The presence of any pathology can throw a pregnant woman into panic, but the most worrying thing is caused by diseases that affect the reproductive organs. Against the background of a full-scale hormonal restructuring of the body, which is associated with the upcoming birth of a new life, very often women are diagnosed with an ovarian cyst during pregnancy.
The neoplasm could develop in the gonad before the moment of conception, but whenever it appears, the expectant mother is always concerned about the question: is the cyst dangerous for her and her child? In this article you will find the answer to the question posed and a lot of useful information about methods of treating cysts during pregnancy.
About the cyst
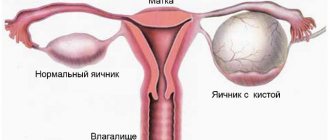
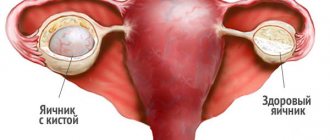
An ovarian cyst is a pathological formation of benign origin, which can form from the corpus luteum, follicle, endometrial and other tissues. Similar tumors can occur on any of the gonads. The size of the formation can vary from a few millimeters to several tens of centimeters. To prevent harmful consequences, it is imperative to treat the cyst, no matter what type it is.
The most common cause of cyst formation is hormonal imbalance, which occurs due to stress, strict diets, overeating, climate change, and alcohol abuse. If the tumor arose due to these factors in the early stages of pregnancy, then in order for the tumor to resolve, in most cases it is enough to simply remove the cause of the hormonal imbalance. Gynecological manipulations (abortion, cesarean section, poorly performed gynecological examination, installation of an IUD), gynecological pathologies and diseases of other organs, as well as harmful living conditions can also provoke the development of a tumor.
As practice shows, a benign tumor of the left ovary during pregnancy is less dangerous for the health of the mother and embryo, since it less often leads to all kinds of complications. This is explained by the anatomical features of the paired organ. A cyst of the right ovary is more dangerous because in this area there is more intense blood circulation and a more branched vascular network.
Causes of ovarian cysts during pregnancy
Can an ovarian cyst develop during pregnancy, and for what reasons? Today doctors cannot answer this question unambiguously. There are certain factors that contribute to the development of ovarian cysts during pregnancy:
- hormonal disorders;
- congenital predisposition of the body;
- diet disorders that provoke hormone imbalance;
- post-traumatic disorders and stress;
- psycho-emotional lability;
- taking contraceptives for a long time;
- early puberty;
- disorders of the monthly cycle;
- overweight or underweight;
- excessively frequent abortions;
- lack of coitus;
- early cessation of lactation;
- infectious processes in the body;
- bad habits;
- inflammatory diseases of the reproductive organs.
What are the dangers during pregnancy?
If a woman is found to have an ovarian cyst and pregnancy at the same time, there is no need to worry too much, since the formation in most cases does not pose a threat to the mother and fetus, although there is still a potential danger of developing various kinds of complications. You need to be wary of cysts that have increased in size to 6 mm or more. Such formations have a high risk of rupture with subsequent spillage of contents into the abdominal cavity. Also, when a rupture occurs, blood loss may develop, which causes severe pain in the abdomen, nausea and vomiting; the woman may lose her blood and be in a state of hypovolemic or hemorrhagic shock. The rupture of a cyst can result in the death of a pregnant woman; also, a similar condition can affect the condition of the fetus, causing the following disorders:
- severe oxygen starvation of the fetus;
- problems with embryo development;
- fetal freezing;
- intrauterine embryo death;
- spontaneous abortion or premature birth.
If the tumor ruptures, an operation should be immediately performed to completely or partially excise the affected organ; this can lead to the loss of the child, but there is also a good outcome from such operations when both mother and child remain alive and healthy.
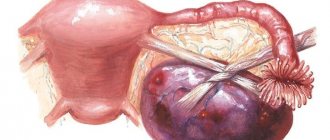
Another dangerous complication is torsion of the pedicle of the neoplasm. This is such a painful condition that the woman takes a forced position, bending over and pressing her knees to her stomach. When the pedicle of the cyst is twisted, the blood vessels that penetrate it are compressed, which leads to the cessation of blood supply and to the death of the neoplasm itself. Necrotic processes are fraught with the spread of toxins and decay products not only throughout the mother’s body, but also through the unborn baby.
Torsion and rupture of the cyst are the most dangerous and common complications, but the possibility of malignancy of the tumor should not be excluded. If the tumor is large, it physically affects nearby tissues and disrupts blood circulation in them, promoting the development of inflammation.
The effect of the cyst depending on the type
A cyst during pregnancy in most cases is not dangerous for mother and child, but the possibility of complications always remains. There are several types of cystic tumors. Let's look at how a cyst affects pregnancy depending on its type:
- luteal or corpus luteum cyst. It appears more often than other varieties, often in early pregnancy. The corpus luteum is transformed into a cystic sac; such a neoplasm resolves on its own when the fully formed placenta takes over the function of producing progesterone. Such tumors are small in size, so they are safe for both the mother and the fetus;
- endometrioid. Due to the tendency to grow rapidly, this type of tumor can cause serious complications. Sometimes the tumor can grow up to 30 cm in diameter, causing severe and persistent abdominal pain. Since there is a high probability of cyst rupture, it must be removed surgically at any stage of pregnancy immediately upon detection;
- follicular. Most often, such a neoplasm occurs when the endocrine system malfunctions, as a result of which the ovaries intensively produce estrogen, and a single-phase anovulatory menstrual cycle begins. Sometimes such tumors can resolve on their own, even without taking medications, provided that hormonal levels are restored. In the early stages of pregnancy, it is necessary to monitor the development of tumors of this type, since their active growth can result in torsion of the cyst stalk or its rupture, which entails poisoning of the body and death of the pregnant woman in the absence of adequate treatment;
- paraovarian. Such a cyst is dangerous due to rupture and torsion of the leg, suppuration and the development of an acute abdomen. It can develop in women of any age due to improper development of the accessory tubules. The tumor has the appearance of a cavity in the appendage, lined with epithelial tissue, which is filled with a mucinous substance with exudate. Since the cyst is supplied with blood by the vessels of the walls of the uterus and its tubes, it can cause their deformation. The only positive point is that this type of tumor does not become malignant;
- dermoid. These are congenital cysts, they appear at the stage of intrauterine development and contain fragments of embryonic tissue under a dense membrane. Often such tumors are detected long before pregnancy during a preventive ultrasound of the pelvic organs. Dermoids cannot be treated conservatively and require mandatory removal.
Symptoms
Small neoplasms may not manifest themselves in any way at the initial stages of their development; they can only be seen during a routine ultrasound. Initially, expectant management is chosen; the pregnant woman will need to come for follow-up visits to the gynecologist more often.
When the tumor begins to increase in size, the following symptoms may occur:
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- problems with bowel movements;
- frequent trips to the toilet “in small ways”.
Pain may appear after physical activity, constipation and abdominal discomfort may occur. Such symptoms are provoked by a cyst that has grown in diameter and presses on the intestines.
Frequent urge to urinate is a normal occurrence for any pregnant woman, but when she also has an ovarian cyst, which has increased in size to more than 6-8 mm, “small” visits to the toilet become too frequent even for the period of pregnancy. If the tumor is very large, it can cause nausea in a woman, even vomiting; the same symptoms can occur if the cystic sac ruptures.
Torsion of the leg and rupture of the cystic sac may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- severe sharp pain;
- increased body temperature;
- bloody discharge from the vagina;
- weakness, nausea, vomiting, fainting – symptoms of acute abdomen;
- when a right ovarian cyst ruptures, the symptoms resemble an attack of appendicitis;
- When a left ovarian cyst ruptures, the symptoms are similar to a stomach ulcer and its perforation.
Treatment during pregnancy
The presence of a cystic formation in the gonad can be determined during a gynecological examination and ultrasound, but it is possible to say specifically what to do with this tumor only after determining its type; until this moment, a woman with any type of cyst is registered and the development is monitored as a neoplasm , and the fruit.
The main tactic when detecting an ovarian cyst during pregnancy is waiting. Small follicular and luteal cysts usually resolve during the 1st trimester. If it is determined that the tumor has developed due to progesterone deficiency, the specialist may prescribe Duphaston. When the tumor continues to grow and does not respond to treatment, surgery is prescribed.
If a tumor appeared or was discovered in the second trimester, there is no need to be afraid, at this stage it does not pose a threat to either the mother or the fetus, and it does not interfere with natural delivery. After the birth of the baby, the woman is recommended to undergo additional treatment. If the tumor is large or is likely to rupture, surgery may be prescribed to remove it.
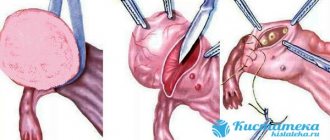
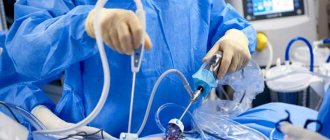
Removal of a cyst during pregnancy is allowed in the 2nd trimester (14-16 weeks). Typically, the laparoscopic method is used for this. The operation lasts 1-1.5 hours under intravenous anesthesia. This is a low-traumatic operation, during which 3 small punctures are made in the anterior abdominal wall, through which all the necessary instruments are inserted. In emergency cases, when the cystic sac has ruptured, the tumor is very large, or there is confirmation of the presence of malignant cells in it, a laparotomy is performed. This is an abdominal operation that carries great risks to the life of both mother and child.
If the complications listed above occur in a pregnant woman in the third trimester, when the fetus has reached a viable age, she is recommended to resort to early delivery through cesarean section, while at the same time the cystic neoplasm is removed during the operation.
Treatment of ovarian cysts discovered during pregnancy
As a rule, functional cystic formations such as follicular cysts and corpus luteum cysts do not require surgical intervention. It is enough to monitor them during pregnancy using ultrasound. Surgical treatment of large ovarian cysts is advisable to carry out at the stage of pregnancy planning.
This refers to ovarian cystic formations that do not regress within three cycles or are pathological. If the ovarian cyst becomes large, it must be removed, as it will undoubtedly pose a threat during pregnancy. There is no doubt about the need to perform laparoscopy or laparotomy in case of torsion and rupture of an ovarian cyst.
It is considered advisable to perform laparoscopic removal of an ovarian cyst during pregnancy only if necessary. As a rule, they first wait until the baby is born, and only then, if necessary, perform laparoscopy and remove the cyst. If the laparoscopic method of treating a cyst in a particular case is unacceptable, then a laparotomy approach is used to remove the cystic formation. During laparotomy, the anterior layer of the uterine ligament is dissected, then the cyst is carefully removed within healthy tissue. In this case, the ovaries are not damaged.
In order to reduce the risk of miscarriage after removal of the cyst, the patient in the postoperative period is prescribed therapy aimed at maintaining pregnancy.
Pregnancy after cyst removal
Pregnancy may well occur after laparoscopy of a cyst and even after laparotomy, but only if only the neoplasm was removed without excision of the ovary. Pregnancy is also possible with one ovary, but in this case problems may arise with conception, then you should resort to IVF.
On the second day after laparoscopy, the patient needs to get up and move independently to prevent the development of adhesions. Since the puncture wounds are very small, the pain will not cause much discomfort to the woman. To prevent the development of infectious complications, a woman is prescribed to drink antibiotics and, if necessary, painkillers for 3-5 days. In a hospital setting, the operated patient is observed for no more than 5 days.
For a week after the operation, a woman must adhere to a diet, eat food mainly in liquid form, be sure to perform hygiene procedures, take a shower, but exclude baths, saunas, steam baths and swimming pools. Puncture sites should be treated with a solution of potassium permanganate. To fully restore reproductive function, your doctor may prescribe hormonal medications. You can start planning conception no earlier than a few months after the operation and with the permission of the doctor.
Planning a pregnancy
After minimally invasive surgery to remove an ovarian cyst or sclerocystic disease, you can plan to conceive a child after 3-6 months. There are no clear deadlines here. It is assumed that after the next control ultrasound and examination by a doctor, the woman will receive further recommendations on how to restore the body or permission to bear a child.
With a successful course of the postoperative period, pregnancy can occur already in the first ovulatory cycle. Menstruation comes 25-35 days after laparoscopy, less often it delays up to 40-60 days. Without contraception during this period, fertilization and implantation of the embryo into the uterine wall may occur. But such a pregnancy rarely ends well. Surgery is a serious stress for the body, and it requires time to recover. The minimum period for rehabilitation after laparoscopy is considered to be 3 months.
After the operation, the chances of spontaneous pregnancy increase, but time is required for the body to recover.
Negative consequences of pregnancy occurring in the first three months after surgery:
- Impaired implantation of the fertilized egg and termination of pregnancy before missed menstruation;
- Spontaneous miscarriage before 22 weeks;
- Premature birth (22-37 weeks);
- Placental insufficiency with impaired blood flow in the mother-placenta-fetus system and the development of fetal hypoxia;
- Intrauterine growth retardation.
It is also useful to read: Nuances of IVF for polycystic ovary syndrome and single cyst
It is difficult to say how long you need to wait after surgery - 3, 6 or 9 months. Everything is determined by the course of the rehabilitation period and the general condition of the woman. If there are no complications, you can plan to conceive a child after 3 months. If there are problems, you should wait at least six months.
The timing of contraception cancellation after surgery is determined by the attending physician individually, depending on the extent of the operation and the course of the postoperative period.
It is important to know
After removal of an endometrioid ovarian cyst or surgery for polycystic disease, you should not delay conceiving a child. A woman should become pregnant within a year after surgery. After 12 months, the likelihood of disease recurrence increases and repeated treatment may be required.
In the first 3 months after surgery, it is recommended to take contraceptives. The best option is combined oral contraceptives. Taking COCs also helps speed up the conception of a child. When the drug is discontinued, ovulation is stimulated. The effect lasts for 2-3 cycles.
Reviews of laparoscopy performed for ovarian pathology vary. Many women note that it was the operation that helped them get pregnant and give birth to a long-awaited child. The effectiveness of surgical treatment for a single cyst is close to 95%, and for polycystic ovary syndrome it is about 70%.
Can a cyst give a positive test?
The development of functional type cysts can most often be provoked by hormonal imbalance, one of the symptoms of which can be an irregular menstrual cycle. It is quite natural that a woman who does not suspect the presence of a cyst on her gonads may perceive a delay in menstruation as a sign of pregnancy. The first thing the fair sex does in this case is, of course, buy a pregnancy test. If conception does not occur, but the test is positive, this may well mean that the woman has a corpus luteum cyst. It is quite possible to confuse a cyst with pregnancy in the early stages, since the neoplasm does not make itself felt in any other way; a visit to a gynecologist can clarify this.
A non-pregnancy test in the absence of conception can show a false positive result not only in the presence of hormone-dependent types of cysts, but also in other circumstances:
- if the test was carried out in violation of the operating instructions;
- if the test has expired or was stored and transported in violation of the standards;
- when using contraceptives;
- with irregular periods;
- during fetal development outside the uterus;
- in the presence of various ailments affecting the functioning of the ovaries.
If a pregnancy test shows a positive result, only a doctor can determine whether this is a symptom of impending conception or whether it is some kind of pathology.
Diagnostics
If a woman becomes pregnant, it is very difficult to suspect that she has an ovarian cyst in the early stages. Usually the tumor is detected during the first routine ultrasound. If the growth dynamics of the cyst is rapid, the woman may be prescribed additional tests to determine its nature: a puncture to exclude a malignant process, as well as a blood test for a tumor marker. It should be noted that tumor markers are not an indicator of the presence of cancer. Their slight increase may also indicate inflammatory processes.
Find out the instructions for using the medicinal herbal collection Alfit 9 for mastopathy of the mammary glands.
About the rules of nutrition and the peculiarities of following a diet for problems with the pancreas is written at this address.
On the page https://vse-o-gormonah.com/zabolevaniya/diabet/norma-sahara-u-beremennyh.html read about the reasons for deviations and about the normal blood sugar level in pregnant women according to the new standards.
https://youtu.be/h6zYjz_z1bY