What is polycystic ovary syndrome
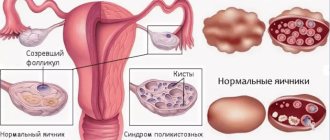
Hormonal imbalance leading to the formation of small cysts and causing enlargement of the ovaries is a female disease called polycystic ovary syndrome. Fluid-filled neoplasms disrupt reproductive function, so ovulation occurs either unplanned or does not occur at all. Often the female disease is asymptomatic or its symptoms may be similar to other gynecological diseases. Only when a problem arises with conceiving a child does it make itself clearly known.
Symptoms of polycystic disease
The name of the disease comes from the word “cyst” - a formation on the surface of the ovaries in the form of a follicle filled with fluid and containing immature eggs. "Poly" means many of these cysts. The disease occurs due to hormonal imbalances, which are caused by an increased amount of insulin produced. Because of this, the girl’s body produces more of the male sex hormone - androgen, which provokes hormonal imbalance. Some scientists argue that the occurrence of the disease is also associated with frequent acute respiratory infections, sore throats, stress that a girl experiences at 10-12 years old, heredity, first and early abortions.
Polycystic disease is characterized by:
- menstrual irregularities (frequent delays in menstruation);
- bleeding;
- increased growth of hair on the body and face according to the male type;
- acne, oily skin and hair;
- sudden weight gain for no reason (in 50% of patients);
- an increase in all parameters of the ovaries, which is visible on ultrasound.
But still, many doctors talk about how imperceptibly this disease develops and how imperceptibly it can proceed, making itself felt only when the woman decides to give birth to a child - and she cannot. Therefore, the sooner it is identified, the better. After all, advanced polycystic disease can lead to infertility, obesity, and gynecological cancer. The patient is also at risk of rupture of the ovary or the cyst itself if it is large.
More on the topic
Is it possible to get pregnant with polycystic disease?
Why can't a woman get pregnant?
When can you get pregnant?
Is it possible to get pregnant and give birth with a baby's uterus?
Is it possible to get pregnant a month after giving birth?
Is it possible to get pregnant with polycystic ovary syndrome?
A confirmed diagnosis is not a death sentence for a woman. PCOS and pregnancy are not mutually exclusive in all cases. In medical practice, there are many examples when patients with this disease were able to conceive, bear, and give birth to a child. This can be done even without treatment, but the main obstacle is the stage of the disease, which significantly affects the possibility of conception.
Articles on the topic
- Testosterone analysis in women - when to prescribe and how to take it, reasons for increased and decreased values
- Stagnation in the gallbladder - signs, therapy with medications, homeopathy, folk remedies and diet
- Pain due to ovarian cysts in women: what to do
How to get pregnant with polycystic ovary syndrome
If the follicle, and with it the egg, are produced regularly, then polycystic ovary syndrome and pregnancy will not interfere with each other. Over the course of a year, a woman will be able to conceive without medical intervention, and to determine the days of ovulation, the doctor will recommend measuring basal temperature. You will have to think about further treatment under the supervision of a gynecologist or endocrinologist after a year. In order for polycystic ovary syndrome and pregnancy that does not follow it to cease to be a cause for concern, it is necessary to normalize the menstrual cycle, and this may take six months or more.
Stages of treatment
First, you need to confirm the diagnosis. After all, other diseases have similar symptoms: hypothyroidism, ovarian or adrenal tumors, hyperprolactinemia. To do this, the doctor prescribes an ultrasound, blood tests for luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). You will also need to take a 24-hour urine test to check for androgen. You must undergo all examinations 2 times, on days 2-3 and on days 21-22 of your menstrual cycle.
If tests confirm polycystic disease, the doctor prescribes hormonal therapy. Patients take medications that normalize the overactive production of androgen in their body, and at the same time stimulate ovulation - the production of eggs. Previously, taking such drugs necessarily led to weight gain, but today there are drugs that do not cause such side effects. For example, Clomiphene has proven itself well on the international medical market. In 70% of patients taking it, ovulation improves, and in 40% it becomes possible to become pregnant. No less often prescribed drugs are: Metrodin, Menagon and Horagon. Physiotherapy, which should be prescribed by a doctor, is also helpful.
If a woman is overweight, she needs to lose it. This is especially true for women with a masculine “apple” figure, when the shoulders are wider than the hips. Their accumulation of fat in the abdomen, chest and shoulders leads to the body producing more male sex hormone.
It happens that hormonal therapy does not produce results. Then a surgical intervention called laparoscopy is necessary - surgical removal of the cysts through small incisions. But the operation can also have a short-term effect: the disease will not bother you for six months to a year. But during this time you can get pregnant and carry a baby. Therefore, in such situations this is the best solution.
How to cure polycystic ovary syndrome to get pregnant
A dangerous female disease that threatens infertility and uterine cancer, can be successfully treated with conservative or surgical treatment. The latter is a last resort when other methods have been tried, but it is necessary to prevent the development of a more serious disease. Traditional healers offer effective treatment methods, and the following methods help solve the problem of polycystic disease and speed up pregnancy:
- Conservative treatment. Polycystic ovary syndrome, but not the cause of the disease, is successfully treated with hormonal therapy. Taking oral contraceptives helps restore the menstrual cycle. A doctor can prescribe pills only after examination and blood tests for hormones.
- Surgical intervention. Progressive pathology is a direct indication of the need for surgery. Laparoscopy is considered the most gentle, in which several small incisions are made and instruments are inserted to remove seals with liquid and adhesions, which helps restore regular menstruation. Wedge resection helps normalize ovulation in more serious ovarian lesions. The surgeon partially removes the pathological tissue, and for a successful result you also need to take hormonal medications.
- Folk remedies are proven recipes based on the gifts of nature that help cope with the treatment of the disease, and pregnancy does not take long to occur.
You should consult with your doctor about the choice and duration of the course; most folk recipes go well with drug therapy, helping to cure the disease:
- Viburnum juice with honey. A natural medicine is prepared from fresh berry juice and flower honey, mixed in equal proportions. For the first week, the mixture is taken in the morning on an empty stomach, starting with a quarter teaspoon; the second week - a third, the next week - a full teaspoon, and on the fourth - a tablespoon of the mixture. Then they take a break for one month and start taking a tablespoon again, gradually reducing the volume to the initial amount every week.
- Peony tincture. This drug can be bought at a pharmacy, and the important condition is to take it strictly according to the schedule, i.e. at the same time for a month. The scheme for taking the solution (1 teaspoon of peony infusion mixed with 1 teaspoon of water) is as follows: three times a day, at a certain time, and after a month, take a break for 10 days, repeat the course three times.
- Red brush. Prepare a herbal tincture in alcohol (vodka), keeping the proportion of 0.5 liters of alcoholic liquid per 80 g of dry red brush. Infuse the mixture for a week, leaving it in a dark place, and then take half a teaspoon three times a day.
Do you need to treat PCOS if you are not planning a pregnancy?
So, if a woman really has PCOS (not just multifollicular ovaries on ultrasound, but the diagnosis is made correctly, in accordance with the criteria), she has less than 6-8 menstruation in 12 months and other causes of anovulation are excluded (no hyperprolactinemia, CAI, thyroid diseases glands, etc.), and today there are no reproductive plans (she doesn’t want to get pregnant now), she is not obese, her weight is ideal, she plays sports and eats right - then the following treatment options can be offered.
- Combined oral contraceptives. It is important to understand that COCs are not able to treat PCOS; it is a symptomatic therapy that is used for:
- protecting the endometrium from hyperplasia and cancer;
- elimination of acne and hirsutism;
- reliable contraception (after all, sometimes with PCOS you can ovulate, and therefore you can get pregnant).
Women who want to become pregnant cannot be recommended or prescribed COCs. There is no rebound effect, these are myths!
By taking COCs in the hope of curing PCOS or getting pregnant during withdrawal , you are simply wasting time, and your doctor knows absolutely nothing about this disease. Stop using COCs and change your doctor.
COCs cannot be prescribed by force. It causes me a storm of emotions when a woman comes to an appointment who takes COCs and has a bunch of side effects from them, but the doctor forbids her to have them. It's a bullshit.
Whether you take COCs or not will not affect your PCOS in the future. Hormonal drugs cannot aggravate PCOS (cause the disease), nor can they cure it. They do not increase or decrease the chances of future pregnancy. Your menstrual cycles will be as irregular after stopping COCs as if you had never taken them.
COCs can be prescribed only to those women who do not want to become pregnant and have no contraindications to taking COCs or side effects from them.
- Vaginal hormonal ring or hormonal patch. The approaches and goals of therapy are the same as when taking COCs.
- The hormonal intrauterine device containing progesterone protects the endometrium from hyperplasia and cancer, but is ineffective in eliminating acne and hirsutism.
- Progestins are synthetic progesterone. Another treatment option is to cycle synthetic progesterone (dihydrotestosterone or any other progestin) for 10 to 14 days every 1 to 3 months.
This causes withdrawal bleeding in almost all women with PCOS, and this treatment protects the endometrium and reduces the risk of endometrial hyperplasia and cancer.
This therapy has no other effects! Progesterone cannot do anything else, it can only protect the endometrium.
Advertising
Taking progesterone from days 16 to 25 of your menstrual cycle will not help you get pregnant. Such treatment is not capable of restoring ovulation or promoting it.
And if you or your friend became pregnant while taking progesterone from the 16th to the 25th day of the cycle, then ovulation “shot”, and progesterone has nothing to do with it. You would still get pregnant if you didn't take anything.
This type of treatment is not suitable for women who want to become pregnant, who have hirsutism and acne.
When to plan a pregnancy after laparoscopy
Although minimal surgical intervention is considered less traumatic, it does introduce limitations. After laparoscopy, pregnancy planning begins with a course of medication to stimulate ovulation. After about three to four months, the functioning of the ovaries will normalize, which will make pregnancy possible. Even complete removal of the ovaries will not be a death sentence for a woman: it will be possible to conceive and give birth to a child through the use of assisted reproductive technologies, stimulation or IVF.