About pathology
Cervical papillomavirus is a common infection that is now quite often found in women of reproductive age around the world. Numerous studies have proven that some of its types can cause the development of malignant neoplasms, so if this diagnosis is confirmed, treatment should be prescribed immediately.
There are several ways of infection with this virus:
- Unprotected sexual intercourse. A woman can become infected not only through vaginal sexual intercourse, but also through other types (anal, oral). Moreover, the virus can enter the body even through a kiss.
- Household way. In this case, you can become infected with the virus in a swimming pool, solarium, sauna and other public places. Often, infection occurs as a result of sharing personal hygiene items with a carrier of the virus.
- Vertical. Transmission of the virus from mother to child. A pregnant woman who has previously been diagnosed with papillomatosis must not only be checked by a gynecologist, but also undergo additional tests, since the virus can make itself felt at any time.
An artificial route of transmission is also known. The virus enters the body when medical personnel use unsterile instruments.
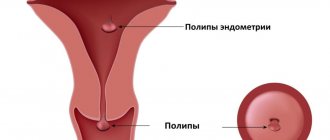
Papillomas in the cervix are of the following types:
- Flat. Single or multiple neoplasms with a rough surface and smooth borders. They rise slightly above the skin.
- Pointed papillomas. A type of wart. Condylomas have the appearance of papillary formations on a stalk. Most often occur in the genital and anal areas.
Causes of papilloma on the cervix
The main causes of papillomas on the cervix are unprotected sexual intercourse and poor personal hygiene (using other people's personal items: towels, toothbrushes, underwear, etc.).
Additional provoking factors for the development of cervical papillomatosis in women can be:
- weak immunity;
- early sexual life;
- frequent change of sexual partners;
- avitaminosis;
- long-term stress and prolonged depression;
- infectious pathologies in acute course;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- venereal diseases;
- cervical erosion;
- hormonal disorders or use of hormonal contraceptives.
Important: the virus remains in the human body for life and, under the influence of the above factors, can recur.
Prevention methods
Since clinical symptoms are absent in most cases, additional examination is required to identify papillomas on the cervix. Basically, examination of the cervix in speculum, colposcopy, and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) are used for diagnosis. If a malignant tumor is suspected, a histological examination (biopsy) is indicated.
Papillomas on the cervix are a dangerous pathology, the occurrence of which can be prevented. There are nonspecific and specific methods of prevention.
Specific
Specific prevention involves vaccination. Today, vaccination is the most effective and safe method of preventing human papillomavirus infection. This helps prevent the appearance of papillomas and protect against cervical cancer.
2 vaccines are registered:
- Cervarix – protects against HPV types 16 and 18;
- Gardasil – protects against HPV types 6, 11, 16 and 18.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with Papillomas will fall off if you add regular
Girls aged 10 to 25 years are subject to vaccination; the vaccination course consists of 3 doses.
The Gardasil vaccine effectively protects against infection with oncogenic strains of HPV
Nonspecific
Nonspecific prophylaxis will not protect against HPV with 100% probability, but will significantly reduce the risk of infection. Nonspecific methods of prevention have several main directions - preventing sexually transmitted infections, strengthening the immune system, and early detection of pathology. The following recommendations will help strengthen the immune system:
- proper nutrition with sufficient intake of vitamins and proteins;
- physical activity;
- avoiding hypothermia;
- timely treatment of concomitant diseases;
- use of medications strictly after consultation with a doctor (especially antibiotics and hormonal agents).
To prevent sexual infection with HPV, barrier contraception (use of condoms) is indicated. Early detection of pathology significantly increases the likelihood of a favorable outcome, so it is recommended to undergo regular gynecological examinations.
It is quite difficult to protect yourself from infection with the papilloma virus. Compliance with the rules of personal hygiene and culture of sexual life will significantly reduce the risk of disease.
The most effective way to protect the body from the influence of an infectious pathogen is vaccination. It is not possible to protect against all types of papillomavirus: vaccinations are designed for HPV 16, 18, 6, 11.
Strains 16 and 18 are responsible for 70% of cases of cervical and anal cancer and approximately 50% of transformations into carcinoma of the vagina, vulva, penis, and lower pharynx. Infection is prevented by Gardasil and Cervarix sera.
Strains 6 and 11 cause genital warts in most cases. To protect against them, the Gardasil vaccine is recommended (the only one registered for vaccination of boys and men).
In some European countries, vaccination against cervical cancer is included in the compulsory vaccination schedule.
Symptoms of cervical papilloma
Human papilloma in women on the cervix is manifested by the following symptoms:
- painful sensations in the genital area;
- the appearance of discharge with an unpleasant odor;
- the presence of vaginal bleeding not associated with menstruation;
- menstrual irregularities;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- deterioration of general condition (loss of appetite, weakness, weight loss);
- the occurrence of edema in the lower extremities (usually only one leg swells).
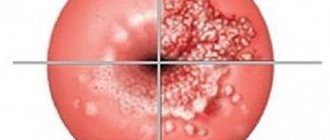
While examining the cervix using mirrors, the gynecologist detects the following changes:
- neoplasms are observed that look like pointed papillae or flat warts (the color of the epithelium remains unchanged);
- the epithelial tissue on the cervix becomes lumpy (indicating an acute course of the pathology);
- the presence of flat condyloma indicates the transition of the disease to a chronic form;
- epithelial dysplasia is a condition that precedes cancer;
- The oncological process most often develops in cases where not only papillomas, but also erosion are observed on the cervix. This is due to the fact that a defect in epithelial tissue provokes the development of papillomatosis.
The symptoms of papillomas on the cervix are very similar to the symptoms of other, no less serious and dangerous diseases, so do not put off visiting a doctor.
Symptoms and signs
After penetration into the body for a certain time, the human papillomavirus on the cervix is not diagnosed. The latent period can last from several weeks to several years. In the later stages, a woman complains of the appearance of uncharacteristic discharge (sometimes mixed with blood), enlarged inguinal lymph nodes, pain during intercourse, burning and dryness of the external genitalia.
Upon examination, the gynecologist determines the clinical picture characteristic of cervical papillomavirus:
- Change in color of the epithelium.
- Visualized cervical papillomas, the symptoms of which depend on the type of pathogen. Squamous cell papilloma of the cervix is characterized by clear boundaries and bright color. Condyloma acuminata is easily palpated and determined visually.
- Lumpiness of the epithelium with compactions and partial discoloration.
- Areas of dysplasia are a precancerous condition characterized by a predominance of atypical cells.
DETAILS: Mushrooms treat papilloma virus - Treatment of papillomas
It is common for papillomas on the cervix to become malignant if they are caused by oncogenic papillomaviruses of high and medium oncogenic risk. In 95% of cases, cervical cancer is caused by type 20, in 50% by type 16, and in 10% by type 18. A relationship has also been established between HPV and breast cancer.
The main symptoms of papillomas:
- manifestation of rashes;
- keratinization of the skin in the affected areas;
- swelling/swelling and redness of nearby skin;
- the appearance of unpleasant sensations in the form of itching or burning in the area where the rash appears.
Symptoms of the presence of squamous cell papilloma depend on the type and location of its location.
The appearance of squamous cell papillomas in the esophagus is very common, which can trigger the development of esophageal cancer. From the medical side, there is no definite answer why papillomas appear on the walls of the esophagus. However, first of all, papillomas are the most common type of diagnosed tumors.
If you have problems with the gastrointestinal tract, heartburn or pain in the epigastric region, contact a gastroenterologist. The main danger is that over time this pathology can turn into a cancerous form.
The main reasons for the appearance of papillomas on the esophageal mucosa:
- advanced form of gastritis;
- constant heartburn;
- eating spicy food;
- alcohol abuse.
When a rash occurs in the larynx, difficulty swallowing occurs, difficulty breathing and impaired diction are observed, and there is a feeling of the presence of a foreign body in the throat.
With a tumor in the stomach, nausea, increased salivation, belching, and pain in the abdominal area are observed.
Papillomas on the cervix during pregnancy
The manifestation of pathology during pregnancy is quite justified, since a woman experiences a change in hormonal levels and, as a result, her immunity sharply decreases. Do not forget that papillomatosis is a dangerous disease that, without appropriate treatment, can provoke the onset of oncology and lead to serious consequences, so a pregnant woman has quite logical questions: how to treat papillomas in the uterus during this period and whether this can be done at all.
It is advisable to treat papillomatosis, since ignoring the disease for a pregnant woman risks:
- termination of pregnancy;
- infection of the child during childbirth (infection can occur both during natural childbirth and after cesarean section).
Therapy is postponed until the third trimester (carried out from 28 weeks) and is carried out with extreme caution. Some doctors do not see any point in treatment at all, since there are risks of complications (exceptions are large condylomas, which interfere with natural delivery; they are recommended to be removed immediately).
In the absence of treatment, in some cases, neoplasms after childbirth decrease and completely resolve. So-called spontaneous healing occurs. But the likelihood of such a phenomenon decreases if a woman suffered from this disease before conception.
If the child was nevertheless infected during childbirth, then he may experience papillomatosis of the bronchi and larynx, and the presence of anogenital warts.
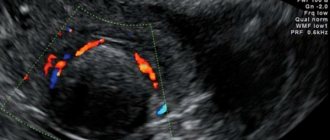
Diagnostics
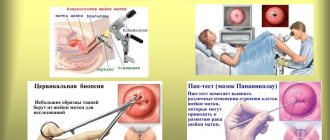
In most cases, the diagnosis of “human papillomavirus on the cervix” is made after the first examination by a gynecologist, but other additional diagnostic measures may be needed:
- colposcopy (diagnostic examination using a colposcope, which helps identify many gynecological diseases in the early stages);
- PCR method (a diagnostic method that helps in biomaterial samples to identify the type of pathogen);
Also, if the presence of papilloma on the cervix is suspected (detection of a malignant process), a cytological examination of the smear is performed.
Pap test results may look like this:
- Classes I and II mean that there are no tissue structure disorders;
- Class III means that additional histological examination is required;
- Class IV and V mean that atypical tissues are present and a process of malignancy is observed.
An important role is played by the differential diagnosis of cervical papilloma from other, no less dangerous diseases:
- Leiomyoma (a neoplasm that develops in the uterine cavity and is benign).
- Endometriosis of the cervix (a common gynecological pathology, which is characterized by the proliferation of tissue related to the uterine mucosa outside its boundaries).
- Erosive pathology (damage to uterine tissue resulting from the negative effects of infections, inflammatory processes and dysbacteriosis).
Doctors whose help you may need: gynecologist, venereologist, oncologist.
Flat (squamous) papillomas: signs, types, treatment
The formation forms on the surface of the epithelium of the cervix. The localization of papillomas covers the genital area. It is possible to diagnose both single and multiple neoplasms, characterized by a variety of shapes and structures.
Exophytic papillomas are pointed. Such formations progress in height. Endophytic papillomas are flat neoplasms that rise slightly above the epithelial surface.
Flat papillomas look like a rough area of mucous membrane. These neoplasms have a wide base and grow horizontally. The area where the flat papilloma is localized is slightly different in color from the rest of the tissue.
The structure of papillomas can be different. In particular, papillomas can be lined with the following type of epithelium:
- cylindrical;
- flat;
- transitional.
Neoplasms contain different amounts of elements that are inherent in connective tissue. In most cases, specialists diagnose squamous cell papilloma of the cervix, which is formed due to connective tissue and the flat appearance of the epithelium.
Squamous and other types of papillomas differ in their latent or incubation period. Thus, education has the characteristics of a disease. The latent period refers to the period of time that includes infection and clinical manifestations.
Treatment of cervical papilloma
Treatment of cervical papilloma is carried out comprehensively: using medications and surgery. It is impossible to cure papilloma at home. Therefore, you should not self-medicate or hope that the disease will go away on its own.
The choice of treatment tactics often depends on the following factors:
- patient's age;
- state of the immune system;
- type of papilloma;
- localization of education;
- the results obtained (presence of concomitant pathologies, etc.).
Drug therapy is carried out using the following drugs:
- immunomodulators (“Likopid”, “Viferon”, “Ginephron”, etc.);
- antiviral drugs (“Cidofovir”, “Isoprinosine”, “Groprinosin”);
- probiotics (help restore microflora);
- vitamin complexes (“Multimax prenatal”, “Kombilipen”, “Elevit”, etc.);
- cytotoxins (“Fluorouracil”, “Condilin”, etc.).
Removal of cervical papilloma can be carried out in the following ways:
- Cryodestruction.
A method in which papilloma is exposed to liquid nitrogen. It freezes the formation, thus preventing the circulation of oxygen in the tissues. After a few days, a scab appears at the site of the papilloma, which disappears after 2 weeks.
- Cauterization.
This method is rarely used separately from others, since it can only reduce the growth rate of papilloma. There are 2 types: electrical and chemical. In the process of electrical cauterization, the neoplasm is exposed to high temperatures, in the process of chemical cauterization - chemical substances.
- Laser.
Today, this is the most effective method of combating papillomas. It has a number of advantages: safety, no scars after the procedure, low likelihood of relapse, recovery in a short time. Its only drawback is its high cost (compared to other methods).
- Radio wave method.
A method in which the papilloma is exposed to radio waves, but is not suitable in all cases. It is contraindicated in such cases: if a person has oncological pathologies, during pregnancy, with inflammation of the skin, etc.
Folk remedies will not help eliminate the disease, but they can improve immunity, so you can drink decoctions from the following medicinal plants:
- ginseng;
- Rhodiola rosea;
- echinacea;
- rose hip;
- aloe;
- elder;
- black currant (leaves);
- Linden blossom;
- Melissa;
- mint;
- dandelion.
Before using traditional recipes, you must consult your doctor.
Treatment
Carrying out colposcopy
In the process of treating all types of cervical papillomas, the following principles are taken into account:
- An integrated approach: in addition to removal of formations, the treatment plan for the disease includes interferon therapy for viral infection, immunostimulation, and antiviral drugs.
- Parallel antibacterial therapy for concomitant infection of the genital tract, restoration of microbiocenosis.
- Vitamin therapy.
Interferon preparations are prescribed both locally in the form of suppositories and systemically (tablets and intramuscular injections). Medicines help make up for the lack of one’s own interferon, the production of which is suppressed by the papilloma virus.
Immunostimulants help increase the production of antibodies, interleukins, and increase the production of T-lymphocytes - the main participants in the fight against HPV. The above medications must be taken before removing papillomas on the cervix. Antiviral medications lead to the elimination of the virus from the woman’s body.
On the eve of removal, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial therapy is carried out if there are signs of infection in the vagina (increased levels of leukocytes, presence of STIs). Surgical procedures are performed immediately after the end of menstruation. Since the cervix is devoid of pain receptors, treatment usually occurs with minimal pain (except for conization). Removal of papillomas on the cervix is performed using the following methods:
- Diathermocoagulation.
- Conization.
- Argon plasma ablation (laser technologies).
- Cryodestruction.
- Radio wave surgery.
Radio wave surgery
The radio wave surgery method allows you to avoid the formation of such serious damage to the cervix as ulceration, scarring, narrowing of the cervical canal, thickening of the mucous membrane, and allergies. In addition, radio waves reduce the risk of relapse to a minimum, whereas with other methods it is 25% or more.
High-frequency radio waves of the Surgitron device cut and coagulate tissue atraumatically, since the electrode does not heat up. Moreover, the method allows for the most accurate removal of papillomas and genital warts without damaging healthy tissue. This leads to scarless healing. The procedure does not cause pain. After removal, body temperature may increase (up to 37-37.5 degrees). On days 7-8, the film under which healing occurred is separated. This may be accompanied by minor bloody discharge.
Radio wave surgery is currently considered the most effective surgical method for treating papillomas and condylomas on the cervix.
Cryodestruction
Removal of genital papillomas of the cervix using liquid nitrogen is also considered a priority method of treating the disease. With traditional cryodestruction (irrigation, exposure with a probe or tampon), freezing leads to damage to healthy tissue, and often the low temperature does not reach the growth zone of the formations. Cryodestruction of viral tumors should be carried out with preliminary instrumental capture of the outgrowth, and the freezing procedure is repeated several times after thawing.
When choosing this method for treating papillomas, you should consult with your doctor in advance about the technique of the procedure. If during therapy one freezing session was not enough, then a second one is carried out after 10 weeks.
Cryoremoval is performed without anesthesia. After removal, at the discretion of the doctor, antibacterial agents can be used to prevent secondary infection. Within 2 weeks there is profuse, watery wound discharge, and pain in the abdomen and back is not uncommon.
Laser technologies
The method is highly effective, does not cause pain during removal, but is expensive and requires highly equipped clinics. With laser evaporation, the affected tissue is excised as accurately as possible, which does not cause scarring, deformation or narrowing of the cervical canal. The laser simultaneously with the excision of the papilloma seals the blood vessels, so bleeding is extremely rare.
After the procedure of excision of papillomas, bloody discharge is observed for 2 weeks.
Diathermocoagulation
photo of papilloma on the cervix
The method of using high-frequency electric current is the oldest method of treating cervical pathology. Removal of tumors with an electrocoagulator is accompanied by the formation of a burn scab and prolonged tissue healing (7-10 weeks). Afterwards, rough scars form and the cervical canal narrows. The procedure is quite painful. The only advantage of diathermocoagulation is its low cost. The method is suitable for a woman who is not planning a pregnancy in the future.
After removal, healing ointments (Levomekol, Methyluracil) are placed in the vagina. Mucous and sanguineous discharge has been observed for a month. Possible pain in the abdomen and lower back. Sometimes a repeat procedure is necessary.
Conization
The presence of inverted cervical papillomas often requires conization. The method involves excision of pathological tissues along with healthy ones. For removal they use a scalpel, laser, electrosurgical method (loop) or radio wave. After the procedure, bleeding, prolonged brown discharge, changes in the menstrual cycle, abdominal pain, and fever are possible. Conization leads to a narrowing of the cervical canal and can cause infertility.
Before treatment with this method, a more thorough preliminary study is required (blood biochemistry, coagulogram, blood test for hepatitis, syphilis and HIV). The procedure is usually performed under local anesthesia.
Drug therapy
The choice of immunomodulating and immunostimulating drugs is made by the doctor on an individual basis.
To restore the flora after removal, suppositories with lacto- and bifidobacteria (Acilact, Lactaflor) are used. To increase the body's defenses, B vitamins are used. Women with a single papilloma on the cervix, as a rule, do not experience a recurrence of the disease.
Surgical excision of viral tumors during pregnancy is carried out after 22 weeks, most often the cryodestruction method is used. Some doctors, after surgical treatment, locally use antiviral immunomodulatory ointments - Panavir, Keravort.
After removal of cervical papillomas, it is recommended to limit sexual activity for a month, and perform body hygiene in the shower. To relieve pain, you can use non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Nimesil, Ibuprofen).
https://youtu.be/VJ7Efq5j2Rg
Prevention of papillomas on the cervix
Cervical papillomavirus will not be able to negatively affect the body if a person is vaccinated. It can prevent the development of oncogenic types of HPV and guarantee stable immunity against this disease.
Contraindications to vaccination are:
- pregnancy;
- breast-feeding;
- presence of HPV in the body (vaccination is given to women and teenage girls who do not have the virus);
- any acute pathology;
- blood diseases.
Opinions about the need to introduce this vaccine are divided. Some consider it a blessing, others the opposite. Therefore, many people have to decide on their own whether to get vaccinated or not.
Doctors also recommend:
- monitor the state of the immune system;
- Healthy food;
- maintain physical fitness;
- treat all diseases in a timely manner.
Parents should communicate with their children about this topic. They should inform adolescents about the importance of safe sex and the dangers of bad habits (alcohol addiction and smoking).
Forecast
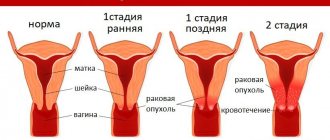
Cervical papillomatosis is not considered a rare phenomenon in our time. The disease is most often diagnosed in women aged 25 to 40 years. It is especially dangerous because it can cause cancer. It is important to begin treating malignant tumors on the cervix at an early stage. Only in this case the disease practically does not recur. In advanced cases, longer and more radical treatment is provided.
Faced with this pathology, many women panic and often hesitate to immediately seek medical help. This should not be done, because about 70% of the population are carriers of the human papillomavirus, and there is nothing shameful in this disease. Only careful attitude towards one’s health and a certain amount of caution can protect a woman from many diseases, including this one.
Causes of pathology
Viral growths that develop in a woman’s reproductive organs are collectively called cervical papilloma.
The causes of formations are the structure of epithelial cells changing under the influence of the human papillomavirus (HPV). The disease is transmitted in one of three ways: through household or sexual contact, or “vertically” - when the baby becomes infected while passing through the birth canal of a sick mother. A common cause of infection is sexual intercourse. The contraceptive in this case is not an obstacle: the virus cells are so small that they can easily penetrate any material. During sexual intercourse, the walls of organs receive microscopic damage. They are invisible to the human eye, but are large enough to allow pathogenic cells to enter the body.
Household causes of human infection:
- using hygiene items from an infected person;
- visiting public bathing areas;
- salon procedures.
The virus may not manifest itself in the human body for a long time; HPV carriers often do not realize that they have a pathogenic strain. The infection is triggered by a weakened immune system. As soon as the defense mechanisms fail under the influence of certain factors, the proliferation of foreign agents begins.
The danger of papillomatous growths in the uterus is that some types of HPV have a high degree of oncogenicity and provoke malignant degeneration of epithelial cells.
Papillomatosis, like other infectious diseases, is often activated during pregnancy, when the body suppresses immune activity to avoid fetal rejection. This process is especially strong in the early stages of pregnancy, when the risk of warts increases.
Extensive growth of condylomas on the cervix can cause problems with fertilization and lead to spontaneous abortion. The key task of the patient and the doctor is to treat infectious manifestations before planning pregnancy.
The virus can be transmitted to the child during birth if the mother is a carrier of the strain and has pronounced formations in the genital area. Passing through the birth canal, the baby comes into contact with the infectious agent. To prevent infection, a woman carrying the papilloma virus is recommended to have a cesarean section.
In medical practice, there are examples of self-healing of warts. More often this happens if the growths appeared during the gestation period. After the birth of a child, the woman’s immune system is restored, which can cause healing.
In most cases, the appearance of papillomas is associated with papillomavirus infection (human papillomavirus, HPV, papillomavirus). The virus can affect any area of the skin and mucous membranes, but the appearance of papillomas on the genital organs (cervix, vagina, vulva) is most dangerous due to the high risk of developing malignant diseases.
About the pathogen
The causative agent of the disease is a microorganism from the papillomavirus family. In total, there are more than 600 types of viruses, all of them are capable of infecting the human body and causing the development of various pathologies. About 40 types of HPV can infect the genitals (including the cervix), among them the most common and dangerous are HPV-16 and HPV-18. It is these viruses that have oncogenic properties, that is, they are capable of causing malignant tissue degeneration.
The main route of infection with HPV is sexual. Sometimes, even after papillomaviruses enter the genital tract, infection does not occur, since the immune system quickly inactivates foreign particles. In other cases, after entering the body, viruses infect the basal layer of the epithelium, causing proliferation of epithelial cells. Papillomas on the mucous membrane do not appear immediately; the incubation period is 1-2 months or more.
Not in all cases of papillomavirus entering the body, the clinical picture of papillomatosis and especially cancer develops. The prevalence of human papillomavirus infection is extremely high - every 3 women are diagnosed with one or another type of virus. But most of them do not develop the disease; such women are carriers of the infection.
Whether the disease will manifest itself or not depends mainly on the state of the immune system - whether the immune system is strong enough to fight the pathogen. All conditions that suppress the immune system can increase the likelihood of HPV infection:
- oncological diseases of any localization;
- hypothermia;
- frequent infectious diseases;
- taking certain medications (systemic and local glucocorticoids, cytostatics);
- kidney diseases accompanied by increased protein secretion (glomerulonephritis, renal failure);
- endocrine diseases (diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism);
- emotional overstrain, distress, chronic lack of sleep.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Plantar papilloma - symptoms, treatment, photos.
It has also been found that the likelihood of infection with HPV increases the presence of STDs (sexually transmitted diseases - chlamydia, genital herpes, syphilis, trichomoniasis) and smoking. Papillomas often appear during pregnancy and disappear after childbirth.
In most cases there are no clinical symptoms. A woman may not even suspect the presence of tumors on the cervix, but the pathology is revealed during a gynecological examination. Less commonly, nonspecific symptoms are present: bleeding from the genital tract, pain in the abdomen, lethargy, and weakness.
There is no specific treatment that would get rid of papillomas. That is why a combined approach is used - local removal of formations is carried out, as well as systemic treatment of a viral infection and strengthening of the immune system. For this purpose, medications and surgical methods are used.
General provisions
During the treatment period, it is necessary to eliminate the influence of provoking factors, as well as follow recommendations aimed at strengthening the immune system:
- eat right (increase your intake of vitamins and proteins);
- avoid hypothermia;
- move more during the day;
- promptly treat concomitant diseases (especially infectious and gynecological);
- sleep at least 7-8 hours;
- avoid emotional overstrain and stress.
In addition, it is necessary to use barrier methods of contraception to avoid re-infection.