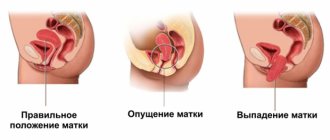
Inflammation of the uterus
Diseases of the uterus can be divided into several main groups: inflammatory diseases, disorders of the anatomy of the organ, neoplasms of the uterus and separate diseases of the cervix and uterine appendages.
Among all diseases of the internal genital organs, inflammatory ones occupy first place and account for about 70%.
At the same time, a large number of nulliparous women suffer from this disease, which negatively affects further reproductive function.
Diseases of the uterus often affect women with an excessive number of sexual intercourse, which in turn lead to the development of infectious diseases of the genital organs.
Inflammation of the uterus is a disease that affects all layers of this organ.
The most common manifestation of the inflammatory process is damage to the inner layer of the uterus, i.e. development of endometritis.
Inflammatory diseases of the uterus occur in every fifth modern woman.
It is worth noting that this disease can ultimately lead to infertility (about 3% of women in our country cannot have children).
Inflammation of the uterus can be completely asymptomatic or hidden, which complicates the process of early diagnosis and timely treatment.
Inflammation of the uterus has a number of main symptoms: the appearance of greenish-yellow discharge, which may have an unpleasant odor, nagging pain in the lower abdomen extending to the rectum or back, frequent and painful urination, general symptoms of intoxication (fever, weakness, apathy).
Diseases of the cervix include pseudo-erosion (ectopia), true erosion, ectropion (eversion of the cervical mucosa), neoplasia (CIN), inflammatory diseases, and cervical cancer.
Symptoms
The first signs of inflammation of the uterus will be a sharp increase in body temperature, which can reach 40 degrees. Often women complain of pain in the abdomen and blood appears in the discharge. Chills are possible, the discharge changes color and acquires an unpleasant odor. Postpartum inflammatory processes appear a few days after the birth of the child. The chronic form passes almost unnoticed.
Chronic inflammation of the uterus
Chronic inflammatory disease of the uterus is manifested by the formation of small cysts, atrophy or hypertrophy, which indicate damage to the endometrium. One of the symptoms is considered to be a violation of the menstrual cycle, the appearance of bleeding. With a chronic disease, even conception is possible, but it will be difficult for the embryo to implant into the affected endometrium, which will not allow the fetus to form normally and can lead to problems with pregnancy. The chronic form is manifested by purulent discharge and aching pain in the abdomen.
Acute inflammation
Called acute endocervicitis, in most cases it affects the muscular layer of the cervix, which leads to an increase in mucus secretions that mix with epithelial cells and exudate, reduces the body's ability to protect against infection and accelerates the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria. Symptoms are general weakness, pain in the lower abdomen, fever, pus in the discharge, leukocytosis, enlarged uterus, pain on palpation.
Inflammation of the uterus causes
Inflammation of the uterus, the causes of which lie in the presence of pathogenic microorganisms, can develop at a young age.
A woman’s uterus is an unpaired organ that is located in the pelvic cavity, consisting of the fundus, body, and cervix.
Diseases of the uterus are associated with the ingress of microorganisms, because the organ itself of a woman who has not given birth (without an abortion or surgical interventions on the uterine cavity) is sterile and has only the Doderlein bacillus in its microflora.
Inflammation of the uterus has the following causes: the presence of a sexually transmitted infection (STI) (gonorrhea, chlamydia, trichomonas, etc.), the use of intrauterine contraceptives, promiscuity (promiscuous sex life), previous abortions, childbirth or other surgical interventions in the uterine cavity, sexual life during menstruation, as well as the presence of foci of chronic infection.
Inflammatory diseases of the uterus can be chronic and result from acute infectious diseases of the internal or external genital organs.
Diet
Proper nutrition is an important aspect of treating any disease at home. Direct nutrition has no effect on the degree and intensity of the development of the process, however, refusal of certain types of foods can affect health indirectly.
It is advisable to avoid fried and fatty foods. Such products negatively affect metabolism. You should also avoid using preservatives, as they can increase swelling and inflammation. For the same reason, give up processed foods and fast food. You should not smoke or drink alcohol, as these toxins can intensify the inflammatory process and make symptoms more pronounced.
Some groups of products are indicated for consumption with this diagnosis. This is food such as:
- Citrus fruits, currants, celery and other foods rich in vitamin C can boost immunity
- Natural fresh vegetables and fruits that normalize the vitamin and mineral balance in the body;
- Fiber necessary for tissue regeneration;
- Foods rich in vitamins A and E, which can remove toxins and relieve swelling.
It is better to replace coffee and tea with natural juices, etc., or even water.
Recipes
Rosehip decoction invigorates no worse than coffee, but is healthier for the body. To prepare it, brew three tablespoons of berries in a thermos. You can drink it with honey or sugar. It's best to cook steamed. Vegetables and side dishes cooked in a double boiler and without oil retain more nutrients. Lean white meat, poultry or white fish can be baked in foil in the oven, also without oil or seasonings.
←Previous article Next article →
Inflammatory diseases of the female pelvic organs are becoming an increasingly pressing medical and social problem every year. The role played in this is:
- The deteriorating ecology of megacities.
- Socio-economic conditions that plunge most people into a state of chronic stress.
- Some sexual freedom.
- Untimely and inadequate treatment of STDs.
- Uncontrolled use of antibiotics.
According to WHO, out of 115 modern antibacterial drugs, 68 have become inactive against microorganisms such as Escherichia coli, Klebsiella, streptococcus and staphylococcus.
The uterus is an organ whose health ensures a woman a happy motherhood, a vibrant and fulfilling sex life, and reflects the hormonal balance in the body. That is why the inflammatory process in the uterus requires close attention from the patient. In turn, the attending physician must have modern knowledge of the pathological process, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Diseases of the appendages
Diseases of the appendages include damage to the fallopian tubes and ovaries of the uterus.
Salpingitis, oophoritis, salpingoophoritis or adnexitis, pelvioperitonitis are the main inflammatory diseases of the uterine appendages in women.
The main symptoms of the disease may be pain in the pelvis and lower abdomen, bloody or purulent discharge with an unpleasant odor, pain during urination or sexual intercourse, changes in general health, and in severe conditions (pelvioperitonitis) clinical infectious shock.
Diseases of the appendages in women can cause adhesions in the pelvic area, obstruction of the fallopian tubes, and infertility.
Endometritis and pregnancy
If you treat inflammation of the uterus correctly and in a timely manner and carry out full rehabilitation measures, then there should be no problems with pregnancy. However, it would be much better not to let the process take its course, but to plan a pregnancy no earlier than 6 months after the disease.
With chronic endometritis, getting pregnant and carrying a pregnancy to term is very problematic. But if this happens, then the good news is that there are practically no exacerbations of endometritis during pregnancy. That is, there is no need to treat endometritis at this stage.
In case of illness in a pregnant woman, treatment aimed at preventing:
- Miscarriage.
- Fetoplacental insufficiency.
- Fetal hypoxia.
- Anomalies of labor.
- Bleeding during childbirth and the early postpartum period.
To do this, you should register as early as possible under the supervision of an obstetrician-gynecologist.
Salpingo-oophoritis
Salpingoophoritis is an inflammatory process localized in the area of the fallopian tubes and ovaries, which, according to the nature of its course, is divided into acute and chronic salpingoophoritis.
The main symptoms will be the presence of nagging pain in the lower abdomen, which radiates to the external genital area or rectum, increased body temperature, general weakness and malaise.
Salpingo-oophoritis leads to disruption of the menstrual cycle in a woman, an increase in the volume of blood loss occurs, pain appears, the regularity of the cycle is disrupted, and the duration of the bleeding period (menometrorrhagia) increases.
Exacerbation of the chronic process can occur with hypothermia, unprotected sexual intercourse, or the presence of concomitant inflammatory diseases. Chronic salpingoophoritis is the result of an untreated infection, a late diagnosed condition, reduced immunity, and frequent and promiscuous unprotected sexual intercourse.
Consequences and prevention of chronic inflammation
The consequences of the disease can be very serious.
- Spread of infection to other organs - pyometra, salpingitis, oophoritis and the most dangerous - sepsis.
- Infertility is the result of irreversible changes in uterine tissue and the formation of adhesions.
- Blood poisoning is the spread of disease through the bloodstream.
- Deterioration in quality of life - disruption of the menstrual cycle, pain during sexual intercourse, chronic pain in the lower abdomen, excessive discharge.
In order to avoid the severe and incurable consequences of chronic inflammation, you must adhere to certain rules:
- carefully observe personal hygiene;
- use barrier methods of contraception;
- refuse abortion;
- regularly undergo scheduled examinations with a gynecologist;
- have sex only with a regular partner, avoid casual relationships;
- After giving birth, visit a gynecologist as planned and have an ultrasound done.
Salpingoophoritis treatment
Salpingoophoritis, treatment, which includes the appointment of barrier contraception, sanitation of foci of chronic infection, control of STIs, the appointment of antibacterial or antiprotozoal drugs, and the appointment of physiotherapy methods is also important.
Inflammatory diseases of the uterine appendages can lead to infertility, so not only early diagnosis and treatment are important, but also rehabilitation methods, which include mandatory physiotherapy.
Methods of physical influence have a positive effect on wound healing, increasing blood flow in the pelvic area, preventing adhesions, restoring the structure of the appendages and correcting their functions.
Cervicitis
The goal of treating pathology is to suppress the inflammatory process using etiotropic antibacterial, antiviral, and antifungal therapy. Immunomodulatory drugs can be used at the same time. Treatment is carried out by local or systemic means with subsequent restoration of the vaginal biocenosis.
Conservative therapy
In an acute process, treatment is selected depending on the type of pathogen. Local exposure is allowed for candidiasis infection and nonspecific inflammation. If there are symptoms of chlamydial, trichomonas or viral cervicitis, systemic therapy is necessary. For etiotropic treatment, the following groups of drugs are used:
- For candidiasis
. Clotrimazole, nystatin vaginal tablets, and butoconazole cream can be used locally in the form of suppositories or cream. In some cases, treatment is carried out with fluconazole capsules. For manifestations of candidal colpitis and cervicitis, anti-relapse therapy is carried out more often than 4 times a year after suppressing the acute process. - With chlamydial cervicitis
. Local treatment is ineffective; systemic antibacterial therapy is prescribed. The drug of choice is azithromycin. Alternative agents belong to the groups of tetracyclines, macrolides, and quinolones. After completing the course, monitoring of cure is necessary. - For trichomonas
. Trichomonas are protozoan microorganisms; a drug with antiprotozoal action, metronidazole, is used against them. If trichomonas are resistant, detected in 2-5% of women, tinidazole is prescribed. - For gonococcal infection
. When determining the symptoms of gonorrheal cervicitis, broad-spectrum antibiotics are used. 3rd generation cephalosporins in combination with azithromycin are recommended. The second line drug is doxycycline. Treatment is provided to both sexual partners. - With HPV
. A unified antiviral treatment regimen has not been developed. The drug based on inosine pranobex has proven itself well. It is used in long courses simultaneously with immunocorrection using suppositories with interferons. - For herpes
. The main drug that suppresses the activity of the herpes simplex virus is acyclovir. It is used in the acute phase in the presence of clinical symptoms - vesicles with liquid contents on the exocervix. An additional line drug is famciclovir. - For mixed infections
. Most often, during exacerbations of chronic cervicitis, a combination of nonspecific microflora and fungi occurs. Combination drugs are prescribed, including antibiotics of different groups and antimycotics.
Subsequent restoration of the microflora is carried out with local preparations, which include lactobacilli. Treatment results can be improved by eliminating the causes of cervicitis and correcting neuroendocrine changes. Lifestyle changes, dosed physical activity, and proper nutrition help. Treatment is effective using physiotherapy methods: diadynamic currents, magnetotherapy, electrophoresis.
Destructive methods
Methods of destructive treatment of cervicitis are used only when inflammation is combined with other background processes in the cervical area. For symptoms of papillomatosis, polyps, leukoplakia, ectropion, true erosion in nulliparous women, gentle methods are first used. If they are ineffective, additional examination is carried out and the approach is changed. Treatment is allowed in the following ways:
- Chemical cauterization
. It is performed with preparations that are solutions of acetic, nitric, and oxalic acid. Medicines are applied to a swab and applied to the lesion. This type of treatment does not lead to the formation of scarring and is well tolerated. - Cryodestruction
. A solution of liquid nitrogen or carbon is used. A prerequisite for treatment is that the size of the lesion must correspond to the diameter of the cooling nozzle, therefore the technique is not indicated for diffuse exocervicitis. After exposure to liquid nitrogen, pathological cells freeze out. The tissues do not scar or deform during healing. - Laser vaporization
. Pathological areas on the cervix are precisely removed using a laser, which heats up the altered cells and leads to their death. The treatment method does not cause severe complications, scar deformation of the cervix, and can be used in nulliparous patients. - Radio wave treatment
. Produced by the Surgitron device. The procedure is painless, and a delicate young epithelium is formed in place of the changed tissues. During treatment, healthy cells remain intact, radio waves affect only the pathological epithelium. - Argon plasma ablation
. It is carried out contactlessly using radio waves enhanced by the action of the inert gas argon. The procedure can be prescribed to women of any age, including those planning pregnancy. Healing is fast, rough scars are not formed.
Surgery
Surgical treatment of cervicitis is recommended in case of simultaneous diagnosis of dysplasia, cervical polyps or papillomatosis. The indication for surgery is cicatricial deformity of the cervix. Hospitalization to the gynecology department is required. Cervical polyps are removed and the bed is cauterized with liquid nitrogen. Other treatment methods may also be used:
- Loop electrosurgical excision
. It is carried out after relief of acute inflammation of the cervix. Using an electric loop, the altered area of tissue is removed, while the vessels are sealed, which reduces the risk of bleeding. The resulting tissues are examined histologically. - Knife conization of the neck. Performed using a scalpel. A cone-shaped section of tissue is removed, with its apex directed into the cervical canal. The operation can be complicated by bleeding, and is rarely used today. After manipulation, the resulting tissues are sent for histological analysis.