Causes of cervical cysts
The factors that provoke the development of formations are varied. The main causes of cervical cysts include:
- Injury to the cervix. The lower segment of the organ is often damaged during childbirth or unprofessional abortion. Injured tissue is often accompanied by blockage and damage to the gland ducts, which provokes the development of neoplasms;
- Hormonal imbalances (menopause, pregnancy). Changes in hormonal levels affect the functioning and condition of the reproductive organs. During menopause, the lining of the cervix thins. As a result, the nabothian glands become more vulnerable and, “defending themselves,” secrete a lot of secretions. Excessive fluid production contributes to blockage of the glandular duct and the formation of a hollow node;
- Infectious lesions. Infectious diseases, regardless of their nature, provoke the development of neoplasms. Due to inflammation, the secretory fluid becomes of a thicker consistency, which contributes to blockage of the gland.
Risk factors include:
- Introduction of the spiral;
- Long-term uncontrolled use of oral contraceptives;
- Metabolic disorders;
- Gynecological curettage;
- Pathologies of the endocrine system;
- Inflammatory processes of the pelvic organs.
Causes
Gynecologists identify the following factors that predispose to the formation of cysts on the cervix:
- Insufficient intimate hygiene, which applies not only to the woman, but also to her sexual partner. The accumulation of genital discharge contributes to the development of the inflammatory process. This serves as a favorable condition for the appearance of neoplasms on the female reproductive organ
- Damage to the cervix due to overly active sexual intercourse, careless medical examination
- Vaginitis, colpitis. Vaginal lesions that change the viscosity of its secretion and the structure of the mucous epithelium
- Mechanical injuries during childbirth; after abortion and other instrumental procedures
- Frequent change of sexual partners (contributes to disruption of the vaginal environment, which reduces local immunity and predisposes to the development of inflammation)
- Endometritis (inflammation of the mucous membrane of the uterine cavity).
A favorable condition for the formation of cysts is a change in hormonal balance. An additional predisposing factor is erosion and cervical dysplasia. Changes occurring inside the epithelium also affect the glands. Timely elimination of these pathologies minimizes the risk of tumors appearing on the female reproductive organ.
Why is a cervical cyst dangerous?
The consequences of neoplasms in this area are rare, of which the following can be distinguished:
- Infertility due to the proliferation of endocervical glands. As a result, serious deformation occurs, blocking the lumen of the cervical canal;
- Suppuration of accumulated secretions in the cystic capsule, which leads to an abscess;
- A large single neoplasm, multiple hollow nodes in the cervical canal irritate the mucous membrane of the organ, which can cause premature termination of pregnancy;
- A cyst or one particularly large neoplasm provokes deformation of the cervix.
Types of cystic formations
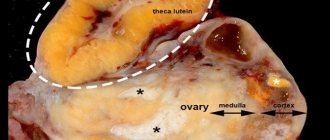
Based on the number of cysts that appear on the cervix, they are divided into single and multiple. In the first case, only one duct of the Naboth glands is blocked, in the second - several. The definition of “Nabothian cysts” in gynecology is used to refer to multiple growths that have arisen on the cervix. Endometrioid neoplasms are also isolated. They are specific cavities. Blood mass accumulates inside them, mixed with the secretion of the nabothian glands. Due to the presence of red blood cells, cystic nodes have a bluish tint and are characterized by bleeding areas (mainly before menstruation).
Types of cervical cysts
Any Nabothian cervical cyst is a small cavity neoplasm filled with liquid contents. Formations of the lower segment of the organ have their differences and are divided into several types:
- A true or retention cyst of the cervix is a neoplasm that occurs as a result of an inflammatory process in the vaginal area, which provokes blockage of the excretory glandular ducts. The development of retention blisters is asymptomatic. The formed neoplasm does not affect hormonal levels and does not lead to cycle disorders;
- An endometrioid cyst of the cervix is a cavity neoplasm, inside of which, in addition to secretory fluid, accumulations of blood are observed. The cause of the development of endometrioid tumors, in most cases, is endometriosis (overgrowth of the endometrium of the organ). These formations are characterized by symptoms, expressed in bloody discharge that appears several days before menstruation;
- An endocervical neoplasm is a cyst of the cervix in the cervical canal on its inner surface;
- A paracervical cyst of the cervix is a cavity neoplasm located in the area of the transition of the cervix to the vaginal area.
The number of neoplasms may vary. In cases where one channel of the nabothian glands is blocked, a single neoplasm occurs. As a result of blockage of the ducts of several glands, multiple cervical cysts develop.
Cervical cyst is a fairly common disease that occurs in women of reproductive age. As a rule, 10-15% of women in this age category suffer from it. A cyst is a process of blockage or expansion of the glands of the cervix. Inflammation occurs in the uterine canal and vaginal part and the excretory ducts of the glands that produce mucus become clogged. The gland becomes larger due to accumulated mucus, which can be observed during ultrasound or colposcopy. Despite the fact that this disease occurs quite often, women usually find out about it late, when they just came for a visit to the gynecologist.
Content:
Signs and symptoms of cervical cysts
As a rule, a cervical cyst does not have pronounced symptoms. There are no changes during the menstrual cycle, no pain or discomfort. The vast majority of patients found out that they had a cyst only during their next preventative visit to the gynecologist. Only a doctor's examination can confirm or refute this diagnosis. Externally, the disease looks like this: in the transformation zone of the cervix there are small white mucous dense formations. They can have different sizes - from a few millimeters to 3 cm. If a woman suffers from an endometrioid cyst, then this disease may have a symptom in the form of small spotting a few days before the start of the menstrual cycle.
If a woman with a uterine cyst has not visited a gynecologist for a long time, and the disease has developed, then this can be determined by the following signs:
- Bleeding outside of menstruation
- Unreasonable pain in the lower abdomen,
- Painful sensations during sexual intercourse with a regular partner,
- Any vaginal discharge without arousal.
Causes of cervical cysts
It is impossible to say with 100% certainty that one or another factor will inevitably lead to the appearance of a cyst, however, some risk factors for the occurrence of the disease can be identified:
- Childbirth. If the cervix was damaged during the birth of the child, its recovery will begin very quickly. This process can cause disruption of the glands and blockage of the ducts, which will lead to the formation of a cyst.
- Abortion. The disease can also develop due to problems during abortion and an unprofessional approach to this procedure.
- Menopause. When a woman begins to gradually exit reproductive age, the lining of her uterus becomes thinner over time, and the glands become more vulnerable. They react more sharply to any irritation, producing more mucus, which in turn clogs the ducts and forms a cyst.
- Infectious diseases. Any infection of the reproductive system can lead to this disease. When inflammation begins, the tissues and glands of the uterus contribute to clogging of the ducts and the appearance of a cyst.
There are also several reasons with a lower probability of occurrence of this gynecological disease:
- Insertion of an intrauterine device,
- Problems with metabolism and hormones,
- Inflammatory processes in the appendages.
Nabothian cysts of the cervix
Nabothian cysts or cervical follicles are small white-yellow dense growths along the vaginal part of the uterus. Many women, without experiencing any external discomfort from this disease, believe that it is not dangerous and belongs to the category of “it will go away on its own.” However, this is a big misconception. The cyst will not resolve on its own and requires a competent approach to treatment.
The glandular cells of the cervix and vaginal area normally produce a certain amount of secret fluid. The glands of the vaginal part were first described by the author Nabotov, from whom they got their name.
The causes of Nabothian cysts are not known. Doctors can only confirm the presence of the disease. However, many agree that a cyst can sometimes arise from:
- chronic inflammatory processes in the genital organs,
- problems with hormonal levels,
- uterine erosion.
Most often it is detected in women 25-45 years old. The ducts from the glands become clogged with squamous epithelium, and a large amount of secretion accumulates in them. Thus, the ducts increase in volume and a cyst forms. The cyst can be either single or multiple. If the formations are small in size, then surgical intervention is not prescribed, but only regular examination. When the gynecologist notices that the cyst is increasing in volume, surgery is often performed to remove it.
There are practically no symptoms of Nabothian cysts, and the disease does not manifest itself. A woman’s problem is usually discovered by a gynecologist during an examination. If a diagnosis of Nabothian cysts has been made, the first step is to undergo a more in-depth examination. As a rule, the list of procedures includes detection of urogenital infections, ultrasound of the pelvic organs, colposcopy, smear for the presence of precancerous changes.
Many doctors claim that the disease does not require any intervention. However, it does not go away and may recur from time to time. Nabothian cysts are sometimes treated by removing them. If the doctor insists on this approach, then you should listen to this in order to avoid the possible spread of the disease. The cyst can also be treated using radio wave or laser therapy. Sometimes treatment is supplemented with medication and physical therapy.
Don't forget about disease prevention. To do this, you need to regularly visit a gynecologist, at least 2 times a year, so that if a disease occurs, the doctor can diagnose it in time and prescribe treatment.
Retention cysts of the cervix
Cervical cysts are different and are divided into several types due to their occurrence and method of formation:
- Traumatic – occur due to tissue displacements and damage,
- Tumor - occurs when the development of the tumor process is deviated,
- Parasitic – formed as a result of the vital activity of parasitic organisms,
- Dysontogenetic – most often congenital individual disorders,
- Retention - occur due to an excess of secretion fluid in the duct of the secretory organ.
Retention cysts can sometimes be congenital in nature, arising during intrauterine development. This neoplasm can make itself felt at any period of a woman’s life when the endocrine or exocrine system is affected. Such a cyst arises in the following way: a clot of secretion or other foreign body clogs the outflow of fluid from the canal or a tumor, and its walls are compressed by scar tissue. Fluid accumulates in the duct, which stretches it. As a result, a cyst forms.
The causes of this disease are inflammatory processes, infections, injuries received during the birth of a child or abortion. Diagnosing a retention cyst is quite difficult. Mainly due to the fact that it practically does not make itself felt. Most women do not have symptoms such as any vaginal discharge, menstrual irregularities, or pain in the lower abdomen or during sexual intercourse. The asymptomatic disease becomes known during a visit to the gynecologist.
When this disease is identified, the doctor conducts a more in-depth examination to understand what caused it, how to treat it, and how to avoid recurrence. For this purpose the following is carried out:
- Colposcopy,
- Examination of smears from the vagina and cervix for microflora,
- Detection of the presence of bacteria: trichomonas, chlamydia, mycoplasma, etc.
A competent doctor, when it comes to treating cervical retention cysts, always approaches the issue individually, taking into account the characteristics of the patient’s body. If a suitable treatment method has been applied, the cervical cyst will disappear without a trace, the functions of this organ will be restored, and the patient will not have problems with sexual activity, as well as with conceiving, bearing and giving birth to a child.
It is only worth noting that doctors today adhere to one of two opinions in terms of treatment. The first advocate surgical intervention to prevent pus from forming in the cyst, which can subsequently lead to undesirable consequences. Others believe that the condition is a possible uterine condition that requires alternative treatment. For each specific case, the gynecologist must decide which path to choose.
Ultrasound of uterine cyst
Ultrasound or ultrasound examination is one of the most important procedures during the diagnosis of cervical cysts. It is prescribed in almost 100% of cases, and it is combined with other procedures: visual examination of the pelvic organ and appendages, colposcopy, vaginal smears. This diagnostic method helps to identify changes in the structure of the cervical tissue, its blood supply, and see changes in size and neoplasms. Thanks to this, it is possible to identify not only a cervical cyst, but also other pathologies.
An ultrasound of the cervix is no different from an ultrasound of the uterus itself, which is familiar to many women. When the cervix is examined through the abdomen, a special gel is applied to the lower abdomen and the ultrasound machine probe is moved over it. If it is necessary to perform ultrasound from the inside, then a transvaginal sensor is used. According to the rules of hygiene, a condom is put on it, coated with gel and used as necessary. The transvaginal method is used when viewing through the abdomen does not provide a complete picture. Both methods are painless and give excellent results in identifying cervical cyst disease.
Women should not be afraid or ignore this procedure when the doctor suspects the presence of a cyst. The results of the ultrasound can give the gynecologist the answer to the question of which treatment method to choose for this patient in order to completely rid her of the disease and prevent relapses.
Consequences of a cervical cyst
Many women who are diagnosed with a cervical cyst are frightened by this disease and are primarily interested in its consequences. The following can be said about this. Although a cyst is called a tumor, by itself it will never develop into an oncological disease and is not malignant. However, sometimes bacteria accumulate in white formations on the mucous membrane of the cervix, which can cause the appearance of a new disease, in addition to a cyst - inflammation of the cervix, the inner lining of the uterine body, etc. These diseases are already really dangerous and can often recur.
Sometimes a cervical cyst can reach an impressive size and cause discomfort during sexual intercourse. In extreme and advanced cases, this disease leads to infertility. This is all that can be said about the consequences of this disease.
If a cyst is discovered during pregnancy, then there is no need to worry. It does not in any way affect the process of bearing a child, his future health and the condition of the mother. As a rule, doctors begin to treat uterine cysts after the woman gives birth.
Removal of a cyst on the cervix (surgery)
After the doctor diagnoses a cervical cyst, he will most likely suggest that the woman have it removed surgically, because medication does not give the desired result. Hearing this, a woman usually gets scared and wonders if this disease is so dangerous that surgery is needed. But there is no need to be afraid of this. The cyst itself is not harmful to health, but it can cause a purulent infiltrate, which will lead to painful inflammatory processes. These processes can cause infertility or problems with future pregnancies.
Before diagnosing a cyst with complete confidence, it is necessary to undergo a colcoscopy procedure and some other tests. When all the tests have the necessary indicators, the doctor prescribes surgical removal of the cervical cyst. This operation is performed on an outpatient basis, and the patient is not hospitalized. Typically, surgical intervention is prescribed at the end of menstruation, in the first half of the menstrual cycle.
The operation process is as follows. To begin with, the gynecologist prepares the woman for surgery. Then he punctures each cyst. Viscous mucus accumulates inside this formation, which is removed thanks to a puncture. Then the cyst site is treated with a special solution to avoid recurrence of its formation. The patient can go home within a few hours after the operation. The operation should not cause complications. The only thing that is possible is a mild aching pain in the lower abdomen, which should go away in 1-2 days, as well as not excessive bleeding. After a couple of days, this discharge may change to yellowish mucus, which should disappear within seven days. To make the healing process faster, 10 days after removal of the cyst, the patient is usually prescribed vaginal suppositories. You should abstain from sexual intercourse at this time. After a month, the woman needs to come for a routine examination.
You can remove a cervical cyst using other methods:
- Cauterization is the most popular method used for this disease. The cyst can be cauterized either chemically or thermally using various medications.
- The radio wave method is a fairly new technique, which is most often prescribed to young women planning to become pregnant soon. The cyst is destroyed by a high-frequency radio wave produced by a special device.
- Laser method - performed using a device that generates a laser beam. The device itself does not come into direct contact with the cervical mucosa. The method is used relatively infrequently.
- Cryotherapy is a method of treating uterine cysts in which it is exposed to liquid nitrogen and low temperatures. This process does not cause pain and is used more and more often in modern clinics.
As you can see, today medicine has several ways to get rid of uterine cysts. The doctor should select the most suitable one for the patient.
Treatment of cervical cysts with folk remedies
In addition to the main treatment prescribed by the doctor, you can also use traditional medicine. But it bears repeating – this is just an addition! Visits to the doctor and compliance with his instructions are mandatory.
Recipe No. 1. To do this, you will need a medium-sized clove of garlic, which you need to wrap tightly in gauze and make a tampon. It should be inserted into the vagina overnight. This procedure can be done for a month.
Recipe No. 2. Hard boil seven chicken eggs, remove the yolks from them, chop them and mix with powdered pumpkin seeds (1 cup). Add half a liter of sunflower oil to the mixture and heat in a water bath, stirring. This mixture should be taken 1 teaspoon in the morning 5 days after 5 days until it runs out.
Recipe No. 3. Collect enough walnut partitions to chop them into 4 tablespoons. Add 3 cups of boiling water to the powder, put on fire and continue boiling for another 20 minutes. After this, leave the broth to cool and strain it through a fine sieve. You need to take it orally 2-3 times a day, half a glass.
Recipe No. 4. For this you need 2 large bunches of fresh burdock leaves. They need to be crushed using a meat grinder to make a paste. Carefully squeeze the juice out of it. Treatment with this remedy goes like this:
- The first two days - drink 1 teaspoon 2 times a day,
- The next two days - drink 1 teaspoon 3 times a day,
- After this, drink 1 tablespoon 3 times a day.
Treatment with burdock lasts a whole course over a month.
If the disease relapses, then therapy with burdock juice can be repeated. The juice should be stored in a dark, cool place in a clean container with a lid. To achieve the best result, the course of treatment with burdock can be combined with the following method.
Recipe No. 5. To do this you will need 2 tablespoons of fresh acacia flowers, 1 glass of alcohol or vodka. Place the plants in a clean container and fill with alcohol. After this, leave the mixture to infuse. Then strain through cheesecloth or a fine sieve. The course of treatment with acacia lasts a month. You need to take the solution like this: dilute it with water in a ratio of 1 part solution to 2 parts boiled water. Take 1 tablespoon orally 3 times a day.
Recipe No. 6. Various herbal remedies can also help cope with cervical cysts. To treat the disease, you can use a collection that consists of:
- Water – 1 glass,
- Chamomile – 3 teaspoons,
- Sea buckthorn leaves – 3 teaspoons,
- Nettle leaves – 5 teaspoons,
- Celandine – 3 teaspoons,
- Rose hips - 3 teaspoons,
- Plantain leaves – 5 teaspoons
All medicinal plants must be crushed and dried. Then pour boiling water over the dishes and pour all the herbs into it. Pour a glass of boiling water over the mixture. Cover the dish with a lid, wrap it in newspaper and a towel. The mixture needs to sit for at least 6 hours. Then strain and drink 1 teaspoon 2 times a day.
Recipe No. 7. Another useful decoction, which has positive reviews from women, consists of boron uterus or zyuznik grass. It is not difficult to prepare these decoctions. To do this, add 1 tablespoon of herb to one glass of boiling water and stir well. Then this decoction should be infused in a thermos or wrapped container for at least 3 hours. You need to take this folk remedy 3 times a day before meals, a third of a glass. Herbs can be changed. Drink an infusion of boron uterus one week, and zyuznik for the second. The course of herbal treatment should not exceed 4-5 weeks.
It is worth recalling once again that traditional treatment cannot be chosen independently without a prior visit to the doctor. The first step is to make a diagnosis, then prescribe traditional treatment. And traditional medicine recipes can be used as a supplement.
Author of the article: Lapikova Valentina Vladimirovna | Gynecologist, reproductive specialist
Education: Diploma in Obstetrics and Gynecology received from the Russian State Medical University of the Federal Agency for Health and Social Development (2010). In 2013, she completed her postgraduate studies at NIMU named after. N.I. Pirogova.
Our authors
Symptoms of a cervical cyst
Small tumors do not cause symptoms. Signs of a cervical cyst appear when the formation is large:
- Possible pain in the suprapubic area;
- The volume of discharge with a characteristic unpleasant odor increases;
- Heavy periods;
- Discomfort and pain during sexual intercourse. In some cases, bleeding is observed.
Symptoms of a cervical cyst are characteristic of many diseases of the female reproductive system, so the occurrence of such manifestations is a reason to immediately visit a doctor. This will allow you to accurately identify the pathology and prescribe timely treatment.
Symptoms of the disease
Most often, the presence of a cyst does not affect a woman’s well-being. The patient may not notice any sensations for a long time, thereby allowing the formation to grow. This is why it is important to visit a gynecologist regularly - at least twice a year with an examination in the chair for women who are sexually active.
Pain in the lower abdomen
Possible symptoms of an endometrioid cervical cyst include spotting a week before menstruation and a week after it. There may be slight bleeding in the middle of the cycle. In addition, a week before menstruation, the patient may experience pain of a different nature - from unexpressed aching to pulsating on different days of the cycle. Often the signal to visit a doctor is severe pain immediately before the onset of menstruation.
Often, a cyst is discovered only when the patient is faced with the inability to become pregnant or experiences pain in the pelvic area for a long time. In this case, either large cysts are detected, or extensive endometriosis, which can threaten not only reproductive health, but also the life of the patient.
Endometriotic cervical cysts often do not manifest themselves with any sensations, so it is necessary to visit a gynecologist regularly (twice a year) for a visual examination of the cervix. An advanced cyst can lead to infertility and other dangerous complications.
Diagnostics
A gynecologist can identify a neoplasm during examination using special instruments. To clarify the diagnosis, the following studies are prescribed;
- Ultrasound examinations of the pelvic organs. The method is informative and accurate. The procedure allows a specialist to examine the cervix and body of the uterus, determine circulatory disorders, and identify structural changes in the organ. Research determines the exact location of the tumor and its size. The procedure is safe and painless. Based on the results of the study, a specialist can not only accurately determine the presence of a neoplasm, but also determine the cause of its development;
- Colposcopy is performed to identify structural changes in the cervical canal;
- A smear on the flora, which allows you to identify the composition of the microflora of the vagina and cervical canal, determine the presence of infectious lesions;
- To assess the condition of the epithelial layer, a Pap smear is performed;
- Blood tests;
- Biopsy. A microscopic section of the hollow node is taken to assess the nature of the neoplasm (benign, malignant);
- To study hormonal levels, an immunoenzyme test is prescribed.
Main symptoms
For a long time, the patient does not realize that she has growths on the cervix. Especially if she does not undergo regular preventive examinations. At the initial stage of development of nodes on the woman’s reproductive organ, no pronounced clinical manifestations are observed. Before the gynecologist detects the cysts, the patient is concerned about minor discomfort and smearing of blood between menstruation.
When the tumor reaches 2 cm in diameter and blocks the cervical canal, the following symptoms occur:
- Menstruation becomes painful, the amount of blood loss is significantly reduced
- There is an increase in overall body temperature
- Due to blockage of the uterine os, attempts to get pregnant are unsuccessful
- There are a large number of clots in menstrual blood
- Intimacy is accompanied by severe discomfort
- The patient is concerned about itching, purulent secretion from the genital tract
Sometimes cysts on the cervix form during pregnancy due to hormonal changes. Their presence aggravates the period of gestation and exposes the child to premature onset of labor. If the cause of cystic growths is inflammatory and infectious processes in the organs of the reproductive system, the patient is concerned about intoxication. It manifests itself as pain in muscles and joints, chills, weakness, decreased blood pressure, and dizziness.
Possible consequences
Complications from cyst formation occur infrequently. Untimely treatment of pathology, proliferation, growth of neoplasms, inflammation of hollow nodes can lead to the following consequences:
- Infertility;
- Disorders of the female reproductive system;
- Spontaneous termination of pregnancy;
- Structural changes in the organs of the gynecological system;
- The occurrence of anemic conditions;
- Development of intoxication, symptoms of sepsis;
- Pain and discomfort during sexual intercourse;
- Decreased quality of life of the patient.
Treatment of cervical cysts
Treatment of cervical cysts depends on the size of the tumor, location, and the presence of an inflammatory process.
A number of doctors are inclined to believe that small tumors do not require intervention; only dynamic monitoring is necessary. In case of suppuration of liquid contents, it can be removed by puncture using Surhydron. After that, treatment of the cervix with Nabothian cysts continues with medication.
Other experts are inclined to believe that the treatment of cervical retention cysts (which are asymptomatic and do not bother the patient) requires removal, since their presence significantly increases the risk of suppuration of the liquid contents of the neoplasm.
In most cases, in the presence of paracervical formations that are small in size and develop asymptomatically, dynamic observation and hormonal therapy are used. The condition is monitored by colposcopy every six months.
Often, to combat small formations, specialists prescribe pharmaceutical and folk remedies for topical use. The use of such drugs provokes spontaneous opening of cysts. At the same time, herbal remedies have a wound healing and analgesic effect.
This approach is especially effective in the treatment of cervical erosion with cysts. Pharmacy and herbal preparations with anti-inflammatory, wound-healing and analgesic effects are prescribed (suppositories with nystatin + suppositories with sea buckthorn oil + douching with chamomile solution).
Traditional remedies have a positive effect:
- Reduce or completely remove the pain effect;
- Accelerate healing after surgery;
- Reduce inflammation, stop the development of erosion;
- Strengthen the immune system of the patient’s body;
- Stabilize the functioning of the reproductive system.
For herbal medicine, folk remedies use baths, irrigations, applications, suppositories, herbal tampons, and ointments. During the course, you must strictly adhere to the recommended dosage. Any ailments or deviations are a reason to visit a gynecologist.
Any medications must be prescribed by your doctor. Self-prescription of drugs without the consent of a gynecologist can be dangerous and lead to serious complications.
Treatment
Some gynecologists classify the cyst as a normal variant. Others believe that a cervical cyst must be removed. However, it is usually considered a benign tumor of the uterus and doctors are in no hurry to remove it. Regular monitoring (ultrasound and colposcopy) may be prescribed.
The cause of formations in the uterus and their development can be prevented by drug therapy:
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- hormonal agents (for endometriotic cysts);
- homeopathic treatment.
Surgical removal of the formation is mandatory when the cyst is affected by infection and the appearance of pus, when the formation enlarges (size exceeds 10 mm), as well as in case of infertility and pain during sexual intercourse or menstruation.
First, the uterine cyst is punctured, then its internal contents are removed. After the procedure, the cystic area of the cervix is treated using the following methods:
- diathermocoagulation (cauterization with electric current);
- chemical cauterization;
- laser cauterization;
- radio wave processing;
- cryodestruction (exposure to cold).
The most painful way of removal is cone amputation. The doctor chooses which method to use.
There are contraindications for surgical treatment of cysts on the uterus. In these cases, cervical surgery cannot be performed:
- during menstruation (the operation is carried out 6-8 days after the end of menstruation);
- with inflammation of the reproductive organs;
- in the presence of acute infection;
- for sexually transmitted diseases;
- for oncology in the genital area;
- during pregnancy and lactation;
- for polyps in the endocervix (in its upper part);
- when fibroids or endometriosis appear.
Treatment of a cyst detected in the uterus during pregnancy is postponed until after birth. For a woman who has given birth, the operation is performed only after the end of lochia (bloody discharge) - after approximately 45 days from the end of childbirth.
Diathermocoagulation
Electric cauterization. An old and rarely used method. The duration of the procedure is several minutes. Local anesthesia is given.
A uterine cyst is cauterized using one of two methods:
- by contact (the electrode acts directly on the tissue);
- through a microarc (the device does not touch the organ).
A crust forms at the cauterization site. Healing time is 6-8 weeks.
- possible bleeding (especially during sexual intercourse and heavy lifting);
- complication of chronic inflammatory processes in the genitourinary system;
- complication of conception and childbirth (the cervical canal may narrow).
There is also a possibility of relapses.
Chemical cauterization
Outdated way. Suitable for eliminating small cervical nodules in nulliparous patients. The procedure uses Solkovagin, a composition of acetic and nitric acids. The procedure is painless.
- possible damage to healthy tissue;
- the appearance of scars;
- There may be no result from one procedure (2-3 sessions may be required).