Laparoscopy for endometriosis, prevention after surgery
Medical portal
- ENT diseases
- Stomach diseases
- Haemorrhoids
- Pancreatitis
- Weight loss
- Edema
- Skin diseases
- Gynecological diseases
Photo
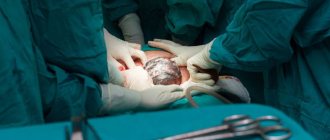
Laparoscopy for endometriosis is used quite often, as it is the most gentle method of modern surgical intervention. The operation in question not only allows you to get rid of infertility, the direct cause of which is the pathology of endometriosis, but also makes it possible to avoid complete amputation of the uterus and other organs of the genitourinary system in which foci of the disease have developed.
Laparoscopy method
Laparoscopy is a minimally invasive option for diagnosing and treating diseases of the abdominal and pelvic organs.
The procedure is carried out using a special device - a laparoscope. To administer it, small punctures are made in the peritoneal area. After this, carbon dioxide is introduced into the cavity and the main instrument is placed. Laparoscopic operations on the ovaries are performed for the purpose of:
- Excision or removal of pathological tissues, foci of endometriosis.
- Treatment and removal of adhesions.
- Cauterization of endometriotic lesions.
- Husking of ovarian cysts of all types.
- Removal of the directly affected ovary if it is impossible to treat it or part of the organ.
During the operation, the doctor makes two punctures in the required area, not exceeding 20 millimeters, and inserts special medical instruments through the holes: a laparoscope, an optical device and a tube with special carbon dioxide fumes that prevent damage to nearby organs and tissues.
With the help of laparoscopic intervention, the doctor can:
- Excise soft tissue affected by endometriosis;
- Cure and eliminate formed adhesions;
- Remove various pelvic organs.
Laparoscopy in the presence of endometriosis is performed very often; it helps to quickly eliminate foci of the disease and preserve the functioning of the reproductive organs.
The advantages of the laparoscopic treatment method are:
- No serious damage to soft tissues and nearby organs;
- Minimum number of contraindications;
- Rapid recovery process after surgery;
- Low probability of developing adhesions and the entry of infectious microorganisms into the reproductive system;
- No extensive scars after surgery.
Internal endometriosis of the uterus is removed only using a laparoscope. To do this, several small punctures are made in the abdominal cavity. After the operation, the appearance of adhesive scars is excluded.
Indications for surgery:
- endometriosis of the reproductive organs;
- spread of the disease to organs adjacent to the uterus;
- pronounced pain syndrome;
- infertility due to endometriosis.
Cysts and adhesions in the fallopian tubes are a common cause of infertility. Laparoscopy ensures the patency of the tubes, giving the woman a chance to conceive a child.
Endometriosis of the vagina and cervix is easily removed using laparoscopy. Abdominal surgery makes no sense.
However, complications may arise after this operation, just as after a conventional abdominal operation. What do they mean?
- A relapse of the eliminated disease is possible, and the focus of tissue proliferation will be much larger than the previous one.
- Re-development of endometriosis is possible, but to a lesser extent.
- It is possible that endometriosis may form at the sites where the peritoneum is punctured.
Contraindications for surgery:
- chronic and acute respiratory diseases;
- cardiovascular diseases and heart defects;
- dysfunction of blood clotting;
- the presence of neoplasms of various etiologies;
- severe exhaustion of the body, various hernias.
Also, laparoscopy is unacceptable for obesity, acute forms of infectious diseases, inflammatory processes in the appendages, and recent abdominal surgeries.
General approaches to removing endometriosis lesions
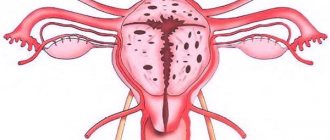
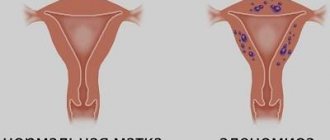
Endometriosis of the uterus is a hormone-dependent disease that has no clear origin. Endometrial cells begin to grow outside the uterine cavity. The causes of such pathological changes have not yet been fully investigated by scientists. The most likely factor in the development of endometriosis is the presence of a hormonal disorder of immune homeostasis.
Laparoscopy is the leading method of surgical intervention in gynecology. Operations performed by laparoscopy have a minimal risk of complications both during and after the intervention. In addition, the rehabilitation period after laparoscopy is easier, which is especially important for patients.
Quite often, laparoscopy as a treatment method is used for endometriosis. Endometriosis develops when endometrial cells located in the inner lining of the uterus are thrown and grow into tissues that are unusual for them. This pathological condition is typical for women in the fertile phase.
To relieve signs of the disease, conservative and surgical treatment is carried out. The choice of treatment tactics depends on the specific clinical case.
A distinction is made between lesions of endometrioid growths on the inner surface of the uterus and cervix - adenomyosis and endometriosis, when lesions are observed in the tubes, ovaries, and in the pelvic cavity. , endometriotic ovarian cysts, damage to the fallopian tubes and adhesions due to endometriosis are considered reasons for intervention through the abdominal cavity through a laparoscope or a traditional incision.
Adenomyosis or internal endometriosis can be removed by curettage. If lesions are detected during hysteroscopy, they are removed and small areas are cauterized.
After surgery to remove endometriotic lesions, hormonal medications are necessarily prescribed to prevent relapse of the disease.
Conservative tactics involve the use of drugs from the following groups:
- hormonal;
- anti-inflammatory;
- antibacterial;
- immunostimulating;
- anti-adhesion.
Surgery for endometriosis usually involves laparoscopy and subsequent cauterization of the lesions. Drug therapy is required before and after surgical treatment.
Indications for surgery Indications for surgery for endometriosis are a common localization of endometrioid heterotopias. Generalized causes excruciating pain and does not respond to conservative treatment methods. It is advisable to perform surgery for limited lesions of the pelvic organs by endometriosis.
Before deciding to perform surgery for endometriosis, the gynecologist takes into account its feasibility, the extent of the lesions, the patient’s age and the risk of damage to adjacent reproductive organs. Sometimes during surgery the rectum and sigmoid colon, ureter and bladder can be injured.
The main reason for surgery for endometriosis is the ineffectiveness of conservative and drug treatment.
The following indications for surgical intervention can be distinguished:
- constant or periodic intense pain in the lower abdomen;
- adhesive process;
- pain during defecation;
- infertility;
- uterine bleeding.
Before deciding whether to undergo surgery for endometriosis, doctors consider the following important factors:
- patient's age;
- the total volume of areas affected by endometriotic lesions;
- the likelihood of damage to the rectum and sigmoid colon, ureter and bladder.
Causes and symptoms of endometriosis
Symptoms of endometriosis for which laparoscopy is usually indicated include:
- vaginal bleeding;
- infertility;
- pain during intercourse;
- chronic pelvic pain;
- urinary problems;
- pain during bowel movements.
Laparoscopy for endometriosis is performed to confirm the diagnosis of endometriosis, but this procedure also allows the surgeon to remove some of the lesions, which reduces unpleasant symptoms.
Although there is no cure for endometriosis, laparoscopy is usually a definitive diagnosis and is an effective treatment for some people.
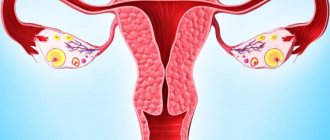
This disease can affect the reproductive and adjacent organs of a woman - the ovaries, cervix, bladder walls, fallopian tubes, peritoneal muscles, vagina, intestines.
Symptoms of endometriosis are:
- nagging pain in the lower back, as with pyelonephritis;
- problems with urination - delayed, with pain;
- unpleasant itching in the perineum;
- pain in the groin area.
The causes of endometriosis can be three factors:
- mechanical - release of menstrual fluid into the peritoneum;
- autoimmune - failure of polyclonal cells;
- hormonal - tissue degeneration.
The disease has 4 stages of development:
- formation of metastases;
- formation of several lesions;
- formation of adhesions and cysts;
- fusion of organs, formation of ovarian cysts.
Laparoscopy refers to diagnosis and treatment at the same time. Using a special probe, a video camera is inserted into the abdominal cavity, which transmits an image of the uterus to the monitor. This study can be combined with surgery if fibroids or other neoplasms are detected.
Possible complications
If a woman has properly prepared for laparoscopy and has completed the entire course of hormonal therapy before and after surgery, then endometriosis rarely recurs after surgery. If, after laparoscopy, it was revealed that there were single foci of inflammation of insignificant size, they need to be treated with medication. As a rule, in such cases the disease will go away on its own.
After removal of the uterus, there is no risk of endometriosis returning. But there may be complications such as the formation of numerous cysts on the ovaries if they have not been removed. The appearance of this pathological process is associated with total hormonal changes in the body.
A less favorable situation after laparoscopy is the recurrence of the disease, but, unlike the initial development of the disease, past foci of the inflammatory process rapidly develop and quickly affect neighboring healthy tissues. This complication is rare and is associated with the body’s individual reactions to tissue damage during surgery.
A side effect after laparoscopy is endometriosis of the postoperative scar. The first symptom of a complication is abdominal pain. Endometriosis occurs repeatedly on scarred tissue, resulting in the formation of polyps and inflammatory foci.
How much does the operation cost? The price depends on the severity of the clinical case, the need to remove the appendages or uterus. The average cost of laparoscopy for endometriosis is from 28,000 rubles.
Endometriosis of the uterus is a disease that cannot be cured with medication. Taking various drugs is aimed only at stopping the further development of the pathological process and normalizing the functioning of the organs of the reproductive system, while the relapse of endometriosis remains extremely high. Therefore, the most effective method of therapy is laparoscopy.
Application of laparoscopy
Laparoscopy is considered an effective way to diagnose and treat pathology. There are a number of indications for this procedure. The use of laparoscopy for endometriosis is prescribed in the following cases:
- abundant regulation leading to the development of anemia;
- conservative methods turned out to be ineffective;
- the disease provoked the formation of ovarian cysts;
- the disease is accompanied by other diseases of the reproductive organ;
- infertility;
- malignant formations;
- a history of pathologies of internal organs due to which hormonal therapy cannot be used;
- proliferation of the endometrium to other organs.
Excision of the lesion is considered the optimal treatment option. After laparoscopy, endometriosis should continue to be treated with conservative methods. This is the only way to avoid relapse.
Price
The price for this procedure varies.
Cost of laparoscopy for endometriosis
| Medical institution | City | Price, rubles |
| Gynecology Clinic GINECO | Moscow | 106000 |
| Medical and innovative center LITs | Saint Petersburg | From 100000 |
| Family Medicine Center | Ekaterinburg | 70000 |
The cost of services varies depending on their composition. The price may or may not include the cost of consumables, anesthesia, etc.
In what cases is laparoscopy not performed?
Doctors usually do not recommend laparoscopy when a person first reports symptoms of endometriosis because, although the incisions are small, laparoscopy is an invasive procedure and carries some risks.
Typically, doctors try to diagnose pathology by performing other, non-invasive procedures. For example, ultrasound is used to diagnose ovarian cysts or fibroids, which can also cause pelvic pain.
Sometimes endometriosis is diagnosed using transvaginal ultrasound.
Sometimes hormonal medications, such as birth control pills or gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, are prescribed without a definitive diagnosis of endometriosis. Patients with endometriosis often notice that their symptoms improve while taking these medications.
However, endometriosis can continue to cause symptoms even with hormonal treatment.
Not everyone is a candidate for hormone treatment. For example, some people cannot take medications that contain estrogen because it may increase the risk of stroke.
Methodology
During the diagnostic procedure, a laparoscope with a camera at the end is inserted into the woman's uterine cavity. This is done through small (no more than 1.5 cm) punctures in the abdominal and uterine walls. The image from the camera is transmitted to the screen, and the doctor has the opportunity to directly examine the uterine cavity and make a conclusion about the existence of lesions directly based on the results of visual diagnostics. The intervention is usually performed under general anesthesia and no more than 1-2 punctures are required.
Operation technique
If the intervention is carried out for the purpose of treatment, then in addition to a laparoscope with a camera (which allows the doctor to monitor the progress of the operation visually), a laparoscope with a loop is also inserted. This loop is used to remove the lesion. If necessary, it can also cut adhesions to reduce pain.
No stitches are required after the intervention. The incisions heal fairly quickly on their own. The full recovery process takes about three weeks upon diagnosis, and about four to five weeks after treatment.
Treatment of endometriosis after laparoscopy must continue. The operation eliminates only the symptom of the disease - the source of tissue proliferation, but does not eliminate its cause - hormonal imbalance. Therefore, if left untreated, endometriosis may soon develop again after surgery. For this reason, therapy with progesterone drugs, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, or combined oral contraceptives is needed.
Diagnosis and surgery
The laparoscopic method of treatment consists of complete excision of the pathological membrane, preventing its regrowth and minimal trauma to healthy organs and tissues.
Removal of endometriosis during laparoscopy is performed under general anesthesia. Next, a qualified doctor makes two holes in the woman’s abdomen, inserts a tube with carbon dioxide into one of them and fills the operated area with it. This action allows the doctor to expand his horizons of the working space and not damage healthy organs and tissues during the treatment.
After the above-described manipulations, the medical specialist inserts an endoscope with an optical apparatus and instruments for excision of pathology - a laparoscope - into two punctures. Depending on the degree of damage to the internal organs, the doctor performs the necessary manipulations, removing the pathological tissue. After completing the treatment, the incisions are not stitched - they are able to heal independently and quickly.
After laparoscopic intervention in the organs of the reproductive system, adverse consequences very rarely develop. But there are cases when after surgery a woman experiences the following unpleasant complications:
- Uterine hemorrhages resulting from impaired blood clotting;
- Development of adhesions on internal organs or skin;
- Unnatural tolerance to anesthesia: problems with the respiratory process, increased blood pressure, muscle spasms, etc.;
- The entry of infectious agents into a woman’s body and the development of inflammatory processes.
The above conditions require immediate professional medical assistance.
The method is fundamentally different from abdominal operations and is considered microsurgical. There are two types of it:
- diagnostic. It is carried out to identify the location of the lesion - the reproductive organ, appendages, intestines. Allows a detailed examination of the peritoneum and pelvic organs without causing significant harm to the body;
- therapeutic and surgical. In this case, pathological areas of the endometrium, endometrioid cysts and adhesions are removed. The recovery period after surgery is only three days.
Diagnostic laparoscopy for endometriosis of the ovaries, uterus or intestines involves preliminary tests, which are also necessary for abdominal surgery. The procedure itself is performed under general anesthesia.
The procedure is considered minimally invasive and relatively safe. Complications are postoperative risks and are not directly related to laparoscopy itself. Among the main ones are the following:
- heavy bleeding;
- penetration of infection into the peritoneal cavity;
- the beginning of the adhesive process;
- damage to the intestines, bladder and urethra.
In addition, recurrence of endometriosis after laparoscopy is possible. For this reason, hormonal therapy in the postoperative period is extremely important. During the manipulation, the reproductive organ is not removed, and therefore it does not lead to infertility. After completing the course of treatment, a woman has every chance of becoming pregnant after endometriosis.
A catheter is placed in the vein, which the anesthesiologist will use later to administer anesthesia.
Surgeons perform laparoscopy using general anesthesia. The anesthesiologist will provide medications and monitor vital signs throughout the procedure.
Laparoscopy for endometriosis proceeds as follows. The surgeon will make small incisions on the abdomen, including near the belly button, to minimize scarring.
The surgeon then inserts an instrument that allows the abdominal cavity to be filled with carbon dioxide gas. Inflating the abdominal cavity with gas helps the surgeon see the pelvic organs.
The doctor can then make further incisions and insert instruments as needed to identify possible areas of endometriosis and remove samples for biopsy or treatment.
After surgery, surgeons remove the instruments and close the incisions with either stitches, staples, or glue. Then a bandage is applied.
Any invasive surgery carries certain risks. The doctor should discuss them with the patient before the procedure begins.
One of the most serious potential side effects of laparoscopy for endometriosis is damage to the intestines, especially if there is damage to the area caused by endometriosis.
Other possible complications of laparoscopy for endometriosis:
- bladder injuries;
- pelvic infection;
- relapse of endometriosis;
- scarring;
- damage to blood vessels.
Ideally, if the surgeon removes the damage caused by endometriosis, the patient will have fewer symptoms and less pain.
However, sometimes more than one laparoscopy procedure for endometriosis is required to remove the lesions, especially if they are extensive. Approximately 40-80 percent of women experience pain again within 2 years after surgery.
Hormone therapy is often prescribed to control endometriosis after laparoscopy.
Laparoscopy combines two functions - diagnosis and surgery. However, compared to conventional surgery, laparoscopy involves puncturing the abdominal cavity in several places. Next, a laparoscopic instrument is used to examine the organs, and, if necessary, remove the cyst, adhesions or fibroids.
During laparoscopy, two instruments are inserted into the abdominal cavity - to inject gas (it is necessary to expand the peritoneum) and to monitor the cavity (the tube is equipped with a video camera). If removal of a cyst or adhesions is required, a tip with a laser is inserted into the cavity. The advantage of laparoscopy is that there is no need to dissect the abdominal cavity or internal organs.
This microsurgical operation is performed under general anesthesia; stitches are placed at the puncture sites. After 14-15 days, the sutures are removed, postoperative scars quickly disappear. However, you should carefully monitor the sutures to prevent infection from entering the peritoneum through punctures.
Rules for the operation
Surgery for endometriosis is performed three days before the onset of menstruation.
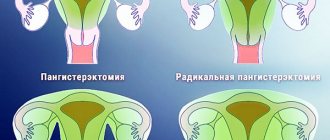
A common form of endometriosis, in which the ovaries and pelvic peritoneum are affected, conglomerate tumors and chocolate cysts are diagnosed, requires immediate removal. In this case, doctors can completely remove the uterus and ovaries. Conservative surgery, during which the unaffected ovary is preserved, is indicated for girls who want to give birth to a child. In this case, complete removal of all endometrioid tumors is indicated.
During a comprehensive diagnosis and examination, the doctor checks the uterus and peritoneum for the presence of lesions. If patients are found to have widespread pathological formations, then surgery for endometriosis has its own difficulties. With this course of the disease, tissue that is very close to the bladder, ureter and rectum is affected. Due to the high likelihood of injury, doctors limit themselves to removing not all endometrioid heterotopias that are located inside the abdominal cavity. Even with such an operation, the development of pathological processes in the future stops. Surgical treatment in women of menopausal age is carried out with radical removal of the uterus and appendages.
Removal of foci of adenomyosis in menopausal women is carried out with ablation - excision of the basal layer to prevent further growth of the endometrium. Young women undergo less invasive surgery. Curettage, cauterization of lesions and hormonal treatment are carried out, introducing a medicated menopause for 6-9 months.
How to prepare for laparoscopy for endometriosis
The laparoscopy operation is carried out without performing a cavity incision, due to which the likelihood of complications during the rehabilitation period is significantly reduced, but despite this, you need to prepare for the procedure in advance.
Diagnostics include tests and ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs. A mandatory step is a consultation with specialized specialists - an endocrinologist, a therapist, a cardiologist. In this way, it is possible to assess the woman’s health status and make a conclusion about whether surgical intervention is possible. If chronic pathologies with aggravated symptoms are detected, proper treatment is carried out.
To avoid the development of complications in the postoperative period, hormonal therapy is prescribed at the preparatory stage, the duration of which is about three months. Often there is a decrease in the size of the lesions. Accordingly, there is no need for surgical manipulation.
The procedure is performed in the morning on an empty stomach. A woman is recommended to refuse dinner in the evening, and after waking up, have a cleansing enema.
The surgeon will often give the woman specific instructions on how to prepare for surgery. These may include:
- have someone pick up the patient from the hospital and stay with the patient for 24 hours;
- refrain from eating or drinking for only a few hours;
- stopping smoking in the days or weeks preceding surgery;
- Avoid taking certain medications on the day of surgery if your doctor recommends it.
Sometimes your doctor will recommend using a special soap in the shower or cleaning wipes the night before or on the day of surgery to help prevent infections.
You should not shower or swim for 48 hours after surgery, so you should shower before going to the hospital.
Doctors also prescribe medications to help with bowel movements. Bowel prep is an unpleasant part of preparing for surgery, but it helps the doctor safely remove damage caused by endometriosis from the gastrointestinal tract.
Causes of pathology
Endometriosis can develop for several reasons. The most common causes of endometriosis are:
- The entry of menstrual blood into the abdominal cavity, when endometrial cells attach to the mucous membranes and begin to grow;
- Hormonal imbalance, as a result of which endometrial growth is inadequately regulated;
- As a result of frequent abortions or surgery on the uterus, after which hormonal levels and endometrial growth are disrupted.
One of the causes of endometriosis is frequent abortions.
Indications and contraindications for
Surgery using laparoscopy is performed in the following cases:
- With extensive growth of endometrial tissue;
- If drug therapy is unsuccessful;
- If a woman cannot conceive a child;
- Endometrioid cystic neoplasms progress;
- The presence of diseases that will rapidly develop with prolonged use of hormonal drugs (they are used to treat endometriosis);
- With the progression of malignant tumors.
Therapy using laparoscopic intervention is contraindicated in the following situations:
- If the patient has recently undergone abdominal surgery;
- There is a serious impairment of kidney function;
- The woman suffers from diabetes;
- There are acute diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- Infectious pathologies progress in the body;
- The girl suffers from intolerance to anesthesia;
- Diseases of the respiratory system;
- The last stages of obesity;
- The girl was diagnosed with a pathological structure of the diaphragm;
- A woman suffers from an increased likelihood of scar tissue formation.
For the above conditions, the doctor prescribes another method of treating endometriosis.
Treatment of endometriosis by laparoscopy is not allowed in all cases. There are a number of absolute and conditional contraindications to this tactic.
Minimally invasive surgery is strictly prohibited in the presence of the following pathologies:
- diseases of the cardiovascular system and respiratory organs. This is due to the fact that during the procedure gas is injected into the peritoneal cavity, which can provoke a spasm;
- conditions in which the blood clotting process slows down, and hemophilia;
- neoplasms of various nature;
- violations of the structure of the diaphragm.
Relative contraindications include the following:
- recent abdominal surgery;
- malignant formations;
- liver failure in acute form;
- severe inflammation in the ovaries;
- infectious diseases;
- overweight.
Symptoms
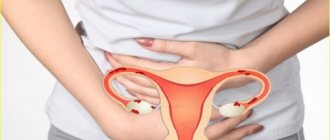
The following symptoms are typical for endometriosis:
Pain due to endometriosis
- Paroxysmal lower back pain;
- Delayed, difficult and painful urination, reminiscent of cystitis;
- Pain in the groin, radiating to the lower region of the peritoneum;
- Discomfort and itching in the vagina;
- Menstrual irregularities and heavy periods.
Some women experience heavy periods throughout their lives and are not a symptom of endometriosis, but if the volume of discharge increases, atypical clots appear, or the cycle gets disrupted, you should immediately contact an antenatal clinic.
Endometriosis after intervention
Removal of affected tissue areas is carried out in several stages. Initially, punctures are made through which the operation will be performed in the future. After this, gas is injected into the abdominal cavity, providing good visibility.
A special instrument is placed into one of the punctures, which is a tube equipped with a camera that transmits an image to the screen. In this way, a complete diagnosis is carried out.
After identifying pathological foci, their size and extent of damage are assessed. At the next stage, a tip with a laser is inserted into one of the punctures and the damaged areas are excised.
No doctor can give an absolute guarantee that endometriosis will not begin to develop again after a while. This disease has not yet been thoroughly studied; the risk of recurrence of the pathological process remains even after surgery.
The recovery period after surgery is about three days. Then the patient is under strict medical supervision on an outpatient basis for half a month.
As a result of the operation, small stitches remain on the body. They are removed in the first week. At this point, the results of scraping and histological examination of the excised tissue are already ready.
It is worth noting that after laparoscopy, in order to avoid the development of possible complications, therapy continues. Without proper treatment, the risk of relapse increases significantly.
As a rule, after surgery, the doctor immediately prescribes hormonal drugs, which the patient must take for at least three months. Also during this period you should adhere to the following recommendations:
- lead a healthy lifestyle;
- properly organize nutrition by including foods enriched with microelements and vitamins in the diet;
- refuse intimacy for one month;
- systematically undergo examination by a gynecologist and other specialists;
- conduct an ultrasound examination one month, three and six months after surgery;
- do not take a bath or visit the sauna for a month;
- take a shower daily;
- measure body temperature twice during the day;
- wash yourself at least twice a day;
- stop taking aspirin;
- do not resort to douching and using tampons;
- Avoid excessive exercise and heavy lifting.
The choice of tactics for postoperative anti-relapse therapy for external endometriosis depends on the stage of the disease and the technical nuances of the operation performed. In the case of severe disease in the postoperative period, it is logical to use GnRH agonists for 6 months, after which it is often recommended to take dienogest or an oral contraceptive that contains dienogest.
Prevention of the disease needs to be carried out not only by those who have undergone therapy and cured the disease through surgery, but also by people who have not yet encountered this problem. Preventive measures include the following manipulations:
- regular preventive observation by a gynecologist at least once a year; you need to see a specialist not when the pathology is already in a severe stage, but even if nothing worries you, because in the initial period it is easier to stop the pathological process;
- therapy for chronic and acute problems of the genital organs;
- normalization of body weight (fighting excess weight);
- normalization of the monthly cycle;
- If possible, you should avoid worries, worries and stress;
- taking hormonal contraception.
When diagnosing endometriosis, the laparoscopic method is preferred because such an operation preserves the patient’s ability to become pregnant in the future. The time of pregnancy is individual in each individual case. If during such a surgical intervention the cause of infertility was identified and eliminated and the patient underwent treatment for endometriosis and other related gynecological problems, then conception can occur in the following months.
The consequence of such surgery as laparoscopy may be bleeding, which can be mistaken for menstruation. Patients are advised to pay close attention to painful sensations in the lower abdomen and bleeding, which in their symptoms resemble menstruation. In some cases, laparoscopy is included in the complex of hormonal treatment, so menstruation may be absent in the period before and after the laparoscopic procedure.
- general health;
- hormonal background;
- patient's age, etc.
Laparoscopy for endometriosis requires some recovery time. Typically, the patient goes home after the surgery is completed, especially if it is just a diagnostic procedure.
However, there are some cases where you may need to spend an overnight stay in the hospital, for example if the endometriosis was extensive and the surgeon took a long time to remove all the damage.
Your doctor may prescribe painkillers for your surgery. Rest and avoiding excess stress on the abdomen may also help.
Avoid heavy lifting for the first few weeks after surgery to reduce the chances of a hernia.
Recovery time after laparoscopy varies, but if there are no complications, most patients can return to their normal activities within a week.
The first time after undergoing a laparoscopy procedure may be more difficult and painful than usual. If necessary, take time to rest and prepare additional painkillers and hygiene products in advance.
There are many ways to help you recover faster after laparoscopy. These include:
- Comfortable delivery home and care in the first days after laparoscopy.
- Placing a pillow or sweater between the seat belt and the abdomen to reduce pressure on the wounds during the ride home.
- During transport, the patient may vomit, so it is better to have a container with you in this case.
- Drink peppermint tea to relieve stomach pain due to the presence of gas. The gas can cause pain in the abdomen and shoulder and can take up to several weeks to leave the cavity.
- Taking quiet walks in the first days after the procedure will help get rid of gas in the abdominal cavity faster.
- Sanitary pads can help manage vaginal bleeding caused by laparoscopy. You should not use tampons or insert anything into your vagina during the recovery period.
- Recover as long as possible, do not go to work or study, trying to do this at home.
After laparoscopy, a woman may be emotional, cry, or feel weak.
It is important to take steps slowly after laparoscopy for endometriosis to ensure a complete recovery.
Laparoscopic surgery
The essence of laparoscopic surgery for endometriosis lies in several points.
- Preliminary inspection. The gynecologist assesses the degree of localization and size of pathological neoplasms.
- Delete. Surgeons remove pathological lesions using one of the methods: coagulation or cauterization.
- Taking samples of excised tissue for histological examination.
There are several sequential stages when performing laparoscopy.
- The doctor makes several small holes in the abdominal wall necessary for inserting manipulators.
- The peritoneal area is pumped with inert gas to improve visibility of the internal organs and separate the walls from adjacent tissues.
- The surgeon examines and then identifies the affected areas, after which they are excised or cauterized.
It is forbidden to eat or drink liquids 9 hours before surgery. Such precautions will help to avoid vomiting or nausea after surgery, or the reflux of food into the airways during anesthesia.
Laparoscopy is performed exclusively under general anesthesia.
Surgery for endometriosis begins with filling the abdominal cavity with a special gas. This manipulation helps improve visibility during surgery. The abdominal wall is slightly raised, and doctors can clearly see all the walls and control their actions.
Small holes are made on the patient’s stomach, the size of which is no more than two centimeters. A laparoscope and other instruments for manipulation are inserted into them. The tube with the video camera displays the image on the monitor screen. Only tissue affected by endometriosis can be removed. They are cauterized by electric current, liquid nitrogen or laser beams. The latter are the most effective and safe today.
During the operation, the blood vessels are carefully cauterized, so the possibility of bleeding is completely eliminated.
The average duration of the operation is about 30 minutes (up to an hour), but in severe forms of endometriosis it takes longer.
At the last stage, the doctor removes all the instruments and applies sutures. After laparoscopic surgery, patients are left with virtually no scars.
Complications after surgery have a probability of only 1%. Possible complications include:
- infection in the abdominal cavity;
- heavy bleeding;
- the presence of adhesions;
- damage to the urethra, bladder or intestines.
One of the indications for laparoscopy is endometrioid ovarian cyst. This pathology occurs when endometriosis spreads to the ovarian area.
An endometrioid ovarian cyst can reach significant sizes and be asymptomatic. As a rule, an ovarian mass is detected during a gynecological examination and then confirmed by ultrasound.
An endometrioid ovarian cyst can cause organ dysfunction and contribute to infertility. In addition, there is an opinion that this form of endometriosis has a risk of degeneration into a malignant tumor.
Many doctors strongly recommend removing endometrioid ovarian cysts using laparoscopy. In the absence of infertility, significant size and signs of oncological suspicion, observational tactics and conservative treatment in women of reproductive age are recommended. This is due to the fact that after laparoscopy, healthy ovarian tissue is affected and the ovarian reserve is often reduced.
Postoperative period
Treatment of endometriosis does not end after laparoscopy.
After surgery, the medical professional recommends that the woman follow these rules:
- Do not visit the sauna or take a hot bath for a month;
- Try to take a shower every day, if possible - twice a day;
- Monitor your body temperature. If there is a deviation from the norm, contact a medical facility;
- Limit yourself from using tampons;
- Try not to douche;
- Eliminate salty, fried and pickled foods from your diet;
- Avoid intense physical activity;
- Walk outdoors more often.
Recovery period
During the rehabilitation period after laparoscopy, a woman is advised to take antibacterial, immunostimulating, and anti-inflammatory drugs. Long-term hormonal therapy is mandatory to avoid relapses of endometriosis. Among the most popular hormonal drugs are Janine, Vizanne, and Buserelin. , as well as other hormones, is used for 6 to 9 months.
During the first two months after surgery, you must avoid physical activity and sexual intercourse. It is important to follow the following specialist recommendations:
- balanced diet;
- fiber should be present in the daily diet;
- giving up bad habits, alcoholic beverages and drugs;
- playing sports;
- walks in the open air;
- maintaining intimate hygiene;
- stop using intrauterine devices.
If after surgery women have had no relapses and no pain during the first five years, then remission is considered stable.
Probability of pregnancy
When can you get pregnant after laparoscopy? It is impossible to give a definite answer: it all depends on the characteristics of the surgical intervention and the recovery of the body.
If adhesions have been removed, you can get pregnant in about three to four months. This time is necessary to restore the functionality of the pipes and relieve tissue swelling. If conception occurs earlier than the specified period, there is a high probability of ectopic pregnancy.
Laparoscopy of endometriotic ovarian cyst requires a long recovery period. Doctors advise giving the body rest for six months, but sometimes conception is successful even three months after treatment.
You can get pregnant after laparoscopy for polycystic ovary syndrome within a month. If an ectopic pregnancy was treated, the body should recover for 6 months. This is due to the need to restore hormonal balance after termination of pregnancy.
Treatment of endometriosis using laparoscopy involves cauterization of inflammation while simultaneously removing adhesions or removing a cyst. Conception can be planned after three months. If hormonal treatment has been prescribed, planning is postponed until the end of the course of therapy.
Possible complications during pregnancy are not related to the operation performed, but to the characteristics of the former disease of the reproductive organs. For example, failure to meet the deadlines for conception after ovarian treatment can lead to miscarriage.
The following complications may arise:
- intrauterine infections as a consequence of inflammatory processes in the reproductive system;
- polyhydramnios as a consequence of the spread of infection;
- placenta previa as a consequence of fibroid removal;
- fetoplacental insufficiency as a result of infection or hormonal imbalance;
- abnormal position of the fetus as a result of surgery on the uterine cavity.
Many women are interested in whether it is possible to give birth on their own after laparoscopy or is it necessary to have a cesarean section? There is no need to worry about this: laparoscopy does not negatively affect the passage of the fetus through the birth canal, so the birth of a child naturally is possible.
Indications for cesarean section are removal of fibroids and other operations that leave scars: there is a likely risk of uterine rupture at the site of the scars.
The possibility of pregnancy depends on the degree of damage to the uterus by endometriosis. Usually, in good cases, pregnancy can occur after 6 months; there are cases that pregnancy occurs earlier - after three months.
If hormonal drugs are prescribed, pregnancy should be postponed until the course has been completed.
This method of excision of lesions allows preserving reproductive function, and therefore in the future a woman can plan a pregnancy after laparoscopy. As a result of the operation, scars form on the walls of the uterus, but they do not in any way affect the likelihood of conception. You will be able to get pregnant six months after surgery. By this time, the body has time to fully recover.
In the process of diagnosing and treating endometriosis, laparoscopy is often used. This is a minimally invasive method that allows you to identify lesions and eliminate them. The method is simple and safe, but in some cases it is contraindicated. Only a doctor can assess all the risks and decide whether this procedure is necessary.
Types of operations
Surgery involves excision or coagulation of abnormal lesions. Common methods of treating the disease include:
- laparoscopy – a minimally invasive form of surgery;
- laparotomy - penetration through the peritoneum to the internal organs;
- through vaginal access.
Surgery to eliminate foci of endometriosis on the pelvic peritoneum
Therapy includes the following stages:
- full diagnostic examination of the problem area;
- determination of volumes and areas of pathological foci;
- preliminary preparation for removal of overgrown tissue - dissection of formed adhesions and other procedures;
- cauterization or removal of problem areas using electric currents, a laser beam or thermal effects.
Surgical treatment of ovarian endometriosis
Surgical removal of endometriosis includes a step-by-step algorithm:
- the problematic ovary is isolated from adhesions, which are cut using a surgical instrument;
- the doctor performs a resection along the boundaries of the unaffected tissue, the body of the focus of pathological activity is excised;
- the location of the lesion is treated with a laser beam or electrodes in order to restore hemostasis;
- internal organs located in the abdominal cavity are washed.
The body of the cyst is sent for histological examination. Removal of the entire pathology is possible if its size does not exceed 3 cm in diameter. Larger tumors are removed in parts.
Surgical treatment of retrocervical endometriosis
In clinics, preference is given to the laparovaginal technique. Excision of the endometriosis lesion occurs through vaginal access, at the same time a laparotomy is performed to control the removal process and assess the severity of the pathological process. At the end of the manipulation, the intervention area is treated with laser or electrode technology.
Laparoscopic surgery
It is a minimally invasive method of surgical intervention with minimal damage when accessing the uterus. Three minimal incisions are made on the anterior wall of the peritoneum through which surgical instruments are inserted.
Full control over the procedure and minor damage during the operation make it possible to preserve the patient’s reproductive function and stop further progression of the disease.
Scraping
Includes two solutions to the problem:
- separate entry - during the operation, the cervix is initially cleaned, followed by the cavity;
- traditional - involves removing all tumors blindly, which often contributes to damage and the development of complications.
The resulting material undergoes histological examination.
First signs of relapse
Most recurrent lesions develop within the first two years after treatment. Signs are classified into local and general.
In the diagnostic process, the role of histological examination is indispensable, because confirmation of the correct diagnosis is impossible without determining the exact morphological parameters.
For a better microscopic assessment of tumor tissue and to identify the type of its growth (aggressive or sluggish), special histochemical diagnostic methods are prescribed.
There is a wide range of treatment approaches, including standard excision and, as a destructive alternative, cryosurgery. curettage, photodynamic and radiation therapy. The doctor prescribes which method will be applicable in each specific case, based on many indicators of the patient’s body condition. The decision regarding which therapy is best to use is made by the oncologist taking into account four factors:
Many therapeutic alternatives are available to treat recurrent basal cell carcinoma, but total surgical excision is still considered the gold standard. Almost all tumors of this type are curable if diagnosis and treatment are carried out as soon as possible.
Micrographic surgery allows you to remove the lesion without affecting healthy tissue. The process involves progressive radial sectioning and inspection of the defect edges in real time. The method is preferred due to its ability to preserve the sensitivity of the scalp and neck.
After eliminating the primary form of this epithelial tumor, patients should be observed clinically and regularly examined. Only 50% of relapses occur within the first 2 years after surgical treatment of basal cell carcinoma, 66% after 3 years and 18% after 5 years.
After undergoing a therapeutic intervention, it is necessary to remember that damaged skin remains susceptible to sunlight, so it is strictly forbidden to expose yourself to ultraviolet radiation.
Preparing for surgery
Before the operation, the patient is traditionally sent to the hospital. Ideally, endometriotic lesions are scraped for histological analysis and to exclude the malignancy of the process.
A consultation with a therapist, endocrinologist and cardiologist is also scheduled. At the same time, it is necessary to take a blood test for coagulation and general tests - based on the results of these studies, the anesthesiologist will work, selecting the optimal option for anesthesia.
In the presence of anemia or chronic infections in the acute stage, these conditions are relieved before surgery. Then hormone therapy is prescribed, indicating the preoperative period and preparation of the body.
Drug therapy
Drug therapy may be prescribed to reduce formations on the eve of surgery. Hormones are prescribed for this:
- Progestin;
- Antigestagenic;
- Antigonadotropic;
- Estrogen oral contraceptives;
- Androgenic.
Iron supplements are also prescribed to improve blood quality parameters, and, if necessary, antiviral and antimicrobial drugs.
Recurrence of endometrioid cyst: symptoms
This pathology has different manifestations. Every patient should remember that the problems will disappear, but the consequences of the disease will remain.
The first thing patients complain about is pronounced pain. It occurs in the projection of the cyst on the first day of menstruation. This is due to the fact that the rejected cells are located not only in the uterus, but also in the cyst. Due to the large number of rejected cells and the influence of hormones, the function of the entire reproductive system is disrupted. This causes severe pain.
If there are too many endometriotic lesions, pain may occur during and after sexual intercourse. This is due to the fact that an adhesive process occurs in the pelvis, accompanied by an inflammatory reaction.
A distinctive symptom of the recurrence of a cyst is spotting brown discharge before or after menstruation. They can last up to 7 days. Such manifestations are associated with the fact that lesions located on the wall of the uterus reject a large number of cells during menstruation.
Repeated pathology leads to absence of pregnancy. This mechanism has not been fully studied. More than 85% of women examined are found to be unable to have children.
Description of the laparoscopic method
Removal of endometrioid lesions using the laparoscopic method is a relatively new method, compared to the duration of use of classical surgery. Laparoscopy refers to a microsurgical method and is divided into two subtypes:
- Diagnostic intervention - allows you to determine the localization of the focus of endometriosis, examining the pelvic organs in more detail with minimal damage to the body.
- Therapeutic intervention - after all diagnostic measures have been carried out and the source of endometriosis has been identified, an intervention is performed to remove the overgrown endometrium, cystic formations and adhesions.
Before prescribing laparoscopic diagnosis of endometriosis, the patient is prescribed general blood and urine tests, venous blood tests for hormones and coagulation.
Contraindications
Despite all the loyalty of the operation, there are certain contraindications that limit the scope of this method. In particular, laparoscopy is contraindicated in the following cases:
- Coronary heart disease, congenital heart defects and cardiopathy;
- Chronic respiratory diseases, since gas in the abdominal cavity can cause pulmonary spasm;
- Slow blood clotting and diabetes;
- Oncological diseases;
- Congenital malformations of the diaphragm;
- Abdominal surgeries performed in the last six months;
- Acute liver failure;
- Infectious diseases in the acute phase;
- Clinical obesity.
In these cases, the doctor may recommend classic surgery or an alternative treatment method.
The classical method of surgery is used in rare cases