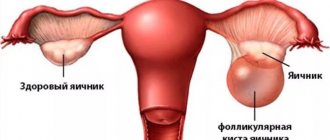
Ovarian cyst rupture: causes
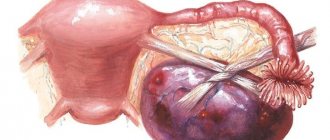
Rupture of an ovarian cyst (apoplexy) is an acute condition that threatens the health and life of a woman, caused by the release of the internal contents of the cyst into the abdominal cavity.
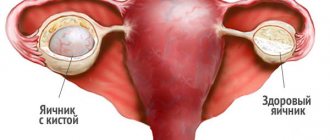
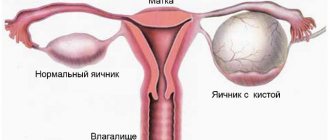
If a woman has a diagnosed cyst, she does not have to immediately rush to the Internet to search for the query: “ruptured ovarian cyst symptoms.” Functional cysts, often encountered in gynecological practice, are very rarely susceptible to rupture, since they usually resolve on their own and do not grow to large sizes. Although even follicular cysts in rare cases, for inexplicable reasons, can grow and burst in a matter of weeks.
But there are types of ovarian cysts that have a high risk of rupture, for example, endometriomas. A woman with a similar diagnosis should especially carefully monitor her health and well-being, so that if an ovarian cyst ruptures, she urgently and purposefully seeks help.
Causes of ruptured ovarian cyst:
- Hormonal imbalance
- Inflammatory processes in the ovaries, making the walls of the follicle cyst thinner
- Congenital bleeding disorder
- Too frequent, intense and harsh sexual intercourse
- Excessive physical exertion (heavy lifting, especially sudden, jerking)
- Injuries
Patients at risk - women who have already been diagnosed with an ovarian cyst - should pay special attention to the reasons listed above, trying, if possible, to exclude risk factors in order to avoid rupture of the ovarian cyst.
Treatment methods
Therapy for pathology begins with balancing the woman’s hormonal levels. This is precisely the problem that becomes key. It is solved by prescribing combined oral contraceptives. As soon as the hormonal levels return to normal, the tumor will begin to decrease in size or completely resolve on its own.
Selecting medications on your own is strictly prohibited. This is done by a specialist based on the obtained tests. Doctors often use another effective technique by prescribing a medicine containing the hormone progesterone. It helps to reduce the size of the cyst, and in the future it can resolve on its own.
Rupture of ovarian cyst symptoms
Cyst rupture is usually accompanied by a clinical picture of the so-called “acute abdomen.”
Before the onset of the main symptoms of ovarian cyst rupture, nagging pain in the lower back, a feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen, and discomfort in the pelvic organs are possible.
Symptoms:
- Increased body temperature (from 38 degrees and above), which antipyretic medications cannot cope with
- Sharp pain in the lower abdomen that increases (doctors compare it to a dagger strike). The pain may radiate to other parts of the abdomen - the upper region, for example
- General weakness, semi-fainting (fainting is also possible)
- Bleeding from the uterus
- Unusual vaginal discharge (especially bloody)
- Nausea, vomiting
- Intestinal disorders
- Blue or pale skin
- Low blood pressure, blood pressure surges
- Rapid heartbeat that increases in intensity
The last two symptoms of a ruptured ovarian cyst are considered especially alarming, as they may indicate internal bleeding, which is life-threatening.
However, this does not mean that you can give up on the other symptoms of a ruptured ovarian cyst listed in the list. All of them should be a reason for immediate hospitalization of the patient and urgent surgery.
You should be aware that symptoms of a ruptured ovarian cyst may differ in nature and intensity, depending on the type of cyst, the general health of the woman and the day of the menstrual cycle when the rupture occurred.
Symptoms of a ruptured corpus luteum ovarian cyst:
- Sharp, piercing pain in the lower abdomen, from which the patient literally folds in half
- Weakness
- Cold sweat
- Signs of intoxication
- Body temperature may remain normal
Symptoms of ruptured follicular (functional) ovarian cyst:
- Dagger pain syndrome in the lower abdomen
- Signs of intoxication
- Body temperature may not rise
- Weakness, dizziness, pale skin, rapid heartbeat, low blood pressure (with hemorrhage in the peritoneum)
- Bloody vaginal discharge
Symptoms of a ruptured endometrioid ovarian cyst:
- Pain in the lower abdomen comes in attacks
- Nausea, vomiting
- Loss of consciousness
- Bloating
- Constipation
- Body temperature may remain normal
Reasons for education
In gynecology today there is no clear answer to the question of what causes the development of two-chamber cysts. Information is constantly being studied and data is being improved.
Practicing gynecologists have identified only a few key points that can cause the appearance of formation.
- Hormonal imbalance. The reason is considered one of the main ones. Against the background of hormone imbalance, the formation of ovarian cysts cannot be ruled out.
- Physiological problems leading to menstrual irregularities. This reason largely provokes the development of a corpus luteum cyst.
- Pregnancy is one of the causes of the disease.
- Diseases of the genital organs suffered by a woman of an inflammatory nature that are of a bacterial nature.
- Surgery on the organs of the reproductive system.
These are just some of the reasons that provoke the appearance of a cyst. Gynecologists note that abortions and late puberty may be the cause of the disease.
It is also necessary to take into account the time of the onset of menstruation; there is an opinion that neoplasms appear more often if menstruation began early, at about 11 years of age.
Diseases of the reproductive system can provoke the development of benign formations.
Rupture of ovarian cyst: diagnosis, treatment
To confirm the diagnosis of a ruptured ovarian cyst, different types of diagnostic tests may be used:
- Ultrasound
- Puncture
- Laparoscopy (examination can be combined immediately with removal surgery)
If there is a suspicion of cyst rupture, the patient is immediately hospitalized, and a final preoperative diagnosis is established in the hospital.
Conservative treatment (drug) can only be used for mild forms of pathology. But more often, rupture of an ovarian cyst is accompanied by complications, so radical surgical intervention is recommended.
The modern method of laparoscopy allows the operation to be performed using the most gentle method.
After the operation, the patient is prescribed anti-inflammatory drugs, physiotherapeutic procedures (to avoid the formation of adhesions), and hormonal therapy. In case of large blood loss, a blood transfusion is performed.
Diagnostics
Sometimes pathology can be diagnosed in the absence of symptoms during a routine examination. A gynecologist can palpate a large lump. But most often a woman turns to a specialist after the first signs appear. In addition to the examination, the following diagnostic methods will be required:
- Ultrasound or computed tomography. With the help of the study, the size of the neoplasm, its location, and also determine how many chambers the cavity contains are determined;
- a biopsy (puncture) allows you to find out the nature of the tumor (benign or malignant). To carry it out, capsule cells are taken and sent for histological examination;
- blood and urine tests;
- a smear is necessary to determine whether hidden sexually transmitted infections are present.
Rupture of an ovarian cyst during pregnancy
It is not uncommon for ovarian cysts to develop during pregnancy.
The consequences of a ruptured ovarian cyst during pregnancy can be dire, including miscarriage or premature birth.
Laparoscopy allows you to remove the cyst at 14-16 weeks of pregnancy - in case of rapid growth of the tumor, which will be confirmed by ultrasound examination.
First of all, it is recommended to undergo removal surgery to avoid rupture of the ovarian cyst for pregnant women with cystadenoma (benign tumor) and endometrioma (“chocolate” cyst). The consequences of rupture of these cysts are the most serious (even hemorrhage into the peritoneum), so they are removed, despite the stage of pregnancy.
Preventive measures
Everyone knows that it is better to prevent a disease than to treat it later. Women definitely need:
- Visit a gynecologist once every 6 months;
- Treatment of inflammation in the peritoneum;
- If a cyst is detected, strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations;
- If the doctor advises removing the cyst, listen to his recommendation;
- Plan conception in advance, get all tests done beforehand;
- If you have any pain symptoms in the abdominal area, you should consult a doctor.
Compliance with all these rules will not lead to rupture of the cyst and further surgical intervention. Only the woman herself can be the first to identify malfunctions in the body and, by contacting a gynecologist in time, will be able to avoid irreversible consequences.
ONLINE REGISTRATION at the DIANA clinic
You can sign up by calling the toll-free phone number 8-800-707-15-60 or filling out the contact form. In this case, we will contact you ourselves.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
Rupture of an ovarian cyst: possible complications
The sooner medical assistance is provided for a ruptured ovarian cyst, the less consequences will be for the female body.
In no case should you ignore the symptoms of a ruptured ovarian cyst, attributing them to a common illness and hoping that they will go away on their own. This can only aggravate the situation, causing infertility (at best).
Complications due to rupture of an ovarian cyst:
- Peritonitis (purulent inflammation of the abdominal cavity)
- Sepsis (blood poisoning)
- Complete removal of the affected ovary
- In some cases, death
Treatment options
Only after a complete diagnosis of an ovarian cyst does the doctor prescribe treatment. It will depend on its size, location and many other features. Small tumors can be treated with conservative methods. Hormonal drugs are usually prescribed. The effect is noticeable if the formation is of a functional type. Therapy lasts several months, then the lump resolves on its own.
In addition, medications are used for complications (suppuration, rupture of the membrane). Anti-inflammatory drugs and antibacterial drugs are used. They may be required if the patient is additionally found to have concomitant genital tract infections.
In other cases, the capsule must be removed along with its contents. Large cysts cannot be cured with medication, so surgery is prescribed. Classic abdominal surgery is used in cases where the thickening has reached a large size. Anesthesia is used for this. The surgeon excises the abdominal cavity and removes the capsule using a scalpel. At the end of the procedure, sutures (most often self-absorbing) are applied. During the recovery period, the patient needs to use antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs.
A less painful method is laparoscopy. It involves making several pinpoint incisions through which the tumor is removed. Laparoscopy is used if it has still slightly increased in diameter.
In the most severe cases, when healthy tissues are also affected, the doctor decides to remove the ovary on which the tumor is developing. However, they try to avoid this. Pregnant women are usually not prescribed surgery unless the cyst poses a threat to her life or health.
A two-chamber capsule on the ovary is a dangerous type of cystic formation. It often degenerates into a malignant tumor, so it requires a quick response. Treatment can be conservative, but most often the doctor decides to surgically remove the cavity along with its contents.
Author: Nasrullaev Murad
Candidate of Medical Sciences, mammologist-oncologist, surgeon
A two-chamber ovarian cyst is a benign neoplasm, which is divided by thin partitions into several chambers, filled with fluid inside, sometimes mixed with blood. The disease is diagnosed in young women, usually under 40 years of age, when the reproductive system is at its peak of activity. Next, we will consider in more detail what a two-chamber ovarian cyst is, its causes, symptoms, as well as methods of diagnosis and treatment.
Cystic neoplasm with septum on ultrasound
Rupture of an ovarian cyst - consequences for a woman
Due to complications, the patient may develop more far-reaching consequences that affect the quality of future life.
Among them:
- Anemia (anemia due to extensive blood loss during rupture)
- Disorders of the abdominal organs due to the consequences of purulent peritonitis, requiring repeated operations
- Adhesions that increase the risk of ectopic pregnancy or infertility
- Infertility or problems conceiving as a result of complete removal of one ovary