life. Even if the child is not infected in utero, when passing through the birth canal, gonococci will certainly enter the ears and eyes of the newborn, which is why he will subsequently develop otitis media and conjunctivitis.
To avoid all of the above problems, experts recommend that women wishing to have a child undergo mandatory screening for the presence of gonococcal infection (gonorrhea) before pregnancy. And besides, during this period sex should always be protected.
Reasons for the development of the pathological process
Infection with Neisseria gonorrhoeae microorganisms most often occurs through unprotected sexual contact with a carrier of the infection. Cases of transmission of the disease through household means (using shared hygiene items, linen, etc.) are extremely rare.
The mucous membranes of the fallopian tubes, cervical canal, urethra, paraurethral and large vestibular glands are most susceptible to gonococcus damage. Depending on what mucous membranes the infected partner’s genitals came into contact with during sexual intercourse, manifestations of the disease in women may occur in the following areas:
- genital area;
- oral cavity (gonorrheal tonsillitis, pharyngitis, stomatitis);
- anal area (gonorrheal proctitis);
- complex development of characteristics (simultaneously in several or all of the listed areas).
Regardless of the location of the symptoms of gonorrhea in women, these manifestations do not differ in characteristic features, so the disease often goes unnoticed. This leads to the fact that the carrier of the infection does not seek medical help for a long time and thereby provokes the development of serious complications.
Diagnostics
To clarify the diagnosis, you will need to perform laboratory diagnostics:
- Collection and microscopic examination of a smear from the cervical canal, vagina, rectum, urethra. The material is stained with gram, methylene blue, or brilliant green.
- Collection of mucus from the urethra and cervix and its placement in nutrient media.
- REEF. In this case, the material is colored with fluorescent dyes.
- ELISA with urine testing.
- RSK. To implement this serological test, you will need to take blood from a vein. This highly sensitive diagnostic method allows you to detect the chronic form of infection.
- PCR. To conduct the study, you will need the patient's urine or smear.
You can do rapid testing for gonorrhea at home. Sometimes standard methods do not allow identifying the causative agent of the disease. This often occurs when the infection is chronic.
In this case, methods of provoking the disease are used:
- Chemical provocation with lubrication of the urethra with a silver solution (1-2% concentration). Applying a solution of 2-5% concentration to the cervical canal.
- Biological provocation. A gonococcal vaccine or Pyrogenal is injected into the patient's muscle.
- Provocation with drinks and food. The patient is asked to drink alcohol or eat spicy or salty foods.
- Thermal provocation. Diathermy is carried out for 3 days. Smears are taken 3 times, an hour after the procedure.
- Physiological provocation. A smear test is performed during menstrual bleeding.
To obtain a reliable result, several types of provocation are simultaneously combined. A smear is taken 3 times every 1-2-3 days.
Practical experience: This story reminded me of my favorite writer Bulgakov. A well-groomed and well-dressed woman came to my appointment, but with fear in her eyes. She said that while traveling for work, her husband had intimate relations with a woman of easy virtue. Moreover, sexual intercourse took place without using a condom. As a result, he contracted gonorrhea. The woman came to get tested and find out her diagnosis. The Gram smear gave a negative result. I performed a provocative smear. It also turned out to be negative. This made the patient very happy. At the same time, I was pleased to work with her, since most often I detect gonorrhea in women during an examination for another reason, or during the development of purulent complications. This diagnosis comes as an unpleasant surprise to them. The whole problem is that Russian women often self-medicate and put off visiting a gynecologist. If there were more responsible patients in the country, as in the case I described, then the prevalence of the disease could be reduced.
Diagnostic measures
The diagnosis of chronic gonorrhea is made after examination. The doctor collects anamnesis and conducts an examination. Physical examination involves palpation of the abdomen. The doctor also examines the genitals. In addition to the physical examination, bimanual diagnostics must be performed. During the examination, the doctor may find that the urethral mucosa is hyperemic. The patient must say what symptoms bother him and how often they occur. Bimanual examination can reveal inflammation in the uterus.
To confirm the suspected diagnosis, blood and urine are examined. The number of leukocytes in the blood is detected. A correctly selected diagnostic scheme allows you to quickly identify the disease. A bacterioscopic examination of a smear allows you to determine exactly where the gonococci are located. Additionally, PCR is prescribed. In general, diagnosis is not difficult.
https://youtu.be/QNaDhlldXZU
How to prevent infection after unprotected sexual intercourse?
After rape or after questionable intimacy without using a condom, preventive measures need to be taken. They must be an emergency.
The likelihood of infection is reduced if you follow these recommendations:
- Empty your bladder immediately after intimacy. It's good if you can do this several times. Pathogenic microorganisms will be removed from the urethra along with urine.
- The inner thighs and perineum should be washed with soap.
- Miramistin or Betadine must be injected into the urethra and vagina using a urological nozzle. The procedure must be performed no later than 2 hours after intimacy has occurred.
- The perineum and inner thigh should be treated with an antiseptic. This could be a solution of potassium permanganate, Chlorhexidine, Miramistin.
Miramistin reduces the risk of contracting sexually transmitted diseases by 10 times: gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, genital herpes.
No later than 2 days later, you need to visit a doctor, and after another 14 days you need to take a smear for testing using the PCR method.
Does the disease go away on its own, who prescribes treatment?
After the appearance of vivid symptoms of fresh gonorrhea, you should not hesitate. The sooner treatment for gonorrhea is prescribed, the faster the recovery and the lower the risk of relapse. The disease does not go away on its own because gonococci constantly multiply. It transforms from the initial form to chronic or latent. It will take a lot of money, effort, and time to treat long-standing gonorrhea. The immune system is powerless against parasites. Over time, the defenses adapt to aggressive foreign microorganisms and therefore react weakly to them. Chronic or latent gonorrhea does not cause inconvenience to a person, but contributes to the development of irreversible negative processes in the body. Complications are discussed at the end of the article.
If your health suddenly deteriorates and all the previously described symptoms of gonorrhea appear, you should immediately make an appointment with a dermatovenerologist. The doctor will conduct an examination, refer you for diagnostics and prescribe treatment. It is important to answer the doctor’s questions honestly and as completely as possible. After receiving the diagnostic results, the dermatovenerologist draws up a treatment program. It is unacceptable to skip medications and continue to lead a chaotic lifestyle. Most patients are forced to treat gonorrhea at home. However, anyone can insist on hospitalization. Treatment of gonorrhea in the hospital is carried out if complications arise or it is impossible to follow the doctor’s recommendations at home.
Treatment of gonorrhea in women
To cope with the infection, the woman will need to take antibiotics. Both sexual partners should receive treatment. During therapy, it is prohibited to drink alcohol or have intimate relations.
If gonorrhea has affected only the organs of the reproductive system, then the patient is prescribed a single administration of an antibacterial drug (oral administration is also possible):
- Ceftriaxone 0.25 g. This drug is the most commonly prescribed antibiotic for the treatment of gonorrhea. It is used for patients of any gender. Ceftriaxone is active against various types of gonococci.
- Gentamicin 2.0 g.
- Sumamed 2 g. As an option, it is possible to take such medications as: Azitrox, Z-factor, Hemomycin, Azicide, Ecomed.
- Cefixime 0.4 g.
- Ciprofloxacin 0.5 g.
If the disease has spread to the upper parts of the reproductive system, the treatment regimen is slightly modified:
- Ceftriaxone 1 g intramuscularly. The drug is administered once a day for a week. The patient is also prescribed Ciprofloxacin 500 mg intravenously 2 times a day for a week and Ofloxacin 0.4 g 2 times a day for a week. Treatment with Ceftriaxone can be supplemented with Doxycycline.
- In addition to the listed antibacterial drugs, other antimicrobial agents can be used, for example, Clindamycin, Hemomycin, Sumamed, Zitrolide, Tetracycline, Rifampicin, Bicillin, Josamycin, etc.
- To boost the immune system and to most successfully fight the disease, a woman is prescribed a gonococcal vaccine. This may be Pyrogenal, Methyluracil, Levamisole, Prodigiosan.
- Autohemotherapy allows you to activate a woman’s own immunity and more successfully resist infection.
It often happens that gonorrhea is accompanied by other sexually transmitted infections. Therefore, the treatment regimen can be supplemented with drugs such as: Doxycycline (treatment course is 10 days) and Metronidazole (treatment course is 5-7 days). The urethra is washed with a solution of silver nitrate, and the vagina is douched with antiseptic agents. For this purpose, a solution of potassium permanganate and protargol can be used. Miramistin and chamomile decoction are also used.
Increasingly, doctors are faced with resistant gonococci that do not respond to standard treatment regimens. Thus, leading UK health expert Sally Davis points out that in 2013, about 80% of patients with gonorrhea did not respond to tetracycline treatment. Therefore, experts insist on complex therapy of the disease using 2 antibiotics at once. Azithromycin should be taken orally, and Gentamicin should be administered as an injection. Alternatively, Azithromycin is taken orally with Gemifloxacin.
If the patient develops complications, then surgery is indicated. Laparotomy with removal of the uterine appendages and lavage of the abdominal cavity is performed for pelvioperitonitis with suppuration (provided that conservative therapy did not achieve the desired result). Acute bartholinitis requires opening and drainage.
Injections for gonorrhea
As a rule, a patient with chronic gonorrhea is treated in a hospital and prescribed:
- Ceftriaxone. Administer once: 250 mg intramuscularly, previously diluted with a solution of 1% lidocaine (2 ml). Used for the diagnosis of gonococcal infection of the pharynx or genitourinary tract. If gonorrhea is complicated, administer 1000 mg intravenously every 24 hours. Duration - 2 weeks.
- Spectinomycin. Intramuscular single injection of 2000 mg. In case of complications, the course lasts 2 weeks, during which injections of 2000 mg are given every 12 hours. Important: you can become infected with gonorrhea again if your sexual partner is not treated! While undergoing treatment, a person should follow the recommended diet, which prohibits the consumption of salty, spicy, smoked, as well as alcohol. The patient is also advised to refuse any sexual intercourse for the entire period of therapy. Chronic gonorrhea is considered cured if there are no symptoms for more than two months after the last injection.
Additional treatment
If a woman is diagnosed with chronic gonorrhea, then it can only be dealt with through the use of broad-spectrum antibiotics. When a patient develops gonococcal pharyngitis, or pathogens attack the intestines, Metronidazole is required (1 tablet 3 times). The course of therapy is 10 days. It is also possible to use Trichopolum vaginal tablets. Before insertion, the tablets are kept under running cool water and inserted into the vagina. Then you need to lie down for at least 30 minutes. Trichopolum is used once a day, 7-10 days.
If a woman suffers from thrush, then antifungal agents will be required. This may be Fluconazole, Miconazole, Pimafucin.
In addition, treatment can be supplemented with medications such as:
- Bifidobacteria, probiotics, prebiotics, acidophilus bacteria. Their use allows you to normalize the microflora of the intestines and vagina, eliminate dysbiosis, normalize the acidity of the environment, and increase immunity at the local level. These may be medications such as: Acipol, Normobact, Yogulact, Linex, Acylact, Bifiform, Bifidumbacterin.
- Local antiseptics. They allow you to speed up recovery and consolidate the therapeutic effect, as they effectively disinfect the vagina. To do this, you can use a solution of Furacilin or Hexicon.
- Vaginal suppositories and tablets with an antibacterial effect: Vagisept, Pimafucin, Terzhinan.
Depending on the characteristics of the disease, the treatment regimen may vary. Self-administration of medications is not allowed.
Prevention and treatment
The basis for effective treatment of gonorrhea in women is antibacterial medications, the prescription of which takes into account the resistance of the gonococcus strain identified in the body to modern antibiotics. During therapy, the patient is recommended to stop drinking alcohol and avoid sexual intercourse. The criterion for diagnosing complete cure is the absence of gonococci in a bacterioscopic smear of the flora of the urethra, rectum and cervical canal. To prevent the disease, it is important to systematically undergo a preventive examination by a gynecologist, maintain personal hygiene, and avoid accidental unprotected sexual intercourse.
https://youtu.be/bAMv5J_VrGY
A set of measures for chronic and extragenital gonorrhea
When gonorrhea lasts for a long time, it is more difficult to achieve positive treatment results. Dermatovenerologists are developing a comprehensive program, including:
- rectal suppositories to neutralize the inflammatory process;
- antibiotics;
- physiotherapy (laser and magnetic therapy);
- immunostimulants (Pyrogenal, gonovaccines).
For anal gonorrhea the following is prescribed:
- "Ciprofloxacin";
- "Benzylpenicillin";
- "Levomycetin";
- rectal suppositories with protargol.
For oropharyngeal gonorrhea, antibacterial drugs are prescribed for rinsing and irrigating the mouth and throat. Saline solutions help eliminate unpleasant symptoms. For eye gonorrhea, anti-inflammatory drops and benzylpenicillin are prescribed. A photo of one of the drugs is presented below.
Immunotherapy and local treatment for gonorrhea
The therapeutic program for patients with gonorrhea also includes injections, the effect of which is aimed at increasing the body's resistance. Immunomodulators are administered intramuscularly every other day. The course of immunotherapy includes 6 to 8 injections. The dose of the drug is increased gradually, observing the reactions of the patient’s body.
For local treatment of gonorrhea, bactericidal ointments and antiseptics are used. They slow down or completely stop the development of gonorrhea. The use of antiseptics and ointments is important when there is a high risk of infection of healthy people through household means. For example, children and parents who do not have sexually transmitted diseases live in the same house as the patient. Topical products prevent the spread of infection. An example of such a gonorrhea treatment program includes:
- washing the urethra with a 2% solution of protargol and 0.25% silver nitrate;
- warm baths or lotions with Furacilin and potassium permanganate for damaged skin;
- urethral lavage with Chlorhexidine (1:5,000).
Local treatment is always supplemented with antibiotics or antibacterial drugs.