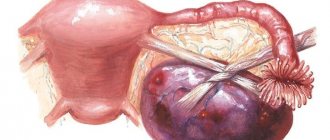
Laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst is the name of a modern surgical technique for removing cystic structures, which involves the least involvement of unaffected tissues in the process and an anemic procedure.
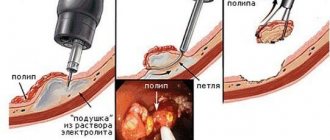
If during abdominal surgery a large incision is made on the abdominal wall, then laparoscopic removal of an ovarian cyst involves performing surgical procedures through three incisions (up to 5 - 10 mm) and a microscopic camera to monitor the process on a computer.
Indications for surgery
Surgeons gain access to the location of the cyst using the following techniques:
- Laparotomy or classic (cavitary, open) surgery to remove an ovarian cyst. This surgery is performed through a wide incision in the abdominal wall. This is the most traumatic removal method, after which a long recovery period is required. Large and giant cystic neoplasms are removed in this way.
- Laparoscopy. With this minimally invasive removal surgery, access to the lesion is made through small holes. Surgeons insert the necessary instruments and a microcamera through the punctures, which transmits the image to the monitor.
- Transvaginal access (through the vagina), which is carried out using a hysteroscope.
What are the criteria for choosing the type of surgical treatment for ovarian cysts - laparotomy or laparoscopy?
Laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst has basically the same indications as abdominal surgery; it differs only in the method of access to the affected ovaries. Although there are certain restrictions.
Indications for elective laparoscopic surgery are:
- ineffectiveness of therapeutic methods in the treatment of retention cysts (follicular, luteal);
- dermoid, paraovarian cyst, endometrioid and mucinous formation (since these neoplasms are not treated with medications and do not resolve on their own);
- large size of the cystic structure and its rapid progression (growth);
- signs indicating a high probability of suppuration, necrosis, rupture of the capsule, twisting of the leg;
- purulent-inflammatory process, ovarian deformation;
- infertility due to disease;
- displacement of the uterus, compression of the fallopian tubes, ureters, intestines, bladder;
- risk of malignant cell degeneration (malignancy).
Kinds
Cysts that occur in women can be divided into two main groups - functional ones, which can be treated with medication, and those that can only be removed surgically (paraovarian, endometrioid, dermoid). To remove tumors of the second type, laparoscopy of the ovaries or the cyst itself is recommended.
The paraovarian cyst grows slowly and is located near the appendages. Having reached a size of up to 20 cm, it compresses nearby organs.
A dermoid cyst contains hair and hair follicles. These formations often grow very large and compress internal organs. The cyst can only be removed surgically.
An endometrioid cyst initially does not give any symptoms; it is formed from endometrial tissue. The right ovary is often affected. But when the cyst reaches a large size (up to 15-20 cm), holes appear in it through which fluid flows out, stimulating the development of adhesions. For treatment, laparoscopy of ovarian cysts is recommended.
With polycystic ovary syndrome, the entire sex gland is often affected - cysts appear both outside and inside the ovary. Polycystic disease very often leads to infertility.
Cystoma of a benign neoplasm
Cystoma is a benign tumor that can degenerate into malignant. It has a stalk with which it is attached to the ovary. Torsion of the leg leads to poor circulation and rupture of the ovary. The method of treatment is laparotomy of the ovarian cyst.
If the cyst is very large, its removal is possible only with the ovary. This type of surgery is called oophorectomy.
For adhesions, ovarian apoplexy and torsion of the cyst stalk, laparoscopy is performed. Apoplexy requires immediate surgical intervention.
The rapid growth of cysts can be an oncological process, so some patients are prescribed additional examinations before surgery, for example, gastrointestinal tract, rheoencephalography, irrigoscopy, duodenoscopy.
Advantages and disadvantages of laparoscopy
Laparoscopy of the ovaries has significant advantages over manipulations that are performed to access the gonads during laparotomy. These advantages include the following features:
- significantly less trauma to intact tissues, since the incisions during laparoscopy are 10 times smaller than during laparotomy;
- multiple optical magnification of surgical objects on the screen, which allows the surgeon to perform manipulations more accurately and carefully;
- there is a low probability of developing postoperative adhesions, since during laparoscopy of ovarian cysts the organs are almost not displaced;
- minor blood loss;
- low risk of surgical infection, since neither gloves, nor tampons, nor even air touch the gonads;
- rare development of postoperative inflammation;
- short postoperative period;
- pain during the rehabilitation period is minimized;
- the possibility of seams coming apart is excluded;
- high cosmetic effectiveness, since the scars after tightening the incisions are very small and almost invisible;
- short recovery period before a new pregnancy;
- the possibility of carrying out diagnostic studies simultaneously with excision of the cyst, since the doctor, using a video camera, is able to more carefully examine the organ and cyst, and take a piece of tissue for histology;
- the possibility of parallel surgical treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome, giving a woman the opportunity to conceive a child.
The disadvantages of laparoscopy include:
- the need for general anesthesia, which, as with other operations performed under general anesthesia, is fraught with certain complications;
- presence of trained medical personnel;
- complex and expensive equipment, which is not always available in regional hospitals;
- the impossibility of performing certain surgical procedures for large cysts, simultaneous removal of the ovaries and uterus in case of detected oncology, the need for suturing large vessels;
- high cost of the neoplasm removal procedure. The price of such a minimally invasive procedure in private medical centers reaches 30,000 rubles. According to compulsory medical insurance policies, laparoscopy is performed free of charge in state clinics.
Recovery and postoperative period
The recovery period begins after surgery and lasts until discharge from the hospital. An important feature here is that recovery includes the woman’s early physical activity - in the evening she needs to get up and walk.
Already 8 hours after laparoscopy, it is reported that you can start eating, but only liquid food, unsalted and non-spicy. Next, you should take food in small portions, but more often. This way the intestines will quickly restore their normal functions.
Discomfort may be caused by gas vapors that were injected during the procedure. Sometimes this creates pain in the abdominal cavity. However, within the first 2 or 3 days, all the gas disappears. Since the harm from the operation is minimal, painkillers are rarely prescribed, only if the woman experiences particular discomfort or many lesions have been removed. These are usually non-narcotic drugs that stop giving approximately 24 hours after removal. Antibiotics are also not prescribed in all cases, as are anti-inflammatory drugs.
Preliminary studies and analyzes
Laparoscopy of the ovaries is done after the following preliminary instrumental and laboratory studies:
- traditional gynecological examination;
- blood tests, general urine tests, blood group and Rh factor tests, biochemical tests;
- blood clotting test (coagulogram);
- blood biochemistry (sugar, protein, bilirubin content);
- blood for infection with hepatitis B, C, syphilis, HIV;
- gynecological smears (survey and oncocytology), bacteriological culture for flora;
- colposcopy;
- electrocardiography;
- fluorography;
- Ultrasound of the uterus with appendages, ovaries, bladder;
- electrocardio- and fluorography;
- checking the level of markers (protein complexes) in the blood that indicate the possible development of oncology;
- consultation with an oncologist.
Patients need to know that the results of some tests are valid for a short period of time (blood and urine tests - within 10 days).
Do you use folk remedies?
Not really
Contraindications
Laparoscopic removal of an ovarian cyst is allowed only if a number of conditions and diseases are excluded. General and specific contraindications include:
- severe course of heart and vascular diseases in the stage of decompensation;
- cerebral hemorrhage;
- hemophilia – a disorder of the blood clotting process (coagulopathy);
- severe hemorrhagic diathesis;
- severe failure of kidney and liver function;
- acute infections (at least 6 weeks must pass from the moment of recovery);
- malignant diseases of any pelvic organs (from grade 2 with the presence of metastases);
- genital and general chronic infections;
- obesity (significant accumulation of subcutaneous fat interferes with laparoscopy);
- chronic inflammation of the gonads, fallopian tubes;
- unsatisfactory examination indicators, including 3 – 4 degrees of purity of the vaginal smear;
- pregnancy;
- acute infectious diseases.
Preparing for surgery
Preparation for laparoscopy includes the following activities:
The diet before laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst begins 2 days before surgery. It involves avoiding fatty, spicy foods, carbonated drinks, legumes (beans, peas and others), baked goods, asparagus, vegetables (cabbage, cucumbers, tomatoes), fruits (grapes, apples, figs) so as not to cause intestinal overflow, cause stomach upset, liver failure. Meals before laparoscopy should include steamed food (porridge, potatoes, dairy products). Mineral water without gas is allowed.
- On the eve of the operation, the last meal should not be later than 6 – 7 pm. You can drink until 10 – 11 pm.
- In the morning, it is also not allowed to have breakfast or take liquids, although patients usually break the ban and drink water or tea. The fact is that the restriction in food and water is forced and is due to the need to minimize the likelihood of reflux of contents from the stomach into the patient’s respiratory tract when she is under anesthesia.
- On the day before laparoscopy, a cleansing enema is performed and hairs are removed from the pubic area.
- Purchase compression stockings that are worn on the day of surgery (they can prevent thromboembolic complications).
Sometimes doctors recommend taking a laxative if you experience constipation. The freed intestinal tract then naturally shrinks, making room for surgical actions and manipulations.
The day before surgery, the patient will be examined by an anesthesiologist. After the examination, the specialist will decide whether to use general anesthesia or epidural (local).
First day
On the first day after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst, the patient is under constant supervision of medical personnel. This is due to not missing possible complications and starting the necessary treatment on time. For severe pain, analgesics are prescribed.
In the afternoon, the first treatment of postoperative wounds is carried out. If necessary, antibiotics are prescribed to prevent inflammation.
After 7-8 hours, you are allowed to carefully get out of bed, drink clean, still water, juices or compotes that do not cause bloating.
Attention: On the first day, sudden, active movements are prohibited. Movements should be slow to avoid dizziness and loss of consciousness.
Features of laparoscopy
It is important for many girls and women to know on what day of the cycle a laparoscopy is performed, how it goes, how long the operation to remove an ovarian cyst lasts, and whether anesthesia is used during it.
Doctors believe that the most optimal time for performing laparoscopy surgery for an ovarian cyst is the first phase of the menstrual cycle, preferably 6–7 days after the end of bleeding.
If the surgeon does not encounter complications or oncology, then the average duration of surgery is from 40 to 90 minutes. The duration is related to the size of the cyst to be removed, the volume of ovarian tissue excised, and existing diseases.
Laparoscopy of ovarian cysts is performed using 2 micro-incisions made to insert very small medical instruments into them. The third incision is for a laparoscope equipped with a tiny camera and LED. At the initial stage of surgery, a small volume of carbon dioxide is injected into the abdominal cavity to lift the peritoneal wall above the internal organs in the pelvis. In an enlarged operating space, it is easier for the doctor to monitor the removal process and easier to manipulate the instruments.
The volume of excised tissue depends on the degree of development of the cyst, its germination into the ovarian capsule, the number of endometrioid foci, detected oncology and other features.
During diagnostic laparoscopy, a specialist will examine the internal organs. If nodular structures are detected, the doctor will be able to remove them immediately. After the excision procedure, the surgeon will stop the bleeding, remove inserted instruments and carbon dioxide, and apply stitches and dressings.
In young patients, if no cancerous changes are detected in the cells, they try to affect the gonads to a minimal extent, preserving their functions for further pregnancy. For women over 47 - 50 years old, it is often recommended to remove the ovary with excision of the cyst in order to maximally protect the patient from malignancy (cancerous transformation of cells) of the gonad, the risk of which increases during this period. This also helps prevent the recurrence of new cystic structures and tumors from developing.
https://youtu.be/_xLucPXFZpI
The scope of surgical intervention is often determined by the doctor at the time of the procedure:
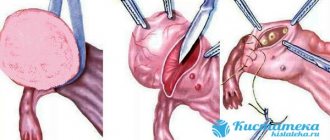
- Cystectomy (husking out the cystic lump). This operation is performed in the absence of signs of cancerous cell degeneration and with intact ovarian tissue. Doctors recommend cystectomy for women of reproductive age and teenage girls.
- Partial resection of the ovary (removal of part of the organ along with neoplasm). Wedge resection is performed when the ovary partially preserves its functions. Such an operation in Moscow costs from 18 to 25 thousand rubles.
- Ovariectomy (removal of the ovary along with the cyst). This procedure is indicated for necrosis and replacement of healthy organ structures with connective tissue. Ovariectomy is often performed during menopause. The cost varies from 15 to 20 thousand rubles.
- Adnexectomy (removal of the cystic capsule, ovary, fallopian tube). Such removal is carried out when cancer is detected, the pathology is complicated, or it has spread to nearby organs.
Removing one of the ovaries does not interfere with conception, since the second one remains. Thanks to this, a woman gets the opportunity to maintain reproductive health and bear a healthy baby.
Laparoscopy of a cyst of the left and right ovary is carried out according to the same scheme.
The following complications may occur after laparoscopy:
- heavy bleeding;
- infectious lesion and further inflammation, suppuration;
- seam divergence;
- injury to the pelvic organs.
General information about cysts and polycystic diseases
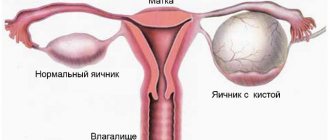
A cyst is a round-shaped formation that forms on the surface or inside the gonad; it has the structure of a hollow bladder filled with a specific secretion, the composition of which depends on the etiology of the tumor. Even though the cyst itself is a benign formation, under certain conditions some types have a tendency to become malignant or malignant. Cystic tumors can appear in ovarian cancer, when an uneven cavity forms inside the malignant tumor due to decay processes. During diagnosis, paraovarian cysts can also be detected, the formation of which involves the fallopian tubes, although the tissue of the gonads will remain healthy.
The following types of cysts are distinguished:
- follicular. It is formed from a follicle that did not rupture during ovulation and, instead of dissolving, began to fill with fluid. There may be bloody streaks inside such a tumor;
- luteal It is formed at the site of a ruptured follicular sac in the corpus luteum; it contains a serous substance and bloody streaks from damaged small capillaries;
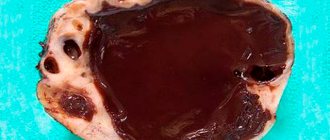
- endometrioid. It develops when the cells of the inner uterine layer begin to grow outside the uterine lining. The endometrioid cyst is characterized by cyclic variability in accordance with the menstrual cycle. Inside it there is a dark, thick substance, for which it is also called a “chocolate” cyst;
- dermoid or mature teratoma. This tumor forms during intrauterine development due to disruptions in the development of the embryo; it can also form in the place of a germ cell that has begun to develop independently. Inside such a tumor there are germinal tissues;
- mucinous. This is a multi-chamber formation that contains mucus inside and can reach gigantic volumes, up to 40 cm in diameter.
Tumors of the follicular type very often appear in large numbers, in such a situation they speak of the presence of polycystic ovary syndrome. In this case, the egg does not ovulate from cycle to cycle, and the follicle increases in size and fills with fluid. Often multiple cysts are located under the external meningeal gland. Other types of neoplasms appear alone.
Recovery after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst
The postoperative period after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst in the hospital lasts 3–7 days. The stitches are removed after 7–10 days. If non-removable material was used, the sutures dissolve on their own. Throughout the recovery period, it is necessary to treat the puncture sites with antiseptic agents to avoid infection and further inflammation. It takes little time to recover and after 6 hours the woman is allowed to get up and eat light food.
After laparoscopic surgery to remove a cyst, you must adhere to the following nutritional principles:
- Avoid foods and dishes that cause increased gas formation (carbonated drinks, cabbage, legumes, grapes, black bread, pastries).
- Eat small meals (5 – 6 times a day).
- Drink up to 2 liters of liquid (in the form of water, fruit drinks, fruit compotes, herbal tea) per day.
- Limit the intake of spices, marinades, fatty foods, and alcohol.
- You are allowed to eat: vegetable soup, lean meats, fermented milk products, porridge (buckwheat, oatmeal, millet, wheat).
Observation after laparoscopy by doctors includes:
- control blood pressure and body temperature 2 times a day (in the first few days the temperature may rise to 37.5 degrees). If the elevated temperature persists for a longer time, this indicates the presence of an inflammatory process;
- control of urination and bowel function. If for some reason urination is difficult, catheterization is performed. For constipation, a cleansing enema is performed.
How many days does it take for all the unpleasant symptoms to go away after removal of an ovarian cyst using laparoscopy? Within 2 days, the stomach, neck, and legs may hurt, which is associated with gas introduced into the peritoneal cavity. As soon as the remaining carbon dioxide in the peritoneum dissolves, the unpleasant phenomena disappear.
Sick leave after laparoscopy is issued for up to 10 days (for complications - for a longer period) from the date of discharge from the hospital.
How many days later can we consider the recovery period after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst to be complete? Depending on the volume and characteristics of the laparoscopic operation, the recovery stage lasts from 2 to 6 weeks. During this time, the body returns to normal functioning.
During this period there are certain restrictions:
- sex (including anal) is allowed only after 30–45 days have passed after the patient leaves the hospital;
- Lifting heavy objects (including bags of groceries) weighing more than 3 kg is prohibited;
- sports activity is possible only after 30 – 60 days with a slow build-up, starting from the minimum;
- It is prohibited to visit the sauna, solarium, swimming pool, beach, or take hot baths;
- Vitaminization of the body is recommended.
After discharge, the patient must undergo a control ultrasound of the pelvic organs after 1, 3, 6 months. If positive dynamics are maintained - every six months.
Sometimes patients worry that there is no monthly bleeding after laparoscopic surgery. Such a disruption of the menstrual cycle can occur because menstruation after laparoscopy of ovarian cysts begins with a slight delay. But within 2–3 months the menstrual cycle stabilizes. At this time, small spotting brown discharge may be observed, which is considered normal. If the delay is longer, you must contact a gynecologist.
Laparoscopy is a gentle surgical treatment option, after which the ovarian cyst does not develop again. But under some conditions the pathology recurs, and to prevent this, the doctor prescribes an additional course of treatment, which includes:
- Taking special hormonal medications: Buserelin, Goserelin, androgenic hormones, combined contraceptive pills with a low dosage of hormones.
- Physiotherapy to speed up healing (only as prescribed by a doctor).
- Absorbable drugs that prevent the formation of adhesions.
Laparoscopy as a method for removing ovarian cysts: basic information about the operation
Using laparoscopic access, you can perform almost all operations that are performed in the open way, i.e.
using a cut. These include: removal of various ovarian cysts, separation of adhesions and restoration of patency of the fallopian tubes, removal of fibroid nodes (with preservation of the uterus), removal of the uterine body and uterine adnexa, and surgery on the fallopian tubes for ectopic pregnancy. Solving some surgical problems, such as eliminating genital endometriosis, is generally impossible without the use of laparoscopy. This technology has opened a new era in the diagnosis and treatment of infertility, allowing for significant improvements in results. Timely detection and removal of ovarian cysts using laparoscopic access has significantly reduced the incidence of ovarian cancer.
The surgeon makes 3 small punctures of the anterior abdominal wall, 5 and 10 millimeters in diameter (as thick as a ballpoint pen). Unlike a traditional (laparotomy) 15 to 20 centimeter incision in the anterior abdominal wall, these punctures do not injure muscle tissue, so patients experience much less pain after surgery and can usually return to normal life within one week.
A puncture of the abdominal wall is carried out with a thin special tube - a trocar. Through it, a small amount of gas is introduced into the abdominal cavity (to create volume), a telescope tube, to which a special small video camera and a light source are connected. This allows you to view the image of the abdominal organs and the surgeon’s manipulations during the operation on the screen of a special TV with high magnification and record the progress of the operation on a video recorder. Through two other trocars, special instruments (manipulators) necessary to perform the operation are introduced into the abdominal cavity.
Diagnostic laparoscopy is usually performed under local anesthesia, operative laparoscopy is performed under general anesthesia, and both last no longer than a normal operation. Painful sensations in the puncture area disappear, as a rule, after 1-2 days, after which the patient does not experience the discomfort characteristic of the postoperative period of traditional surgical operations.
The advantage of endoscopic operations is their low invasiveness, short stay of patients in hospital (2-3 days), rapid restoration of health and ability to work after interventions. Carrying out the operation under multiple magnification makes it possible to carry out any surgical intervention more accurately and less traumaticly.
Minimal trauma to the anterior abdominal wall contributes to the rapid restoration of the functions of all organs and systems: breathing, activity of the cardiovascular system, motor-evacuation function of the intestines and bladder. During the wound healing period, there is no pain, which eliminates the need to prescribe strong painkillers. In addition, there are no postoperative scars, which is observed in conventional incision operations.
Both diagnostic and operative laparoscopy may not be performed in all patients. The main contraindication to laparoscopy is a massive adhesive process in the abdominal cavity associated with major abdominal surgeries that the patient has undergone in the past due to, for example, peritonitis, intestinal obstruction, etc. In this case, there is a high risk of life-threatening intestinal damage during laparoscopy with serious consequences for the patient.
Another serious contraindication to laparoscopy is severe cardiac dysfunction, because This operation is performed with the patient upside down and the abdominal cavity filled with gas, which can cause cardiac decompensation.
An approximate list of tests required for hospitalization: (if necessary, the scope of the examination can be expanded by your attending physician)
| * | Validity period of tests from the date of delivery to surgery |
| 1. General blood test | 2 weeks |
| 2. General urine test | |
| 3. Clotting time | |
| 4. Platelet count | |
| 5. Prothrombin content | |
| 6. Fibrinogen content | |
| 7. Bilirubin content | |
| 8. Total blood protein content | |
| 9. Blood glucose level | |
| 10. Urea content | |
| 11. Blood type and Rh factor (the stamp in the passport is not enough) | |
| 12. Wasserman reaction, blood for HIV, HBs Ag, HB C Ag. | 3 months |
| 13. Vaginal smear for flora and degree of purity | 2 weeks |
| 14. Smear for oncocytology | 1 year |
| 15. Fluorography data | 11 months |
| 16. ECG (with interpretation) | 1 month |
| 17. Feces on helminth eggs | 1 year |
| 18. Consultation with a therapist | |
After the final diagnosis has been made, the woman must undergo tests for laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst, which is usually performed on an outpatient basis:
- General blood and urine analysis;
- Blood chemistry;
- Markers of viral hepatitis;
- Blood test RMP-microprecipitation reaction (syphilis);
- Blood type and Rh factor;
- Coagulogram;
- Blood test for hormones;
- Vaginal smear;
- Ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs;
- Fluorography of the lungs;
- Electrocardiography;
- Consultation of related specialists.
The list of tests for ovarian cysts may vary depending on the clinical picture and the presence of additional diseases in the patient.
A few days before laparoscopy, it is necessary to exclude from the diet foods that increase gas formation in the digestive tract (cabbage, carbonated drinks, brown bread, legumes and other products). A day before, you need to do a cleansing enema or take laxatives. The last meal of the day should be no later than 6 p.m., and the last drink of water no later than 10 p.m. On the day of the operation, it is forbidden to drink or eat; if you are very thirsty, you are allowed to wet your lips with water and rinse your mouth.
Immediately before laparoscopy, pubic and perineal hair is removed, a bath is taken, after which no care products (lotions, creams, etc.) should be applied.
At the oncology clinic of the Yusupov Hospital, preoperative examinations are completed as quickly as possible on the basis of one medical institution. Patients are hospitalized incredibly quickly, and hospital stays are kept to a minimum.
Laparoscopic surgery is a direction that is dynamically developing in modern medicine. In the presence of an ovarian cyst, there are three main types of laparoscopic operations:
- Resection is a method that minimizes the traumatic effect on healthy ovarian tissue. The essence is to cut the ovarian membrane, isolate and remove the formation.
- Enucleation - during surgery, the cystic formation is placed in a special plastic container. This prevents rupture of the formation in the abdominal cavity, as well as the potential spread of the tumor process. The surgeon carefully removes the cyst without affecting the ovarian tissue.
- Ovariectomy of the ovary is a method of removing the cyst along with the ovary. It is used for large formations, as well as suspected malignant process. The doctor isolates the ovary and fallopian tube, ligates and removes them in a special container.
When choosing the type of laparoscopy, doctors at the Yusupov Hospital take into account
nature, size and location of the ovarian cyst. With timely diagnosis of the disease, it is possible to apply organ-preserving treatment, which is especially important during reproductive age.
After final verification of the diagnosis, the patient is indicated for surgical treatment. Indications for laparoscopic surgery for ovarian pathology are:
- Polycystic ovary syndrome;
- Rupture of an ovarian cyst;
- Torsion of the cyst pedicle;
- Diagnostics of formation (to confirm the diagnosis).
The advantages of this method over other types of surgical intervention are:
- Minimal trauma to healthy tissues;
- Aesthetic appearance of the abdominal wall after surgery;
- Speedy recovery and return to your previous lifestyle.
At the Yusupov Hospital, laparoscopy of ovarian cysts is performed under general anesthesia. On the day of the operation, the patient is consulted by an anesthesiologist who assesses the woman’s condition and decides whether there are any contraindications to surgery. The use of tracheal intubation allows you to regulate breathing and maintain the required depth of immersion in anesthesia.
On the operating table, the patient is in the Trendelenburg position - this is a forced position of the body when the head tip tilts down 30º. This position provides access to the ovaries by moving the intestine toward the diaphragm. After processing the surgical field, a puncture is made in the abdominal wall, through which carbon dioxide enters the cavity.
Thanks to the gas, the space between the internal organs increases. This allows for better visibility during surgery. Then a laparoscope, a special instrument with a light source and a camera attached to the end, is inserted into another hole. After advancing the instrument to the ovaries, 2 more incisions are made in the lateral sections of the abdomen, which are intended for the introduction of additional instruments.
If there is a need for wide access, then all instruments are removed and surgeons begin laparotomy.
Depending on the type and location of the cyst, removal can be done in different ways (at the discretion of the doctor). Once completed, a thorough check is carried out, after which the instruments are removed and the carbon dioxide is sucked out. Skin sutures and an aseptic bandage are applied.
- Ovarian cysts are a common cause of lower abdominal pain and infertility.
- They come in different origins and structures, but a cyst of any type at a certain stage of its development may require surgical treatment.
- A modern gentle surgical method is laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst, which allows to shorten the length of hospitalization and speed up the patient’s postoperative recovery.
Conception and pregnancy after ovarian laparoscopy
A healthy pregnancy after cyst laparoscopy is normal, even if one gonad is removed. In 85 out of a hundred patients, pregnancy occurs within a year after surgical treatment.
When can you get pregnant after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst? The timing of conception and possible pregnancy after laparoscopy is determined by the severity of the diagnosis. Recommendations for different diagnoses are slightly different. For example, if you have endometrioid formation or polycystic disease, it is advisable to get pregnant within a year.
But it is recommended to plan a pregnancy after such a minimally invasive operation no earlier than 3 months later. This time is required for the stitches to be completely tightened, the tissues to be restored, the body to rest and be saturated with vitamins. So, if pregnancy after laparoscopy occurs after 4–8 weeks, the likelihood of its termination is much higher due to insufficient hormonal activity of the ovaries and incomplete tissue healing.
It is worth getting pregnant after enucleation or excision of a cyst (especially if the ovary has been removed) after 6 months. Before conception, you should undergo all examinations recommended by your doctor and pass the necessary tests.
Possible complications
The probability of complications after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst is no more than 2%.
It can be:
- Discomfort from the digestive system (nausea, vomiting);
- hyperemia, inflammation, suppuration of sutures;
- increased temperature, increasing weakness, feverish state;
- bleeding not associated with the menstrual cycle;
- symptoms of thrombophlebitis.
Symptoms of complications requiring immediate medical attention after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst:
- heat;
- heavy bleeding;
- bloating, constipation;
- pain syndrome.
All these unpleasant consequences of laparoscopy require identification of the causes of complications and mandatory medical care.