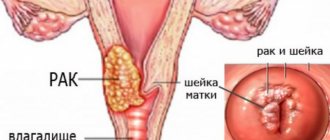
The cervix is a narrowing area of the lower part of the organ, connected to the vagina through a through cervical canal. During a routine examination or during colposcopy, the doctor may detect neoplasms, erosion, or changes in the characteristic structure of this part of the uterus in the patient. In this case, a cervical biopsy is prescribed as one of the diagnostic methods that makes it possible to detect malignant cells in the early stages.
The meaning of the procedure is to take a tissue sample for subsequent analysis of epithelial cells and the layers located under their surface for the presence of malignant or benign formations.
Indications for use
Diagnosis begins with an examination using a colposcope, a gynecological device that has the ability to magnify the areas being studied up to 40 times. In addition to examining the surface of the cervix, during colposcopy it is possible to take samples to detect structures that have signs of pathology. To study pathological structures, a biopsy is performed, prescribed when changes are detected, the most common of which gynecologists include:
- acetowhite epithelium, determined by a change in the color of tissues treated with acetic acid to lighter shades; the presence of such a deviation may indicate dysplasia, the presence of human papillomavirus, leukoplakia;
- vessels that do not show a reaction when interacting with acetic acid, small veins and arteries, an atypically tortuous structure of capillaries and red dots on mucous surfaces caused by an expansion of the localization area of the vascular network;
- inflammatory processes and the presence of signs of erosion in the tissues of the cervix;
- atrophy and degenerative changes in the area being studied;
- areas that are not stained with a solution of alcoholic iodine, the presence of such a symptom may be a sign of atrophy, leukoplakia, dysplasia;
- proliferation of the endometrium outside the uterine cavity;
- detection of deep damage to epithelial cells, indicating the occurrence of an oncological process or dysplasia of the area.
Another indication for prescribing a biopsy is the diagnosis of conditions that caused pathological changes detected during examination or taking a smear, such as:
- Dysplasia (precancerous condition), in which analysis of epithelial cells reveals atypical elements that have a tendency to degenerate into oncological tumors.
- Leukoplakia, presented as a white spot with clear contours. Pathology is determined by the accelerated formation of the cornea, an increase in thickness and coarsening of the flat epithelial tissues of the organ.
- Local proliferation of the mucous membrane of the cervical canal and the lining of the cervix, indicating the presence of benign formations - polyps.
- Condylomas, belonging to the group of sexually transmitted diseases, are cone-shaped pointed growths located on the mucous membranes of the uterus.
- Ectopia, which is degenerative changes in the mucous surface of the vaginal part of the uterus. A biopsy is mandatory if bloody discharge is found on the surface of the mucous membranes.
- Single formations identified by the results of a cytological smear that have a disturbed structure of the cytoplasm or nucleus.
After prescribing a diagnosis, the attending physician examines the patient’s condition, excluding possible contraindications to the procedure, and determines the type of intervention. Among the conditions that preclude a biopsy, gynecologists identify:
- Poor health and poor health of a woman.
- Presence of abnormalities in blood clotting parameters.
- The presence of inflammatory or acute infectious processes in the cervix or the uterine cavity itself.
- Menstruation.
- First or third trimesters of pregnancy.
https://youtu.be/WALhKBJwzwQ
What not to do after the procedure
In medicine, there are a number of types and methods of performing cervical biopsies. OXY-center specialists use the safest and most informative of them. In each case, we take into account the individual characteristics of the patient, the indicators of her tests and examination results in order to resort to a specific technique in favor of the reliability of the data obtained or painlessness for the body.
The fact is that the most informative method, which is highly accurate, is the “knife” taking of materials - this is an extended biopsy of the cervix. But in this case, a significant amount of tissue is damaged. Therefore, our specialists rarely resort to this technique.
Other methods of manipulation are less invasive and help preserve the integrity of cervical tissue:
- Conization. This technique involves taking a cone-shaped tissue sample. This leaves a pinpoint wound on the surface of the pharynx of the cervix. However, thanks to the special shape of the sample, specialists can assess the condition of both surface structures and underlying tissues. The material is taken under local, regional or general anesthesia, depending on the sensitivity of the patient.
- Scraping. When performing such a biopsy of the cervix using a special instrument - a curette, part of the mucous membrane is removed from the pharynx. The material contains a large number of epithelial cells, which makes it possible to assess their condition with a fairly large sample. Often performed under spinal anesthesia.
- Loop electrosurgical biopsy. This technique is the most painless and minimally invasive. The material is collected using a thin metal thread through which a weak electric current passes. However, due to temperature effects on the sample, this method is not very informative. Therefore, they resort to it only for special indications. To take the material, specialists numb the cervix with spinal or local anesthesia.
All types of procedures take no more than an hour. The duration depends on the chosen technique and the individual characteristics of the patient’s body structure.
Cellular composition
There are quite a lot of pathological conditions that require mandatory further examination, and one of the most reliable ways to obtain a reliable result is a cervical biopsy.
Among the pathologies for which a biopsy is performed are:
- Presence of changes in cytological examination of the cervix. Among them there may be pathological cells similar to cancer or cervical dysplasia, etc.
- The appearance of a pathological focus in the cervix during colposcopy. These may include iodine-negative areas, the presence of erosion or ectopia, especially in the case of chronic inflammation in the vaginal cavity, contact bleeding from the cervix in the absence of pathology in the uterine cavity, etc.
- Definition of leukoplakia.
- Detection of polyps or condylomas on the surface of the cervix.
In order to exclude the development of possible complications after the procedure, it is necessary to exclude possible conditions that could aggravate the process.
Among them are:
- The presence of inflammatory processes on the cervix or vagina, carriage of specific sexually transmitted infections.
- Discharges that are pathological in nature.
- Pathology of the hemostatic system. This may be a blood clotting disorder, the presence of thrombophilia or changes in hemostasis.
- Lack of technical equipment, insufficient qualifications of a specialist, as well as insufficient compliance with the rules of asepsis and antiseptics.
- State of pregnancy. This is especially true in the first and last trimesters of pregnancy. In the second trimester of pregnancy, the contraindication is relative; a biopsy is allowed if the possible benefit of obtaining the result outweighs the risk. This is important if a malignant process with rapid progression of pathology is suspected.
The choice of method directly depends on the attending physician, since his choice is based on the disease with which the woman is being referred, as well as the expected volume of tissue collection.
To perform a biopsy, a woman must undergo a set of examinations aimed at preventing the development of complications:
- Among them are general clinical examinations, including determination of coagulation,
- It’s worth taking a smear for flora,
- Availability of a smear for oncocytology,
- Colposcopy result,
- Analysis for the presence of sexually transmitted infections, as well as hepatitis and syphilis,
- Testing for HIV infection.
The procedure is done primarily to relieve pain. During the procedure with anesthesia, the patient is hospitalized for 2 days.
Sighting
This is a common method of procedure. The doctor uses a needle with a small diameter and uses it to take a biopsy sample. This method is recognized as the best for diagnosing uterine cancer pathologies.
Gives very accurate results. A layer of tissue is taken with a laser beam. Healing takes little time. But when using a laser, there can be quite unpleasant residual effects.
When using a radioknife, the risk of side effects is reduced. Healing of cervical tissue occurs quickly. Discharges appear rarely, their volume is insignificant. Complications after radioknife are extremely rare. Anesthesia is not required for the analysis.
Wedge biopsy
Otherwise, this method is called conization. This is an unsafe examination method. During a biopsy, the doctor uses a scalpel. This operation is performed in the gynecology department of the hospital.
Using a surgical knife, the doctor excises different types of tissue. After the intervention, stitches are applied.
Healing after a wedge biopsy takes a long time, and this process is accompanied by more or less pronounced pain. A large amount of discharge may appear.
This biopsy uses an electric current. A loop is placed on the area of the cervix, into which an electric current is turned on. Electric cauterization is often used in the treatment of uterine dysfunction.
Circular biopsy
During this examination, tissue is taken from the cervical canal. Surgeons use a scalpel and a radio knife. The procedure is performed under general anesthesia and only in a hospital setting.
When using curettage, tissue is scraped out using a curette. The use of painkillers is mandatory.
Conchotomnaya
This is a type of fine-needle biopsy using a surgical instrument - a conchotome.
After the biopsy it is prohibited:
- work with loads (over three kilograms);
- insert tampons into the vagina (from a week to a month, depending on the type of biopsy);
- do not practice intimate contacts for one month;
- Do not go to the steam room, swimming pool, or wash in the bathroom for up to a month.
Types of biopsy
The type of surgical intervention chosen will depend on the type of disorder suspected, its severity, and the woman’s general health. Depending on the gynecologist’s recommendations, one of the following types of biopsy may be performed:
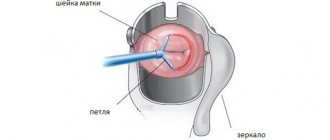
- A puncture, pinpoint or targeted type of procedure is performed by sampling tissue with a special hollow needle and is carried out in areas containing altered structures. It does not provide pain relief, since unpleasant sensations (mild tingling or pressure) are present for a few seconds.
- Loop, or electrosurgical, biopsy, in which material is taken from an area of damaged tissue by peeling it off after local anesthesia. To take a sample, an instrument is used that has the shape of a loop and passes an electric current. The latter, according to some doctors, creates a burn in the affected area, which affects the reliability of the results obtained. Healing after this procedure takes longer, and bleeding from the vagina may occur for several weeks.
- Conization of the cervix, a wedge-shaped or knife operation, is performed by cutting out a small section of triangular-shaped tissue from the diseased organ using a scalpel. Before the procedure, epidural, spinal anesthesia or general anesthesia is given. Incisions in the neck are made in such a way that the resulting sample contains all the pathological areas of the organ.
- A circular biopsy is performed using a radio wave knife or scalpel under anesthesia. The circular version of the procedure differs in that a large area of the organ is sampled with the obligatory capture of a tissue sample of the cervical mucosa.
- A conchotome biopsy is performed after local anesthesia and resembles a puncture type, but a special instrument similar to scissors is used - a conchotome.
- Endocervical curettage is the scraping of material from the cervical canal after intravenous anesthesia.
- Laser - taking tissue using a laser knife under general anesthesia. This technique is characterized by a low degree of tissue damage and a shorter rehabilitation period, while the time during which blood flows from the vagina is reduced to several days.
- The radio wave procedure is performed using a Surgitron device equipped with a radio wave knife. Like the previous method, this intervention does not cause complications; residual effects associated with the operation disappear within a few days.
Conization of the cervix - how is the operation performed?
The main reason for the development of changes in the epithelial layer of the cervix is HPV.
Some HPV strains have a high level of oncogenicity and more often lead to the development of cervical cancer. In this regard, part of the removed tissue is sent for histological or immunohistochemical examination.
The operation of conization of the cervix is not only a diagnostic, but also a therapeutic procedure and is performed only if there are serious changes in the epithelial layer of the cervix.
Therefore, before receiving a referral for conization, the patient must undergo a series of studies in order to confirm the feasibility of such an operation.
Before conization, the patient must undergo:
- colposcopy - examination of the changed part of the cervix using a microscope (if necessary, an additional biopsy of the cervix is performed);
- HPV test;
- cytological biopsy (smear for oncocytology).
Most often, cervical conization surgery is performed under general anesthesia. Six hours before surgery, it is forbidden to consume food and liquid, chew gum and smoke.
After short-term anesthesia using a scalpel, electric knife, or radio knife (radio wave conization of the cervix), part of the cervix is removed.
To stop bleeding, sutures are placed and cauterization is performed - diathermocoagulation.
After conization of the cervix, the patient remains in the hospital for a day, under the supervision of a doctor. The results of a cervical biopsy after histological or immunohistochemical examination are sent to the doctor after 10-14 days.
Conization and biopsy of the cervix - discharge after the procedure
Discharge after conization of the cervix can be observed for 2-4 weeks. The discharge may be bloody, mucous-brownish, scanty, with an unpleasant odor.
Discharge after a cervical biopsy can be observed for 2-3 weeks. Also, a small amount of blood may be released for 10-14 days after a cervical biopsy.
If bleeding, purulent discharge, fever or abdominal pain occurs, consult a doctor immediately.
What needs to be done to speed up the healing of the cervix
Within 7-21 days, the scab may pass away after conization of the cervix or biopsy (the timing is individual for each patient).
For 4-6 weeks after conization, it is forbidden to lift weights, play sports, or visit the sauna or swimming pool. You should also avoid sexual activity and the use of tampons during menstruation. For 1-1.5 months you need to monitor your stool (avoid constipation).
On the recommendation of a doctor, antibacterial, antiseptic or immunomodulating suppositories can be prescribed to reduce the risk of developing an inflammatory process, as well as suppositories with D-panthenol (Depantol) to accelerate mucosal regeneration.
Preparation for the procedure
Preparation for the examination includes a number of recommendations, the adherence to which determines not only the possibility of complications, but also whether it will hurt during the procedure. A biopsy is done on days 5-7 of the cycle. This increases the likelihood of successful healing before the next period and reduces the possibility of inflammatory processes.
The preparatory stage includes a doctor’s assessment of the patient’s health status, examination of medical history, and discontinuation of medications that increase the risk of bleeding.
After the examination, the gynecologist writes out a referral for tests:
- smear to study microflora;
- blood and urine tests;
- determination of urea, sugar, bilirubin levels, liver tests;
- test for mycoplasmosis, chlamydia, ureaplasmosis;
- analysis for HIV, syphilis, hepatitis of a viral nature;
- blood clotting indicators;
- colposcopy and PAP smear.
Before the biopsy, they discuss what should not be done in preparation. 2 days before the intervention you need to exclude:
- douching and using tampons;
- introduction into the vaginal area of medications not recommended by a doctor;
- smoking and drinking alcohol.
Other recommendations before performing a biopsy:
- It is necessary to ensure sexual rest for several days before the intervention.
- Changing the dosage of hypoglycemic drugs or insulin after consultation with an endocrinologist.
- Given the possible bleeding after the procedure, it is recommended to have a pack of sanitary pads.
- Before the operation, you must take a shower, including washing the external genitalia.
Indications and contraindications
When a patient, when visiting a gynecologist, complains of an irregular menstrual cycle or strange discharge, she undergoes an extended colposcopy before a biopsy is prescribed. To carry it out, the mucous membrane is treated with a special reagent and changes are monitored. At the first stage, a cotton swab is soaked in 3% acetic acid and the neck is lubricated; if white spots appear on it, it means there is damage to the tissues. In addition, the surface of the cervix is treated with iodine to detect inflammation and viral lesions.
If the diagnosis reveals precancerous changes, polyps, erosions, genital warts, or a papilloma virus that can cause a tumor is detected, a biopsy is used.
A uterine biopsy allows you to fully learn about the structure of cervical cells and determine the structural signs of the disease, which allows the doctor to make a timely diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment.
A biopsy cannot be performed if a preliminary examination shows the presence of an inflammatory process in the pelvic organs. Therefore, drug treatment is carried out before this. In addition, the procedure is not prescribed if the patient is menstruating, has blood diseases, or is pregnant, because in the early stages there is a risk of miscarriage, and in the late stages, premature birth is possible. A biopsy during pregnancy can only be done if the malignant tumor is growing rapidly.
Preparation for the procedure
Before the operation, a woman needs to prepare. To do this, the specialist will definitely refer you for an ultrasound and colposcopic examination. It is also necessary to be tested for HIV, hepatitis, syphilis and hidden sexually transmitted infections.
When the procedure is performed using anesthesia, you should not drink, eat, or take medications for 12 hours before surgery. Sexual rest should be maintained for two days, and it is also recommended to avoid the use of tampons and douching.
Before the operation, the patient must undergo instructions explaining the possible consequences after the biopsy. After which you need to sign an agreement to carry out the manipulations. When all the details of preparation for the procedure have been followed, the biopsy begins.
How the research is carried out
Depending on the type of biopsy, the procedure is performed in a hospital setting under general anesthesia or using local anesthesia in a antenatal clinic. After examination, to reduce sensitivity, the gynecologist injects lidocaine into the tissue of the cervix or irrigates it with a spray with this substance.
After this, the dilator is inserted into the vagina, the cervix is grabbed and lowered to the entrance area, and the organ is treated with iodine or acetic acid to detect areas with altered cells. Pathological tissues are removed.
Types of procedure
The procedure may vary. There are several methods by which a cervical biopsy is performed:
- Radio wave is the least traumatic and is considered a minimally invasive method. Excision occurs by exposing the cellular structure to elevated temperatures, the liquid part of which is subject to evaporation. The main method for carrying out the impact is a loop through which high-frequency radio waves are sent to the selected area. The loop does not touch the fabric when impacted. The method is painless, maintaining complete tissue integrity, without bleeding.
- Laser – excision is carried out using a laser. The event is carried out with the patient in pain, so doctors recommend administering drugs that neutralize painful discomfort - general anesthesia.
- Conchotome - the procedure is carried out using a specific object: a conchotome, which looks like scissors. Inpatient treatment is not required, but excision is most often painful, so the person is first injected with a painkiller.
- Loop - during the procedure, the effect is carried out using an electric current directed through a loop. The procedure is painful, so local anesthesia is necessary. But there is no need for hospitalization.
- Puncture is a common method of collecting material for morphological analysis. The procedure is carried out under the control of colposcopy, while the doctor removes those areas of the epithelium that cause the most concern. The procedure is carried out using the puncture needle method. No specific preparation or pain relief is required;
- Wedge resection - the doctor takes material from the affected tissues for diagnosis in the form of a cone, so that the affected layer and the next one are captured. The surgical intervention is traumatic, so an anesthesia procedure is performed, due to the fact that everything is carried out using a simple scalpel, without using current or radio waves.
The choice of type of procedure depends on the ongoing disease, severity, as well as the general condition of the patient.
A biopsy of the endometrium of the uterus is prescribed if suspicious pathologies were identified during examination at the antenatal clinic. This procedure helps confirm the diagnosis if uterine endometrial cancer or dysplasia is suspected.
The study helps determine which cells are in the endometrial tissue: malignant or benign. Depending on the answers, further examination and treatment are prescribed.
If during a visual examination the gynecologist sees suspicious areas, a smear test for infection and calposcopy will be prescribed. After this, a biopsy procedure is performed.
Indications for a biopsy can be very diverse, namely:
- Cervical erosion
- Changed color of the epithelium
- The presence of papilloma on the surface of the cervix
- Iodine-negative areas on the cervix
- Detection of abnormal cells in a cytology smear
- Polyps
- Condylomas
- Leukoplakia
- The presence of rough areas on the mucous membrane of the cervix
A biopsy is an accurate way to diagnose changes in the uterus, so under no circumstances refuse to undergo this procedure. Early detection of oncological processes will help save lives.
Recommendations during the recovery period
Recommendations to be followed during rehabilitation:
- If there is pain, put a warm compress on the lumbar area, wrap yourself in a wool scarf, or take a painkiller.
- To speed up wound healing and prevent scarring, suppositories such as Depantol may be prescribed.
- You cannot use tampons or douche for a week after an excisional biopsy and a month after conization, or lift loads weighing more than 3 kg.
- Avoid taking a bath, visiting the sauna and swimming pool for 15-30 days after the procedure.
- Avoid sex for 6-8 weeks after conization, 1 month after excisional biopsy, and 1 week after core biopsy.
During healing, you should use absorbent pads, wash your external genitalia daily, and wear cotton underwear.
Possible complications
Negative consequences are associated with the entry of pathogenic microflora into damaged tissues, one of the reasons for which may be poor hygiene. As a result, you may experience:
- Pain in the lower abdomen.
- Discharge that has an unpleasant odor or a yellow tint.
- General deterioration of condition and increased body temperature.
- Itching in the perineal area.
- The appearance of dark blood clots.
Causes for concern may be bleeding from the vagina not associated with menstruation, disruptions in the menstrual cycle, suspicion of extensive conization, in which the removal of excess tissue can lead to ectopia.
Radio wave biopsy of the cervix
A radio wave biopsy is performed by applying an electric current to the tissue. The operating frequency is small, does not exceed 4 MHz. It is not dangerous to humans, but it is enough to cause local tissue destruction.
The most commonly used device is Surgitron, which causes minor damage by evaporating fluid from the cells. This process causes the tissue to be cut.
Electric waves immediately seal the incisions, which reduces blood loss, and the operation is not as painful as when using a scalpel.
The procedure lasts 10-15 minutes. Local anesthesia is usually given. You can do without it altogether. This is due to the nature of the pathology and the condition of the patient. Having cut off the changed part of the organ, the doctor completes the operation.
Decoding the results
The doctor identifies abnormalities by analyzing the tissue taken. According to the WHO classification, he classifies the detected changes as mild, moderate, severe forms of dysplasia or carcinoma. In addition, the specialist determines HPV in cells and the depth of tissue damage in the presence of pathological formations. Decoding the examination results allows us to classify violations into groups:
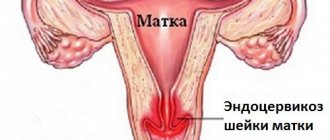
- Background pathologies that do not develop into cancer cells, but represent the basis for the development of endometriosis, endocervicosis, polyps, leukoplakia, cervicitis, true erosion, ectropion, scars.
- Precancerous conditions, which under favorable conditions with a 50% probability can turn into cancer cells, for example adenomatosis, dysplasia in the presence of background processes or a healthy neck, leukoplakia with atypical properties.
- Malignant formations at an early stage, developing without symptoms, having clinically pronounced forms.
The reliability of the data obtained during a biopsy is almost 100%; the procedure makes it possible to determine the nature of pathological changes and prescribe treatment. The only limitation for frequent intervention is the possibility of the formation of scar tissue that impairs a woman’s reproductive abilities.
Uterine biopsy during pregnancy
There is no categorical ban on performing a cervical biopsy during pregnancy, since in some cases delay can lead to serious complications. However, if the pathology is not dangerous and immediate diagnosis can be delayed until after birth, it should be postponed. Such intervention in the cervical area during pregnancy up to twelve weeks can become a factor provoking a miscarriage, and at later times it can cause premature birth. The most optimal time for a biopsy after childbirth is one and a half months after it.