A cyst is a sac-like tumor that is located in the vestibule of the vagina. Over time, the cyst may increase in size due to the accumulation of fluid, air or other substances in the body. The disease can remain asymptomatic for a long time. Diagnosed using gynecological examinations. At the initial stage, drug treatment is prescribed. In advanced form, removal surgery is performed.
A vaginal cyst can be located on both the external and internal parts. The tumor can be as large as a tennis ball or very small. The cyst has a round or oval shape. It is an elastic ball filled with transparent mucous contents, light yellow or dark brown. The outer part of the tumor is in contact with the muscle tissue of the vaginal walls. Usually the size does not exceed 10 cm in diameter. Cyst most often affects the anterior wall of the vagina. According to statistics, cysts are diagnosed in women suffering from dysplasia.
Thanks to modern medicine and special equipment, vaginal cysts are detected and treated in the early stages. There have been no cases of development from a cyst to a malignant tumor. As the disease progresses, pain increases and a lot of discomfort is created. To save yourself from unwanted consequences and complications, seek help from doctors in a timely manner.
Causes
A number of reasons for the formation of a cyst in a woman’s vagina have been identified. There are several main factors of appearance:
- congenitality;
- injuries;
- implantation cyst.
Congenital factor refers to the abnormal development of the vaginal walls. This is formed during the girl’s uterine life. Formations can develop on both sides of the external opening channels. Often this cyst is in the anterior part of the wall, but can be located deeper. The vestibule cyst is due to the fact that it is located quite close to the vaginal opening, and a woman can detect it on her own.
Traumatic ones most often result from rough sexual penetration, as well as traumatic impact in the groin area. An implantation cyst occurs after surgery. For example, abortion or postpartum trauma.
The development of a cyst can also be caused by:
- failure to comply with hygiene rules;
- bacterial infections of the vagina;
- complications during pregnancy;
- postpartum complications;
- artificial pregnancy loss;
- injury;
- painful sex;
- dysplasia;
- endometriosis;
- gonorrhea, chlamydia, trichomonas.
The cause of a cyst in the vagina is determined by its visual appearance and location. The following types exist:
1. Bartholin cyst. Located on the Bartholin glands, which secrete a natural fluid to lubricate the labia.
2. Gartner's cyst. Appears as a result of the non-disappearance of the embryonic canals. Remaining secretions can lead to the development of a cyst.
3. Muller. Appears anywhere in the vaginal wall. A common type of cyst. Develops from materials left behind after fetal development.
4. Epidermal. Location – lower part of the wall. It is difficult to notice, it is small in size. The most common type of cyst that occurs as a result of traumatic injuries.
This truly female disease has no age category. Both newborns and older adults are at risk. Only a few percent of girls are diagnosed with a cyst at a young age. A woman can live her whole life and not even know about the existence of this pathology in the absence of causes, complaints and symptoms.
Sharp and rough penetration during sexual activity most often provokes the appearance of a cyst. Bruises and micro tears appear on the vaginal wall.
Why are vaginal cysts dangerous?
The neoplasm can be located either superficially or penetrate deep into the tissue, reaching the paravaginal tissue.
Its size usually does not exceed a walnut, but sometimes it can grow to the size of a large chicken egg. Consistency – tight or soft elastic. Upon examination or in the photo, it can be seen that the cystic formation looks round, has an ovoid or round shape. The outer walls of the vaginal cyst are formed by connective tissue with the inclusion of single muscle fibers. The internal cavity is lined with cubic, prismatic or columnar epithelium. The contents are transparent, serous or mucous, color – from light yellow to dark brown.
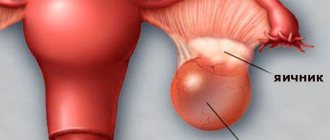
A cyst in the vagina is a retention neoplasm that is localized in the walls of the organ. Its size can increase due to the accumulation of fluid in it.
A tumor of this nature can be located superficially on the wall, or penetrate into its deeper layers, reaching the peri-vaginal tissue.
Although, in most cases, the tumor in the vagina is not large, sometimes it can reach the size of a walnut or a chicken egg. The structure of the formation can be soft or tight-elastic.
The outer walls of the cyst are composed of connective tissue, partly muscle, and the internal cavity is covered with cubic or columnar epithelium.
Inside the formation there is mucous or serous contents of a yellow or light brown hue.
Depending on how the cyst appears, they can be congenital or acquired. The development of the former occurs from the embryonic parts of the paraurethral and Müllerian ducts, as well as Gartner's ducts, and the latter are localized in the lateral walls of the vagina, on the fornix, and can transfer to the parametric tissue. Congenital cysts are often combined with vaginal malformations.
Secondary or acquired cysts are also called implantation cysts. They can develop against the background of a surgical abortion, birth injuries, or surgical interventions for vaginal fistulas. Most often they are located in the posterior wall of the lower parts of the organ.
Cystic formations are of the following types:
- Congenital - cavities filled with transparent contents, located on the anterior vaginal wall. These formations are soft, elastic, located deep, so they are detected only when straining. The gynecologist sees the formation in the form of an elastic bubble. Such a cyst is easily “recessed” deep into the tissue and becomes invisible if the woman lies down.
- Acquired ones are denser and harder, palpable in any position. They can occur anywhere in the vagina. Sometimes cysts begin to grow, blocking the entrance to the vagina and interfering with sexual activity. Acquired cysts are often the result of tissue ruptures during childbirth, abortion, or violent sexual games, such as fisting.
- Endometriotic - foci of endometriosis in the vagina. These formations increase before the onset of menstruation and subside after it. They are often multiple. Periodically, such cysts rupture on their own or during sexual intercourse, releasing dark brown fluid. In place of spontaneously opened cystic cavities, scars form, reducing the elasticity of vaginal tissue. The reasons for the formation of endometrioid cysts are hormonal disorders.
Symptoms of vaginal cysts are varied - from a complete absence of discomfort to severe pain, like an abscess. An increase in the size of the formation leads to discomfort during sexual intercourse and the sensation of a foreign body in the lumen of the genital tract.
Sometimes vaginal cysts fester. The patient's temperature rises, chills occur, and her general condition deteriorates. There is severe pain in the vagina, radiating to the perineum and rectum. Without treatment, the cyst breaks through to form a fistula. In severe cases, blood poisoning may occur.
Large cysts, growing, affect the function of neighboring organs - the bladder, urethra, rectum. Cystic formations create problems during childbirth, interfering with tissue stretching and causing ruptures.
If the cystic formation is soft, elastic and does not create discomfort, it does not need to be removed. In this case, the woman is periodically observed by a gynecologist. In case of growth, suppuration, or impact on the functioning of neighboring organs, mandatory removal of the cyst is indicated. For a woman planning pregnancy and childbirth, it is better to get rid of the formation in any case, since it will interfere with childbirth.
There are several surgical methods for treating vaginal cysts:
- Puncture with aspiration of contents is a puncture of the walls through which the contents of the formation are removed. The procedure is performed on an outpatient basis under local anesthesia, but after such an intervention the cysts often appear again. It is mainly carried out when huge cysts are detected during pregnancy.
- Marsupialization is a method in which the cyst is dissected and its walls are sutured to the vaginal mucosa. The channel that removes mucus opens and the cyst no longer appears.
- The radical method, in which the formation is removed with the membrane, provides 100% absence of relapses, but cannot always be performed with vaginal access. Because some cysts grow deeply into the surrounding tissue, the tumor must be excised through an incision in the skin of the abdomen. Now such an intervention is carried out using the endoscopic method, so it does not leave rough sutures or scars.
Although this type of neoplasm does not turn into cancer, vaginal cysts need to be treated. The advisability of removal and the type of surgical intervention can only be determined by a doctor. If endometriotic cysts are detected, the underlying disease is treated.
Symptoms
When small in size, the cyst does not cause any inconvenience to a woman throughout her life. There is no sensation when having sex or urinating. Most often, a cyst of this size is diagnosed during a routine examination. If the cyst is large, there is a chance that the cyst may become infected with bacteria found on the skin. Also, sexually transmitted infections caused by non-compliance with hygiene rules can lead to infection of the cyst. Cause purulent inflammation, abscess.
A cyst accompanied by an abscess has symptoms of intoxication of the body. Fatigue and weakness, dizziness, nausea, and vomiting appear.
A cyst occurs as a result of the presence of abnormal development. Blockage of the canal leads to the accumulation of secretory fluid. Its outflow into the vagina is disrupted. Thus, a blockage occurs, and over time the duct begins to overgrow. If you discover a growth on your own, but it does not cause discomfort or pain, do not panic. To establish and confirm the diagnosis, undergo a gynecological examination.
This type of endometrium is rare. Occurs during mechanical damage to the vagina. The cavity is filled with liquid, has a brown color and bloody inclusions. Patients experience severe pain in the lower abdomen, as well as pain when visiting the toilet. Severe menstrual pain. The following signs of a malignant tumor are distinguished:
- significant increase in body temperature;
- sudden weight loss;
- lack of appetite;
- uterine pain;
- compaction is felt through the abdominal cavity;
- change in color of discharge, presence of odor;
- fast fatiguability.
Diagnostic procedures
The cyst is diagnosed during an examination by a gynecologist using auxiliary instruments. A transvaginal ultrasound is performed. Be sure to purchase a special gynecological kit. The cyst is also detected during a routine ultrasound.
The first and most important point is to question the patient for complaints. The severity of symptoms will help determine the extent of the disease. Mandatory procedures include passing general urine and blood tests. A bacterial smear of the vagina is also taken for testing.
When this diagnosis is established, girls and women must visit a proctologist and urologist to exclude and prevent other concomitant diseases.
Failure to diagnose a cyst in a timely manner can cause infection of the vaginal tissue. Purulent inflammations will be cystic in nature. Severe pain can occur as a result of the bursting of the soft-elastic or tight-elastic tissue of the bag. After treatment, the pathology relapses.
DIAGNOSTICS
Vaginal cysts are diagnosed during a gynecological examination using speculum; They look like round or oblong formations of tight-elastic or soft-elastic consistency. Vaginal cysts are differentiated from prolapse of the vaginal walls, cystocele, rectocele, urethral diverticula; If necessary, urologists and proctologists are involved in diagnostics.
Before surgery to remove a vaginal cyst, colposcopy, bacteriological and microscopic examination of smears are additionally performed. Using ultrasound, the position of the cyst relative to the parametrial tissue, rectum and bladder is clarified.
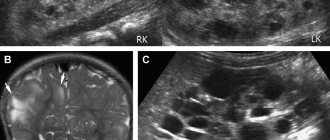
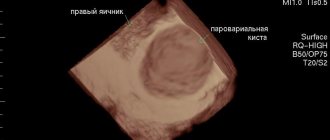
An ovarian cyst is diagnosed using:
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- Doppler measurements;
- Computed tomography;
- MRI.
When a cyst is first detected, its condition is monitored for 3 months. If the cyst is functional, it disappears on its own.
A cervical cyst is detected when:
- Gynecological examination;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- Colposcopy.
A cyst formed on the Bartholin gland is identified during examination. Ultrasound examination makes it possible to determine its shape and features. If an infection is to blame, then tests are carried out to identify urogenital infections, and antibacterial therapy is carried out.
A vaginal cyst is detected during a gynecological examination. To determine its size, an ultrasound examination is performed.
During a gynecological examination using speculum, vaginal cysts are clearly visible. They look like oblong or round formations, soft or elastic consistency.
Differential diagnosis is carried out with the following diseases:
- urethral diverticula;
- rectocele;
- cystocele;
- prolapse of the vaginal walls.
If necessary, the gynecologist can refer the patient for consultation to doctors of another specialization (proctologist, urologist).
If removal of a cystic formation is indicated, a preoperative examination is performed, which includes:
- ultrasonography;
- microscopic and bacteriological examination of smears of discharge from the vagina, cervical canal and urethra;
- colposcopy.
Selection of a clinic
You should take seriously the choice of the clinic where you want to undergo surgical removal of a vaginal cyst. Choose only qualified specialists with extensive experience in carrying out such operations. Experts offer little-known and effective treatment methods. The price must correspond to the quality. The main goal is to work for results, the patient’s speedy recovery.
The location of the hospital and operating rooms plays a big role. It is necessary to have modern equipment for performing operations and all types of diagnostics. A sufficient number of medical workers to ensure control of the rehabilitation period. Availability of comfortable beds and comfortable conditions for hospital stay.
Types of operations
In other cases, the treatment method is surgical. There are two main types of treatment for vaginal cysts:
1. Puncture. Using a syringe and biopsy needle, fluid is removed from the cystic sac. The method is temporary. Over time, the cavity begins to fill with fluid again. It is used, for example, during pregnancy, when surgical intervention is contraindicated for a woman.
2. Complete removal of the formation. During surgery, the doctor completely removes the growth with fluid. The operation is performed under anesthesia. Also during childbirth in the process of removing perineal tears. The method is used quite rarely. This is the most extreme case of deletion. There is a possibility of complications affecting the urinary duct. Due to removal and stitches, the visual aesthetic appearance is lost.
3. Marsupialization. It is also possible to have surgery to drain the fluid from the capsule and suturing its shell to the vaginal wall to prevent re-accumulation. This is the safest type of surgery.
Complications
Gartner's cyst is not an obstacle to conception and birth of a child. In addition, such a benign formation is not a contraindication to natural childbirth and does not affect menstrual function. However, women with this diagnosis should be under the dynamic supervision of a doctor.
In case of incomplete enucleation, which is often noted during puncture aspiration, there is a high probability of recurrence of the cyst. The operation to remove a benign tumor does not affect the woman’s health in any way and the prognosis is quite favorable.
Contraindications
Surgery should not be performed during menstruation. There is also a list of contraindications:
1. Bad urine and blood tests.
2. Lack or excess of platelets, leukocytes, and erythrocytes in the blood.
3. Low or elevated hemoglobin levels.
4. Severe cardiovascular insufficiency.
5. Infectious disease.
6. Drug intolerance.
7. Old age.
8. Oncology.
Progress of the operation
The anesthesiologist administers local anesthesia to the patient. The surgeon makes a longitudinal incision with a scalpel in the desired area. Performs the necessary actions with the cyst shell. Then, catgut or silicone threads are used to stitch the wall incisions. The seam is treated with an antiseptic. The patient is brought back to his senses.
The prospect of a complete cure is quite high. In most cases, no complications arise and the healing period occurs as quickly as possible. The cyst is a benign tumor, so its transformation into a cancerous tumor is completely excluded and has not been encountered in medical practice. If the fluid is not completely cleared, there is a possibility that the vaginal cyst will reappear.
You should not touch the cyst if it does not cause any complaints. There is a possibility that complications will occur after surgery. Formation of suppuration or fistula.
The Gartner cyst is the safest. It is not a contraindication for conception, pregnancy and childbirth. Does not disrupt the menstrual cycle. But the woman should be under constant supervision of a specialist.
Getting rid of a cyst at home and using folk methods can lead to complications or bleeding. Do not use any medications or supplements without a doctor's prescription.
Removal of vaginal vestibule cyst
Due to the fact that the vaginal vestibule cyst is located almost near the vulva, it is quite easy to detect. Enucleating such cysts is also not difficult.
The surgeon makes an incision into the mucous membrane down to the cyst capsule. Then carefully separates the capsule from the tissues surrounding it. He ligates the pedicle of the cyst and cuts off the cyst itself.
Currently, when performing this operation, most gynecologists prefer an oval incision, since it reduces the likelihood of damage to the cystic sac with leakage of its contents into the vaginal cavity and into the surgical wound, which can cause infectious complications in the postoperative period.
Rehabilitation
The period of rehabilitation and therapy is short. Healing and resorption of sutures occurs quickly. The woman has been in the hospital for a couple of days. Next, as you feel better and have the doctor’s permission, you can switch to a day hospital.
Already after 2-3 days, movement is allowed. Without making sudden movements or bending. Do not lift heavy objects. Within a month, the menstrual cycle is restored. Supportive housing may be worn after surgery.
The seams are treated with antiseptic solutions to prevent infection. Do not drink alcoholic beverages and stop smoking. Do not take vasodilators.
Prevention
Timely diagnosis and removal helps women avoid problems during pregnancy. All visits to the gynecologist should not be painful, and examinations will be performed with care by the gynecologist. An asymptomatic cyst does not have a negative effect on the reproduction of the female body.
If you find a cyst, immediately make an appointment at the clinic. To reduce the risk of its occurrence, observe the following points:
Always keep your vagina clean. A healthy lifestyle, painless and protected sex are the main factors for the health of the female genital organs. Use lubricant to normalize the vaginal environment during sex, to avoid damage and pain. By following these steps, the incidence of vaginal cysts decreases or disappears completely.
A vaginal cyst is not a terrible disease, which can be easily and simply dealt with by following certain rules. If a growth is detected and enlarged, or characteristic symptoms appear, consult a gynecologist in a timely manner. You should not self-medicate. Start the process of deterioration and make the disease progressive.
Treatment
This disease can be treated in one way - a surgical operation aimed at removing the vaginal cyst from the tissues of this organ. This procedure can be carried out in several ways:
- puncture aspiration - but such medical intervention has only one drawback, it is a temporary effect. Some time after removal, the tumor begins to accumulate fluid again;
- marsupialization is the safest method of treatment that can be used by girls and women during pregnancy. The procedure consists of dissecting and emptying the cyst, followed by suturing the walls and mucous membrane;
- A radical method of eliminating a cyst is to make an incision on the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity, through which the tumor is removed. At the end of the operation, catgut sutures are applied.
If a small vaginal cyst is detected, dynamic monitoring of its development is required.
In addition, vaginal cysts can be treated using traditional medicine. To do this, you should use recipes for decoctions and tinctures based on:
- burdock;
- cabbage leaves;
- golden mustache;
- celandine and milk;
- wormwood and St. John's wort;
- string and yarrow;
- sage, nettle and knotweed.
It is worth remembering that folk remedies can only be used as prescribed by the attending physician, especially for girls and women carrying a child.
There is no specific prevention of such a disease; it is only necessary to regularly and carefully follow the rules of personal hygiene, limit yourself from hypothermia and properly monitor the development of pregnancy.