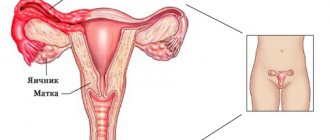
Ovarian dysfunction is a violation of the hormonal function of the reproductive system. This disorder often develops against the background of disorders in the endocrine system, as well as inflammation in the internal female genital organs. The greatest danger is that ovarian dysfunction can cause breast cancer and even infertility.
- Etiology
- Pathogenesis
- Symptoms
- Dysfunction at different periods
- Reproductive period
- Premenopausal period
- Teenage years
- Pregnancy and dysfunction
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- ethnoscience
Etiology
The cause of ovarian dysfunction may be pathologies that provoke menstrual irregularities. The main aspects include the following:
- inflammatory processes in the body;
- ailments of the uterus, ovaries;
- endocrine disorders;
- hormonal imbalance;
- medical abortion or spontaneous abortion;
- intrauterine device;
- external irritants - taking medications, incorrect contraception, sudden climate change, radiation.
The reasons that can cause this disorder are also metabolic disorders, obesity and diabetes.
Of all the above, the most dangerous can be called medical abortion during the first pregnancy. As statistics show, most often there is only one consequence - infertility.
Inflammatory processes can occur due to the following factors:
- lack of personal hygiene;
- hypothermia;
- using contraception that causes irritation.
Ovarian dysfunction can also develop due to prolonged nervous overstrain, exhaustion of the body and irrational distribution of time for work and rest.
https://youtu.be/cKH-ikflKIQ
Definition of disease
Ovarian dysfunction is a failure of their hormonal function. Most often, the disease can occur as a result of endocrine disorders and inflammatory processes. Any disturbance in the functioning of this organ can lead to instability of the entire body, especially the woman’s reproductive system. That’s why representatives of the fairer sex, when making a diagnosis, are immediately concerned with the question: “If I have ovarian dysfunction, is it possible to get pregnant with this pathology?” There can be no clear answer to this question. Agree that most often a person learns about the disease only when he visits a specialist about infertility. And here everything is in the hands of the specialist and the patient.
Symptoms
- menstrual irregularities;
- painful sensations in the lower abdomen, which often radiate to the lower back;
- uterine bleeding;
- severe premenstrual syndrome - apathy, irritability, characteristic pain in the lower abdomen;
- the onset of amenorrhea (absence of menstruation for more than 5 months).
Ovarian dysfunction
In addition, the general clinical picture may be supplemented by the following symptoms:
- yellow or green discharge;
- burning and discomfort during urination (as with cystitis);
- sharp, unpleasant odor from the vagina;
- foamy discharge.
Even if you have one or more of the above symptoms, you should immediately contact a gynecologist. Delay or self-medication can lead to the most tragic consequences, including infertility or cancer. It is also worth noting that the symptoms described above may indicate other gynecological diseases. Treatment with folk remedies is practically inappropriate here. The fact is that without a complete diagnosis it is impossible to detect the true cause of the disease.
Illness and pregnancy
These two phenomena are very closely connected. After all, a woman who dreams of becoming a mother in the future must take all measures to restore the reproductive function of her body. If this condition is delayed a little, it is fraught with endometriosis, uterine fibroids, mastopathy, breast cancer and infertility. Since ovarian dysfunction and pregnancy are strongly related, treatment of the pathology should be carried out under the supervision of an endocrinologist. The first step that needs to be taken is to restore the physiological ovulation cycle. For this purpose, hormonal drugs Clomiphene, Humegon or Pergonal are prescribed. You should start taking them from the fifth day of the menstrual cycle and drink them until the ninth day inclusive.
Monitoring is carried out using ultrasound. Thanks to it, the speed and degree of development of the follicle is recorded. When they reach the desired size, hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) is injected. This is what causes ovulation.
This therapy is carried out for three menstrual cycles in a row. Subsequently, the drug “Progesterone” is used, at the same time the basal temperature is measured and an ultrasound examination is performed.
There is no need to worry, modern medicine will stabilize menstruation and regulate the onset of ovulation. A woman will be able not only to become pregnant, but also to safely bear a child. But there is one condition: the expectant mother must be closely monitored from the very early stages of pregnancy.
Dysfunction at different ages
Conventionally, dysfunction can be divided into subtypes according to age groups:
- dysfunction in adolescents;
- pathology of the premenopausal period;
- dysfunction of the reproductive period.
Ovarian dysfunction during the reproductive period
In most clinical situations, ovarian dysfunction of the reproductive period is manifested by a significant increase in estrogen levels. As a result of this, the following diseases may occur:
- malignant breast formations;
- mastopathy;
- uterine tumor;
- endometriosis;
- infertility.
Also among the mandatory list of symptoms is the absence of ovulation and pain in the lower abdomen.
Dysfunction of the premenopausal period
Uterine bleeding must be added to the general list of symptoms. Such bleeding is caused by the fact that as a result of pathology, disturbances in the maturation of uterine follicles are formed. Also, with this pathology, an ovarian tumor can be diagnosed. Symptoms are pronounced.
Ovarian dysfunction in adolescence
A disorder of this nature at this age can be caused by the following reasons:
- disturbances in brain function;
- diseases of an infectious nature (most often meningitis);
- inflammatory processes;
- viral diseases.
Even if complications are not noticed during this age period, this does not mean that the disease will not remind itself in adult life.
Pregnancy and dysfunction
Many women are afraid that ovarian dysfunction and pregnancy are incompatible. And indeed it is. According to statistics, if a woman develops a disease during adolescence, then in the future it can become the main cause of infertility or miscarriage. Therefore, it is important to promptly notice the first signs of progression of the pathology in order to immediately contact a qualified doctor for help.
Causes of ovarian dysfunction
The ovaries are the main organ producing female sex hormones. They are part of a complex hormonal system consisting of:
- hypothalamus;
- pituitary gland;
- adrenal glands;
- directly to the ovaries.
We can talk about normal hormonal balance only if each link in this chain is fully functioning, since a failure in any of them will lead to imbalance of the entire system.
Ovarian dysfunction is considered a multifactorial disease because it is usually caused by a complex of causes. All factors can be divided into two groups:
- primary or congenital, which are formed in the child even before he is born;
- secondary or acquired, appearing due to various diseases or hormonal disorders.
Primary dysfunction is caused by:
- malformations of the embryo;
- disruption of a woman’s hormonal balance during pregnancy;
- various infectious diseases in women during pregnancy, especially in the second trimester;
- genetic disorders and hereditary pathologies, especially autoimmune ones.
Secondary dysfunction can be due to a wide range of causes.
Disturbances in the normal process of hormone production by the ovaries can be caused by various factors.
We recommend reading about acute adnexitis. You will learn about the causes and symptoms of the disease, diagnostic methods, treatment in the hospital and at home. And here is more information about the treatment of salpingoophoritis with antibiotics.
Problems in the hypothalamic-pituitary link
Pathological processes in the ovaries can be triggered by insufficient or excessive amounts of releasing factors in the body, which are produced by the hypothalamus. Disturbances may also affect the functioning of the pituitary gland, which produces certain hormones necessary for the normal performance of its functions by the female body.
The cause of hormonal imbalance can be neoplasms in the pituitary gland of various etiologies, as well as various mental disorders.
Diseases of the endocrine system
Pathologies in this group that can cause dysfunction include:
- diabetes;
- thyrotoxicosis and other disorders of the thyroid gland;
- pathological processes in the adrenal cortex;
- obesity caused by hormonal imbalances.
The cause of all these diseases is the excessive or insufficient production of various hormones.
Ovarian dysfunction
Dysfunction can be caused by the following pathological processes related to this group of problems:
- infectious damage to the ovaries, appendages and uterus themselves, caused by pathogenic microorganisms;
- neoplasms in the organs of the reproductive system;
- endometriosis of the genitourinary system of various etiologies;
- scleropolycystic disease and premature ovarian failure syndrome.
Systemic diseases
Organ dysfunction can be caused by serious problems in other systems of the female body:
- urolithiasis, pyelonephritis, nephropotosis, renal failure and other kidney diseases;
- severe cardiovascular failure;
- leukemia, anemia and other blood diseases;
- systemic disorders of the hepatobiliary system.
External factors
Problems with the production of hormones by the ovaries can be caused not only by internal diseases, but also by reasons not related to disturbances in the functioning of body systems:
- Constant excessive physical activity, nervous strain, climate change, constant stress, excessively long exposure to the sun or solarium, taking certain medications, anorexia.
- Improper lifestyle, exposure to radiation, frequent vaginal douching without indications or doctor’s prescriptions.
- Incorrect use of intrauterine contraceptives, untimely replacement of the IUD, previous surgical interventions in the ovaries or other organs of the reproductive system, injuries in the genital area, abortions, miscarriages, premature birth.
Frequent abortions are especially dangerous for the normal functioning of organs, since hormonal changes in the body occur during pregnancy, and its sudden interruption can cause an imbalance.
Risk factors for the occurrence of dysfunction include hypothermia, frequent colds and viral diseases, as well as sexually transmitted infections.
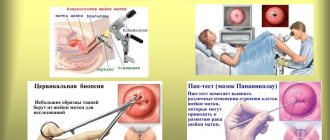
Diagnostics
Despite the fact that the symptoms of ovarian dysfunction are well expressed, the doctor will be able to make a final diagnosis only after a correct diagnosis. The following events are required:
- analysis for sexually transmitted diseases;
- taking a smear to diagnose vaginal microflora disorders;
- Ultrasound – diagnostics;
- general urine analysis;
- hysteroscopy;
- therapeutic and diagnostic curettage;
- CT scan of the brain.
Only after collecting all the tests is a course of treatment prescribed. Also, during a personal examination, you should pay special attention to the patient’s menstrual calendar and exclude surgical pathology - ectopic pregnancy and tumor. After a gynecological examination, a further diagnostic program is prescribed.
Diagnosis of the disease
In order to make a diagnosis of “ovarian dysfunction”, the doctor will need to carry out a set of procedures that are aimed at identifying the causes of the pathology:
- Ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland, adrenal glands, pelvic organs.
- The concentration of sex hormones in urine and blood is determined.
- Bacterial culture and microscopy of vaginal secretion for flora. These procedures help determine the presence of infection.
- Blood test for the presence of thyroid and adrenal hormones.
- X-ray of the skull, MRI of the brain to exclude pituitary gland disorders.
- Curettage of the cervical canal for further examination.
- Electroencephalography of the brain to study for the presence of pathological changes in it.
It cannot be said that every woman with ovarian dysfunction will have to undergo all these examinations. The approach to each patient must be individual, and only the attending physician should prescribe the necessary procedures. You need to remember one thing: the sooner you start treatment, the easier it will be to cope with it.
Those women who have a chronic pathology should visit a gynecologist two to four times a year, even if they feel great.
Treatment
Under no circumstances should you self-medicate. In order to prescribe the correct course of treatment, you must first find out what caused the progression of this pathology. Only a gynecologist can do this correctly by examining the patient and thoroughly studying the medical history.
The main course of treatment is aimed at the following:
- eliminating the cause of the pathology;
- stopping bleeding (if any);
- restoration of normal hormonal process.
If the disease is diagnosed at an early stage, outpatient treatment is usually carried out. If other signs are present, the patient must be hospitalized.
If it is not possible to stop the bleeding with medication, then curettage of the uterine cavity mucosa is performed. Based on the results of this process, further therapy is prescribed.
Curettage of the cervix
The further course of treatment depends on what caused the development of the disorder. Typically, your doctor may prescribe the following:
- hormonal drugs;
- vitamin complexes;
- homeopathic medicines.
It is especially worth paying attention to your lifestyle. Excessive alcohol consumption, promiscuity and smoking can also cause ovarian dysfunction. Therefore, the drug course of treatment can be supplemented with the following methods:
- physiotherapy;
- reflexology;
- psychotherapeutic assistance.
It is worth noting that girls or women who have suffered from this disease are contraindicated in the future from installing the IUD as a method of contraception.
Drug treatment: drugs
Treatment for premature ovarian failure (dysfunction) usually focuses on problems associated with estrogen deficiency.
Estrogen therapy. The therapy may help prevent osteoporosis and relieve hot flashes and other symptoms of estrogen deficiency.
Your doctor will usually prescribe estrogen with the hormone progesterone. Supplementing with progesterone protects the uterine lining (endometrium) from precancerous changes caused by estrogen.
The combination of hormones can induce menstruation, but this does not restore ovarian function. Depending on your health, hormone therapy can be continued until approximately age 50, before natural menopause.
In older women, long-term estrogen therapy is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease and breast cancer. However, in young women with premature ovarian failure, the benefits of hormone therapy outweigh the potential risks.
Calcium and vitamin D supplements. Supplements are important for the prevention of osteoporosis, especially if there is a lack of essential elements in the diet or there is a lack of sunny days per year. Your doctor may perform bone density testing before starting supplementation to have a baseline bone density before starting therapy.
For women ages 19 to 50, the recommendation is 1,000 milligrams of calcium per day through food or supplements, increasing to 1,200 mg per day for women age 51 and older.
The starting point for vitamin D intake for adults is 600 to 800 international units (IU) per day, through food or supplements. If your blood levels of vitamin D are low, your doctor may prescribe higher doses.
Treatment with folk remedies
Now we will try to figure out how to treat ovarian dysfunction with folk remedies.
There are two types of therapy: douching and taking the medicine orally. With the help of traditional medicine, you can relieve the symptoms of the disease. Of course, the effectiveness of such drugs increases many times if they are used in combination with medications.
For oral administration the following are used: tincture of wintergreen, licorice, coltsfoot decoction, sweet clover herb, marshmallow root, thyme, nettle leaves, St. John's wort flowers, yarrow.
The following are great for douching: an infusion of immortelle leaves and flowers, black elderberry flowers, and oak bark.
After treatment
After treatment is completed, the woman will have to adhere to some rules:
— It is forbidden to install an intrauterine device for some time.
— In order to normalize the functioning of ovarian hormones, you will have to take progesterone medications. They are prescribed from the sixteenth to the twenty-sixth day of the cycle. Seven days after the course of treatment, menstruation should begin. Its normalization occurs with the help of hormonal combined contraceptives.
In addition, a woman should continue to lead an active lifestyle, eat right and worry less. And, of course, visit your doctor.