What's happened
The female half of the population is often diagnosed with various cysts. Their formation is facilitated by an overripe follicle, inside of which there is an egg nucleus.
In the middle of the menstrual cycle, a natural rupture of the follicle occurs. As a result, the nucleus is released, which helps the woman conceive.
When fertilization does not occur, the egg dies. In place of the follicle, a corpus luteum appears, capable of producing hormones. Normally, it leaves the female body during the onset of menstruation, which contributes to the repetition of the cycle.
On this topic
- Female reproductive system
Differences between cytology and colposcopy
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- December 6, 2020
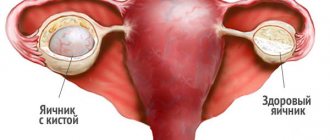
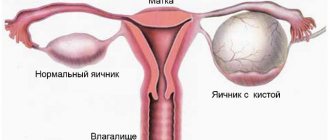
A hemorrhagic cystic formation is formed when the follicle does not rupture, its cavity is filled with fluid, and it remains inside the ovary.
This is a growth with an empty cavity. It forms on the surface of the ovary and fills with blood clots.
The development of a pathological process on the right ovary is often noted. This is explained by the increased intensity of its blood supply, in contrast to the left organ, which is fed with blood fluid through the renal artery.
https://youtu.be/Vn5U5U-hwyw
Classification
Depending on the location, a hemorrhagic cyst can be unilateral, which occurs in most cases, or bilateral.
In size, cystic neoplasms can range from several millimeters to several centimeters and are classified into two types:
- functional;
- pathological.
Small-sized formations have a predisposition to disappear on their own. For cystic growths of impressive volume, surgical intervention or drug therapy is required.
Possibility of conception
It is advisable to plan pregnancy no earlier than 3–4 months after removal of the hemorrhagic cyst by laparoscopy, and 6 months after laparotomy. This period is necessary for the complete restoration of ovarian tissue, strengthening the body, and complete healing of the sutures.
https://youtu.be/yFu38wj00vs
A cyst is a capsule that can form on any organ.
This benign neoplasm does not pose a threat to the life and health of its “owner” and can even resolve.
But when the cavity of such a capsule is filled with blood, pus or serous fluid, a simple cyst turns into a hemorrhagic one, which can lead to quite sad consequences.
Causes
One of the most common provoking factors is hormonal imbalance, which can be caused by various conditions:
- pregnancy;
- taking medications that contain hormones;
- disorders ;
- menopause;
- stress;
- medical miscarriage;
- diseases of the endocrine system.
The reason for the formation of a hemorrhagic cyst is the occurrence of inflammatory processes in the body that affect one of the organs, as well as diseases, the route of infection of which is sexual intercourse.
As a rule, a functional cyst that arises from a whole follicle is not dangerous to women’s health and disappears on its own.
When blood fluid enters the cavity, the cyst takes on a hemorrhagic form. Such growths form at the site of a burst follicle from the corpus luteum.
On this topic
- Female reproductive system
Echosigns of adenomyosis
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- December 4, 2020
The main danger lies in the fact that the contents of such a neoplasm can penetrate into the abdominal cavity and provoke the development of more serious, often irreversible consequences, even death.
Hemorrhage can be observed both in the cavity of the growth itself, and can be diffuse in nature, which is even more dangerous to health, since blood is poured into the peritoneum. Such a disorder can be provoked by lifting weights, excessive physical exertion, or active sexual intercourse.
Consequences and complications of hemorrhagic cyst
A cyst with hemorrhagic contents that occurs against the background of functional ovarian formations is prone to spontaneous regression. It resolves on its own within 1-3 months. The woman does not experience any sensations. You can find out that the pathology has gone away by performing an ultrasound.
In rare cases, the cyst does not regress and continues to grow, leading to the development of complications:
- Torsion of the legs. It is noted when a formation forms on a thin cord. Occurs after physical activity or sex. Accompanied by severe pain in the lower abdomen, nausea, vomiting and signs of abdominal tension. Threatens ovarian necrosis and loss of function.
- Capsule rupture. Risk factors and symptoms are similar to torsion of the cyst stalk. A distinctive sign is the appearance of bloody discharge from the genital tract. With continued bleeding, a decrease in blood pressure and loss of consciousness are observed. Threatens the development of peritonitis.
- Infection. Suppuration occurs with concomitant infection of the ovaries. Leads to an increase in body temperature and increased pain in the lower abdomen. Without treatment it leads to peritonitis and sepsis.
Malignancy is not typical for hemorrhagic cysts. A follicular formation is not capable of becoming a malignant tumor, since there are no corresponding cells in its structure. Corpus luteum cysts almost never become malignant. There is no reliable data on this issue, but by default it is considered exclusively benign.
Hemorrhagic ovarian cysts affect a woman’s reproductive function in different ways. Conceiving a child against the background of follicular formation is almost impossible. While it exists, ovulation does not occur. A luteal cyst does not interfere with the conception of a child and can persist until 18-20 weeks.
Symptoms
Often, patients may not be aware that they have a disease such as a hemorrhagic cyst, since it does not show any signs. As the pathological process develops, it is accompanied by:
- bloating, heaviness, discomfort in the lower abdomen;
- nausea;
- painful sensations from the affected organ;
- increased fatigue;
- heavy bleeding during menstruation;
- irregular menstruation.
Hormonal imbalances may be indicated by a rash on the face, frequent mood swings and increased glandular glands.
According to most experts, the course of a hemorrhagic cyst of the right ovary is much more severe than when the organ is affected on the left side. This is due to the increased blood supply to the appendage located on the right.
As a result, if blood fluid enters the pathological organ excessively, the risk of complications increases.
Methods of therapy
When treating a hemorrhagic ovarian cyst without surgery, the patient needs to apply a cold compress to the lower abdominal cavity and lie down more. The doctor usually prescribes treatment with anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drugs, agents that produce a resolving effect. But if there are complications and regression of the cyst, it is necessary to immediately perform one of the following types of surgical treatment.
The final diagnosis of hemorrhagic cystosis is made based on the following conditions:
- Patients feel nagging pain in the lower abdomen, as well as attacks of nausea.
- When examined by a gynecologist, pain in the abdominal area is detected during palpation of the iliac region. There is an enlargement of the appendages, which can also be painful.
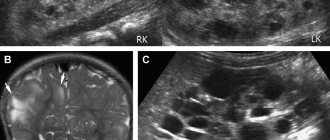
- Ultrasound reveals a round anechoic neoplasm, with septations inside and uneven structures in the ovary.
- A laparoscopic examination highlights changes in the form of ovarian tuberosity, as well as the presence of a cystic neoplasm filled with contents on it. In cases of inflammation accompanying cystosis, fibrin deposits may be found around the ovaries.
- MRI can reveal the degree of development of a hemorrhagic cystic neoplasm. MR signals in the case of this pathology will be more intense than with other cysts.
Hemorrhagic contents of a cystic formation
It is important for women undergoing treatment to strictly follow the recommendations of their doctor. During an exacerbation, it is better to follow a limited regime while staying in bed, and apply a cold compress to the lower abdominal area. As a rule, during this period, medications with antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects are prescribed in order to prevent the development of complications in the form of bleeding in the ovarian area or, which is much more dangerous, in the peritoneal cavity.
The characteristic features of hemorrhagic neoplasms in the form of cysts are difficult to treat, therefore, if hormonal drugs and drugs with absorbable properties are ineffective, the only way to help is surgery.
A hemorrhagic cyst of the left ovary usually does not require treatment. More often, the functional formation resolves on its own when the triggering unfavorable risk factors are eliminated in the next menstrual cycle. However, tumors must be monitored: ultrasound is repeated every month. If the study reveals repression of the process, then the woman does not need therapy.
In the absence of dynamics, the tumor is located on the right side due to the increased risk of complications: rupture and torsion, many gynecologists prefer to start treatment. To eliminate the pathology, drug hormone therapy or surgical treatment is used.
Medication
In most cases, functional formations regress on their own. If the tumor is large enough, a woman needs to limit her sex life and sports to prevent rupture. In order to speed up the process, patients are prescribed hormonal contraceptives for 1–2 cycles. Then the dynamics of the pathology is monitored.
Long-term hormone therapy is indicated for patients who are not planning pregnancy in the near future. This is due to the fact that long-term treatment is required to obtain a lasting result. Some experts are convinced that there is a risk of recurrence of the hemorrhagic cyst after discontinuation of drugs in a short cycle of use. Surgical removal of the formation is considered more effective.
Laparoscopy is usually used to remove cysts. During the intervention, uncomplicated tumors are removed and the ovary is practically not injured.
A serious situation occurs when there is suppuration or rupture of the lesion. In this case, it is not always possible to save the ovary. After excision of the appendages on one side, a woman may well become pregnant and carry a child.
Removed tissues are always sent for histological examination to study the cellular structure and exclude tumor transformation.
Diagnostics
To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor prescribes a special diagnostic examination.
Survey
When talking with a patient, the specialist hears mainly complaints about pain in the lower abdomen from the affected organ. This condition is often accompanied by nausea.
Inspection
The procedure is accompanied by discomfort and pain. Upon palpation, an increase in the size of the ovary is observed, which indicates the formation of a neoplasm.
Ultrasonography
Using this method, it is possible to confirm that there is an anechoic formation, which has a round shape and partitions on the inside. This growth is located on the surface of the organ.
Magnetic resonance imaging
Using MRI, you can identify the stage of growth formation. If hemorrhagic contents are present, the signals become more intense.
Laparoscopy
It makes it possible to visualize changes in the ovary, the surface of which becomes lumpy, and a cyst with contents of a liquid consistency is clearly visible on it. If inflammation is present, fibrinous deposits will be visible on the surface of the affected organ.
Proper diagnostic measures make it possible to select the correct and most effective treatment, which will allow the woman to return to her previous lifestyle.
Treatment
Based on the results of the diagnostic study, the specialist makes a decision regarding the method of carrying out therapeutic measures. In this case, it is necessary to take into account the size of the cystic tumor, the severity of the clinical picture and the likelihood of complications.
Medication
In cases where the course of the pathological process is not accompanied by pronounced symptoms and the risk of negative consequences is minimal, preference is given to drug therapy.
If the formation of a cyst was provoked by hormonal disorders, Duphaston is prescribed.
Taking contraceptive drugs (Janine) gives a positive result in the presence of small cysts. The effect of the medication is aimed at reducing nodes and eliminating the pathological condition. This remedy helps reduce the load on the ovaries.
On this topic
- Female reproductive system
Do I need to remove an ovarian cyst if it doesn’t bother me?
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- December 4, 2020
During drug therapy, the patient is constantly under the supervision of a specialist and regularly undergoes ultrasound examinations.
If an inflammatory reaction is diagnosed, the doctor prescribes antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Operational
In cases where no positive result is observed from drug treatment and the cystic neoplasm continues to grow, surgical intervention is prescribed. Indications for surgery may also include:
- the likelihood of complications in the form of cyst torsion, rupture or suppuration;
- diagnosing a hemorrhagic node in a teenage girl.
Operational activities can be carried out in several ways.
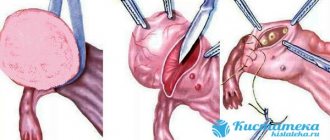
Husking
It is one of the most commonly used techniques in the treatment of cystic formation. When performing such an operation, specialists are able to preserve the affected ovary, as well as reproductive function.
Removal of the cyst and its contents without affecting the organ itself is possible in cases where there are no prerequisites for degeneration into a malignant tumor, and also if the growth is small in size.
Wedge resection
This method is indicated for changes in tissue resulting from compression by a cystic neoplasm, which creates difficulties during ovulation. Using the laparoscopic method, part of the ovary, which has a triangular shape, is removed.
Oophorectomy
Radical surgery is prescribed for women who have reached 45 years of age, or if the patient has already given birth, she has a high risk of rupture of the formation.
During the procedure, only the pathological ovary is removed, which does not interfere with future pregnancy planning.
How to treat hemorrhagic ovarian cyst
Since hemorrhagic cysts are functional, surgical intervention is required only if there is a high risk of their rupture. In other cases, patients are prescribed conservative therapy, which consists of taking hormonal medications.
If such a tactic for treating a hemorrhagic cyst is chosen, then women should undergo regular ultrasound so that the doctor can monitor the dynamics of the process, since in the absence or stopping of regression of the tumor, the patient is recommended to remove the formation surgically.
If the patient has obesity or anorexia, she is recommended to take measures to normalize body weight in order to normalize hormonal levels and increase the effectiveness of the therapy.
Depending on the size and location of the cystic cavity, the woman’s age and her desire to have children in the future, the type of operation is determined.
Enucleation of the cyst
This method of surgical intervention is used most often, since it allows you to preserve the ovary and its reproductive function, since it involves removing only the cyst. It is indicated in the absence of prerequisites for the development of cancer.
Wedge resection
During the operation, in addition to the cyst, a triangle-shaped section of the ovary must be removed. It is carried out when organ tissue changes due to prolonged compression by a neoplasm or other reasons.
How is surgery to remove an ovarian cyst performed?
https://youtu.be/TGyKC7zbY4s
Removal of an ovary with a cyst
Such radical surgery is performed less and less often today. Typically, it is performed on patients over 45 years of age with large or multiple tumors and a high risk of rupture.
- But if a woman is diagnosed with a hemorrhagic cyst on the left ovary and the decision is made to remove it, she will still be able to get pregnant thanks to the remaining right ovary.
- In women during menopause, the fallopian tube may also be removed along with the ovary.
Complications
If you do not seek qualified help in a timely manner, this can lead to serious consequences, of which in most cases rupture of hemorrhagic formations and their suppuration occur.
Cyst rupture is a common complication. The greatest danger is the development of peritonitis, which is caused by the penetration of tumor contents into the peritoneal cavity, which requires emergency surgical intervention.
Often, in the presence of a cyst, problems with conception arise. But if pregnancy has occurred, its course may become complicated due to a pathological process, which often manifests itself in the form of regression of the tumor under the influence of hormonal changes.
On this topic
- Female reproductive system
Can there be a delay and a positive test for an ovarian cyst?
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- December 4, 2020
Until 15 weeks, doctors choose a wait-and-see approach. If the cyst persists, surgery is prescribed followed by removal of the tumor, which will prevent such consequences as:
- cyst rupture;
- compression of the uterus;
- abnormal position of the fetus;
- malignancy of the process.
To prevent such consequences, at the first suspicion of a disease, you should immediately contact a medical facility.
Consequences of developing ovarian cysts
The consequences of the development of cystosis in the ovary are very diverse. Most often, complications such as rupture of the cystic formation and suppuration in the ovarian cyst occur.
Rupture of the cystic formation is the most common complication that occurs with the development of ovarian cysts. This type of complication occurs as a result of the cyst enlarging and putting pressure on the surrounding pelvic organs. The main consequence of rupture of the cystic formation is the development of peritonitis. Peritonitis is accompanied by inflammation of the peritoneum. When this complication develops, emergency surgery is performed to clean the abdominal cavity from the spilled contents of the cystic formation. Simultaneously with the process of cleaning the abdominal cavity, operations are carried out to resect the remnants of the cyst.
Developing hemorrhagic ovarian cysts provokes the development of complications such as infertility.
When cystosis develops during pregnancy, the most negative complication is miscarriage. During pregnancy, the condition of the cyst is regularly monitored. If necessary, it is removed by laparoscopy.