Symptoms and treatment of urethritis in women can vary significantly depending on the individual characteristics of the body; it is necessary to treat. Untimely treatment of inflammatory lesions of the urethra in women can lead to the pathology becoming chronic. In the most advanced cases, an ascending urinary tract infection may develop.
Urethritis is an inflammatory disease that affects the urinary tract, that is, the urethra. Inflammation of the urethra in women is one of the most common diseases of the genitourinary system. But since in the most common cases the development of urethritis is accompanied by subtle symptoms, women do not pay attention to the development of inflammation or seek medical help in the later stages of the disease.
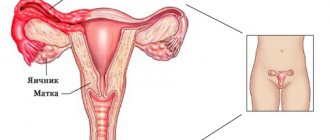
Anatomy and physiology of the female urethra
The urethra, or urethra, is the final structure for the passage of urine from the bladder. Female structural features include:
- short length (3–5 cm) compared to men (up to 18 cm);
- wide diameter when stretched (up to 10–15 mm);
- the presence of three narrowed areas (internal at the exit from the bladder and 2 in the area of the external sphincter);
- one expansion closer to the bubble;
- the presence of Skene's secreting glands, which are an analogue of the prostate gland in men, which in every tenth woman during sexual arousal secrete a fluid similar to prostatic fluid.
The urethra runs in front of the vagina through the pelvic floor muscles. At the same time, at the exit, her own muscle corset is weakened.
Compared to the male urethra, the female urethra has features that must be taken into account in treatment
The process of urine excretion involves reflex relaxation and closure of the channel, contraction of the bladder walls, and intravesical pressure.
Functions of the urethra in women:
- evacuation of the accumulated volume of urine from the bladder;
- providing support for muscle tone to create a reservoir with a volume of up to 15 ml;
- one of the erogenous zones.
It is impossible to treat the urethra as a simple tube. Urethritis in women breaks down the reflex functioning system, which subsequently affects sexual intimacy.
Possible complications of urethritis
As a rule, complications of urethritis occur against the background of a long course of the disease in the absence of treatment or in cases where therapy has been ineffective. Among the possible complications, experts name:
- prostatitis - usually occurs with chlamydial urethritis;
- cystitis – develops when the inflammatory process spreads to the bladder;
- vulvovaginitis – inflammation of the vagina;
- orchitis is an inflammatory process that develops in the testicles;
- colpitis, endometritis, adnexitis - diseases in which the inflammatory process affects the female internal genital organs;
- male and female infertility.
In men, complications of urethritis include inflammation of the male gonads, testes and seminal vesicles, as well as impotence.
Causes of urethritis in women
All types of urethritis are divided into 2 large groups:
- non-infectious;
- caused by infectious pathogens.
The non-infectious nature of inflammation is observed when:
Candidal urethritis in women
- mechanical damage to the urethral mucosa from passing stones during urolithiasis;
- injury during an examination of the bladder with a cystoscope, the procedure for removing urine with a catheter, or intentional actions;
- allergic reactions;
- malignant neoplasms;
- diseases of the genital organs;
- venous stagnation in the pelvis.
Inflammation can be a consequence of defloration or radiation therapy.
Infectious pathogens play a leading role in inflammation of the urethra. If symptoms and treatment are determined by pathogenic flora, then urethritis is specific. This group includes sexually transmitted infections:
- gonococci (gonorrheal);
- trichomonas;
- chlamydia;
- mycoplasmas;
- herpes viruses (herpetic urethritis) and genital warts.
One of the practical classifications divides all urethritis in women and men according to the medical profile of the doctor who needs to be contacted for treatment into:
- gonorrhea - dealt with by venereologists at the dermatovenerological dispensary;
- non-gonorrheal (non-gonococcal) - you should go to the clinic to see your local physician.
Since patients do not know without analysis what nature of urethritis is bothering them, it is best to start with a therapist, then follow his direction. Often women turn to a gynecologist. This does not change the tactics of examination and identification of the cause of the disease.
Inflammation with classic signs is considered nonspecific. Its causes are most often:
- staphylococci;
- coli;
- streptococci;
- Proteus;
- fungi of the genus Candida.
The listed flora is classified as conditionally pathogenic, since it is constantly present in the body. When combined with additional factors, it causes inflammation. Some authors classify fungal urethritis as a group of specific diseases.
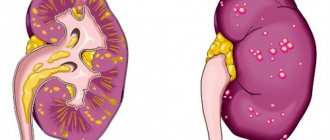
Inflammatory urethritis due to urolithiasis
Often, urethritis can be a complication of urolithiasis. Stones form in the urinary tract, which cause the development of an inflammatory process. With urolithiasis, the formation of salts of phosphoric, oxalic and uric acids occurs. Inflammatory urethritis against the background of urolithiasis develops as a result of irritation of the mucous membrane of the urinary tract by these acids.
It is also possible that sand and stones get into the urethra along with urine, as a result of which its walls are injured and an inflammatory process develops.
Inflammatory urethritis can also result from the formation of tumors in the urethra. Malignant formations are almost always accompanied by inflammatory reactions of the body.
What factors contribute to the disease?
In addition to the impact of a specific pathogen, the following factors influence the occurrence of inflammation in the urethra:
- hypothermia of the body;
- injury to the genital organs, disruption of innervation during surgery on the uterus and vagina;
- decreased immunity after suffering stress or serious illness;
- undermining the body’s protective function through poor nutrition and restrictive diets;
- consequences of alcoholism;
- hypo- and vitamin deficiencies;
- the presence of chronic inflammatory diseases (tonsillitis, tuberculosis, sinusitis, caries, cholecystitis, adnexitis);
- diseases of the urinary system;
- pregnancy and menopause;
- ignoring the rules of personal hygiene.
Diagnostics - what tests to take?
Based only on an external examination of the organs of the genitourinary system, not even the most experienced doctor will be able to say unambiguously that the patient actually has urethritis. After listening to the man’s complaints and conducting a visual examination of the condition of the penis, the doctor prescribes the following types of tests and diagnostic procedures for the patient:
- bacterial culture of mucus taken from the surface of the walls of the urinary canal (the nurse inserts a special cotton swab, which is sterile, into the urethral cavity and collects the mucous contents in order to further examine it in the laboratory and establish the type of microorganisms that provoked inflammation);
- blood from a vein (it is necessary to donate 15-20 ml of venous blood so that doctors can conduct a biochemical analysis of it and make sure that the patient does not have sexually transmitted diseases);
- blood from a finger (a standard analysis, after which the doctor receives data on the qualitative and quantitative composition of vital blood cells in the form of platelets, erythrocytes, leukocytes, phagocytes, lymphocytes);
- urine (this biological fluid is carefully studied in a laboratory, where medical personnel isolate the strain of microorganisms that dominate the male genitourinary system);
- X-ray (a special type of X-ray of the pelvic organs, which shows the location of all the urinary ducts, and the places where they are inflamed are displayed as dark spots);
- urethroscopy (a complex diagnostic procedure that involves inserting a urethroscope probe into the urethral cavity, which is equipped with a microscopic camera and transmits an image to a computer monitor and, accordingly, information about the condition of the walls of the urethral mucosa).
If the inflammatory process spreads beyond the urinary canal with the involvement of tissues of other organs of the genitourinary system in the pathological condition, it is possible to prescribe an ultrasound diagnostic of the prostate gland, urinary canal, kidneys, and scrotum. In most cases, the need for this examination arises in complicated forms of urethritis, when its development is caused by a staphylococcal or streptococcal infection.
How does infection occur?
The causative agent of infection can enter the urethra in three ways:
- contact - in a descending direction with urine from the source of infection in the kidney, bladder;
- sexual - during unprotected sex with a sick person;
- hematogenous - spreads through the bloodstream and with the movement of lymph from its own chronic foci of inflammation.
Depending on the nature of the spread of infection, urethritis is distinguished:
- primary - occur with direct penetration of an infectious agent into the urethra (from the bladder, during sexual contact);
- secondary - microbes enter hematogenously from the pelvic organs, intestines, or other chronic focus.
Nongonococcal type of urethritis
Depending on the cause that caused the development of inflammation, several types of urethritis are distinguished. First of all, the classification based on the bacterial agents that caused the disease is considered traditional. Based on this, a distinction is made between non-venereal (non-specific), caused by bacteria of pathogenic microflora - fungi, streptococci, E. coli, and venereal, caused by chlamydia, gardnerella, mycoplasma and other types of similar sexually transmitted pathogens.
In urology, this type of disease is also known as non-gonococcal urethritis, which can have both infectious and non-infectious origin.
Considering the type of bacteria or virus that provoked the development of inflammation, the following types are distinguished:
- ureaplasma;
- herpetic (herpes);
- candida;
- gonorrheal;
- chlamydial;
- trichomonas;
- mycoplasma
Symptoms of urethritis
Let's look at the signs of urethritis in women using the example of the course of bacterial inflammation.
You can read more about the specific symptoms of urethritis depending on the nature of the pathogen in this article.
According to the clinical course, the forms of the disease are distinguished:
- spicy;
- chronic.
The acute form occurs after an incubation period after exposure to microorganisms (sexual contact, bladder catheterization).
The duration of the latent period is determined by the state of the body: when weakened, inflammation appears after a few hours
The woman feels:
- sudden pain and pain when urinating;
- itching, burning in the area of the urethral outlet;
- the discharge is mucopurulent or purulent in nature;
- unpleasant smell.
In the case of allergic urethritis, a woman simultaneously has:
- nasal congestion;
- skin rash;
- lacrimation;
- dyspnea.
An examination by a urologist reveals slight swelling of the mucous membrane and redness of the surrounding tissues of the external urethra.
Features of chronic urethritis:
- symptoms are not constant;
- itching and burning are minor;
- as a rule, chronic cystitis is associated with frequent painful urges;
- urinary incontinence may occur.
Secondary bacterial urethritis does not manifest itself for a long time. Pain during urination and discharge is rare, mild, and more disturbing in the morning. During the day it is forgotten. In girls, there may be no pain at all; the mother notices discharge and itching in the intimate area. Upon examination, the doctor reveals gluing of the external opening of the urethra.
Prevention
As a preventative action, simple rules should be followed:
- Maintain personal hygiene, especially in the genital area.
- Do not have sexual intercourse until recovery.
- In case of infection, you should be treated together with your sexual partner.
- Avoid hypothermia.
- Limit food intake that causes esophageal irritation.
- Lead a healthy lifestyle.
- Support the body with vitamin supplements.
- Do not try to treat yourself with antibiotics until the cause of the inflammatory process is identified.
- With recurrent signs of urethritis, women need to drink at least 8 glasses of fluid per day, avoid drinking coffee and alcohol, which irritate the bladder.
Diagnostics
Urine examination is carried out using the three-glass sample method. The collection is carried out during the first morning urination, sequentially in three jars (it is required that the woman does not urinate for four hours). It is taken into account that signs of urethritis are detected in the first portion. Typically you get the following result:
- in the first portion - the urine is cloudy, there are a lot of leukocytes (due to inflammation in the urethra);
- in the second - there are fewer of them;
- in the third - absolutely not.
Bacterioscopy of urine under a microscope sometimes makes it possible to identify specific pathogens; special methods of staining the sediment are used
Discharge from the urethra is examined by culture on bacterial media, and at the same time the sensitivity of the flora to antibiotics is determined.
In difficult cases, the PCR (polymerase chain reaction) technique is used. It allows you to identify the pathogen by its DNA even in the latent stage of the disease. The material is taken from the wall of the urethra with a disposable probe; the procedure is complicated due to the short size of the urethra in women. The method is especially important in determining herpetic and chlamydial urethritis.
Urethroscopy is performed under local anesthesia. Often, a woman is pre-treated with a week's course of antibiotics to prevent the infection from spreading.
Urethroscopy is combined with cystoscopy (examination of the bladder walls), the tumor may be the direct irritating cause
Ultrasound examination can reveal concomitant cystitis and diseases of the pelvic organs.
Mictional cystourethrography is a diagnostic method related to radiopaque, in which a contrast agent is introduced into the bladder, which allows one to take a series of images and identify impaired patency, tumors, shadows of stones, and adhesions.
Women should definitely undergo an examination by a gynecologist to exclude inflammatory diseases of the genital organs and cervix as a cause of urethritis.
Diagnosis of infectious urethritis
To confirm the presence of infectious urethritis in the body, a two- or three-glass test method is used. When the disease develops, the first portion of urine should be cloudy; it contains a large number of leukocytes, which indicate an inflammatory process in the body. In the second portion of urine, the number of leukocytes decreases, and in the third, as a rule, it already corresponds to the norm.
Diagnosis of urethritis of bacterial origin also consists of bacterioscopic examination of discharge from the urethra. In order to clarify the type of infectious agent and its sensitivity to antibacterial drugs, a culture of the discharge or flush from the urethra is carried out.
Treatment
Treatment of urethritis in women does not require hospitalization. The disease is not considered severe and is usually treated on an outpatient basis. To do this, you first need to undergo an examination prescribed by a doctor to find out the cause, type of pathogen, and select the most effective anti-inflammatory drugs.
You can learn about the features of therapy for different forms of urethritis in this article.
If the infection is caused by a sexually transmitted infection, it is recommended to treat the male partner as well.
During the treatment period, the patient will require a restrictive regimen:
- you should stop having sex;
- sharply reduce physical activity;
- keep your feet warm and avoid the slightest hypothermia;
- in your diet you will have to give up salty, pickled, smoked dishes and foods, alcohol in any form;
- significantly increase the volume of fluid you drink (up to 2 liters), if there are no contraindications due to other diseases;
- include dairy dishes, cereals, fruits and vegetables in your daily diet.
The treatment regimen includes drugs with various anti-inflammatory effects; injections, tablets, vaginal suppositories, and local baths are used.
The course of antibiotics ranges from five to ten days. The most commonly used:
- group of fluoroquinolones (Ciprofloxacin, Leofloxacin, Ofloxacin, Gatifloxacin);
- macrolide antibiotics (Roxithromycin, Azithromycin, Clarithromycin);
- semisynthetic penicillins (Amoxiclav, Flemoxin, Augmentin).
The dosage is selected by the doctor depending on the severity of inflammation, weight and age of the patient. You cannot cancel it yourself or take it longer than the prescribed period. Microorganisms develop resistance to the drug and have no further effect.
Intramuscular injections of drugs from the cephalosporin group (Cefatoxime, Ceftriaxone, Cefuroxime) are used much less frequently. Such indications arise if a woman has a concomitant disease of the stomach or intestines, if an ascending infection is suspected and there is a threat of pyelonephritis.
The photo shows a popular antifungal agent in tablets
The nature of treatment depends on the type of pathogen:
- for a disease caused by fungi, antifungal agents are prescribed (Terbinafine, Fluconazole);
- if the pathogen belongs to mycoplasmas - the imidazole group (Ornidazole, Metronidazole, Tinidazole).
For severe allergic manifestations and itching, Loratadine, Diphenhydramine, Suprastin are recommended.
To enhance the effect, the same drugs are prescribed in vaginal suppositories. Absorbed into the pelvic vessels, the composition of the suppositories has an anti-inflammatory effect on neighboring organs.
For local irrigation at home, the following are recommended: warm sitz baths with a solution of potassium permanganate or herbal decoctions.
If necessary, the doctor prescribes douching procedures and the introduction of antiseptics such as Collargol, Protargol, Miramistin into the urethra. To do this, you will have to visit a urologist throughout the course.
The following physiotherapeutic techniques are used:
- vaginal electrophoresis with Furadonin, the active electrode is also placed in the pubic bone area;
- diadynamic currents in the lumbosacral zone.
In order to support the immune system, a woman is prescribed multivitamins, ginseng tincture, lure, aloe (herbal immunomodulators). With secondary urethritis, the result of treatment of the underlying disease is important.
Treatment of chronic nonspecific urethritis
The treatment tactics for nonspecific urethritis are determined by the type of pathogen, the severity of symptoms, and the presence of complications. If urethritis is combined with cystitis, complex systematic therapy is required.
Treatment of chronic urethritis is based on the use of antibacterial drugs. As an additional therapy, solutions of dioxidine, collargol and silver nitrate are instilled into the urethra.
Procedures are carried out and medications are prescribed to strengthen the immune system.
What folk recipes can be used for urethritis?
Urethritis must be treated with medications. It is impossible to replace them with folk remedies. However, the anti-inflammatory properties of many plants may well help medications. For this purpose, herbs and fruits are selected that also have diuretic, antimicrobial and antispasmodic properties.
Recommended to be taken orally with food and drink:
- juices from lingonberries, cranberries, carrots (we are talking only about fresh juices without preservatives and sugar);
- celery greens, parsley, beets;
- A decoction is prepared from the berries and leaves of black currant (half a liter of boiling water for 3 tablespoons of the dry mixture), infuse it for 30 minutes, drink it 2-3 times a day;
- prepare a mixture in milk from the leaves and stems of parsley (simmer in the oven for 1 hour);
- a decoction of linden blossom is known for its ability to relieve burning and pain when urinating;
- Cornflower flowers are dried and used as tea.
How and with what to treat urethritis in men?
Treatment of urethritis is a complex and lengthy process that requires a man’s perseverance, patience and disciplined implementation of all recommendations received from the attending physician. After the doctor has all the information on the test results, the patient is formulated a treatment regimen and prescribed medications belonging to the following drug groups.
Antibiotics
Drugs against urethritis are selected individually based on which particular strain of the microbe was sown during laboratory analysis of mucus taken from the walls of the urethra. Most often, doctors use antibacterial agents such as Erythromycin, Biseptol, Tetracycline, Azithromycin, Amoxilav, Bicillin, Furazolidone, Metronidazole, Nitroxoline. These medications can be prescribed in the form of tablets or administered into a man’s body in the form of intramuscular injections. This is already determined by the attending physician.
Ointments and creams
A separate group of medications, the use of which helps organize effective treatment of urethritis. The ointment is applied directly to the surface of the inflamed tissues of the head, as well as to the tissues located around the entrance to the urinary canal. Ointments such as Levomekol, Syntomycin, Heparin, Vishnevsky ointment, Salicylic-Zinc paste have proven themselves to be the best. For fungal urethritis, creams such as Pimafucin, Clotrimazole, Nizoral are used.
Antiviral agents
If the disease is caused not by a bacterial infection, but by viral microorganisms, then in 90% of cases the cause of the disease is the penetration of the genital herpes virus into the urethra. For the treatment of herpetic urethritis, it is recommended to take Acyclovir, Herpevir, Valtrex, Famciclovir. These antiviral medications are available in the form of tablets and ointments. To achieve maximum therapeutic effect, it is recommended to use both categories of drugs.
How can a woman prevent urethritis?
To prevent urethritis, a woman must exclude possible routes of infection. For this:
- you should be more selective about your sexual partners, exclude unprotected sex and casual contacts;
- do not neglect personal hygiene, regular washing with weak disinfectants;
- do not use alcohol solutions or soaps for hygiene, which lead to severe irritation of the urethra;
- exclude from food foods that irritate the urinary organs (spicy spices, pickles, canned food, smoked meats);
- dress according to the weather, avoid hypothermia, do not wear trousers that sharply compress the stomach (cause stagnation in the pelvis);
- monitor the condition of teeth, promptly treat sore throats and other acute bacterial infections.
Although urethritis is not a fatal disease, it leads to serious disruptions to a woman’s health. Constant pain and itching contribute to irritability, cause insomnia, and reduce ability to work. Preventing the disease is much easier than treating the advanced form. With all the described manifestations, a woman must immediately contact a therapist or gynecologist. You should not self-medicate and turn the disease into chronic inflammation.
Causes
Urethritis, diagnosed in representatives of the male half of the population, is a specific disease and the localization of the source of inflammation exclusively in the urethral cavity suggests that the cause of the disease is the presence of the following causative factors.
Unprotected sexual intercourse
One of the most common mechanisms of transmission of pathogenic microflora from a sick person to a healthy one. At risk are young men who are not yet married, or who, despite being married, still lead a promiscuous sex life. In this case, it is enough just once to have intimate intimacy with a woman in whose vagina there is an excessive amount of bacterial infection, so that the pathogenic microorganisms enter the mucous membrane of the man’s urinary canal and begin their division. After 5-10 days, the infected person begins to feel the first symptoms of the disease. To avoid urethritis, it is enough to use barrier contraceptives in the form of condoms. Read about ureaplasma and gonorrheal urethritis.
How is the disease classified?
The most rational classification is according to which urethritis is divided into gonorrheal and non-gonorrheal, and the latter into two large groups: venereal, etiologically associated with sexual intercourse, and non-venereal, caused by other reasons.
Venereal nongonorrheal urethritis includes:
bacterial;- aseptic chronic (Welsh type);
- syphilitic;
- soft chancroid;
- Trichomonas;
- postgonorrheal.
The group of non-venereal nongonorrheal urethritis includes:
- traumatic (chemical, mechanical, thermal);
- tuberculosis;
- for infectious diseases;
- herpetic;
- dermatous (symptomatic);
- for neoplasms;
- stagnant.
On our website you can learn about the following types of urethritis:
- nonspecific;
- acute and chronic;
- non-infectious;
- chlamydial;
- candida;
- allergic.
The main differences between urethritis and cystitis are described here.
Non-infectious inflammation of the urethra
Occasionally, urethritis of non-infectious etiology occurs.
The reasons may be:
- allergic reactions;
- urethral strictures;
- oncological formations;
- burns or traumatic damage to the urethral wall;
- metabolic disorders (urolithiasis or excretion of salts in the urine);
- congestion in the veins of the penis.
For different diseases, the prognosis and treatment methods differ.
Allergic reactions occur after contact with an allergen.
But in the absence of such contact for a long time, all symptoms disappear.
In the treatment of such urethritis, the most important thing is not only to relieve the current inflammation, but also to identify the allergen and stop further contact with it.
In oncological pathologies, urethritis is secondary.
The underlying disease is a malignant tumor.
Treatments are aimed at eliminating it.
In case of successful fight against cancer, inflammatory processes in the urethra stop.
Traumatic injuries to the mucosa are most often the result of medical manipulations.
Such urethritis is often detected after transurethral operations, bladder catheterization, cystoscopy, scraping, etc.
That is, in cases where the instrument penetrates the urethra and can injure the wall of the canal.
The resulting inflammatory reactions are usually short-lived.
Symptoms go away after a few days as the damaged mucosa regenerates.
Congestion in the submucosal layer of the urethra can be caused by sexual excess or low physical activity.
They cause urethritis on their own.
In addition, they create favorable conditions for nonspecific microflora.
Therefore, congestive urethritis can transform into bacterial.
Medicines for cystitis and urethritis
Therapy for complex pathology is aimed at solving several priority problems:
- Normalization of the balance of microflora in the vagina. If the slightest traces of infectious agents remain in it, the process of their penetration into the urethra will be constant.
- It is necessary to increase the body's defenses, since prolonged inflammatory processes in the organs of the genitourinary system significantly weaken the immune system. In addition, cystitis seriously weakens the walls of the bladder.
- When treating complicated urethritis, it is important to strengthen the walls of the urethra.
Treatment of cystitis and urethritis is complex and includes a course of taking various medications and other therapeutic methods.
Candles
Vaginal suppositories are widely used in modern gynecology for the treatment of inflammatory infectious diseases, including cystitis and urethritis. They are usually prescribed as part of a course of therapy simultaneously with tablets, injections and other methods. The most commonly used candles are:
- Genferon . One of the best representatives of immunomodulatory drugs on the modern pharmaceutical market. The drug is effective for inflammatory processes in the urethra caused by various pathogenic flora. Genferon affects the activity of immune system cells and at the same time enzymes that suppress the ability of viruses to reproduce.
The drug has the ability to accumulate in the female body, as a result of which its positive effect on the immune system is prolonged.
- Metronidazole . An effective means of combating anaerobic bacteria that cause genitourinary infections. The drug affects the respiratory system of pathogenic microorganisms, causing their death. Metronidazole is especially indicated in the treatment of urethritis caused by Trichomonas and Gardnerella.
- Fluconazole . A broad-spectrum antifungal drug that can suppress the enzymatic activity of fungi. Fluconazole is actively used both in the treatment of inflammatory processes in the bladder and urethra, and in their prevention.
- Yodovidone . These are suppositories with an antiseptic effect and antibacterial effect, which are carried out due to the release of iodine upon contact with the skin.
Other medications used in the form of suppositories include Voltaren and Indomethacin suppositories, which have an analgesic effect due to their ability to suppress the production of inflammatory hormones.
Antibiotics
When treating cystitis and urethritis, broad-spectrum antibacterial agents are used, since these diseases can be caused by several pathogens. The choice of a specific drug is determined by the doctor depending on the form of the pathology:
- Cephalosporins and sulfonamides are effective for nonspecific cystitis and urethritis.
- If the causative agent of the infection is gonococci, drugs of the erythromycin group, Rifampicin or Cefuroxime are prescribed.
- If trichomonas are detected in tests, patients are shown Metronidazole or Ornidazole.
- If the inflammation is caused by a fungal infection, Nystatin, Levorin or Imorazole are prescribed.
In addition to broad-spectrum antibiotics, modern pharmacology has drugs developed specifically for the treatment of genitourinary infections. Thus, one of the most effective drugs for the treatment of cystitis is Nolitsin, which belongs to the group of fluoroquinolones.
Among other “highly specialized” drugs, one can highlight Monural, which is taken once and has a very high degree of impact on pathogenic microflora.
For information on the treatment of bacterial urethritis in women, watch this video:
Physiotherapy
Similar techniques have proven themselves in the treatment of inflammatory processes in the female genitourinary system; they are used to relieve pain due to cystitis and help restore normal urine flow. The following physiotherapeutic procedures are most effective:
- Magnetophoresis – medications are injected into the bladder mucosa using a magnetic field.
- Electrophoresis - stimulates metabolism, promotes tissue regeneration of the mucous membranes of the bladder and urethra.
- Ultrasound improves blood circulation and has an anti-inflammatory effect.
- Vibration therapy improves blood circulation and has an analgesic effect.
- Amplipulse – has a positive effect on the tone of the bladder.
Inductothermy
In addition to hardware methods, others are widely used:
- treatment with mineral water – for the treatment of cystitis, low-mineral sulfate waters are very useful, which are recommended to drink a glass 4 times a day for 25 days;
- mineral sitz baths - you can use sodium chloride and radon baths to relieve inflammation.
Physiotherapy methods are selected by the doctor strictly individually, depending on the nature of the disease, the general health of the patient and the presence of contraindications.
We recommend reading about trichomonas vaginitis. You will learn about the causes and symptoms of trichomonas vaginitis, the possibility of urethritis, diagnosis and treatment. And here is more information about ureaplasmosis in women.
Prevention of cystitis and urethritis is important. These diseases most often occur in women after the onset of sexual activity, so it is very important to be responsible in choosing sexual partners and to use protective equipment during intimate contacts. It is also very important to observe the rules of personal hygiene, eat properly and rationally, and avoid hypothermia.
Any genitourinary infection is fraught with many complications, so a woman should be very careful about her health.
Simple methods of prevention
Prevention of urethritis involves taking measures to prevent both the initial penetration of infection into the body and its re-exacerbation. It includes a list of simple recommendations:
- observe the rules of intimate hygiene;
- avoid hypothermia and colds;
- carry out nutritional correction;
- establish a daily routine;
- take medications aimed at suppressing the activity of the pathogen;
- undergo regular comprehensive examinations
- strengthen the immune system through hardening, walking, and feasible physical activity;
- use barrier contraceptives;
- have sexual contact with only one sexual partner.
Neglecting the rules of prevention is undesirable. The examination must be carried out at intervals of 6 months. It is recommended that women who have previously been diagnosed with inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system visit a doctor more often.
Auxiliary treatment
In addition to the main course of antibiotics, other methods are used to treat acute signs of the disease - physiotherapy, local measures.
Physiotherapy is indicated for the chronic form, but is contraindicated for the acute form. Magnetic therapy, UHF, electrophoresis, and laser therapy are used. However, they need systematicity and medical supervision.
Inflammation of the urethra in men involves local treatment, the medicine is introduced directly into the urethra. For this purpose, Dioxidin, Miramistin, and Hydrocortisone medications are used. Local manipulations have good effects and are part of the complex treatment of urethritis. These drugs cope well with pathology and have many positive reviews.
Often men with inflammatory processes in the intestines, pancreas, gallbladder and other organs are susceptible to this disease.
Home » Urology » Urethritis
Drugs for gonorrheal urethritis
The choice of medications directly depends on the cause of the disease. For gonorrheal urethritis in women, antigonococcal drugs are prescribed. Nongonorrheal inflammation of the urethra caused by other pathogenic microorganisms is treated with specific antibiotics that have a detrimental effect on a specific pathogen.
Non-infectious urethritis occurs much less frequently. They can be caused by trauma during insertion of the catheter, an allergic reaction of the body, or a metabolic disorder. In this case, anti-inflammatory drugs and antiallergic drugs are prescribed to stop pathological processes in the urethra. Thus, before treating urethritis, it is necessary to establish its cause, and for this you will have to contact a venereologist or gynecologist.
A common gonorrheal urethritis is characterized by mucopurulent discharge from the urethra, which is yellowish-white in color. Often women mistake such discharge for leucorrhoea. In addition, there are complaints of frequent urge to go to the toilet, pain and a burning sensation during urination. Since, in addition to the urethra, gonococci affect the walls of the vagina and the cervical canal, urethritis is usually accompanied by vaginal discharge of a mucopurulent nature, pain in the lower abdomen, and mild bleeding that appears after sexual intercourse or between menstruation.
The following drugs are used to treat urethritis caused by gonococcus:
- penicillins (in particular intramuscular injections of Benzylpenicillin, Bicillin-1, -3, -5, Ampicillin for oral administration),
- aminoglycosides (Spectinomycin, Netromycin),
- Augmentin,
- cephalosporins (Ceftriaxone, Cefotaxime),
- macrolides (Azithromycin, Josamycin, Clarithromycin),
- tetracyclines (Doxycycline),
- Ofloxacin.
In most cases, the first-line drugs for gonorrheal urethritis are penicillins. The remaining tablets are prescribed if during the study the pathogen was found to be resistant to penicillins, their use did not produce the desired therapeutic effect, or chlamydia was found in addition to gonococci. Do not forget that very often gonococcal infection is associated with gardnerella, trichomonas and fungal infections. In such cases, it is necessary to prescribe several types of antibiotics at once:
- For gonorrheal-gardnerella infection, antigonococcal drugs are combined with Metronidazole.
- For gonorrheal-trichomonas urethritis, the simultaneous use of protistocidal (Trichopol, Flagyl) and antigonococcal drugs is necessary.
- Gonorrheal-fungal urethritis requires the use of polyenes (Nystatin, Levorin) or azole drugs (Nizoral, Ketoconazole) together with antigonococcal drugs.
Reviews from men
Patients who were treated for urethritis in an inpatient department note that this is a very insidious disease that requires a systematic approach and long-term therapy. There is a direct correlation in that the sooner a man sees a doctor, the less time it will take to recover. In most cases, antibiotics were used in the form of tablets and injections. Painkillers were prescribed to relieve discomfort in the urethra. The average treatment time is 10-15 days. Chronic forms of urethritis are treated for 2-3 months and still periodically the disease recurs, after which the man has to undergo a second course of therapy. Despite the complexity of the treatment, the recovery rate is high, but only if all the recommendations of the attending physician are strictly followed and alcohol is completely abstained.
Treatment of acute urethritis, list of drugs
Uncomplicated urethritis in women can be successfully treated – comprehensively and step-by-step. For female urethritis, antibiotic therapy is the most effective stage of treatment. Its effectiveness is due to the correct choice of the drug, which is selected purely individually, taking into account the high sensitivity of a particular pathogen to it.
In order not to waste time while the pathogen is determined, antibiotics with a broad (universal) property are prescribed. Among the most popular:
- Drugs from the cephalosporin group: Cefotaxime, Cefazolin, Ceftriaxone. Drugs of the sulfonamide group in the form of “Sulfazol” or “Urosulfan”. Macrolide antibiotics: Azothromycin or Clarithromycin. Fluoroquinolone drugs such as Clinafloxacin.
- Sexually transmitted infections are treated with Erythromycin, Tetracycline, Cefuraxime, Oletethrin, Rifampicin, etc.
- For fungal origin, antifungal drugs are selected - Natamycin, Levorin, Nystatin and Clotrimazole.
- Antimicrobial drugs and analogues of “Benzidamine”, “Ornidazole”, “Metronidazole”, “Chlorhexidine”.
- For viral etiology of the disease, antiviral drugs are indicated: Anciclovir, Famciclovir, Ganciclovir, Ribavirin.
Tablet medications, drugs for intramuscular or intravenous injections are prescribed. In accordance with the symptoms of urethritis in women, antibiotic drugs are selected according to schemes - for monotherapy (prescription of one antibiotic), combined schemes of 2, 3, and 4 phase treatment.
Treatment with antibiotic drugs is supplemented by installations - the introduction of antibiotics directly into the urethra using catheterization and intravaginal suppositories.
Vaginal suppositories for urethritis are selected according to three categories: those with antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and antiviral properties. Among them are Hexicon, Polygynax and Betadine.
An indispensable condition for successful therapeutic treatment is a correction of the diet with plenty of fluid intake.
Urethritis - consequences
The lack of therapy for this pathology is fraught with the spread of the inflammatory process throughout the genitourinary system. The bladder, uterus and appendages may be affected. The primary complications are
- cystitis;
- vaginitis;
- vulvovaginitis.
With the ascending spread of the disease, gynecological diseases such as:
- colpitis;
- adnexitis;
- endometritis.
Urethritis in women, the symptoms and drug treatment of which are caused by the pathogen, provokes disturbances in the reproductive system. Urethritis that occurs during pregnancy can negatively affect the gestation process. In the short term, this disease can provoke disturbances in the development of the fetus. In the later, 2-3 trimester, urethritis becomes the cause of:
- premature placental abruption;
- premature birth.
Possible complications
Like any other inflammatory disease localized in the area of the genitourinary system, urethritis in men can provoke the development of associated complications and negative consequences for the body, expressed in the following pathologies:
- chronic or acute prostatitis, which occurs due to the penetration of infection from the urinary canal into the prostate gland, for the stable operation of which its exceptional sterility must be ensured (a similar complication is quite often observed with posterior urethritis);
- inflammation of the testicles and seminal vesicles, which is an extremely dangerous disease for men’s health, because it is fraught with disturbances in the production of sperm and the onset of male infertility;
- damage to the walls of the urinary canal and penetration of microbes into the kidneys (infection of the latter organ can cause the development of renal failure and a man’s dependence on the artificial kidney apparatus);
- hormonal disruptions, expressed in a sharp decrease in the level of male sex hormones (this factor negatively affects the psycho-emotional state of the patient, the man becomes irritable, aggressive, there is a sharp change in mood);
- disorders of sexual function (impotence, weak erection, premature ejaculation, lack of attraction to the opposite sex, pain in the urethra during sexual intercourse).
Regardless of what complication arises as a result of a man having urethritis, each of the described diseases poses a threat to the health of the genitourinary system, and also significantly reduces the man’s quality of life, excluding the possibility of leading a full personal life.
FAQ
Most men, who first encounter the symptomatic manifestation of an inflammatory process in the urethra, ask well-founded questions to which they do not have comprehensive answers. It is believed that after diagnosis, patients have the following questions.
Which doctor treats urethritis in men?
A urologist treats inflammation of the walls of the urinary canal. If the patient lives in a small locality where there is only one district hospital, then this specialist may not be included in the staff structure of the clinic. In this case, you can also seek medical help from a surgeon, infectious disease specialist or dermatologist. You should not be afraid of visiting a surgeon’s office, as we are not talking about an operation or any other surgical intervention on a man’s body. Simply, according to the internal organization of medical institutions, it is doctors of this profile who are entrusted with the responsibility of seeing men with genitourinary diseases, if the position of a urologist is completely absent from the staff, or there is no doctor with this specialization.
Is it possible to have sex?
During the period of treatment of urethritis, it is not recommended to engage in sexual relations, since sexual intercourse can aggravate the clinical picture of the disease and transfer it to the acute stage. The thing is that during sex the static load on the organs of the genitourinary system increases, the tissues of which are already in an inflammatory state, and an additional rush of blood will become a catalyst for the development of the disease. There is also a well-founded risk that the infection in the urethra will be transmitted to a sexual partner and the woman will soon experience similar symptoms of the disease. Considering the length of the incubation period for urethritis, the first signs of the disease will appear after 7-10 days. It is better to abstain from sex completely or use condoms.
Does urethritis go away on its own without treatment?
Every man should remember and understand for the rest of his life that urethritis is a disease that will not go away on its own. It can only temporarily, when the patient’s immune system becomes stronger, enter a latent stage. The man gets the false impression that the disease has subsided, and along with it pain, itching, burning and mucous discharge from the urinary canal have gone away. In fact, literally 1-3 months pass and the symptoms of urethritis return again, but with more intense signs of their manifestation.
You should not waste time trying to get rid of urethritis on your own or live with the prospect that after some time the disease will subside. This position always ends with the transition of inflammation of the urinary canal to a chronic form, the spread of pathogenic microflora throughout all organs of the genitourinary system with the further manifestation of various kinds of complications. After this, curing the disease becomes extremely difficult and the man has to take a large number of potent antibacterial drugs, most of which are administered intramuscularly.
Urethral condylomatosis
Another cause of viral inflammation may be papillomavirus.
It causes the appearance of intraurethral condylomas.
These formations reach a length of 1 cm.
They are localized in the distal part of the urethra and can extend beyond the canal.
Read also Analysis for ureaplasma
Although often a viral infection spreads to the entire urethra and even penetrates the bladder.
Condylomas can also form there.
The process of their appearance is accompanied by itching and sometimes painful sensations.
The condylomas themselves can become injured, tear off, block the flow of urine and provoke reflux.
Classification of the disease
When symptoms appear, treatment for urethritis in men is tailored to the etiology, intensity, and stage of the pathology.
| Infectious | Non-infectious |
Caused by various pathogens, they are divided into:
Mixed urethritis appears due to infection with several pathogens at once. |
|
Urethritis is divided into primary, which appears as a separate disease, and secondary, which develops against the background of other pathologies. The flow can be acute, subacute and torpid. Chronic disease occurs with varying intensity - high, moderate or low activity.
Nonspecific urethritis is caused by microorganisms that constantly live in the body, staphylococci. At the same time, the immune system is not able to cope with pathogens on its own. Specific is caused by gonorrhea, chlamydia, etc., appears in tuberculosis.
Desquamative urethritis develops against the background of chronic degenerative processes. This leads to a narrowing of the canal and the formation of pus inside. Interstitial inflammation of the urethra occurs due to hypothermia. This type of pathology is accompanied by elevated temperature and is very difficult to tolerate.
Signs in children
Urethritis is extremely rarely diagnosed in children. The cause of the disease can be the following pathological conditions:
- Allergic reactions.
- Oncology.
- Urolithiasis disease.
- Installation of a catheter for the purpose of performing any medical procedures.
- Hyperplasia.
In addition, in children, signs of urethritis may appear against the background of insufficient hygiene rules, wearing tight underwear made of synthetic materials, improper washing, and general hypothermia of the body. Also, the cause is often cosmetics containing a large number of components harmful to babies.
Common symptoms of urethritis in children:
- Burning and itching in the genital area.
- Painful sensations during the act of urination.
- Increased body temperature (this warning sign does not appear in all cases).
- Redness of the external outlet of the urethra.
Clinical manifestations of urethritis in boys:
- The presence of blood streaks in the urine.
- Frequent urge to urinate.
- Purulent discharge from the urethra.
- Change in urine color. Urine becomes dark and cloudy.
In girls, when the inflammatory process develops, the following symptoms appear:
- Itching of the external genitalia.
- Frequent urge to urinate.
- Painful sensations in the lower abdomen.
- Cutting in the urethra.
In adolescent children, the clinical manifestations are the same as in young children. However, the former tolerate the disease more easily. Lethargy, fatigue and high body temperature in most cases only bother children in the first years of life.
Regardless of the severity of symptoms, treatment of urethritis should not be delayed. This threatens the development of all sorts of complications. A child who experiences pain during the act of urination begins to consciously refuse to drink drinks and also restrain the urge. The most harmless consequence is incontinence.
Most often, in the absence of treatment or with improper therapy, urethritis quickly becomes chronic. It is extremely difficult to treat and regularly reminds itself of painful sensations and other unpleasant symptoms. Other possible complications: vaginitis, cystitis, infertility, renal failure. In addition, against the background of the inflammatory process, the sensitivity of the genitourinary system to infections subsequently decreases.
Diagnosis of the disease
This diagnosis can be made by a doctor after collecting anamnesis and obtaining laboratory results.
During the examination, the doctor will examine the underwear for the presence of discharge and the lumen of the opening of the urinary canal. Palpates the penis along the urethra and scrotum to rule out orchitis. A rectal examination of the prostate may also be necessary.
From the analyzes you will need to do:
- Complete blood test - based on the cell ratio, the doctor will determine the degree of inflammation.
- A general urine test is necessary to determine the cause of a non-infectious nature.
- Bacterial seeding of biomaterial (urine, seminal fluid) is needed to identify the pathogen. For the same purposes, more complex studies are done - ELISA, PCR, antibody titer.
- Ultrasound of the genital organs is necessary to determine the extent of the process.
Such an integrated approach will allow us to more accurately determine what led to the development of the disease, as well as select the most adequate methods of therapy.
Treatment of urethritis with folk remedies
Medication therapy has come a long way, but urethritis in women is often treated with folk remedies that are still not outdated to this day. Natural components contain microelements and vitamins that help reduce the symptoms of the disease and improve the health of the body. However, it is recommended to use folk remedies as an addition to the treatment of urethritis.
Here are a few folk recipes that will help you cure this unpleasant disease:
- Parsley tincture. This remedy must be taken every few hours, three tablespoons. To prepare the tincture, pour one tablespoon of raw material with half a liter of water and leave to infuse overnight. In the morning the tincture will be ready.
- Two glasses of yellow zelenchuk tincture (daily value) will help get rid of the problem. To prepare the tincture, pour one tablespoon of herb into a quarter liter of hot water. In twelve hours it will be ready to eat.
- Black currant leaves (3 tsp) should be poured with half a liter of boiling water and drunk as tea.
- Cornflower flower tincture. Take two tablespoons of this remedy twice a day, before meals. The remedy is prepared as follows: the flowers of the plant are poured with a quarter liter of boiling water. Afterwards you need to wait a few hours.
By taking various tinctures, you bring the moment of recovery closer. They are easy to prepare at home.
Useful video
For information on the diagnosis and treatment of cystitis, watch this video:
Similar articles
- Ureaplasmosis in women: causes, symptoms, incl.
men... Even normally, women can have ureaplasmosis. The reasons for the development lie in unprotected sexual intercourse and other reasons. Symptoms are often mild, causing the infection to become chronic. Treatment with drugs is necessary for both women and men. Read more - Genital herpes in women: symptoms, analysis...
Since 90% of people have herpes itself, it is transmitted sexually or through mucus, an exacerbation can occur at any time. Once genital herpes is diagnosed in women, there cannot be a complete cure. Nevertheless, it is worth doing everything to prevent it from becoming recurrent. Read more
- Trichomonas vaginitis: symptoms in women, treatment...
Trichomonas vaginitis develops under the influence of Trichomonas parasites. The disease has unpleasant symptoms and brings a lot of discomfort. It also provokes urethritis. The woman should be treated as quickly as possible. Read more
- STD infections: list of infections in women, which...
Due to unprotected and active sex with different partners, you can get STD infections. Their list is quite extensive, and the symptoms are initially invisible to many. What are the hidden infections in men and women? How to treat if you couldn’t protect yourself? Read more
What is the danger of urethritis?
In terms of complications, women are, on the one hand, more fortunate than men, and on the other hand, less fortunate. Since the urethra is shorter in women, the outcome of inflammation, which manifests itself as scarring and stenosis (narrowing) of the urethra, rarely occurs. And if it does occur, it can be treated quickly and simply, since the short urethra is accessible throughout its entire length for reconstructive plastic surgery. In men, stenosis can occur in several areas and quite deeply, which poses significant difficulties for radical treatment.
On the other hand, in women it is the insignificant length of the urethra that leads to the fact that urethritis quickly turns into cystitis, with inflammation spreading to the mucous membrane of the bladder. Therefore, very often these two inflammatory processes occur together in women, and it is impossible to establish which pathology arose first.
Also, inflammation of the urethra can transform from an acute process into a chronic one. And treating chronic urethritis and cystitis in women is not an easy task.
Diagnosis of the condition
The first stage of examining a woman with suspected cystitis and urethritis is a gynecological examination. Making an accurate diagnosis causes certain difficulties, since the symptoms of urethritis are often vague. Unfortunately, women often consult a doctor when signs of the inflammatory process are evident. Upon examination, the doctor may detect hyperemia of the external opening of the urethra and a certain amount of discharge when pressed.
The diagnostic scheme for these diseases, as well as other inflammatory pathologies of the female genitourinary system, is standard and does not cause problems. The key points in the process of determining the diagnosis are the following:
- First of all, it is necessary to exclude other possible diseases that occur with similar symptoms - neoplasms of various etiologies, polyps, pyelonephritis and other inflammatory kidney diseases.
- Identify the causative agent of infection and analyze the resistance of strains to antibiotics.
- Be sure to examine both sexual partners.
Clinical research includes the following methods:
- General urine analysis. An important diagnostic sign is color, transparency, the presence of impurities characteristic of an infectious lesion - mucus, pus, fresh red blood cells, protein inclusions, an increase in the number of leukocytes above five in the field of view, the presence of pathogenic microflora.
- General blood analysis. An indicator of the presence of an inflammatory process is a high level of leukocytes and an increase in ESR, the predominance of segmental neutrophils in the leukocyte formula.
- A urine culture test is carried out to determine the causative agent of infection and determine the resistance of the identified pathogens to different groups of antibacterial drugs.
- Mandatory smear of the contents of the urethra for bacteriological examination using PCR methods and under a microscope.
- Ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs.