Pain in the ovaries - for an explanation of the causes and treatment of this symptom, women often turn to the gynecologists of our Leib Medic medical center, which is conveniently accessible for treatment from many districts of Moscow. Treatment of pain in the ovaries is one of the specialized areas of our medical center, where experienced responsible doctors of various specialties work, including gynecologists. The cause of pain in the ovaries can be the following diseases, pathologies and conditions that require professional treatment or observation:
- ovarian apoplexy
- polycystic ovary syndrome
- ovarian cyst
- the presence of microbial lesions of the ovaries
- ovarian cancer
- natural causes of ovarian pain
- pain in the ovaries during abortion
- pain in the ovaries when taking birth control pills
- pain in the ovaries during artificial insemination
The female reproductive organ system is represented by the uterus and ovaries. The ability to produce offspring and the health of the unborn child depend on the condition of the ovaries. However, more than 70% of women, especially in cities, suffer from various problems of the reproductive system, including the ovaries. Much of the reason for this is the lifestyle that modern ladies adhere to and especially their clothing. After all, even in severe frosts, women prefer to wear miniskirts instead of warm clothes.
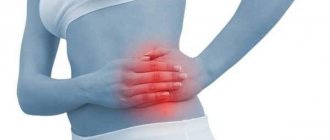
Why do my ovaries hurt, left or right?
Typically, pain in the ovarian area is cramping and stabbing in nature. However, based on these signs, it is impossible to accurately determine that it is the ovaries that are hurting. After all, inflammation of appendicitis, kidney disease and digestive system have the same expression. Therefore, you should not diagnose yourself; you can see a gynecologist at our medical center in Moscow.
In some cases, the pain may be periodic. In this case, the pain manifests itself either in the lower abdomen, then in the kidney area or in the pubic area. At times you may experience leg cramps. Pain in the left ovary is rare and mainly indicates a harmful external influence. If there is pain in the left ovary, most likely it is due to the medications you are taking.
Pain in this area indicates problems with the reproductive system or hormonal phenomena. Both types of illness can lead to complications, so you should not delay the examination. Only an experienced doctor will be able to accurately determine the disease and say exactly why the ovaries hurt.
Video: Oophoritis - inflammation of the ovaries
https://youtu.be/stVMtwF8ceM
- Abdominal pain in the navel area
- Temperature before menstruation 37 and above
- Pain in the hand
- Aching and nagging pain in the right lower abdomen in men
- Seething in the stomach
- Right side hurts when walking
- Rash with itching on the legs in the form of red dots
- Why does hair split?
- Woman's bladder hurts
- Eyelids become red and swollen
- Why do the hair roots on the head and crown hurt?
- What to do if your throat hurts, it hurts to swallow, but you don’t have a fever?
Treatment of ovarian apoplexy at Life Medic
Ovarian apoplexy is one of the most serious problems. In this case, hemorrhage occurs in the ovary, which poses a threat to the normal functioning of this organ. To understand how this happens, it is necessary to consider the menstrual process in a woman’s body:
1. When an egg matures in a follicle, it must receive sperm.
2. This does not happen and due to the death of the egg, menstruation occurs.
3. The blood of the dead egg filling the follicles is removed from the body.
So at this time, these organs are especially tense, as they are filled with blood, and the risk of damage to blood vessels also increases. When the walls of the ovary cannot withstand it, the blood entering it from the artery spills inside.
Causes of ovarian apoplexy
In general, the right pair is more often susceptible to apoplexy, since it is larger and more blood circulates in it than in the left. Therefore, the right ovary hurts more often. Blood enters the right organ directly from the aorta, and the left one through the blood vessels of the kidney. This also causes increased pressure and tension in the right organ. So, if for some reason the right ovary hurts, then the reason is most likely apoplexy.
Ovarian apoplexy most often occurs in teenage girls and young women. In many ways, it is this group that is at risk, since the reproductive organs most actively perform their function in them. In very rare cases, apoplexy can result from mechanical damage. Other causes of apoplexy
In addition to natural processes, hemorrhage can be caused by:
- overly active sex
- improperly performed gynecological procedure
- excessive stress on muscles
These are all mechanical factors. However, there are also pathogenic factors:
- pathology of the uterus;
- tumors;
- varicose veins;
- improper healing after surgery or injury;
- ovarian inflammation
So pain is a symptom not only of disorders in these organs themselves.
Symptoms of ovarian apoplexy
The main sign of apoplexy in a woman’s body is acute pain in the ovary or lower abdomen, which aches. And usually the right ovary hurts. However, the disease may be accompanied by other signs:
- vomit;
- dry mouth;
- tachycardia;
- stickiness of sweat;
- hypotension;
- pale skin color;
- temperature increase.
Usually, additional symptoms indicate that the accumulation of blood has reached its critical level and an attack of pain may soon occur. When the right or left ovary is pulled, it is necessary to urgently consult a doctor, otherwise complications are possible.
Answers to basic questions
The main questions that worry women and to which you need to know the answers so as not to miss a serious illness or complication.
When to call a doctor
You should call an ambulance in case of sharp, sudden, throbbing pain, accompanied by nausea, vomiting, fever, and general weakness. With these symptoms, the patient requires mandatory hospitalization.
If there is throbbing pain on the side of the left or right ovary, this may indicate torsion of the cyst stalk.
An increase in temperature, spotting, pulsation in the lower abdomen after hysteroscopy or ablation (curettage) of the uterine mucosa requires immediate medical intervention.
There is throbbing pain, nausea, vomiting, abdominal tension, bleeding - the main symptoms of a ruptured tube during an ectopic pregnancy, spontaneous miscarriage (abortion), ruptured appendix - you urgently need to call an ambulance.
Important: Such conditions, which doctors call “acute abdomen,” are dangerous to health and life. Therefore, you should not hesitate to see a doctor.
Pulsation radiating into the leg is a consequence of diseases such as complications of a hernia, femoral or inguinal, purulent inflammation of the appendages, acute appendicitis. The best decision is to call an ambulance for immediate hospitalization.
Which doctor should I contact for pain in the ovary?
If you experience mild pain that does not require urgent medical intervention, you need to make an appointment with your local gynecologist and undergo an examination. If there is an assumption that the symptoms are caused by other concomitant pathologies, the doctor will prescribe consultations with the appropriate specialists.
What tests can doctors prescribe for pain in the ovary?
The list of studies depends on the presumptive diagnosis, the possibilities of outpatient or inpatient treatment.
Main research:
- general or detailed blood and urine tests,
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs,
- intravaginal gynecological examination.
If infectious inflammation of the reproductive organs is suspected, vaginal smears or bacterial culture of microflora, sexually transmitted infections (mycoplasma, chlamydia, ureaplasma, gardnerella, gonococcus, candida) are prescribed.
If syphilis or HIV is suspected, an appropriate venous blood test is prescribed.
To identify endocrine disorders of the reproductive glands, blood tests are prescribed for the following hormones:
- LH - luteinizing,
- FSH – follicle stimulating,
- testosterone, estrogen, prolactin, progesterone,
- TSH – thyroid stimulating,
- SHBG – sex hormone binding globulin
- DEA-S04 – dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate.
If a thyroid disease is suspected, additional tests for hormone levels are prescribed:
- T4-thyroxine,
- T3 – triiodothyronine,
- AT-TPO and AT-TG – antibodies to thyroid peroxidase and thyroglobulin.
If viral pathologies are suspected, blood tests are prescribed to possibly detect cytomegalovirus, papilloma viruses, herpes, and Epstein-Barr.
To clarify the diagnosis and simultaneous treatment, puncture and laparoscopy may be prescribed.
Can the ovaries hurt?
Of course they can. But it is impossible to independently determine whether the glands or other pelvic organs are suffering. Only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment. If pain occurs, it is not recommended to take analgesics on your own, so as not to blur the clinical picture of a possible disease.
When the ovaries hurt
Pain syndrome in the lower abdomen, on the right or left, can manifest itself in various diseases of both the pelvic organs and the abdominal organs. Therefore, in such cases, differential diagnosis is necessary to exclude concomitant pathologies.
Why does the ovary hurt?
Tingling in the ovary is not always a sign of pathology. Symptoms such as aching, stabbing pain, aggravated by walking, can be observed after ovulation, when the contents of the follicle enter the abdominal cavity.
Tingling in the area of the right ovary occurs during pregnancy, as the growing fetus puts pressure on the glands and fallopian tubes.
In any case, only a specialist can make an accurate diagnosis.
How to understand that it is the ovary that hurts
It is impossible to answer unequivocally the question of why women’s ovaries hurt without a full examination. If the ovary is pulled for a long time, after menstruation, you definitely need to consult a gynecologist.
Why does my right ovary hurt?
The right ovary hurts and pricks when the egg matures in it. This is the so-called ovulatory syndrome, which does not require emergency treatment. The right ovary can be pulled before, sometimes during menstruation, during rough sex. The pain may be due to a developing cyst, benign or malignant tumor. Infections, hormonal disorders, endometriosis, apoplexy, ectopic pregnancy, torsion of the pedicle of the cyst, appendix provoke pain on the right side.
What size of ovarian cyst is considered large - what to do How to distinguish thrush from another infection How long does it take for thrush to appear after infection Multiple uterine fibroids of large and small sizes
Why does my left ovary hurt?
Accordingly, similar causes of pain in the right ovary may appear in the left. But the left ovary hurts and stings less often than the right. The reason is that on the right side there are more arteries supplying the female organ. The gallbladder and appendix are located on the same side. Pain on the left side can be caused by the sigmoid colon, which is stretched due to untimely bowel movements.
Why do ovaries hurt in women?
Ovarian pain can be a natural physiological reaction of the body that occurs before and after menstruation, or it can be caused by pathological processes. Another reason is the abolition of long-term use of oral contraceptives. After stopping the medications, the functioning of the glands is restored, which is accompanied by aching symptoms, tingling, and nagging pain. Discomfort also occurs after surgery, which goes away after complete healing of the operated organ.
What to do if your ovaries hurt
Whatever pain you experience, you should definitely consult a gynecologist.
After the examination, the doctor will determine the causes, establish a diagnosis, give recommendations for therapeutic exercises, and prescribe medication or surgical treatment.
Please note: Many gynecological pathologies do not always have a clearly defined clinical picture. And it very often happens that when visiting a doctor, the gynecologist notes with regret that the disease is advanced. This is especially tragic for ovarian cancer pathologies.
Where do the ovaries hurt?
Paired organs are located in the lower abdomen, in the iliac region. Accordingly, pain occurs there.
Adnexit
Pain, constant, aching, with inflammation of the ovaries most often occurs on the right side, does not depend on the female cycle. Differentiation from appendicitis is necessary, especially if fever, nausea, and vomiting occur.
Ectopic pregnancy
A sharp pain radiating to the hypochondrium and shoulder occurs when the fallopian tube ruptures. Accompanied by bleeding, weakness, dizziness, loss of consciousness. History: delayed menstruation, weakly positive pregnancy test. Help must be urgent. Apoplexy
If ovulation is too rapid, damage to the ovary occurs, followed by bleeding. The main symptoms are severe pain, weakness, cold sweat, and poor health. Surgical treatment may be necessary.
Cancer
The first stages are asymptomatic or with subtle manifestations. Sometimes a woman consults a doctor when the cancer has already reached the third or fourth stage. Therefore, if pain occurs, it is better to receive qualified advice and the necessary treatment than to later suffer from complications or end your life with premature death.
Treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome at Leib Medic
Polycystic ovary syndrome is one of the main diseases leading to infertility. Cystosis develops very slowly and it is rarely possible to detect it in the initial stages. It is usually diagnosed accidentally, during the next examination. Tingling in the left or right ovary can be a symptom of a similar disease. However, polycystic disease can be expressed by tingling in the right ovary. The disease occurs due to improper formation of the egg. Sometimes due to pathologies of the ovary itself. In both cases, it is difficult for the egg to leave the organ and over time the channels begin to accumulate tissue of residual eggs and polycystic disease develops. Also, a large number of underdeveloped eggs accumulate in the organ itself. Polycystic ovary syndrome mainly occurs in women under 35 years of age. It is especially dangerous for teenagers who are just beginning to menstruate. The presence of cystosis, in addition to periodic pain, causes disruption of the menstrual cycle. So polycystic disease has a direct effect on hormonal functions. This can disrupt hormonal processes, which usually leads to cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, etc.
Causes of polycystic ovary syndrome
The exact reasons for the occurrence of polycystic ovary syndrome have not yet been identified. All patients had the following pathologies, which presumably lead to the development of this disease:
- endocrine system imbalance;
- insulin oversaturation;
- chronic inflammation;
- obesity;
- heredity.
Any of these pathologies can lead to the formation of ovarian cysts.
Symptoms of polycystic ovary syndrome
Doctors identify the following symptoms of cystic disease:
- abnormal menstruation;
- hypertrachia (excessive hairiness);
- skin problems;
- pulling sensation in the ovary area;
- excessive weight.
All these signs are associated with pain that occurs in the lower abdomen.
Pain whose causes require treatment
If you experience severe, prolonged, sharp pain, you should not self-medicate; you should definitely consult a doctor. The following diseases require competent medical treatment:
- inflammatory diseases of the female organs,
- benign or malignant tumors,
- cysts, endometriosis,
- miscarriages, ectopic pregnancy,
- concomitant diseases that cause pain in the gonads.
With an ovarian cyst
The pain, depending on the type of cyst and its progression, is of a different nature and appears at different times. May occur during sexual intercourse or physical activity. When the leg is twisted or an ovarian cyst ruptures, paroxysmal, severe pain occurs.
The patient is concerned about:
- heaviness, feeling of fullness,
- aching pain in the lower abdomen, perineum, radiating to the lower back, sacrum, rectum,
- menstrual irregularities,
- bloody, spotting discharge,
- difficulty urinating, with frequent urge,
- nausea, fever, fainting.
Painful symptoms are caused by gynecological diseases such as adnexitis, salpingoophoritis (simultaneous inflammation of the ovaries and fallopian tubes), apoplexy (rupture of ovarian tissue), polycystic disease, and ovarian endometriosis.
Untreated, neglected cysts lead to serious complications - their ruptures, pedicle torsion, development of tumors, infertility, adhesions. Women undergoing IVF may develop ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome, associated with an excessive amount of medications that increase ovulation.
To avoid these complications, doctors, based on the type of cyst or cystic formation, prescribe medication or surgical treatment. One of the treatment methods that is not often used is puncture, which removes aspirate (contents) from the cystic ovarian cavity.
Related to the menstrual cycle
Ovulatory syndrome - pain in the ovaries before menstruation, after ovulation, is often associated with an insufficiently mature corpus luteum. In this case, partial detachment of the uterine epithelium occurs, which causes discomfort.
The period during which the egg leaves the follicle is characterized by micro-tears of the membrane and micro-hemorrhages. This period occurs during ovulation in the middle of the monthly cycle and is also characterized by a slight pain syndrome. Pain usually occurs on the side on which the egg matures. The occurrence of severe, sudden pain may be a signal of ovarian rupture. And in this case, immediate medical assistance cannot be avoided.
Pain during menstruation, according to doctors, occurs in the uterus itself, which vigorously rejects the mucous layer if pregnancy has not occurred. The ovaries can also hurt, but this is due to pathological processes in them, stressful conditions or nervous strain.
If pain begins to bother you after menstruation or during menopause, you need to pay attention to the possibility of gynecological pathology.
During pregnancy
Pain during pregnancy can be caused by non-obstetric (non-gynecological), pathological or natural, physiological causes.
Symptoms and causes of non-gynecological pain are associated with exacerbation of chronic pathologies, such as:
- cystitis - inflammation of the bladder,
- exacerbation of cholecystitis,
- pyelonephritis,
- appendicitis.
Physiological pain, aching, not severe, is caused by sprained ligaments, muscle tissue, displacement of internal organs by the uterus, which gradually increases its size. They are temporary and not dangerous to the body.
Pathological - the most unpleasant, can occur at different stages of pregnancy, caused by the following reasons:
- inflammation of one or both ovaries,
- cyst or its rupture (apoplexy),
- spontaneous miscarriage (abortion),
- consequences of IVF (in vitro fertilization).
Ovarian pain before childbirth is associated with increased activity of hormones that cause softening of cartilage tissue, ligaments, and separation of the pelvic bones. These processes cause uncomfortable pain, which doctors call false.
During and after sex
One of the main causes of pain during sex may be an uncomfortable body position (posture) or a rude attitude of a partner. Pain after sex can be associated with the onset of ovulation or psychological problems in a woman. These problems, with respect and mutual understanding between partners, are resolved positively.
Burning, tingling, nagging pain appear after sex with inflammation of the ovaries, endometriosis, and tumors of the appendages. Sharp, unbearable pain occurs with apoplexy.
Important: High-quality sex is an important component for maintaining a woman’s health. Without good emotional and physiological release, venous stagnation occurs in the pelvic organs. This leads not only to pain, but also to neuropsychiatric disorders.
After surgery
It is clear that with any surgical intervention, discomfort is almost inevitable. After puncture of the ovaries, nagging, aching pain and slight bleeding appear, but after five days or a week these phenomena usually subside.
Minor pain is a natural consequence of surgical interventions to remove a cyst and other operations on the organ. They may intensify with the development of complications - postoperative bleeding, pelvioperitonitis, adhesions.
Microbes in the ovaries
Of course, the presence and large accumulation of harmful microorganisms in the organs of the reproductive system leads to inflammatory processes and gives rise to pain in the ovary. When the number of such microbes reaches a critical level, thrush and candidiasis develop.
At the same time, thrush indicates a decrease in immunity in a woman’s body, when candidiasis, like a fungal disease, develops as a result of:
- excess sugar in a woman’s body;
- hormonal surges;
- any infectious disease;
- excess antibiotics;
- poor hygiene of the intimate area.
For both thrush and candidiasis, the symptoms are almost identical and are expressed:
- in the presence of unpleasant odors;
- presence of itching;
- pain when urinating;
- inflammation of the genital organs;
- pulls the ovary;
- pain during sexual intercourse.
This disease can be cured with the help of anti-inflammatory and antibacterial agents.
Ovarian cyst pain
A cyst is a benign neoplasm. If it is large in size and begins to put pressure on neighboring organs, then this provokes pain. The cyst may rupture. In this case, intense sharp pain appears. In this case, surgery is performed, otherwise the pathology may develop into peritonitis. If the tumor is small, the pain spreads to the back area.
Torsion of the cyst causes pressure on the veins, which occurs in the pedicle of the formation. Veins have a thin wall and experience greater pressure. Compression of blood vessels provokes stagnation of venous blood.
Arteries are involved in the process, which causes the formation of necrosis. The inflammatory process can spread to nearby pelvic organs. The severity of the symptoms depends on the degree and speed of development of the pathology.
Complete torsion is characterized by the following symptoms:
- unilateral pain in the lower abdomen of an acute nature;
- muscle tension in the abdominal wall;
- lack of stool and gas;
- presence of nausea and vomiting;
- tachycardia;
- lowering blood pressure;
- temperature increase;
- loss of consciousness;
- delayed urine output;
- presence of cold sweat;
- discharge of blood from the vagina.
Usually the provocateurs of torsion are:
- sudden movements;
- physical overload;
- bearing a fetus;
- period after childbirth;
- intestinal diseases.
If the tumor is small in size, pain may not be noted in polycystic disease. Most women experience aching pain in the lower abdomen and lower back. Researchers cannot explain the reason for provoking pain. Some doctors believe that they are caused by the proliferation of the ovaries, which begin to put pressure on neighboring organs.
Rupture of an ovarian cyst on the right is provoked 4 times more often than on the left.
Predisposing factors include:
- endocrine system disruption;
- lability of emotional background;
- inflammatory processes in internal organs;
- development of fibrosis;
- menstruation irregularities;
- the presence of adhesions and tumors in the pelvic area;
- blood stagnation in the pelvic vessels;
- varicose veins in the ovaries;
- presence of polycystic disease;
- abnormal position of the uterus.
Pain in the ovaries is provoked by physical activity or examination of the vagina during gynecological examinations. In some cases, cyst rupture occurs even at rest or sleep.
Ovarian cyst - treatment in Moscow, Life Medic clinic
Ovarian cyst is a common disease that occurs in women, and specialists from the Moscow medical center Life Medic assist patients in treating ovarian cysts using specialized techniques. Unlike polycystic disease, when tissue of underdeveloped eggs accumulates in this organ, when a cyst forms under the ovary, usually the right one, the cortical ovary swells pouch. This happens due to the accumulation of yellow cell fluid in it, which is actively released during the post-ovulation period. However, yellow cells are not always to blame. So:
- a cyst may be an accumulation of dead ovarian tissue, leading to the development of cancer;
- a thick-walled cyst usually results from epidermal deposition;
- a capillary cyst is usually a manifestation of natural organic processes;
- a multi-chamber cyst is a consequence of the accumulation of various tissues, including fluids, which also leads to cancer.
The exact reasons for the formation of cysts in women have not yet been established. Many experts argue that the main causes may be hormonal pathologies. In addition, there have been cases where the formation of a cyst was accompanied by chronic inflammatory processes. Usually, it is not possible to detect the presence of a cyst by observing external manifestations, because the formation of a cyst does not have any symptoms. Most cases are detected during a routine examination by a gynecologist. With excessive physical exertion or very intense sexual intercourse, pain may be felt in the right ovary.
Discomfort in the ovarian area during ovulation
As you know, all women of childbearing age have their own individual menstrual cycle.
It consists of 3 phases. In each period of the menstrual cycle, a woman may complain that the ovaries are pulling. Ovulation is accompanied by pain quite often. It is characterized by the release of an egg into the abdominal cavity. This process is accompanied by changes in the gonads. The dominant follicle ruptures when the egg is released. During this period, some women experience unexpressed nagging pain in the right or left groin area. Unpleasant sensations occur on the side where the follicle ruptured.
Ovulation occurs in the middle of the menstrual cycle. In addition to discomfort in the ovarian area, it is accompanied by other symptoms. Among them are increased sexual desire and the release of clear, thick mucus from the vagina. Ovulation lasts only 1 day, during this period the probability of conceiving a child reaches its maximum.
Ovarian cancer
Ovarian cancer is detected in older women up to 70 years of age. In more than thirty percent of cases it leads to death. Basically, such malignant formations in the reproductive system are divided into the following groups:
- initial, when a cancerous tumor arose in the ovary itself for no apparent reason;
- secondary, when cancer causes the death of benign cells;
- Metastatic cancer appears due to cancer cells entering the ovaries from another organ through the blood.
The causes of cancer cells in the body are still unknown. Doctors attribute most cases to age and heredity. In addition, hormonal processes are of no small importance.
The signs of a malignant tumor are quite obvious. So in cancer there are:
- a feeling of discomfort reminiscent of a digestive tract disorder;
- persistent feeling of fatigue;
- constant feeling of the presence of a foreign object in the abdomen.
The growth of the tumor causes pain in the left ovary or in the right and difficulty urinating. In addition to a decrease in the amount of menstrual flow, the woman is attacked by apathy and depression does not leave her.
Natural causes of ovarian pain
It is not necessary that a certain pathology be present in the body if there is pain in the lower abdomen. During the week before menstruation, a feeling of discomfort in most women is considered normal. At the same time, the ovary hurts before menstruation. This is a manifestation of natural physiological processes. In addition, the ovary hurts during menstruation for the same reasons.
Another category of natural causes of pain in the lower abdomen is associated with the natural expansion of the uterus and the accumulation of yellow cells due to a woman’s pregnancy. Typically, abdominal pain is felt in the first trimester. But they are not frequent or regular, but appear in isolated cases. However, during pregnancy, the fact that the ovary hurts on the right or left may be the result of some other reasons that will lead to complications and harm the woman’s body and the fetus. These include:
- inflammatory processes;
- infectious diseases;
The most dangerous form of inflammatory processes is inflammation of the ovaries themselves. This disrupts the formation of yellow bodies, which leads to underdevelopment of the fetus at the initial stage of pregnancy. In this case, the left or right ovary colitises, since the inflammation primarily affects it.
How the appendages hurt in women: symptoms
The nature of pain in the appendage area depends on the causes of its occurrence.
When the appendages hurt severely, the pain occurs in paroxysms, is accompanied by an increase in temperature and the appearance of weakness, the doctor may suspect the development of oophoritis. With chronic, low-grade inflammation, the menstrual cycle is disrupted, sexual desire worsens, and pain occurs during sexual intercourse.
Sharp and severe pain in the appendage area often indicates pathologies that require immediate medical intervention. This situation is possible with hemorrhage in the ovary, its rupture, torsion of the stalk of a tumor or cyst, or ectopic pregnancy.
Important! The pain that appears in the appendage area cannot be tolerated. In some situations, refusal of prompt medical care can cause death.
Colitis ovary
When ovulating, women feel a tingling sensation in the ovaries, which can last for several hours in a row. A sharp stabbing pain, which is accompanied by a drop in blood pressure, weakness, and pale skin, may indicate ovarian apoplexy. Dagger pain also appears with tubal abortion, rupture of the fallopian tube, torsion or rupture of the cyst.
If the patient's ovaries hurt, symptoms of blood loss appear. As a rule, a woman’s blood pressure drops sharply, a painful shock occurs, and she faints. In such situations, urgent surgery is required.
Pulls the ovary
A visit to the gynecologist is often accompanied by a woman’s complaints that her right ovary is being pulled. Examination usually reveals the formation of a cyst or tumor. Nagging pain is also characteristic of polycystic disease and endometriosis.
It is important to establish the reason why the ovaries are pulled. Pulling sensations appear with the development of gonadal cancer. Malignant tumors may cause only minor discomfort over a long period of time. As the disease progresses, the abdomen enlarges and the functioning of the intestines and bladder is disrupted.
Often the appendages begin to hurt in patients who have been stimulated to ovulate. This may indicate the development of hyperstimulation syndrome. With this condition, bloating is possible, which develops due to metabolic disorders and fluid accumulation.
During ectopic implantation of a fertilized egg, nagging pain may occur. They are caused by the growing fertilized egg stretching the surrounding tissue.
Many pregnant women complain of pain. The appearance of discomfort is associated with excessive stretching of the ligamentous apparatus that supports the uterus.
Important! It is advisable to tell your gynecologist about any unpleasant sensations at your next visit. The doctor will be able to conduct a thorough examination and rule out the occurrence of infectious and inflammatory diseases.
Abortion as a cause of pain in the ovaries
An incorrectly performed abortion procedure can cause pain in the ovaries due to infections or damage to the ovaries when the fetus is removed. Both ovaries can hurt at the same time. This is one of the few reasons why the left ovary hurts, since in most cases the pain radiates to the right. Typically, such symptoms appear exclusively in the first week after the procedure. In addition, the abortion procedure can lead to disruption of menstrual processes and the functioning of endocrine organs. But most of all, the organs of the woman’s reproductive system suffer from this procedure, mechanically or otherwise. Therefore, after an abortion, the risk of infertility is very high.
Pain in the ovaries when taking birth control pills
More than half of the world's women prefer to avoid unwanted pregnancy by using oral contraceptives. However, most of them have no idea what exactly the effect of such pills on the body entails. Thus, most of these drugs accelerate or inhibit hormonal processes. This is mainly a consequence of the need to increase the production of estrogen, which activates the menstrual process and prevents pregnancy. If, along with the right one, the left ovary hurts, then the reasons are precisely this effect on the uterus. Typically, ovarian colitis occurs in 90% of such patients in the first three months after starting medication. This is normal if, along with the right one, the left ovary colitises. However, if the pain does not go away longer than this, then perhaps due to a hormonal imbalance, a cyst or something else has formed in the ovary.
What to do if your ovaries hurt?
So, what to do if your ovaries hurt. When pain occurs in the pelvic area, rest is necessary. It is necessary to limit yourself from stress, both physical and emotional. It is also worth reconsidering your diet; you may need to go on a diet. In your diet, you should limit yourself from salty and excessively fatty foods. It is recommended to consume more dairy products, fresh fruits and vegetables.
Folk remedies for such a symptom are absolutely not advisable. But after consulting a doctor, you can take mud baths and salt baths. Medicinal decoctions should also be taken in consultation with your gynecologist. An experienced doctor will also tell you what to do if your ovaries hurt.
If acute pain occurs, you must call an ambulance. You should not try to figure out the reasons on your own, even if this has been observed and successfully eliminated before.
The role of the ovaries in the female body
In size, they are no larger than a peach pit. When there are no pathologies in the body, the left one is always somewhat smaller in size compared to the right one. This organ is a composite organ and is represented by a cortex and connective tissue. Disruption of these components causes general malaise and problems with the functioning of other organs of the female body.
Reproductive function of the ovaries
This paired organ plays a major role in the process of reproduction. After all, they are the ones who produce eggs, which, after fertilization by male sperm, give rise to the birth of a new embryo. They are located on both sides of the uterus, in the pelvic region. Immediately after fertilization, the ovulation process stops and the ovaries begin to produce a temporary protective layer for the future fetus - yellow bodies. However, this layer disappears after the formation of the uterine placenta. Usually replacement occurs after the first 20 weeks of pregnancy.