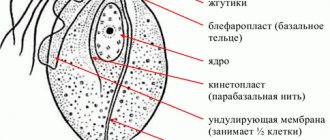
Few people know that a person has to share his body with many microorganisms. One of the representatives of the internal flora of the digestive tract is a bacterium called Helicobacter pylori. Eradication, what is it? Eradication is a term that refers to the complete destruction of all forms of H. Pylori.
Modern medicine believes that this microorganism provokes inflammatory processes in the stomach and duodenum. To prevent gastritis and the formation of ulcers, it is necessary to carry out eradication - specific therapy aimed at eliminating Helicobacter pylori. This treatment method has many features that you need to know about for the success of therapy. Even if you follow all the rules and recommendations, it is not always possible to completely eliminate bacteria from the body. Leading medical centers have an eradication rate of 80%.
Indications for use
Eradication therapy is aimed at destroying viruses or bacteria in the body. Since a huge problem in medicine is damage to the gastrointestinal tract by Helicobacter Pylori bacteria, a technique has been developed to counteract these microorganisms. In such a situation, indications for eradication may include:
- gastroesophageal reflux (reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus);
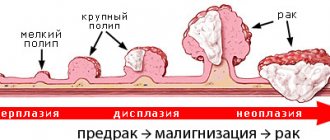
- precancerous conditions;
- consequences of surgery to remove a malignant tumor;
- peptic ulcer of the stomach, duodenum;
- MALT lymphoma of the stomach (tumor of lymphoid tissues).
Helicobacter Pylori eradication is prescribed to patients who are planning long-term treatment with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Indications for using the technique are often:
- chronic atrophic gastritis;
- gastropathy (inflammatory diseases of the mucous membranes and blood vessels of the stomach from the effects of drugs);
- autoimmune thrombocytopenia (rejection by the immune system of its own platelets);
- Iron-deficiency anemia;
- prevention for people who have relatives with a history of stomach cancer.
Last changes
At the last meeting, leading scientists in the field made a number of changes to the recommendations listed above. This is the fundamental position from which all specialists start.
- Helicobacter pylori, regardless of symptoms and manifestations, causes an infectious disease.
- The disease directly affects the appearance of dyspepsia (deviations in the gastrointestinal tract).
- Treatment along one of the lines can be used only after using all non-invasive diagnostic methods recommended by the scientific community.
- Invasive methods (for example, endoscopy) are used only if the patient's country or region of residence has a below-average prevalence of the disease.
- Eradication of Helicobacter pylori consistently reduces the likelihood of complications.
- The most preferred method for diagnosing the disease is the urease breath test, but it should not be used for patients taking antacids (medicines that prevent heartburn).
- The intensity and frequency of treatment courses are calculated based on statistical data on the spread of the disease in the patient’s region of residence.
- The combination of proton pump inhibitors and clarithromycin can only be used in certain regions. Only if the tolerance level is more than 15%, it is worth considering other treatment methods and replacing the drug with an analogue.
- As a replacement for clarithromycin, it is worth using multicomponent treatment using bismuth.
- If there is no effect after using bismuth, it is necessary to use drugs of the fluoroquinolone group.
- If there is no result from using the two methods described above, it is recommended to conduct a study to determine the patient’s response to antibiotics.
- For patients who are at risk and are prone to stomach cancer, it is better to undergo screening diagnostics.
There is also an expanded version of the regimens used for eradication therapy in Russia. It takes into account the characteristics of the country's residents' resistance to the disease and offers advanced treatment methods described in the recommendations of the Maachtricht Meeting of Gastroenterologists.
Purpose of the procedure
Eradication of Helicobacter pylori is a special method of treatment. It is aimed at creating a favorable atmosphere for the patient to carry out procedures. The technique has several goals:
- reduce the duration of treatment;
- create comfortable conditions for compliance with the regime;
- limit the number of types of drugs used - combination drugs are used;
- eliminate the need to follow a strict diet;
- prevent the development of side effects;
- speed up the healing of ulcers.
Ecadification is popular among doctors and patients due to its cost-effectiveness - inexpensive drugs are used, and effectiveness - the condition improves from the first days of therapy. The procedures pursue the following goals:
- reduce the number of medications taken per day - medications with a prolonged action and increased half-life are prescribed;
- overcome bacterial resistance to antibiotics;
- provide alternative eradication regimens in the presence of allergies, contraindications, or in the absence of treatment results;
- reduce the toxic effects of drugs.
Possible side effects
Therapy involves taking several powerful drugs at once. Against this background, side effects are possible.
Sometimes patients experience the following symptoms:
- darkening of stool;
- dizziness;
- stomach ache;
- development of diarrhea;
- flatulence;
- allergic reaction;
- the appearance of a metallic taste in the mouth;
- gagging;
- a sharp decrease in body weight;
- headache;
- rise in temperature.
Requirements for eradication recommended by WHO
Doctors around the world dealing with infections caused by Helicobacter pylori have reached international agreements. They include the creation of standards and schemes that increase the effectiveness of diagnostic and therapeutic techniques, called Maastricht. The information is regularly updated and currently contains the following requirements for eradication:
- positive treatment results in 80% of patients;
- duration of therapy is no more than 14 days;
- use of drugs with low toxicity.
The Maastricht recommendations contain the following requirements for medical procedures:
- interchangeability of medicines;
- reducing the frequency of taking medications;
- slight resistance (resistance) of Helicobacter pylori strains to drugs;
- ease of use of treatment regimens;
- the occurrence of side effects is no more than 15% of patients; their effect should not interfere with the implementation of treatment procedures.
Doctors came to the conclusion that the proposed methods reduce the number of complications that arise. Two lines of eradication are recommended, which require compliance with the following sequence:
- The treatment process begins with first-line regimens.
- If there are no positive results, they move on to the second.
- Treatment monitoring is carried out one month after completing the course of all measures.
Special instructions for taking a gastroprotector
De-Nol is contraindicated for use by children aged 0-3 years, pregnant women, those with hypersensitivity to the active substance, the presence of insufficiency and other severe kidney diseases. Lactating women during treatment for Helicobacter pylori and for 2 months after therapy need to feed the child artificially. Bismuthate is not compatible with ethanol, so you should not drink alcohol while using them.
For Helicobacter, it is better to take De-Nol to destroy H. pylori together with Metronidazole and Amoxicillin. In case of intolerance, tetracycline is used, but the gastroprotector substance reduces the absorption of this antibiotic. To prevent dysbiosis in the gastrointestinal tract, you need to additionally take pro- and prebiotics.
Some products or medications affect the action of De-Nol and reduce the destruction of Helicobacter infection. Therefore, you should not take the following for half an hour before and after taking the pill:
- milk;
- milk soups, porridges, cocktails and other dishes with its addition;
- fresh fruits or their juices;
- anacidic drugs;
- solid food.
You can continuously treat Helicobacter with De-Nol for no longer than eight weeks, and after you finish taking it, you cannot use other products containing bismuth for two months. This is necessary so that the body is cleared of bismutate tripotassium dicitrate, and subsequently there is no overdose.
Drugs
Several groups of medications are used for eradication. They are included in treatment plans. To counteract the bacterium Helicobacter Pylori, the use of antibiotics is mandatory. Doctors prescribe medications taking into account contraindications and side effects. The following drugs from the groups of antibacterial agents differ in their effectiveness:
- penicillins – Amoxiclav, Amoxicillin;
- macrolides – Azithromycin, Clarithromycin;
- tetracyclines – Tetracycline;
- chlorofluorinols – Levofloxacin;
- ansamycins – Rifaximin.
The second group of drugs used in the eradication of Hilobacter pylori includes anti-infective drugs. They are highly toxic; doctors must take into account contraindications for use. The eradication regimen includes the following medications:
- Metronidazole;
- Nifuratel;
- Tinidazole;
- McMiror.
Bismuth-containing agents show high effectiveness in counteracting the bacterium Helicobacter Pylori. These drugs are resistant to the acidic environment of the stomach, form a protective film on the mucous membrane, and accelerate the scarring of ulcerations. The drugs used in eradication have a minimum of side effects and contraindications. This group includes the following tools:
- Bismuth subsalicylate;
- De-Nol;
- Bismuth subnitrate.
The eradication treatment regimen for peptic ulcers includes proton pump inhibitors (PPIs). These drugs reduce the aggressive effect of the acidic environment on the mucous membranes. Medicines create destructive conditions for the existence of microorganisms. PPIs have an antacid effect - they neutralize hydrochloric acid. The products destroy bacteria that comfortably exist in it. The group includes the following drugs:
- Rabeprazole;
- Omeprazole (Omez);
- Pantoprazole (Nolpaza);
- Esomeprazole;
- Lansoprazole.
Articles on the topic
- Omnik - instructions and mechanism of action, contraindications, side effects, dosage regimen and analogues
- Anticholinergics - what they are and when they are prescribed, classification based on the principle of effect, contraindications
- What is parenteral administration - description and types of method
Helicobacter pylori eradication schemes
Treatment methods for gastric and duodenal ulcers are constantly being improved. This is due to research conducted by doctors around the world. The first Helicobacter pylori eradication schemes included two methods:
- Monotherapy. This technique involves the use of antibiotics or bismuth-containing agents. Due to its low efficiency, it is rarely used.
- Two-component eradication scheme. It is distinguished by the use of both groups of drugs from the first method, and has an effectiveness of 60%.
Research by medical scientists led to the creation of new eradication schemes, which were proposed at the Maastricht conferences. Modern methods include:
- Three-component therapy, characterized by an effectiveness of 90%. Anti-infective agents are added to the dual treatment regimen.
- Four-component eradication, which contains proton pump inhibitors in addition to the previous option. The method achieves positive results in 95% of cases.
First line
The Helicobacter pylori eradication scheme can be used in several versions. Treatment begins from the first line. Doctors select medications depending on the patient’s condition; the duration of treatment can be increased to two weeks. The standard three-component scheme includes the use of the following means:
| A drug | Dosage, mg | Number of appointments per day | Duration of treatment, days |
| IPN at the doctor’s choice: Omeprazole, Rabeprazole | 40 | 2 | 7 |
| Clarithromycin | 500 | 2 | |
| Amoxicillin | 4 |
If necessary, doctors prescribe a four-component eradication regimen. It involves the use of such medications:
| A drug | Dosage, mg | Number of appointments per day | Duration of treatment, days |
| Bismuth tripotassium dicitrate | 120 | 4 | 10-14 |
| Clarithromycin | 500 | 2 | |
| Amoxicillin | 4 | ||
| Esomeprazole or Omeprazole | 40 | 2 |
If, as a result of diagnostic tests, atrophy of the mucous membranes is revealed in a patient, an eradication technique is used without the use of proton pump inhibitors. The regimen includes the following medications:
| A drug | Dosage, mg | Number of appointments per day | Duration of treatment, days |
| Bismuth tripotassium dicitrate | 120 | 4 | 10-14 |
| Clarithromycin | 500 | 2 | |
| Amoxicillin | 4 |
If treatment of stomach ulcers caused by the bacterium Helicobacter pylori is required in elderly patients, a truncated eradication regimen is used. It includes the use of the following medications:
| A drug | Dosage, mg | Number of appointments per day | Duration of treatment, days |
| Bismuth tripotassium dicitrate | 120 | 4 | 14 |
| Amoxicillin | 500 | 4 | |
| Lensoprazole or Pantoprazole | 40 | 2 |
Second line
If the eradication regimens used do not produce results, the following treatment options are prescribed. The second line involves the use of three schemes, all of them four-component. The first regimen includes the following medications:
| A drug | Dosage, mg | Number of appointments per day | Duration of treatment, days |
| Bismuth tripotassium dicitrate | 120 | 4 | 14 |
| Tetracycline | 500 | 4 | |
| Omeprazole or Pantoprazole | 40 | 2 | |
| Metronidazole | 500 | 3 |
Before prescribing drugs, doctors conduct tests to identify the pathogen and its sensitivity to antibiotics. The second eradication scheme involves a combination of the following:
| A drug | Dosage, mg | Number of appointments per day | Duration of treatment, days |
| Bismuth subsalicylate | 120 | 4 | 14 |
| Amoxicillin | 500 | 4 | |
| PPI – Omeprazole or Esomeprazole | 40 | 2 | |
| Nufantel | 400 | 2 |
In all eradication options, doctors additionally prescribe vitamin complexes. Scheme No. 3 is a four-component therapy, which includes the following medications:
| A drug | Dosage, mg | Number of appointments per day | Duration of treatment, days |
| Bismuth tripotassium dicitrate | 120 | 4 | 14 |
| Tetracycline | 500 | 4 | |
| Physician-selected proton pump indicators | 40 | 2 | |
| Rifaximin | 500 | 3 |
Treatment regimens for gastritis with low and high acidity
One of the most common causes of gastritis is infection by Helicobacter pylori. The bacterium penetrates the mucous membranes of the digestive tract, and its waste products become provoking factors for the formation of ulcers and erosions. Gastritis can be accompanied by increased or decreased acidity of gastric juice. Treatment regimens for different types of diseases differ.
With increased stomach acidity
For erosive gastritis with increased acidity of gastric juice, cytoprotective agents are used. Drugs in this group increase the resistance of the gastric mucosa to negative factors and waste products of bacteria. The treatment regimen may also include bismuth nitrate, magnesium oxide and calcium carbonate (in the form of suspensions). The disease requires the mandatory use of antacids, enveloping and adsorbent agents.
For low stomach acidity
Reduced acidity of gastric juice implies the use of medications that increase the production of hydrochloric acid. Liontar or Plantaglucid are used as an addition to the main line of therapy. The first preparation contains citric and succinic acid, the second - plantain juice. Substances stimulate secretory function and restore the functioning of the glands.
Nutrition during treatment
During eradication, no special diet is required. The exception is bleeding in the stomach or perforation of an ulcer. In other cases, nutritionists recommend including in the diet:
- homemade crackers;
- low-fat soups;
- river fish;
- pasta;
- lean meat;
- milk and water based porridges;
- vegetable oil;
- vegetables - boiled or baked - potatoes, carrots, zucchini, beets;
- berry compotes;
- jelly;
- tea.
During the eradication period, it is advisable to use warm dishes - hot or cold are irritating to the stomach. The following are prohibited:
- spicy, fatty sauces;
- alcohol;
- fried foods;
- fatty broths;
- smoked meats;
- canned food;
- marinades;
- fatty fish, meat;
- spicy seasonings;
- raw fruits and vegetables (during an exacerbation);
- mushrooms;
- pepper;
- sweets;
- cakes;
- garlic;
- onion;
- strong coffee, tea.
Folk remedies
Home treatment cannot replace eradication prescribed by a doctor. Folk remedies will be an addition to treatment regimens. It is important to coordinate them with your doctor. To speed up the healing of ulcers, take a decoction of flaxseed, which has an enveloping effect on the gastric mucosa. To prepare it you will need:
- Take a teaspoon of seeds.
- Pour a glass of boiling water over them.
- Leave covered for 2 hours.
- Shake to separate the seed from the mucus.
- Strain.
- Drink during the day in 4 doses.
Traditional healers recommend using raw chicken eggs for peptic ulcers once a day, before breakfast. The course of treatment is two weeks. A decoction of St. John's wort and yarrow has an antimicrobial effect. To prepare it you need:
- Take 100 grams of each herb.
- Add a liter of boiling water.
- Leave for 30 minutes.
- Strain.
- Take 100 ml before meals three times a day.
- The course of therapy is a month.
When treating peptic ulcers caused by Helicobacter pylori bacteria, it is recommended to use propolis. Treatment must be agreed with your doctor. Propolis is a natural antibacterial agent that regulates stomach acidity. Traditional healers recommend this recipe:
- Freeze 50 g of propolis to make it easier to chop.
- Take 0.5 liters of milk.
- Add crushed propolis.
- Place in a water bath for 30 minutes.
- Add a spoonful of honey.
- Drink a glass warm at night.
- Can be stored in the refrigerator for 48 hours.
- The duration of treatment is from two weeks.
Normalization of microflora after eradication
The use of antibiotics leads to disruption of the intestinal microflora. To restore the condition after the eradication procedure, drugs of two groups are used. One of them is probiotics, which contain live microorganisms - bifidobacteria, lactobacilli. Doctors prescribe the following drugs:
- Enterol;
- Linux;
- Acipol;
- Biosporin;
- Bifiform;
- Lactobacterin;
- Bificol;
- Lactoferon;
- Sporobacterin;
- Floradophilus;
- Vitanar;
- Hyalact;
- Colibacterin;
- Bifidumbacterin.
The second group is prebiotics, which create conditions for the proliferation of beneficial microorganisms. The drugs stop the development of pathogenic bacteria and restore the biological environment of the intestine. After eradication, patients take the following medications:
- Portalak;
- Hilak-Forte;
- Duphalac.