Palpation results
There is an opinion that the cervix changes its position or position according to the days of the menstrual cycle, or more precisely, its phases.
Immediately after menstruation, it is located low to the entrance to the vagina and has the shape of a cone. It is easy to reach with your finger, and to the touch it resembles the tip of your nose.
Closer to ovulation, the cervix becomes softer, it is more difficult to reach it with a finger, and abundant viscous discharge appears, reminiscent of egg white. In the middle of the cervix you can find the entrance to the cervical canal, where the discharge comes from. In women who have given birth, the external os (entrance to the cervical canal) is always slightly expanded, regardless of the phase of the cycle.
After ovulation, the cervix takes its original position (as after menstruation) and only before the onset of menstruation does it soften again. If pregnancy occurs, it remains tight and closed. They say that in this way you can easily determine your pregnancy before the start of a missed period, in the earliest stages.
Schematic representation of its changes.
Basic diagnostic methods
The main diagnostic methods include the following:
- Carrying out an inspection using mirrors to identify lumps and growths.
- Examination of a smear, which is taken from the surface of the cervix to detect malignant cells.
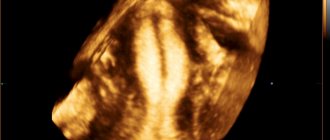
- Performing an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs. This is done to identify the volume of endometrial thickening, and, in addition, to detect lumps.
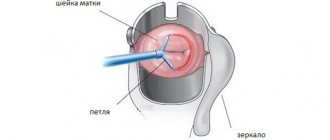
- Performing a hysteroscopy allows the doctor to detect the presence and number of polyps along with their size. It also allows tissue analysis to be taken for biopsy.
- Taking a tissue biopsy from the cervix.
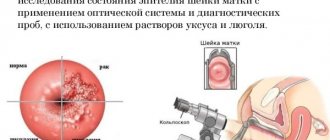
- Extended colposcopy. Such an analysis is required to determine the presence of factors such as dysplasia, ectopia, leukoplakia and erythroplakia.
An examination is necessary even if the lump on the cervix is small. Any type of it can reappear immediately after removal, which largely depends on its type. In particular, Nabothian cysts, polyps and fibroids often recur. Often, those tubercles with bumps that women palpate on their own turn out to be ordinary scars remaining after destructive surgical treatment of pathologies, and, moreover, after childbirth.
Next, let's move on to consider advice from gynecologists and find out what recommendations they provide to their patients so that they do not experience such a phenomenon as lumps on the uterine cervix.
What to do if you feel a lump on the cervix?
How to do a vaginal self-examination
- Wash your hands. Trim your nails. You can wear sterile medical gloves.
- Squat on the toilet or raise one leg on a stool.
- Gently insert your middle finger into the vagina until you feel the cervix (it is located at a depth of 3-6 cm). Also, with certain skills, you can feel a small depression there - this is the opening of the cervical canal. Please note the following:
- how deep is the cervix from the entrance to the vagina (how far did you have to immerse your finger);
- consistency: soft, like pursed lips, or hard, like the tip of your nose;
- the neck is located at an angle or closer to the center;
- the external os is open and soft or tightly closed.
Ball on the cervix
Content
- 1 Reasons
- 2 Diagnostics
- 3 Treatment and prevention
Some diseases of the reproductive system, as well as hormonal imbalances in women, can provoke tissue modifications and the appearance of various neoplasms in the form of balls and tubercles on the cervix. Most often they are discovered during a gynecological examination of the cervix or during self-examination.
Causes
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytcopyright
Lumps or balls that appear on the surface of the cervix can have different origins. They can be painful or not, be the result of a serious illness, or not cause any harm to the female body at all.
A ball on the cervix may appear for the following reasons.
- Cyst. In this case, a tumor in the form of a ball is formed due to blockage of the nabothian glands located in the walls of the cervix. This disease is asymptomatic and is detected only during colposcopy.
- Benign formations are cervix polyps. In this case, the compaction poses a threat of malignancy, and therefore requires prompt diagnosis and removal. Most often it is formed due to hormonal changes in the body.
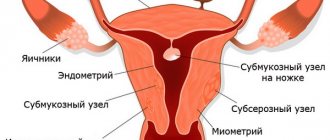
- Cervical fibroids. In this case, a small lump or nodule forms on a stalk, which is an overgrowth of muscle tissue. This tumor is removed because it can interfere with conception and the normal course of pregnancy.
- Malignant tumor. The most dangerous cause of the appearance of a ball on the cervix. The main type of treatment is usually surgical removal followed by chemotherapy.
- Scar. Compaction can occur after surgery or difficult childbirth, when tissue ruptures and subsequent scar formation occur. Uneven healing of the injury site can also occur after mechanical damage, injury or rough sexual intercourse. In this case, damage occurs to the mucous membranes of the cervix and disruption of the integrity of the integumentary epithelium.
- Papillomatosis. Papillomas in the form of a ball or tubercle arise due to the persistence of the papillomavirus. Depending on the type of HPV, the doctor determines treatment tactics. Papillomas initiated by HPV with a high risk of carcinogenesis pose a health threat and require removal with parallel antiviral treatment.
- Erosion. This is another reason for the appearance of a ball or bump on the cervix. In this case, the mucous membrane is damaged and an ulcer appears.
In order to accurately establish the cause of the ball on the cervix, its structural features and size, it is necessary to undergo a whole range of diagnostic measures.
Diagnostics
If you find any lump or bump on the walls of the genital organs at home, you should immediately consult a doctor.
A gynecological examination of the cervix is the first and one of the most important stages in the diagnosis of a number of diseases.
Using special instruments, the doctor can examine the lump, determine its approximate size, location and other external characteristics. After this, the following types of studies may be prescribed.
- Taking a smear for cytology. This allows you to obtain preliminary information about whether the tumor is benign or malignant.
- Ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs. Using this method, you can determine the location of the ball, which is a nabothian cyst or fibroid, and identify other structural changes in the cervix.
- Hysteroscopy. The procedure is carried out using a special instrument - a hysteroscope, which allows you to study in detail the structure and morphological features of polyps, fibroids and other formations. In addition, the method allows you to take a small section of tissue or mucous membrane for further study of the cellular composition.
- Metrography. The principle of the method is similar to radiography, only in this case it involves the introduction of a contrast agent into the uterus. With the help of this study, you can obtain data on the relief of the uterine cavity, identify all the irregularities, balls and growths.
- Extended colposcopy will identify ectopia or dysplasia.
After detailed information about the ball on the cervix has been received, the doctor prescribes the optimal and most effective treatment.
The type of treatment is prescribed depending on the initial cause of the ball on the cervix and the degree of pathology.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytabout
The most commonly used methods are laser removal, treatment of the tumor with liquid nitrogen, and exposure of the affected area to radio wave radiation.
In the initial stages of the disease, as well as in case of hormonal disorders, the gynecologist may prescribe the use of appropriate hormonal and antibiotic medications, multivitamin complexes and agents that enhance the regeneration of cervical tissue.
It is important to understand that the method of treatment also depends on whether the girl gave birth or not. Some methods, such as cauterization using an electric loop, are strictly contraindicated for girls. After the procedure, a scar remains on the surface of the genital organs, which can interfere with normal conception and pregnancy.
To prevent the ball from reappearing on the cervix, a number of rules must be followed.
- Use barrier and hormonal contraception methods to avoid infection and unwanted abortion.
- Regularly visit a gynecologist for timely detection of tumors.
- Observe personal hygiene rules.
- Have a measured sex life without frequently changing partners.
Compliance with these recommendations is a good preventive basis not only for the appearance of cervical tumors, but also for the development of most diseases of the female reproductive system.
Balls on the cervix can have different causes. Timely consultation with a doctor and diagnosis of the problem are the key to successful treatment of cervical diseases.
BeTeshka is your assistant in pregnancy planning
Lumps, bumps, tumors and pimples
During self-examination, women can feel a hard lump the size of a pea or slightly larger on the cervix with their finger. What it is? Naturally, only a gynecologist will announce the diagnosis. He will examine you on a chair using a special gynecological mirror and visually assess the existing changes (if any), whether it is lumpy or not. But most often what is felt during pregnancy, at the beginning of the menstrual cycle or immediately before menstruation is not a lump or a tubercle, but simply the cervix.
Other possible reasons:
- Nabothian cysts (especially if there are a lot of lumps);
- candilomas (like dysplasia and cancer, they are provoked by the human papillomavirus, but not by the oncogenic strain);
- ectropion - eversion of the mucous membrane of the cervical canal outward, towards the vagina, as a result of childbirth;
- rupture after childbirth;
- scar after cauterization - treatment of dysplasia;
- malignant tumor - usually with cancer at this stage there are already other symptoms, for example, foul-smelling, purulent vaginal discharge, bleeding outside the menstrual cycle;
- polyp is a benign neoplasm, a growth emanating from the cervical canal or even the uterine cavity; requires removal as it can degenerate into cancer.
Dear readers, in order to avoid injuries to the soft tissues of the vagina and cervix, do not perform self-diagnosis, especially if you have signs of an infectious process (thrush, vaginal dysbiosis, etc.). Detecting pathology in time and receiving treatment is, of course, good. But even a doctor cannot diagnose herself by simply palpating the cervix! A visual inspection is required. Once every 6-12 months, visit the gynecologist’s office for preventive purposes and you will be sure that nothing threatens your health.
Types of cervical tumors and principles of classification
Despite the current International Statistical Classification of Diseases (ICD-10), other nomenclatures are used in clinical practice to describe identified cervical tumors. They are based on the origin and histological structure of the tumors, the degree of malignancy of the tumor cells.
All neoplasms are divided into benign and malignant. In addition, there are so-called pre-tumor and background diseases - local tissue changes that increase the risk of cell malignancy and require active follow-up. Such conditions most often affect the mucous membrane and can be detected during a targeted examination of the woman.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with a growth in the nose in humans: types, causes and treatment
If a malignant tumor of the cervix is detected, the TNM oncological classification is additionally used. To do this, evaluate the invasiveness of the tumor, the involvement of underlying tissues and adjacent organs in the process, and the presence of regional and distant metastases. This allows you to determine the stage of the disease.
Based on the type of growth, tumors are divided into exophytic (increasing outward) and endophytic (deepening). The latter, in relation to surrounding tissues, can be invasive (growing) or non-invasive.
According to histological classification, there are several types of pathological formations of the cervix:
- Neoplasms of epithelial origin (squamous and glandular type). They are the most common and often potentially malignant. Benign squamous cell tumors include papillomas, condylomas with signs of human papillomavirus infection, squamous cell and transitional cell metaplasia. And malignant squamous cell carcinomas are of keratinizing, non-keratinizing, verrucous and papillary types. Glandular tumors are cervical polyp, Müllerian papilloma, glandular dysplasia and carcinoma in situ, various types of malignant adenocarcinomas.
- Tumors of stromal (mesenchymal) origin. The most common are leiomyomas, leiomyosarcoma, endometrial and endocervical stromal sarcoma, and embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma.
- Cervical fibroids originating from the muscular layer.
- Tumors of mixed type, in the tissues of which there are epithelial and stromal elements.
- Neoplasms of another type: lymphoma, blue and melanocytic nevus, melanoma, teratoma and some others.
- Metastatic tumors, similar in structure to the cells of the primary lesion in various organs.
Identification of any neoplasm in a woman is the basis for subsequent dynamic observation with repeated histological examination of tissues. This is necessary for timely diagnosis of signs of cell malignancy and the appearance of another tumor focus.
What does the appearance of a tubercle mean?
Statistics show that only 15% of women of reproductive age undergo routine examination. This explains the high diagnosis of malignant tumors, reaching 35%.
In 65% of cases, a growth that appears on the neck turns out to be a diagnostic sign:
- Benign polyp.
- Submucosal nodule.
- Erosion.
- Pseudo-erosions.
- Myomas.
- Cysts.
- Papillomas.
If a growth appears on the cervix or a pea-sized bump that feels lumpy to the touch and purple in color, then most likely it is a polyp.
A moving ball on a stalk in 5% of cases means the formation of a submucosal nodule. The presence of such a formation prevents conception, as it disrupts the natural progression of sperm.
The growth may be a sign of cervical fibroids, which was previously considered a precancerous condition. In fact, a myomatous node does not lead to the development of oncology and does not require removal unless it grows.
Prevention
Preventive measures are aimed primarily at reducing the risk of malignant tumors. These include:
- Sexual hygiene in compliance with the principles of safe sex, prevention and timely full treatment of STDs.
- To give up smoking.
- Regular visits to the gynecologist or examination room for preventive examinations. For women at risk, screening includes not only a visual assessment of the condition of the cervix and vaginal walls, but also a smear for oncocytology. And the presence of any changes is the basis for regular colposcopy.
- Vaccination against human papillomavirus infection in teenage girls.
- Virological examination if any signs of HPV infection appear to determine the oncopathogenicity of the pathogen and assess the risk of developing cervical cancer.
https://youtu.be/2m7SaWfstJ4
Cervical tumors are one of the most pressing problems in gynecological oncology. With early detection and timely, comprehensive treatment, all of them are curable. Therefore, preventive examinations are the basis for women to preserve not only reproductive health, but also life itself.
Reasons for appearance
The appearance of a growth in the area of the uterine cervix can be explained by inflammation and blockage of the nabothian glands. If the outflow from the gland is disrupted, a cyst forms in this place.
Rough bumps on the cervix are formed as a result of scarring of tears caused during childbirth. The appearance of such bumps can be caused by:
- abortion;
- taking hormonal contraceptives.
Pryshchikov
The reasons for the appearance of moving or static pimples on the cervix can be:
- chronic diseases of the endocrine system;
- early sexual life;
- frequent change of sexual partners;
- rough sex;
- stress;
- unprotected sex.
Polypov
Tubercles of polyps appear on the cervix as a result of:
- weakening of the immune system;
- inflammation of the genital organs - endocervicitis, adnexitis, endometritis;
- hormonal disruption of the ovaries;
- scraping.
Causes
Cervical cancer ranks third among cancer pathologies in women, most often the disease occurs between the ages of 35 and 55 years.
Causes of oncological processes:
- human papillomavirus;
- genital herpes, HIV, chlamydia;
- deficiency of vitamin A, C;
- weakened immune system;
- prolonged contact with radioactive and toxic chemicals;
- early or frequent abortions;
- scarring and trauma to the cervix;
- promiscuity;
- stress, overwork.
The presence of malignant tubercles is indicated by bloody discharge after sex, during menopause, or copious vaginal discharge with a cheesy consistency mixed with blood, pus, and an unpleasant odor. With cervical cancer, menstruation lasts more than a week, cramps in the lower abdomen radiate to the lumbar region, the temperature rises, the woman is worried about swelling of the legs, weakness, and chronic fatigue.
If you discover a tubercle on the cervix, you should not panic - according to statistics, only 20% of such neoplasms are malignant.
Since tubercles on the cervix can appear at any age, women should know what it is, how the pathology manifests itself, and how dangerous it is. Even the most harmless gynecological problem should not be neglected - timely consultation with a doctor will help save energy, time and money, and in some cases even life.
Main methods of treatment
Benign lumps on the cervix are treated using the following methods:
- cryotherapy;
- laser therapy;
- cauterization with liquid nitrogen;
- radio wave therapy.
The radio wave method is considered the most gentle method of treatment. It is used to remove benign growths when planning pregnancy.
Drug therapy
For polyposis, drug treatment is used:
- hormonal contraception;
- antibiotics;
- with anti-inflammatory effect;
- vitamin complexes.
Surgery
Balls that have not reached a significant size are removed by cauterization. Small abscesses are punctured. For significant nodes, surgery is performed.
Intervention may be required for polyposis. The procedure is performed using a hysteroscope under visual control.
A gentle type of operation that preserves reproductive function includes treatment of the tubercle with a laser beam.
Some women, when carrying out hygienic procedures, may feel a tubercle on the cervix, let’s try to figure out what it is. It’s worth saying right away that such formations are far from uncommon, but in most cases they do not pose a threat to the health and life of the girl.
Medical opinion in this regard is ambiguous. Some experts argue that therapy is necessary, while others, on the contrary, assure their patients that regular regular monitoring is sufficient. In some situations, a tubercle on the cervix indicates a serious illness, but not many people know how to determine this. Therefore, the topic should be disclosed as completely as possible.
What other symptoms are characteristic of growths?
Small tumors usually do not cause any external symptoms. They can be detected during preventive, screening or random gynecological examinations. Lack of complaints is the main reason for untimely consultation with a doctor and a tendency to partially comply with treatment recommendations. This tactic of a woman’s behavior is a risk factor for late diagnosis of cervical cancer and significantly worsens the long-term prognosis of the disease.
The appearance of complaints usually indicates the development of complications or that the tumor has reached a sufficiently large size. Neoplasms can compress nerve endings, grow through the thickness of the cervix into surrounding organs, disintegrate, ulcerate, and become injured. All this is common and is accompanied by the development of certain symptoms.
The most likely symptoms of a cervical tumor are:
- Discomfort and pain in the depths of the vagina or lower abdomen during sexual intercourse - both during friction and when a woman reaches orgasm.
- Intermittent acyclic bleeding, which may indicate traumatic damage to the surface of the tumor, its disintegration, or germination of the vessel wall. Their volume can vary from isolated streaks of blood to profuse bleeding.
- Painful sensations in the lower abdomen, rectum, sacrum of a constant nature. May be associated with tumor growth, compression of nerve endings, displacement and reactive inflammation of adjacent organs.
- Pathological vaginal discharge of a purulent nature or in the form of a clear yellowish liquid. And the disintegration of a cervical tumor is usually accompanied by foul-smelling leucorrhoea.
- Swelling and varicose veins of the external genitalia and asymmetric lymphostasis of the lower extremities. They arise due to compression of the lymphatic and venous vessels by a large tumor or conglomerate of lymph nodes affected by metastases.
When a tumor grows into the bladder or rectum, signs of dysfunction of these organs appear. The formation of rectal and urinary fistulas is also possible. Benign cervical tumors, even large ones, do not lead to the development of such symptoms; this is a sign of invasive cancer.
Many reproductive pathologies are accompanied by changes in the uterine cervix. These tumors can be quite painful to the touch. A lump on the cervix requires close monitoring. This frequency symptom signals the progression of a serious illness.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Growth in the anus in women
Collapse
A ball formed on the cervix is usually a benign polyp. Almost always, the growth of this neoplasm is not accompanied by specific symptoms.
The polyp is discovered during an examination by a gynecologist. Externally, it looks like a purple or reddish growth on the cervix.
In the photo there is a uterine polyp
The lump on the cervix can be quite large or the size of a pea. The tubercles are mobile and static.
Submucosal nodules occur in 5% of all cases. In some cases, they have a thin stalk and descend into the vagina. In this case, a specialist can diagnose cervical fibroids.
Previously, it was believed that myomatous node contributes to the development of oncology. Today this possibility has been refuted. But if the fibroid progresses quickly, it needs to be removed. This neoplasm prevents successful conception and pregnancy.
https://youtu.be/Bn428TU5f8w
A gynecologist should be visited when the pain accompanying the lump does not disappear after 72 hours.
A pimple on the cervix indicates the presence of:
- Myomas.
- Papillomas.
- Pseudo-erosions.
- Erosion.
- Cysts.
- Polyps on the mucous membrane.
Some gynecologists argue that this tumor may be a precancerous condition. Sometimes the presence of a pimple on the uterine cervix signals the development of a malignant process.
Reasons for appearance
The main reasons why tubercles appear on the cervix are presented in the table.
| Cause | Factor |
| Nabothian gland cyst | If the glands located on the cervix become clogged, cysts form there. They do not have specific symptoms and are often detected by chance. |
| Scar tissue | Formed during delivery, as well as during surgical interventions. If the growing scar tissue forms unevenly, specific bumps form. Mechanical damage can provoke the growth of scar tissue. |
| Benign tumor | Formed against the background of taking contraceptive drugs or artificial termination of pregnancy. |
| Cancerous tumor | It develops for a number of internal and external reasons. |
Small lumps on the cervix, which are characterized as “pimples,” often appear due to hormonal imbalance. This happens due to:
- frequent and severe stress;
- endocrine pathologies occurring in a chronic form;
- unprotected sex;
- promiscuity of sexual relations.
Another reason is early sexual activity.
They appear against the background:
- adnexitis;
- endometritis;
- endocervicitis;
- improper functioning of the ovaries;
- various scrapings;
- impaired immunity.
Additional alarming symptoms are untimely vaginal bleeding and the appearance of other vaginal discharge. The alarm should be sounded when purulent impurities are present, accompanied by a putrid odor.
The diagnosis is made as follows:
- inspection using a mirror;
- ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs to detect growths;
- metrography.
The most accurate diagnostic method is hysteroscopy. With its help, the specialist identifies polyposis, determines the location and parameters of neoplasms.
During hysteroscopy, a specialist takes biological material for examination. This manipulation eliminates the occurrence of malignant processes.
Metrography is prescribed when, during the initial examination, an uneven surface of the uterine cervix is detected. This method allows you to clarify the nature of the growths. In this case, a contrast agent is injected into the organ cavity.
https://youtu.be/dH9qVzW3Z78
The therapeutic approach depends on the cause that provoked the appearance of the tumor. If a tubercle has formed on the cervix due to the development of a non-oncological disease, then treatment includes:
- Cryotherapy.
- Laser therapy.
- Radio wave treatment.
- Cauterization with liquid nitrogen.
The type of treatment depends on the size and stage of development of the cystic neoplasm. Small cysts disappear on their own. For this reason, a specialist can simply observe them for a while.
Scars on the uterine cervix are not an indication for treatment.
You can get rid of them when planning a pregnancy. They are removed by radio wave radiation. This is the most gentle method that does not leave burns or injure surrounding tissues.
Prescribed for polyposis. The main methods of treatment are presented in the table.
| Type of therapy | Description |
| Hormonal | Combined contraceptives are used. The main goal of treatment is to stabilize hormonal levels. Other goals include stopping the growth of the polyp, eliminating the painful syndrome and normalizing the menstrual cycle. |
| Antibiotic | Prescribed for the infectious-inflammatory nature of polyposis. The use of Erythromycin, Doxycycline, Metronidazole, and Cefotaxime is recommended. |
| Anti-inflammatory | Prescribed for concomitant inflammatory diseases. It is recommended to take Ketoprofen, Diclofenac, Ibuprofen. |
| Vitamin | Prescribed to stimulate the immune system. It is recommended to take B vitamins, zinc, magnesium, and iron. |
If the lump on the uterine cervix is small, it is removed by cauterization or puncture.
The main indication for surgery is the presence of large abscesses. Timely surgery prevents infection.
The operation is also performed using a laser. This is a minimally invasive method, also used quite widely. The laser beam is directed at the tumor. Spot removal brings remarkable results. Reproductive functions are not affected.
A lump on the cervix takes a long time to heal. Therefore, it is very important to prevent its occurrence. Prevention recommendations include:
- Streamlining your sex life.
- Strict adherence to all hygiene recommendations.
- Timely treatment of erosions.
- Regular observation by a gynecologist.
- Timely treatment of inflammatory pathologies.
It is also important to avoid artificial termination of pregnancy, as this leads to the formation of scars on the tissues of the uterine cervix.
The human papillomavirus can be transmitted through household contact. Therefore, it is very important to be careful when sharing dishes and hygiene items.
Childbirth must be carried out correctly. A woman must strictly adhere to all the recommendations of the gynecologist. The birth control procedure itself must take place in the maternity hospital. Before this, the woman undertakes to carefully prepare for childbirth.
All tears formed after childbirth must be stitched up. This applies even to those breaks that do not bleed.
Any neoplasms that appear in the uterine cervix can recur. In this case, there is a risk of developing cancer. The reappearance of polyps is due to non-radical therapy.
Conclusion
Observation by a gynecologist should be systematic and regular even when a woman has no special health complaints. This will help to detect pathology in a timely manner and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Unfortunately, no more than 15% of women follow this recommendation. Therefore, in 35% of cases, a person aged 35-45 years is diagnosed with cancer.
Don't panic if your cervix feels lumpy to the touch. But this alarming symptom should not be left to chance either.
Polyps are characterized by bleeding or heavy periods. Large polyps appear as white discharge and pain in the lower abdomen. Neoplasms cause miscarriages in women of reproductive age, and sometimes infertility. During menopause, heavy bleeding occurs, which leads to weakness and dizziness due to low hemoglobin.
Symptoms
Often after childbirth, girls develop lumps on the cervix, what this is can be explained by the doctor after a thorough examination of the patient. Such situations are a common occurrence for those who had this process with certain complications, for example, there were tissue injuries, then scars formed, and it is in these places that the cervix will be lumpy to the touch. In the absence of pain, discomfort and other unpleasant sensations, such formations do not pose a danger.
However, if a lump on the cervix, a photo of which can be viewed on specific resources and ultrasound images, bothers a woman, pain appears when pressing on it, and it also rapidly increases in size, an urgent consultation with a doctor is required. Almost any gynecological disease, if treated at the initial stage, can be easily eliminated.
What could it be?
So, lumps near the cervix, what could they be?
- These may be cysts that form due to deterioration of the patency of the cervical glands.
- These are also often papillomas, which are tubercles or growths that appear on the lining of the uterus when the corresponding virus is activated; they are usually benign in nature.
- It could also be a benign tumor. Such a neoplasm in itself is not dangerous, but can degenerate into a malignant tumor. It is worth keeping in mind that it is impossible to independently determine its character, especially from a photo. A lump on the cervix - what else could it be?
- The presence of complicated ectopia or erosion of the cervix, which manifests itself against the background of an inflammatory process or hormonal disorder; sometimes the disease can be accompanied by a slight discharge of blood after sexual intercourse or ichor.
- Presence of a polyp. In this case, the pathological area may bleed, which will require immediate removal; sometimes such a formation degenerates into a malignant form.
- The presence of fibroids, that is, a myomatous node formed due to the proliferation of the muscle layer, while flat lumps may appear along with small neoplasms on the stalk; in rare situations, tissue deformation can spread to the vagina.
Previously, fibroids were considered a neoplasm that tended to degenerate, but now the possibility of malignancy of a pathological node into a cancerous tumor is refuted. But it still needs to be removed, since it prevents conception, and, in addition, interferes with the natural bearing of the child, thereby causing bleeding.
Polyps
A neoplasm on the cervix may be a cervical polyp. They are some kind of growths of the mucous membrane of the cervical canal. Its main symptom is the sensation of a tubercle on the surface of the organ. As for the frequency of diagnosis, a lump on the cervix the size of a pea (slightly larger or smaller than this size) is detected in women during menopause.
Doctors assure that such a tumor on the cervix is benign, but if you do not control the process of its vital activity and do not carry out proper treatment, you may miss the moment when it begins to transform into a malignant formation. This is what colposcopic images look like for a benign cervical tumor (shown below).
Colposcopic photo of the tumor. Source: turistam.net
We will also consider the factors under the influence of which polyps form on the reproductive organ of women:
- Inflammatory and infectious diseases of a chronic nature, including cervicitis, adnexitis, endometritis, venereal pathologies;
- Hormonal imbalance - in this condition, the functioning of the ovaries is disrupted, which often leads to an increase in the level of estrogen production, and progesterone, in turn, decreases, as a result of which the mucous membrane of the organ thickens and a tubercle appears on the cervix, a photo of which can be seen in the article;
- Injuries to the mucous membrane of the cervix of various etiologies: abortion, curettage for medical reasons, complicated childbirth;
- A neoplasm on the cervix can be a consequence of stressful situations, constant overexertion, depression, psycho-emotional shock;
- A lump on the cervix may appear as a result of pregnancy, diabetes or dysbiosis in the vagina.
Polyp during pregnancy
Polyps according to their structure and formation are divided into:
- mucous membranes;
- glandular;
- fibrous;
- glandular-fibrous;
- adenomatous (atypical).
All types of polyps are classified mainly by their size; in some cases they can grow up to 2-3 centimeters, but often these are growths 2-3 mm in diameter.
They also vary in shape:
- compacted;
- round;
- in the form of a drop;
- like a rooster's comb.
The structure of growths on the uterine cervix can be either on a thin stalk or on a fairly wide base. As for the structural color, polyps of any type come in pale pink, bright red, and also burgundy with a bluish tint.
Similar to endometrial polyposis, cervical polyps are divided into:
Adenomatous - such neoplasms are called atypical; they have a different homogeneous structure and can grow to 40 mm or more. Such growths are characterized by a significant risk of transformation into oncology and cervical cancer, which is why, following their surgical removal, women are almost always prescribed chemotherapy;
- Glandular-fibrous - the structure of these growths reveals a glandular structure and a connective tissue base. As usual, such neoplasms do not exceed 25 mm in diameter;
- Fibrous - formed from connective tissue. Such polyps usually occur in women who have crossed the age of 40 and quite often develop into a malignant tumor;
- Mucous - similar polyps develop from the glandular structures of the cell. It happens that such growths are observed in women of childbearing age, and rarely grow larger than 15 mm. This type of polyposis almost never occurs again and very rarely can develop into cancer.
If this neoplasm is discovered during pregnancy, then you should not panic.
If conception has already occurred, then polyps cannot affect a successful pregnancy and childbirth. As a rule, such growths are removed without difficulty after the birth of the child.
In some situations, bleeding may occur due to trauma during sexual intercourse, or due to a gynecological examination.
A distinctive feature of polypous formations in women in an interesting position is that their polyps begin to develop more rapidly and acquire a pronounced color.
The appearance of polyps is for the most part a consequence of more complex pathologies. These neoplasms often play the role of background, and naturally, without any manifestations.
This is where their threat to the health of the female body lies. Without eliminating cervical canal polyps in a timely manner, any woman runs the risk of ending up in a cohort of cancer patients.
In addition, a number of difficulties arise with polyps:
- Blood loss, which leads to anemia and iron deficiency;
- Compression of the polyp by the uterine cervix requires surgical intervention;
- Infertility.
- Interruptions in the production of hormones and for this reason an imbalance;
- Miscarriages during pregnancy, in any trimester;
- The ability to transform a growth into an oncological neoplasm of the reproductive organ.
Cyst
Having felt the tubercles on the cervix, every woman is interested in what they are. Gynecologists say that this may be a cystic formation. The fact is that on the surface of the organ there is a mucous membrane containing Nabothian glands. Thanks to them, mucus is released, which acts as a protective barrier against pathogenic and opportunistic microorganisms. If there is a malfunction in the reproductive system, the duct becomes clogged, fluid accumulates in it, the pathological area swells and a cyst forms.
It is not enough to feel a formation on the cervix, what it could be, and what the reasons for its appearance also need to be considered. So, following medical data, experts identify the following reasons for the development of cystic formations:
- The period of healing of the genital organs after labor;
- Infectious lesions of the reproductive organs;
- Menopause.
If there is a lump on the cervix the size of a pea (photos can be seen in the article), they do not show any signs. However, they gradually increase in size, as a result of which the woman begins to feel discomfort in the lower abdomen and pain during sexual intercourse. The same symptoms are present in malignant formations.
Causes of tubercles
Often, during intimate hygiene, a woman feels various changes in the structure of the tissues of the genital organs. Many patients are most interested in the question of why various neoplasms appear. Mostly such formations have the form of tubercles that appear on the neck of the reproductive organ. Such a symptom may indicate dangerous diseases occurring in the female body.
Experts identify some reasons that can trigger the appearance of lumps on the cervix:
- Nabothian gland cysts. Cystic formations on the cervix appear as a result of blockage of the glands located on the cervix. Nabothian gland cysts do not cause pronounced symptoms, so they can be identified only after a thorough diagnosis by a doctor.
- Surgical interventions and labor that cause tissue scarring. The growth of tissue indicates an organ injury, which ends in the appearance of a scar. In some cases, uneven scarring of the tissue occurs, resulting in the appearance of dense tubercles on the cervix. Mechanical damage to the uterine tissue can occur after a blow or sexual intercourse.
- Benign neoplasm. A small bump by itself is not capable of causing any harm to a woman’s body. At the same time, there is a danger that a small benign tumor may eventually transform into a malignant tumor. It is for this reason that when such growths are detected in a woman, experts recommend that they be removed.
- Erosion. One of the common reasons for the formation of a ball on the neck of the reproductive organ is considered to be erosion. Subsequently, it can develop into an ulcer and cause fluid discharge that contains blood. The main method of treating epithelial ectopia is cauterization. The insidiousness of cervical erosion lies in the fact that in the absence of effective and timely treatment, it can transform into a malignant tumor.
- Myomatous node. The cause of fibroids is considered to be the growth of the muscle layer located in the area of the cervix. The consequence of this pathological process is the protrusion and formation of a round pea, which can grow rapidly. In some cases, fibroids take the form of a pedunculated node that can penetrate from the cavity of the reproductive organ into the vagina. It is necessary to remove such myomatous formation if it tends to progress. The fact is that a tumor can cause infertility and prevent further pregnancy.
Another common cause of a lump on the cervix is a polyp, which, like a tumor, can bleed. If this happens, it is necessary to remove the formation. Moreover, polyps can transform into cancerous tumors, so experts also recommend getting rid of them.
Generalized table: