What it is
Effusion is a manifestation of inflammation or excess blood in organs and tissues. The composition of free fluid in the pelvis can be serous, fibrinous, or contain pus and blood.
More often it is detected during an ultrasound examination of organs in the pelvis, because in most patients the pathology develops without pronounced symptoms. Only a tenth of women go to doctors with complaints of vaginal discharge, pain in the lower abdomen, a burning sensation, and changes in the nature of menstruation.
Even with asymptomatic development of the pathology, constant effusion in the pelvis is an important sign of the disease, which a professional will identify. He will look for inflammation of the genitals, tumors, possible internal bleeding or ectopic pregnancy.
Less commonly, ultrasound visualizes a small amount of fluid behind the body of the uterus. This is the contents from the burst follicle during the release of a mature egg, which is considered normal. In a few days it resolves.
Repeated examination will not detect the effusion. The next month in a healthy woman this physiological process will repeat. It is also a sign of ovulation, which is important for those who are planning to have children but are having difficulty getting pregnant.
Fluid in the pelvis: causes
Free fluid in the pelvis may be normal, but more often it indicates a disease
First of all, it should be noted that the presence of a certain amount of fluid in the pelvic area is a completely natural phenomenon. This does not always indicate any pathology.
For example, free fluid quite often forms in the body due to the course of menstrual processes. In particular, the appearance of this substance is associated with ovulation, which is associated with the penetration of fluid from the follicle into the space behind the uterus. In this case, there will be very little substance, which is why after a few days, during a second examination, it will not be visible at all.
The appearance of free fluid in the pelvis can be caused by the following pathologies:
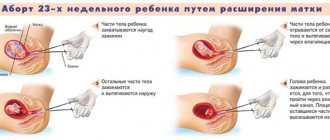
- Inflammatory processes. Inflammation of a certain pelvic organ is one of the most common causes of free fluid. In particular, the disorder may be associated with inflammatory processes inside the ovary or be caused by its rupture. In addition, inflammation can be a consequence of surgical termination of pregnancy or infectious diseases.
- Ectopic pregnancy. In most cases of ectopic pregnancy, embryo development occurs in the fallopian tube. Due to this pathology, it first becomes deformed and then ruptures. As a result, blood enters the abdominal cavity, thus making up the bulk of the fluid in the pelvis.
- Internal bleeding. Pathological processes in the abdominal organs can often provoke hemorrhages. In addition, the cause of bleeding can be injuries. In this case, the blood, under the influence of gravity, enters the pelvic cavity, thus accumulating and provoking further complications.
- Tumors. The pathological process, called ascites, is characterized by the release of fluid during the development of various malignant neoplasms. These include all kinds of cysts and cancerous tumors. In addition, this process can accompany diseases of the liver and various gastrointestinal organs.
- Endometriosis. A disease associated with the growth of endometrial tissues that line the cavity of the fallopian tubes beyond the boundaries of this organ. There are many causes of this disease, but most often they occur in women of reproductive age who have experienced inflammatory infectious diseases of the pelvic organs. With this disease, the affected organs bleed significantly, increasing the amount of fluid.
In general, there are various reasons for the appearance of free fluid in the pelvis, and in most cases, an increase in the amount of such a substance indicates a pathological process.
Characteristic symptoms and signs of the disorder
Pain in the lower abdomen, discharge, changes in the nature of menstruation - signs of pathology
As you can see, an increase in the amount of fluid in the pelvis is not an independent disease, but a sign that indicates a pathological process. However, the presence of fluid can also be normal and be caused by certain changes in the female body. In view of this, the relevant question is how to distinguish a norm from a pathological condition.
Most diseases of the female reproductive system are expressed by a large number of characteristic symptoms. They may indicate the presence of pathology, and thus characterize an increased amount of fluid in the pelvis as a violation, and not as the norm.
Symptoms of diseases:
- Pain in the lower abdomen. This symptom is the most common and accompanies almost every gynecological disease. Pain can be of varying intensity and nature. According to experts, cutting pain in the lower abdomen is considered the most dangerous, as it indicates serious pathological processes in the pelvic organs.
- Discharge. In general, the presence of discharge is a normal physiological process. However, if the secreted substance has an unpleasant, pungent odor, or contains blood clots and is not of a natural color, this is evidence of serious violations. Such a symptom may indicate a variety of bacterial and fungal diseases, as well as a number of other diseases.
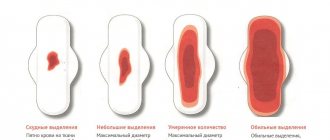
- Menstrual irregularities. The presence of abnormalities in the cycle that are not provoked by certain negative factors most often indicate the presence of a gynecological disease. In addition, the presence of the disease may be indicated by severe pain during menstruation with heavy bleeding, which is not typical for many women.
- Burning sensation. The occurrence of a burning sensation and itching in the genital area, in the vast majority of cases, indicates various infectious diseases. Moreover, these symptoms can manifest themselves to a minor extent or be pronounced, while causing a lot of discomfort and unpleasant sensations.
- Unpleasant sensations during sexual intercourse. The presence of gynecological diseases is directly indicated by the presence of any unpleasant sensations during sexual intercourse. In particular, women may experience quite intense pain, making it impossible to have an active sex life.
- Infertility. The inability to become pregnant for a long period of time is a symptom of quite serious diseases. Often such a disorder is associated specifically with gynecological diseases, especially if it is accompanied by other symptoms described above.
In general, free fluid in the pelvis cannot act as an independent symptom of the disease, and can indicate a pathological process only in the presence of other signs of the disease.
Possible reasons
The main reasons for the appearance and accumulation of fluid in a woman’s pelvis are pathologies of the genital organs and some acute diseases in the abdominal cavity.
There are a large number of pathologies that affect the accumulation of effusion behind the body of the uterus.
The following are distinguished:
- purulent inflammatory diseases of the genital organs (endometritis, salpingitis, adnexitis, oophoritis and others);
- endometriosis (proliferation of endometrial cells);
- neoplasms in the genital organs (cysts, fibroids), cancerous tumors;
- internal bleeding due to injury, rupture, or ulcerative perforation of organs in which blood quickly accumulates
- an ectopic pregnancy that develops and ruptures the fallopian tubes;
- peritonitis (inflammation of the serous layer of the peritoneum);
- Meigs syndrome.
Recommendations
If a woman went for an ultrasound for preventive purposes or as prescribed by a doctor and in the conclusion she was told that there is free fluid behind the uterus, she should definitely visit a gynecologist. What this means, free fluid behind the uterus, only a doctor can say, since it is necessary to assess the general condition of the internal organs.
If there is a tumor, inflammation or other disorder, the doctor will notice this during a gynecological examination. If necessary, the specialist will prescribe an additional examination, in particular a gynecological smear, laparoscopy or other procedures.
Based on the results of a comprehensive examination, it will be possible to say whether the free fluid is the result of a pathological process. If the disease is confirmed, treatment will be prescribed.
Warning signs
Pelvic effusion is difficult to detect, so patients do not consult a doctor. To prevent the neglect of the disease that caused it, you need to listen to your body and pay attention to the following symptoms:
- pain of variable intensity in the lower back, pelvis;
- bloating, distension of the abdomen;
- swelling expressed on the face and limbs;
- numbness of the limbs with a tingling sensation;
- painful menstruation with altered cycles and discharge of blood clots;
- vaginal discharge with a specific odor and color;
- lack of sexual desire.
Definition
Hydroperitoneum - what is it? This term refers to the accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity. The entire abdominal cavity, as well as the pelvic cavity, is lined with a thin membrane - the peritoneum.
This thin film covers the internal organs and the walls of the pelvis and peritoneum, forming numerous pockets, depressions and cavities. Any liquid that finds itself in the peritoneal cavity in one way or another mechanically flows into these natural depressions under the force of gravity and forms fluid levels. It is these fluid levels that are detected during studies - CT, MRI, X-ray and ultrasound.
Regarding hydroperitoneum in gynecology, we are interested in the pelvic pockets, in which doctors detect fluid during an ultrasound examination of the uterus and appendages. An example of such natural recesses are two natural pockets:
- The utero-vesical space is the pocket between the uterus and bladder.
- The retrouterine space is a fairly deep pocket between the uterus and the rectum, called by doctors the space of Douglas. As a rule, it is in this pocket that the fluid levels are found.
We use the term “liquid” all the time. I would like to say a few words about what liquid media can be found in the pelvis.
- Contents of opened ovarian cysts and ovulated follicles. This is the most common and completely normal version of the “accidental find”.
- Blood is a dangerous option, indicating that bleeding has occurred or is still ongoing in the abdominal or pelvic cavity.
- Inflammatory exudate - as a rule, this option is combined with inflammatory diseases of the female genital area, but there are other situations.
- Pus is an extreme variant of the previous point, when the inflammation is in an advanced, purulent form.
- Ascitic fluid is a sign of ascites, that is, a massive accumulation of fluid in the peritoneal cavity, resulting from the sweating of the liquid part of the blood and lymph into the abdominal cavity.
- Fluids from other departments and systems - urine, bile, intestinal contents, flowing under the force of gravity into the pelvic cavity and its pockets.
It is important to understand that a sonologist cannot always say what exactly a given liquid looks like. A homogeneous mass will be more likely to be serous fluid, ascitic transudate, or fresh blood. Heterogeneous with inclusions may turn out to be pus, coagulated blood, bile.
Doubts sometimes have to be resolved surgically. To do this, they use the procedure of culdocentesis - a puncture of the posterior vaginal vault with a special puncture needle. Thus, the needle ends up directly in the retrouterine space, from where you can draw liquid into a syringe for examination and evaluate it visually or send it for examination. The procedure, of course, is carried out in a gynecological hospital under intravenous or local anesthesia.
Pathology in old age
In older women, pelvic fluid formation is found not only outside the uterus. Often found inside an organ. It can be purulent, mucous and bloody. In this case, a diagnosis is made - serozometra.
It appears due to the following pathologies:
- hormonal imbalances in the premenopausal period.
- endometriosis;
- polyps in the uterus;
- complications of diseases of the genitourinary system.
The amount of effusion may be small and difficult to visualize on ultrasound. Significant volumes are also detected that can be easily palpated in the lower abdomen.
Symptoms of serozometra appear all at once or several at a time. It is characterized by pain in the lower abdomen - pulling and aching. Vaginal discharge increases and has a gray tint, urination becomes more frequent. Pain is pronounced during sexual intercourse and after completion.
Ultrasound also detects fluid in the fallopian tubes. The reason is a violation of the blood supply and lymph flow in them. If left untreated, closed cavities develop in the tubes, stretching the walls of the organs, and adhesions appear.
Is this the norm?
According to numerous gynecologists, only the complete absence of any type of fluid in the area of the uterus and fallopian tubes can be considered normal. However, you should not immediately fall into despair if during the examination it was possible to determine the presence of fluid, since this symptom itself cannot be considered a bad indicator. In order for a gynecologist to be able to accurately diagnose the presence of an inflammatory process in the pelvic area (weight in the area of the uterus or behind it is one of the main signs of pathology), the total volume of fluid should be taken into account, as well as the day of the menstrual cycle. If the fluid in the uterine area is in small volumes, then this phenomenon is not considered a pathology.
In some cases, the presence of a small amount of fluid behind the uterus can be a good sign that a woman has ovulated. This means that the woman should soon become a mother. However, in all other cases you need to be wary; the presence in the uterine area most likely indicates various serious diseases, among which are:
1 Polyps;
2 Endometriosis;
3 Ectopic pregnancy (in this situation there will also be bloody impurities in the fluid);
4 Inflammatory process in acute or chronic form, including in the ovarian area (salpingitis, adnexitis).
As you can see, there are indeed reasons for concern. In addition, after surgery (caesarean section, post-abortion period, laparoscopy), certain deviations also occur. In such a situation, it makes sense to talk about the presence of a pathological process in a woman. If there is a possibility of diseases, then it is necessary to prescribe a puncture - a sample of the existing fluid, which is located behind or directly in the uterine cavity itself. It is recommended to carry out this procedure using laparoscopy.
It is also necessary to know that in some women, fluid accumulation is observed not only in the uterus, but also in the area of the tubes. In this case, it is recommended to prescribe urgent treatment, because if a large amount of fluid accumulates, there is a possibility of pipe rupture. In this case, their contents will spill into the abdominal cavity, peritonitis may occur, which without urgent surgical outcome will cause death.
In addition, it should be noted that even if there is a small amount of fluid accumulated in the uterine area, there is a possibility that the woman has a cancerous tumor. It is for this reason that if the doctor finds fluid in or behind the uterus, this symptom should under no circumstances be ignored; be sure to follow the doctor’s instructions. If we talk about the presence of a malignant tumor, then against its background the woman should also develop other symptoms, thanks to which the gynecologist can assume the presence of cancer. Such symptoms may include the following:
1 The presence of pain in the lower abdomen, which may be accompanied by a feeling of cold;
2 Vaginal discharge that has a foul odor;
3 The presence of unpleasant sensations, feelings of discomfort, painful manifestations are possible during sex.
Diagnostic measures
To identify the main reason for the presence of fluid in the pelvis, laboratory tests are performed. A blood biochemistry test helps assess the general condition of a woman’s body. A blood test for tumor markers will indicate the presence of a neoplasm.
Using puncture, effusion is obtained. They conduct a study of its chemical composition, the presence of bacteria, fungi, and viruses in it. They study cytology and identify tumor cells.
An ultrasound of the pelvic and abdominal organs is performed to diagnose pathologies in them. If gastrointestinal diseases are suspected, fibroesophagogastroduodenoscopy is prescribed. A mammogram is performed to rule out a tumor in the breast.
Based on the results of ultrasound examination, other instrumental methods and laboratory tests, the doctor makes a final diagnosis.
Ultrasound
To understand what free fluid behind the uterus means in a particular case, you need to pay attention to its quantity. It is quite difficult to measure the volume of free fluid, since it spreads in the space behind the uterus. Therefore, the doctor measures the height of the fluid level.
If the height is less than 1 cm, then most likely the cause of formation is physiological. At a height of 1 cm to 5 cm, pathology is suspected. If the height of the liquid level is more than 5 mm, then this is most likely a sign of pathology, so the patient needs to undergo a comprehensive examination.
https://youtu.be/VeRIWSTd54o