A cyst is a benign neoplasm in the ovarian cortex, formed due to a disruption in the process of release of the corpus luteum of the follicle. Pregnancy after removal of an ovarian cyst is a topic that interests many women who have undergone laparoscopy or full abdominal surgery. Any functional disturbances in the functioning of the genital organs and surgical interventions in the pelvis bother women, because... theoretically reduce the chance of conception. But are ovarian cysts as dangerous for reproductive function as many women who want to have children think? This is interesting to many women: pregnant women, those who have given birth, and those who are just planning motherhood.
Could a cyst be a sign of more serious problems?
According to statistics, cysts most often go away on their own during one or several menstrual cycles, after which normal ovarian function is resumed - the maturation of follicles and the release of eggs. In this case, it is easy to understand whether it is possible to get pregnant.
But there are a number of other negative factors:
- hormonal imbalances;
- surgical interventions;
- injuries.
They negatively affect female reproductive function in general, and the functioning of the ovaries in particular. Hormonal imbalance is one of the key factors that reduces the efficiency of the ovaries and complicates a woman’s reproductive function. When the body's hormone balance changes towards androgens (testosterone), ovarian function suffers.
One of the dangerous complications that reduces the ability to conceive is polycystic ovary syndrome. In this condition, many small cysts form on the surface of the ovaries, containing eggs. When the balance of sex hormones changes towards androgens, the process of egg release slows down or stops altogether.
How does pregnancy proceed after laparoscopy?
Pregnancy after laparoscopy does not have any special differences. It proceeds the same as any other pregnancy. Problems may arise due to a history of gynecological diseases. The likelihood of developing the following complications increases:
- Termination of pregnancy in the initial stages;
- Abnormal presentation of the fetus (as a result of removal of myomatous nodes);
- Placental insufficiency;
- Polyhydramnios.
Polyhydramnios - description
Women who have undergone laparoscopy due to infertility are under special control when pregnancy occurs. In order to detect deviations in time, you should regularly attend preventive examinations, take the necessary tests in a timely manner and monitor your well-being. Polycystic ovary syndrome requires hormonal support in the first trimester.
Does surgery affect fertility?
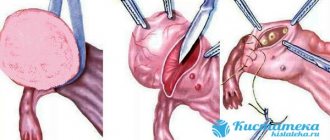
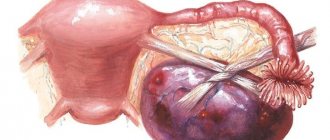
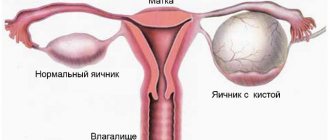
An ovarian cyst is formed when, for some reason, a mature follicle does not rupture, releasing an egg into the fallopian tube towards the uterus, but remains in the ovary. Under the influence of hormones, the follicle begins to fill with fluid, forming a sac with a diameter of several millimeters to several centimeters. This happens under the influence of female and male sex hormones, stress, trauma and other factors.
Is it possible to get pregnant in this case? A single cyst does not always mean a serious problem. If, according to the gynecologist's indications, the cyst was removed, then the ability to conceive and bear a child is preserved. Pregnancy after an ovarian cyst is quite possible if a woman follows simple rules after surgery.
Ovarian cyst: is it possible to plan a baby?
Ovarian cyst is a disease that occurs in many women of childbearing age. Most often, cysts appear in patients with menstrual irregularities. The cyst can be functional or organic. Functional cysts disappear on their own after several cycles or are eliminated with hormone therapy.
It is not dangerous to plan a child with such a cyst. Even if treatment has been carried out, you will not have to wait several months. If the cyst does not disappear within about two months, laparoscopy is required. Most types of cysts cannot be gotten rid of without surgery. It is imperative to remove the cyst before planning a pregnancy. The least dangerous cysts, which most often go away without treatment, include corpus luteum cysts.
Important! If a cyst is found in the ovaries, it is important to understand its type, size and effect on the body of a woman thinking about pregnancy. The most dangerous for those planning a pregnancy is an endometrioid cyst.
Often, after unsuccessful removal of an endometrioid cyst, women experience infertility. This formation in the ovaries has a negative impact on the reproductive system, which leads to an irregular menstrual cycle. The appearance of an endometrioid cyst is caused by an inflammatory process, so it often affects nearby internal organs.
Over time, the endometrium grows into the ovarian tissue, which leads to scarring and disturbances in the process of egg production. Surgical removal of endometrioid ovarian cysts is the only treatment method. If laparoscopy is used for elimination, patients have an increased chance of becoming pregnant.
After the operation, a rehabilitation period is required, including hormone therapy. There is no need to rush into conceiving a child, even with a removed endometrioid cyst, because this formation may appear again. Pregnancy, which is considered the best preventative method for this pathology, allows you to prevent relapse. Pregnancy after an ovarian cyst is possible, but a consultation with a gynecologist is first necessary.
How to avoid complications?
The main thing after surgery in the pelvic cavity is to avoid the formation of adhesions. To restore blood circulation in the reproductive organs, the woman should begin to move the next day after surgery. To avoid inflammation after surgery, antibiotics are prescribed for 5-7 days.
In gynecological practice, before an operation to remove a cyst, the gynecologist prescribes a hormonal examination to understand whether a woman can become pregnant at all. If a specialist discovers that there is an imbalance of gonadotropins (sex hormones), then after removing the cyst, the doctor prescribes hormonal medications to restore normal function of the endocrine system. Usually, complete elimination of all unfavorable factors affecting conception occurs within 2-3 months.
Do complications after surgery lead to infertility?
If the situation develops favorably in the postoperative period (no inflammation, adhesions, hormonal imbalances), the woman manages to become pregnant after the body has fully recovered.
If complications arise during surgery or in the postoperative period, the function of the ovary on which the cyst was located may decrease slightly. For example, adhesions in the fallopian tube can impede the movement of the egg to the uterine cavity for fertilization. But even in this case, the woman’s reproductive function is preserved. If the cyst affects only one of the ovaries, and the second is healthy, then the answer to the question of whether it is possible to get pregnant is positive. As a paired organ, the ovaries work alternately: in one menstrual cycle, the follicle matures in the right, in the second - in the left. There are cycles without ovulation at all, when the ovaries “rest”.
Is it possible to perform laparoscopy during pregnancy?
During pregnancy, laparoscopic surgery is performed only if there are compelling reasons. Possible risks are assessed in advance. Indications for laparoscopy are as follows:
- Necrosis of myomatous node;
- Cystic formations;
- Inflammation of the appendix;
- Torsion of the appendage or cyst;
- Malignant tumors.
Necrosis of myomatous node - description
Laparoscopy is recommended to be done in the second trimester of pregnancy. It is during this period that the likelihood of developing complications decreases. All the baby’s organs are already formed, and the risk of premature birth is not so high.
If you cannot get pregnant after removing the cyst
Theoretically, removal of the cyst should increase the chances of conception, because. after removal of the foreign body, the ovary receives an impulse that stimulates the release of the egg. If, after the procedure, problems with conception persist, although no complications arose after the operation, then another reason for the decrease in fertility can be assumed.
The most common obstacles to getting pregnant are:
- “lazy” ovary syndrome, when ovulation occurs quite rarely;
- ovarian depletion;
- hormonal imbalance that makes ovulation difficult;
- hidden inflammatory process of the uterus or appendages.
To accurately identify the cause, a gynecologist must conduct a comprehensive examination, including a blood test for sex hormones (estrogen, progesterone, testosterone), and an ultrasound of the pelvic organs. Depending on the results of the examination, the doctor may prescribe hormonal therapy to stimulate ovulation, as well as physical treatment in case of endometriosis, tubal obstruction or other diseases of the female reproductive organs. It is better to give preference to natural and gentle methods. An excellent example is the peptide bioregulator Ovariamine. It has a focal effect on the ovaries, helping to restore the functional reserve of their cells, thereby participating in the preparation of the ovaries for conception.
Thus, it is possible to become pregnant after removal of a cyst; the main thing is to follow the recommendations of your doctor and use modern safe means to restore and maintain the physiological function of the ovaries.
Share:
Pregnancy after laparoscopy: when can you conceive, how long before you plan to have a baby again?
Many women are diagnosed with pathologies that progress in the organs of the reproductive system, which cannot be cured with medication.
The most optimal treatment method used in such cases is laparoscopy. It is practically painless and allows you to recover in a short time.
Why is such an intervention better than conventional surgery, and how can it affect further conception planning?
Laparoscopy is a modern surgical method of treatment and diagnosis, which involves performing a minimally invasive operation. Since the surgeon does not need to insert his hand into the incision during the procedure, the hole in the patient’s body is made of a small diameter, sufficient to accommodate a laparoscope with a video camera attached to it.
During the operation, a set of special devices is used, which is called endovideo-resistant. It consists of an electrosurgical generator, a carbon dioxide supply system and equipment for obtaining and recording images. All manipulations performed by the surgeon are reflected on a special monitor.
Laparoscopy allows for highly accurate diagnosis of diseases of the pelvic and abdominal organs, when it is not possible to make a diagnosis using other research methods. Laparoscopic operations provide detailed information about the affected area.
The main advantage of laparoscopy is the short recovery period, after which the patient can return to a normal lifestyle.
The operation is prescribed for patients with:
- obstruction of the fallopian tubes;
- infertility;
- benign myometrial hyperplasia;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- adhesions of the fallopian tubes;
- multilocular ovarian cyst.
For several weeks after the procedure, a woman needs to protect herself from physical activity and intimacy. The appearance of bloody discharge after manipulation is considered normal. If they do not stop within a month, you should consult a gynecologist.
Since the period of time required to restore the body depends on its physiological characteristics, it is individual in each case. Most often, pregnancy after laparoscopy occurs within a year.
You should not begin sexual activity for at least a month after the procedure, because... During this period of time, the risk of infection remains. Full recovery of the female body is observed only after 3 months. From this moment on, the first attempts at conception are possible.
According to statistics, only a fifth of women can conceive a child 3 months after hospital treatment. In the following months, the chance of getting pregnant doubles. A third of the fair sex finds itself in an “interesting situation” six months after the procedure.
If the indication for the procedure was obstruction of the fallopian tubes, the woman is not recommended to plan conception earlier than after 3 months. This period is necessary to normalize the functioning of the paired sex glands and restore the tissue of the fallopian tubes, which swell as a result of tugging during laparoscopy.
Since ovarian function is restored gradually, the chance of getting pregnant in the first months after the procedure is very small. Gynecologists also recommend postponing conception because within 12 weeks there remains a high risk of developing an ectopic pregnancy. During this period, women are prescribed oral contraceptives, which allow the ovaries to rest.
Further withdrawal of the drug stimulates the ovulation process, so the likelihood of pregnancy after tubal laparoscopy increases significantly. However, if the complications that arise cause the removal of one fallopian tube, you most likely will not be able to get pregnant quickly.
Pregnancy after an ovarian cyst can be planned after at least 3 months. Despite the fact that ovarian function is restored within 30 days after the procedure, conception that occurs earlier than the recommended period can provoke various complications.
In order to prepare the body for the process of bearing a baby after removal of the cyst, women are recommended to take birth control pills. They help restore hormonal balance and help normalize the functioning of paired sex glands. After taking the pills, ovulatory function increases.
Laparoscopy is also prescribed for polycystic ovary syndrome, when cysts form in large numbers on the surface of the gonads. Restoration of the functions of the operated organ occurs within 30 days. After removal of multiple ovarian cysts, gynecologists do not advise postponing pregnancy, because The reproductive function of the gland is lost within a year.
After uterine fibroids
In this case, laparoscopic surgery is performed to remove benign tumors in the muscle tissue of the uterus.
After removing myomatous nodes, it takes at least six months for good scars to form in their place.
The optimal period for planning conception after removal of uterine fibroids occurs after 8 months. In some cases, the final formation of the scar occurs only after a year.
If laparoscopy was performed during an ectopic pregnancy, the woman is prohibited from becoming pregnant for the next 6 months. This is the minimum period that the body needs to restore the level of hormones disrupted due to termination of pregnancy. When conception occurs against the background of hormonal imbalance, this negatively affects the development of the fetus.
After endometriosis
Endometriosis is the pathological growth of the mucous layer of the uterus outside of it. Endometrial cells appear in areas of the reproductive system such as the cervix, fallopian tubes, bladder and other nearby organs. Signs of endometriosis are brown discharge that appears in the middle of the menstrual cycle and nagging pain in the lower abdomen.
It is not possible to determine the pathological process at the initial stage using ultrasound diagnostics, since the growth of endometrial cells in the uterus is insignificant. Due to the insufficient thickness of the mucosal layer, the fertilized egg cannot implant in the uterine cavity.
Using laparoscopy, areas of tissue affected by endometriosis are removed. After it, the likelihood of conception increases significantly, since after the procedure and appropriate treatment, the endometrium in the uterine cavity is formed in the required volume. You cannot plan a pregnancy after the manipulation for 3 months.
Since laparoscopic surgery is performed on certain days of the menstrual cycle, the nature of the regulation remains virtually unchanged. Discharge in the form of blood is observed in women for several days after laparoscopy, since during the procedure the integrity of the organs of the reproductive system is compromised. Gradually the color of the discharge becomes yellowish.
A woman's next period may begin with a slight delay. In some cases, the appearance of nagging pain, changes in the duration and abundance of menstruation are observed - this is acceptable and is not a sign of a pathological process.
Representatives of the fair sex who have undergone a laparoscopic procedure should not worry about the possibility of conception. Pregnancy after laparoscopy of the fallopian tubes or other organs of the reproductive system occurs quite quickly. Moreover, minimally invasive surgery can eliminate most causes of infertility in women.
How long should you wait to start planning your pregnancy? It depends on the diagnosis and individual characteristics of the body. In most cases, unprotected sex is allowed 12 weeks after laparoscopy.
Throughout the gestational period, the expectant mother may experience health problems that cannot be solved without surgical intervention. Laparoscopy allows a woman to avoid abdominal operations, during which the child may be harmed. Using a minimally invasive procedure, you can make an accurate diagnosis and get rid of pathologies.
The degree of risk of pregnancy complications depends on what disease is detected in the expectant mother. Laparoscopy is prescribed for pregnant women when:
- ectopic pregnancy;
- tumors of the gonads in the 2nd and 3rd trimesters;
- torsion of the ovary or uterine appendages;
- acute appendicitis at any stage of gestation;
- fibromyoma.
Possible complications of the operation:
- damage to the uterine wall;
- spontaneous termination of pregnancy;
- hypoxia in a baby;
- allergic reaction to medications.
In most cases, women after minimally invasive operations deliver by cesarean section. This allows you to avoid serious complications that are dangerous to the health of the child and mother.
The question of the method of conducting labor is decided individually with each woman in labor, with the exception of those cases when the operation was performed on the reproductive organ. If a woman has undergone laparoscopy of the fallopian tubes or paired gonads, she may be allowed to give birth naturally, provided that the test results do not indicate the development of a pathological process.
The procedure is prescribed to women who are faced with pathologies of the reproductive system. The operation is of a therapeutic and diagnostic nature. Its distinctive feature is the low level of trauma. The operation is performed in the following cases:
- Cystic formations;
- Adhesive process;
- Thickening of the ovarian capsule;
- Tumors of a benign or malignant nature;
- Ectopic pregnancy;
- Decreased fertility of unknown origin.
Adhesive process - description
The operation stimulates the function of the ovaries, promoting the development of a full-fledged egg. It is considered especially relevant when the membrane of the appendages is thickened. In this case, the surgeon cuts the capsule. Already in the next cycle, the egg will be able to easily leave the follicle.
Adhesions and foci of endometriosis are also eliminated, which makes it easier for the embryo to pass through the fallopian tubes and implantation. According to statistics, conception occurs in 85% of cases after laparoscopy. Six months after the procedure, the likelihood of getting pregnant decreases, since the gynecological problem may return. When planning pregnancy after laparoscopy, the following factors are taken into account:
- Purpose of the operation;
- Patient's age;
- The presence or absence of complications;
- Success of surgical intervention.