What is polycystic ovary syndrome in a woman?
Polycystic ovary syndrome is a pathological condition accompanied by changes in the structure and function of the ovaries, manifested by chronic anovulation and increased levels of androgens. In turn, an increase in the amount of male sex hormones can be caused by both dysfunction of the ovaries and changes in the function of the adrenal glands. In women, polycystic disease manifests itself with various symptoms:
- excessive hair growth;
- problematic skin;
- hair loss on the head;
- seborrhea;
- ovulatory dysfunction;
- irregular, scanty periods;
- infertility.
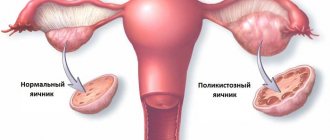
Disturbances in the functioning of the glands - pituitary gland, hypothalamus, adrenal glands, ovaries - cause not only suppression of fertility, but also changes in female appearance. Polycystic ovary syndrome in gynecology is considered a hormonal disorder characteristic of women of young childbearing age. A large number of small cysts are formed in the ovaries, which are follicles that have not reached ovulatory size. Cysts are localized along the periphery of the ovaries, which increase in size.
As polycystic disease develops, the disease gradually maintains itself: follicles that have stopped developing are a source of androgens.
Rules for taking Ovariamin
For conception
To plan pregnancy or to prepare for pregnancy in women who do not have problems with the menstrual cycle with a slight decrease in estrogen, Ovariamin should be taken from the 3-4th day of the new cycle (after the start of menstruation) until the onset of expected ovulation (14-15 days of the cycle). The daily dose varies from 3 to 9 tablets, it is selected individually taking into account test results.
A 20-day regimen is also often used for those who do not have serious disorders and are preparing to become a mother: 2 tablets in the morning and evening are prescribed to be taken for 20 days. When treating infertility, the doctor checks changes in the following indicators:
- the presence of ovulation;
- LH, FSH levels;
- estradiol level in the blood.
The course of treatment lasts no more than 3 months; the ineffectiveness of Ovariamine for infertility indicates insufficient diagnosis of general or gynecological pathology.
How to take during menopause
The menopause period is accompanied by a decrease in the level of female sex hormones. Most of the symptoms of this condition are caused by a lack of estrogen. Ovariamine can be an effective replacement for hormonal drugs to treat symptoms of menopause, such as hot flashes, decreased libido, and emotional lability.
The advantages over hormones are that Ovariamin itself stimulates the production of estrogen in the body, and replacement therapy, on the contrary, reduces the production of its own hormones according to the feedback principle. Ovariamine is prescribed in a 20-day course for 1 month, the initial dosage is 4 tablets per day (2 tablets 2 times a day), if ineffective, the dosage can be increased to 9 tablets per day (3 tablets 3 times a day).
Read also Sanatorium treatment for infertility
Cycle disruption
Menstrual irregularities occur due to organic damage to the reproductive organs, or as a consequence of hormonal imbalance. Ovariamine, having an effect on ovarian tissue, is effective for infertility:
- caused by long-term use of COCs;
- during anovulatory cycles caused by a decrease in estradiol - then the egg is not released from Graaf’s vesicle, and ovulation does not occur;
- alimentary factors leading to menstrual dysfunction - lack of nutrients in the diet;
- infertility of unspecified nature.
The course of infertility treatment usually lasts 20 days, according to the standard regimen, 2 tablets 2 times a day. Treatment is carried out for up to 3 months, during which the doctor may prescribe a blood test for hormones and an ultrasound, based on which the dosage is changed to 9 tablets per day and the number of doses is extended to 30 days per month. The appointment should be made based on the initial data of blood tests for FSH, LH and estradiol.
Causes of polycystic ovary syndrome
There are various classifications of this pathology. PCOS can be primary, caused by congenital pathology of the ovaries, secondary polycystic ovaries develops due to changes in the functioning of the glands as an acquired pathology. The secondary process may be a consequence of disorders in the hypothalamic-pituitary system or the result of a wide range of endocrine disorders, for example, in obesity. It is customary for specialists to differentiate between ovarian and adrenal hyperandrogenism, since their approaches to treatment are different.
There are risk factors for polycystic ovary syndrome:
- changes in insulin metabolism;
- excess weight;
- burdened hereditary history.
Against the background of disorganization of the ovaries, androgens cannot be transformed into estrogens, as in healthy women. The reason is a decrease in the production of aromatase enzymes. Follicles lose their ability to dominate, ovulation does not occur, and the body suffers from excess androgens.
One of the links in the pathogenesis of polycystic ovaries is the formation of insulin resistance. Therefore, polycystic disease is considered as a variant of metabolic syndrome, accompanied by impaired fat and carbohydrate metabolism. The most common sign of decreased glucose tolerance and changes in fat metabolism is excess weight. Subsequently, type 2 diabetes mellitus develops, which most often occurs in menopausal women with a history of polycystic disease.
Attention! The incidence of type 2 diabetes in PCOS is 60-70%.
Factors that provoke polycystic disease are:
- stress;
- severe infections;
- injuries to parts of the central nervous system;
- progressive weight gain;
- endocrine pathologies (hypothyroidism, hyperprolactinemia).
Long-term neuroses can disrupt the coordinated work of the entire endocrine system due to chronic hard work of the adrenal glands, so experts consider psychosomatics as a provocateur of polycystic ovary syndrome.
Polycystic ovary syndrome in teenage girls
Polycystic disease in adolescence manifests itself as an initial disturbance of the menstrual cycle. If a healthy girl has normal menstruation within 1-2 years, then with primary polycystic disease there is always a long cycle, scanty periods or amenorrhea. The typical symptoms of PCOS gradually appear. In the absence of medical care, persistent infertility develops.
Studies show that girls with a genetic predisposition to PCOS, even in the absence of clinical and ultrasound signs of ovarian damage, have glucose tolerance.
Side effects
- Weight fluctuations (weight gain, weight loss)
- Increased blood pressure (BP)
- Liver dysfunction
- Allergic reactions to the components of the drug (hives, itching, redness, rash, etc.)
- Decreased libido (sexual desire)
- Nausea, vomiting, stomach pain
- Mood swings, apathy, depression, anxiety
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Swelling of the mammary glands
- Pain in the mammary glands
- Failure of the menstrual cycle
- Breakthrough bleeding
- Intermenstrual discharge of unknown origin
- Thromboebolism (venous, arterial)
- Erythema multiforme
- Varicose veins
Rare but possible:
- Hypertension
- Chloasma
- Tumors
- Liver dysfunction
- Erythema nodosum
- Crohn's disease
- Worsening symptoms of angioedema
- Nonspecific ulcerative colitis
- Effect on insulin resistance, changes in glucose tolerance
Interaction with other drugs
Concomitant use with antibiotics and enzyme inducers may cause breakthrough bleeding and decreased protection.
Simultaneous use with a number of drugs (barbiturates, primidone, carbamazepine, phenytoin, rifampicin, etc.) increases the clearance of sex hormones.
Read the instructions carefully and consult a specialist.
Symptoms of polycystic ovary syndrome
Symptoms of the disease are divided into:
- mandatory, which are registered in 100% of women with polycystic disease;
- Ultrasound signs;
- common, typical for 50% of patients;
- occurring in less than 50% of women.
Obligatory include menstrual irregularities in the form of oligomenorrhea or amenorrhea (scanty periods or their absence) starting from the first menstruation, infertility of primary origin associated with the lack of ovulation. Women of reproductive age are characterized by miscarriage due to hyperandrogenism.
Commonly encountered symptoms include increased hair growth, increased levels of LH, DHEA sulfate and testosterone in the blood.
Symptoms such as obesity, thinning and hair loss, oily skin and acne are reported in less than 50% of women.
Signs that link insulin resistance and PCOS are dark areas of skin under the breasts, in the armpits, and on the neck, especially at the back.
Mood changes are also a concern for women with polycystic disease. Tearfulness, depression, irritability, mood swings – these are the complaints made by patients.
Discharge with polycystic ovary syndrome does not change its normal character. Against the background of hormonal imbalances in PCOS, discharge may become more abundant. As a rule, when treated with contraceptives, vaginal discharge increases in volume.
Is it possible to get pregnant if diagnosed with PCOS?
Because PCOS can affect menstrual cycles by preventing ovulation, pharmacological treatment is sometimes required to help your body ovulate. Regular ovulation is the key to achieving the long-awaited pregnancy. Whether you ovulate naturally or with the help of medication, conception can occur during intercourse or intrauterine insemination.
Clomid (clomiphene citrate) is a common medication prescribed by doctors to stimulate ovulation in women. It works by helping the ovary grow an egg that will eventually mature and be released. However, newer studies show good results using letrozole in women with PCOS.
If these medications are not effective, there are other options. Injections are also widely used. These types of medications are usually a form of the hormone FSH, the main hormone produced by the body that stimulates the growth of the egg follicle each month. You will need to learn how to give yourself these injections and also visit your doctor frequently to monitor follicle growth using ultrasound.
Finally, your doctor may recommend in vitro fertilization. During IVF, a medicine is given that stimulates the ovaries, which allows many eggs to grow and mature. These eggs are surgically removed after maturity and fertilized in the laboratory. The embryos grow within a few days, after which they are placed back into the uterus in the hope that they will implant and cause pregnancy. This is a much more intensive form of treatment, and not everyone is ready to begin this process.
Polycystic disease and excess weight
Polycystic ovary syndrome is characterized by a certain type of obesity. Fat is deposited mainly around the waist, abdomen, and also on the shoulders. In addition, obesity of the “apple” type in polycystic disease is accompanied by insulin resistance.
Important! Obesity with polycystic ovaries is characterized by a ratio of waist to hip circumference equal to 0.85, in addition, acanthosis is recorded.
Excess adipose tissue impairs the sensitivity of cell receptors to insulin, which leads to impaired glucose utilization. In addition, fat cells are a source of estrogen, forming hyperestrogenism. A general hormonal imbalance due to excess weight in many women leads to polycystic ovary syndrome.
Other medications for ovarian cysts
What to do to eliminate a cyst on the ovary if its appearance is caused by pathogenic microflora? In this case, “Utrozhestan” or “Lindinet 20” will be powerless as long as the body is affected by foreign microorganisms. In such a situation, doctors prescribe antibiotic therapy.
"Terzhinan" is a drug of the required spectrum, which has proven itself as a method of treating diseases of the reproductive system in women. Treating a Bartholin gland cyst without surgery also requires taking antibiotics. In parallel, you can use tampons with Vishnevsky ointment, which has an antibacterial and healing effect.
The formations are often accompanied by pathologies of the genitourinary system, so diuretics, such as Veroshpiron, can be prescribed in combination with basic medications. Well-thought-out therapy with anti-inflammatory drugs is of great importance, which include:
- "Wobenzym";
- "Distreptase";
- Metronidazole, etc.
Gynecologists often prescribe Indomethacin, which has an anti-inflammatory effect. Together with oral medications, you can use other treatment methods, for example, tampons with Dimexide. The therapeutic complex necessarily includes vitamins, minerals and trace elements designed to strengthen the immune system and increase the body's strength.
Vitamins for ovarian cysts are folic and ascorbic acid, vitamin E. If a woman is diagnosed with a large endometrioid cyst, this can cause pain in the lower abdomen. Drugs such as No-shpa, Diclofenac, Diclovit, etc. help eliminate them.
Diagnosis of polycystic ovary syndrome
Diagnosis of polycystic disease begins with taking an anamnesis. Next, the doctor begins the examination. Particular attention is paid to areas with hirsutism: the chin, the area of skin above the upper lip, the nipple area, chest, back, legs. The presence of acanthosis is also determined - darkening of the skin in the axillary region, the back of the neck, folds under the breasts, and skin over the joints of the hands. A woman is questioned about hair loss and skin problems.
Height and weight are measured and body mass index is calculated.
To determine the presence of ovulation, basal temperature is measured for three months, as well as folliculometry using ultrasound.
Ultrasound for polycystic ovary syndrome is one of the key methods for identifying the syndrome. It is on ultrasound that the first signs of structural changes are determined.
Important! An ultrasound should be performed in the first phase of the cycle - on days 7-10.
During the ultrasound examination, enlarged ovaries are determined, in each 11 or more follicles are visualized, having a diameter of up to 1 cm and/or the volume of each appendage is more than 10 cm³. The photo below shows what polycystic ovary syndrome looks like during an ultrasound examination at the beginning of the cycle.
On palpation, the ovaries are dense, mobile, moderately enlarged in size, their surface is smooth, while the uterus can be reduced.
What tests to take for polycystic ovary syndrome
Diagnosis of polycystic ovary syndrome involves the mandatory determination of certain blood parameters, in particular, hormones and indicators of carbohydrate metabolism.
Necessary tests:
- thyroid-stimulating hormone;
- follicle-stimulating hormone;
- luteinizing hormone;
- testosterone;
- estradiol;
- DEA sulfate;
- prolactin;
- progesterone;
- cortisol;
- anti-Mullerian hormone;
- sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG).
In addition to hormones, the following indicators are determined:
- lipid profile, including high and low density lipoproteins, triglycerides and cholesterol, atherogenicity index;
- insulin and glucose levels;
- glycated hemoglobin;
- glucose tolerance test.
Tests are taken strictly on an empty stomach. When determining prolactin three days before the test, sexual contact, palpation of the mammary glands, stress and strong emotions are excluded. To identify true cortisol levels, it is also important to minimize stressful situations before donating blood. If the amount of cortisol or prolactin increases, blood is donated two more times. If these indicators remain elevated in 3 samples, hyperprolactinemia and adrenal pathology are confirmed.
Indicators such as FSH, LH, prolactin, estradiol are taken on days 2-5 of the cycle or on days 7-9 for very long cycles. Progesterone needs to be monitored a week before the expected menstruation; you can take the test on days 21-23 of the cycle. Difficulties in determining the day of progesterone delivery in polycystic ovary syndrome are associated with the lack of ovulation.
When diagnosing polycystic ovary syndrome, it is advisable to determine indicators over 2-3 cycles for a reliable picture.
To determine the tumor or non-tumor origin of polycystic disease, a dexamethasone test is performed. The drug is administered over several days, and then the level of androgens (DHEA sulfate, total testosterone, cortisol) is assessed. If the indicators have decreased by more than 50%, the tumor genesis of hyperandrogenism is excluded.
Interpretation of tests for PCOS
Every second woman with signs of polycystic ovary syndrome has an increase in DHEA sulfate, which indicates pathology of adrenal function.
An increase in 17-OH-progesterone in the blood also gives reason to believe that the origin of polycystic ovary syndrome is due to dysfunction of the adrenal glands.
In order to distinguish acquired from congenital adrenal dysfunction, you should donate blood for adrenocorticotropic hormone, which will be normal in the acquired form.
Anovulation in polycystic ovary syndrome will be indicated by low progesterone levels a week before menstruation. On the 2-5th day of menstruation in polycystic disease, the ratio of luteinizing hormone to follicle-stimulating hormone is more than 2.5, and total testosterone also increases.
AMH in polycystic ovary syndrome also exceeds its norm.
Results of tests for carbohydrate and lipid metabolism:
- fasting blood glucose level is more than 6.1 mmol/l;
- glucose tolerance is impaired: 2 hours after the stress test, its level ranges from 7.8 to 11.1 mmol/l;
- the amount of fasting insulin is normal;
- high-density lipoprotein (“good cholesterol”) level is below 1.2 mmol/l;
- increased cholesterol levels (more than 5.2 mmol/l).
Important! An increase in the level of androgens in the blood and signs of polycystic ovary syndrome can occur with hypothyroidism, therefore, as part of the diagnosis, the level of thyroid-stimulating hormone is determined.
Additionally, high prolactin levels also cause some of the symptoms of PCOS.
PCOS and Infertility: Treatment Options
Infertility is usually diagnosed after a woman has been unable to become pregnant for 12 months or longer. Knowing the risk, doctors can begin fertility treatment earlier. Miscarriages are also common in PCOS and can be caused by imbalances in sex hormones and higher insulin levels.
Lifestyle Modifications
Changes in your lifestyle can go a long way in regulating your hormones and preparing your body for pregnancy. This in turn can improve egg quality and restart ovulation, increasing your chances of conceiving. It has been proven that if you are overweight, you only need to lose 5% of your total body weight to achieve the pregnancy you want. Making changes to your diet, exercise, reducing stress and quality of sleep can improve your fertility.
Healthy diet
The PCOS diet should include foods that contain small amounts of unprocessed carbohydrates.
These include fruits, vegetables, beans, lentils and grains such as quinoa and oats. It is recommended to use unsaturated fats such as olive oil, nuts, seeds, fish and avocados.
Whenever possible, avoid refined or processed sources of carbohydrates, these include crackers, white bread, white rice, pretzels and sugary foods such as cookies, cakes and candy.
If you don't know where to start, consider consulting with a nutritionist who can help you make lasting changes to your diet.
Regular physical activity
Research shows that regular exercise can improve ovulation and insulin resistance. In studies, women with PCOS who did moderate exercise three or more days a week had better fertility rates than those who followed a low-calorie diet plan.
Try to have at least 30 minutes of physical activity every day. The simplest and most accessible type of physical activity is a walk, which can be done every day.
Acupuncture
Acupuncture can help you get pregnant. Alternative treatments improve hormonal balance, BMI, and endometrial thickness in women with PCOS. Acupuncture can be performed alone or in combination with fertility treatments.
Pharmacological methods of treating PCOS
Inositol
Mio and d-Chiro Inositol in a 40:1 ratio improved egg quality and ovulation in women with PCOS after just three months, and was even better than metformin, compared with which the combination of Mio and DCI showed significantly better weight loss results , ovulation and pregnancy rates (46.7% vs. 11.2%).
N-Acetylcysteine
N-acetylcysteine (NAC) is a powerful antioxidant that fights oxidative stress and has been shown to improve pregnancy and ovulation better than placebo.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D is not only a vitamin, but also a hormone. Vitamin D receptors have been found in women's eggs. Vitamin D supplementation improves egg quality and ovulation in women alone or during reproductive therapy.
Metformin
Metformin is the most common drug used to treat diabetes and is also recommended to reduce insulin resistance in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. For many, metformin may also improve menstrual patterns. There are studies that show that metformin may also reduce the risk of miscarriage and gestational diabetes.
Clomid and Letrozole
Sometimes women with PCOS need help improving ovulation despite diet and lifestyle changes. Traditionally, doctors prescribe clostilbegit, which helps improve ovulation. Newer research suggests that letrozole may work better than clostilbegit, as it does not increase estrogen like Clomid and results in fewer multiple pregnancies.
Gonadotropins for PCOS
Using gonadotropins may also help women with PCOS. Gonadotropins consist of the sex hormones FSH, LH, or a combination of both. Your doctor may suggest combining these hormones or using them on their own. For example, letrozole with LH.
Another option your doctor may suggest is the use of gonadotropins with the IUI (intrauterine insemination) procedure. It involves placing specially washed sperm directly into the uterus through a catheter. The sperm can be from a donor or your partner.
The main risk of gonadotropins is ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS). This is when the ovaries overreact to fertility medication. If hyperstimulation goes undetected, it can be life-threatening.
Intrauterine insemination (IUI)
Intrauterine insemination (IUI) is a fertility procedure designed to coincide with ovulation. Your partner will be asked to prepare a sample of semen, which is then "washed" or separated from the other elements of the semen and collected into a smaller, more concentrated volume. The sample is placed into a thin, sterilized soft catheter and insemination is performed.
The procedure is as follows: the woman sits on a chair, as during a gynecological examination, at the beginning the doctor gently cleanses the cervix, inserts a catheter into the vagina and introduces sperm into the uterine cavity. It is necessary to remain in a prone position for several minutes after insemination. Success rates for IUI are approximately 15 to 20 percent and vary depending on a number of factors such as your age, type of ovarian stimulation, sperm motility and others.
In Vitro Fertilization
In vitro fertilization (IVF) is a more invasive and expensive procedure that is used when all other fertility treatments fail. IVF involves the use of injectable drugs to stimulate the ovaries to produce a large number of mature eggs. The eggs are then removed from the ovaries and combined with sperm. If they are fertilized, one or two embryos are transferred to the uterus. This procedure is known as embryo transfer. After two weeks, you should take a pregnancy test to find out if this cycle was successful.
How to treat polycystic ovary syndrome
The goal of treatment for polycystic ovarian transformation is to restore the menstrual cycle and ovulation, and reduce the symptoms of hyperandrogenism.
Treatment involves non-drug methods, drug therapy, and surgery.
Non-drug treatments include:
- physical exercise;
- normalization of body weight;
- limiting the daily calorie intake.
These methods of combating polycystic ovarian disease form the basis of treatment, regardless of the cause. Even with a normal BMI, they review the diet and reduce the amount of simple carbohydrates and unhealthy foods.
Treatment of polycystic ovaries includes taking medications depending on the provoking factors and causes of the pathology. Surgical intervention is most often necessary for reproductive function.
The optimal solution for treatment for pregnancy is IVF. A long protocol is used, and laparoscopy is performed before entering it, if necessary.
Laparoscopy for polycystic ovary syndrome
Laparoscopic intervention on the ovaries for polycystic disease is necessary for reproductive function. Often, diagnostic laparoscopy turns into therapeutic laparoscopy when the diagnosis is confirmed on the operating table.
Important! Laparoscopy is not a method for eliminating hyperandrogenism and irregular menstrual cycles in polycystic disease. The intervention is carried out strictly according to indications.
The following types of interventions for polycystic disease are distinguished:
- drilling;
- resection;
- decorating.
Ovarian resection for polycystic disease involves excision of part of the organ affected by the cysts, but is not performed when the cysts are located along the entire edge of the ovary. This operation significantly reduces the ovulatory reserve and is dangerous for infertility.
Traditionally, laparoscopic drilling is performed to treat infertility in polycystic disease. Incisions and punctures of the sclerocystic capsule on the ovaries allow you to quickly resume ovulation within several months after surgery.
During decortization, the upper thickened layer of the ovaries is removed.
For all types of interventions, laser technologies can be used to improve the quality of laparoscopy and reduce the risk of bleeding.
There are certain indications for surgery for polycystic ovary syndrome:
- lack of effect from ovulation stimulation;
- high levels of luteinizing hormone;
- concomitant endometriosis;
- tubo-peritoneal infertility.
In parallel with laparoscopy, hysteroscopy is often performed and the patency of the fallopian tubes is certainly assessed. These measures are necessary to exclude other types of infertility, as well as for subsequent stimulation of ovulation (if necessary).
To prevent adhesions during the operation, internal organs are treated with special solutions (crystaloids, hyaluronic acid, fibrin concentrate, hydrogel, etc.), and after the operation early waking up is recommended.
Active planning is recommended immediately after surgery.
Treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome with drugs
The list of drugs for the treatment of polycystic ovarian changes is determined by the cause of the disease. For disorders of carbohydrate and fat metabolism, insulin synthesizers of the biguanide class are prescribed, most often the drug Metformin is used.
If polycystic ovary syndrome is accompanied by an excess of luteinizing hormone and increased hair growth, oral contraceptives are used. To prescribe COCs for the treatment of PCOS, the level of sex hormones must be determined.
Important! In the treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome, oral contraceptives with an antiandrogenic effect are used.
Irregular menstrual cycles with polycystic disease are a reason to prescribe progesterone drugs (Duphaston is most often prescribed).
If polycystic ovarian changes occur against the background of increased prolactin levels, dopamine receptor agonists (Cabergoline, Bromocriptine) are taken. In case of hypothyroidism - thyroxine preparations.
Additionally, vitamins are prescribed that affect the hormonal regulation of the menstrual cycle.
Metformin (Siofor, Glucophage)
Increased blood glucose levels, excess weight due to polycystic disease and impaired glucose tolerance are reasons for prescribing Metformin (trade name Siofor, Glucophage). This drug reduces the amount of sugar in the blood, as well as triglycerides, “bad” cholesterol in the form of low-density lipoproteins. Thanks to Metformin, it is possible to reduce weight (or stabilize it) in case of polycystic ovarian changes, in particular, in the absence of effect from diet. But, despite treatment with this remedy, it is still necessary to adhere to a dietary diet.
Duphaston and Utrozhestan
Analogues of the second phase hormone progesterone are the drugs most often prescribed for the drug treatment of polycystic disease in girls. Duphaston is a synthetic analogue of progesterone. The tablets do not have corticoid or androgenic activity, therefore they are successfully used for polycystic ovarian pathology. The drug is prescribed from days 16 to 25 of the cycle, 10 mg twice a day. Treatment lasts 3-6 months.
Duphaston ensures the normalization of the structure of the endometrium, replacing the hormone of the corpus luteum, which does not form due to the lack of ovulation. Thus, the regularity of the menstrual cycle is improved. If a woman is planning a pregnancy, then in the first phase, ovulation inducers are prescribed, and after the follicle ruptures, Duphaston is prescribed, which is continued to be taken for 10 days. If pregnancy has occurred, the pills continue to be taken until the 20th week, since against the background of polycystic ovary syndrome and hyperandrogenism, there is a possibility of miscarriage.
A natural analogue of progesterone is the drug Utrozhestan, which is taken orally for PCOS. The dosage regimen is similar to that of Duphaston. The dosage for polycystic disease is 200 or 400 mg per day.
Contraceptive and other hormones
Oral contraceptives for the treatment of ovarian disease should be combined, namely, contain an analogue of the second phase hormone - progesterone derivatives. The drugs usually consist of ethinyl estradiol, drospirenone, dienogest, cyproterone acetate. COCs for polycystic disease are taken as a contraceptive regimen.
Important! The effectiveness of contraceptive therapy is assessed no earlier than after 6 months of taking the medication.
In preparation for IVF, the presence of endometrial hyperplasia, and also if there is no effect from COCs, GnRH agonists are used, in particular Buserelin, Triptorelin, Leuprorelin once a month for three months. The drugs cause artificial menopause, therefore they are most often used in preparation for IVF for polycystic disease. After such treatment, it is possible to obtain a larger number of eggs of good quality.
Diana is 35
The antiandrogenic effect of the contraceptive Diane-35 allows it to be used in the treatment of polycystic disease. The contraceptive is monophasic, each tablet consists of ethinyl estradiol and cyproterone, an analogue of progesterone.
The tablets are taken for 6 months with subsequent monitoring of effectiveness. The contraceptive is suitable for the treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome at a young age, improves the properties of skin and hair. A pronounced effect occurs after several months of use.
Jess plus
Among the antiandrogen drugs widely used in the treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome, Jess Plus is often prescribed, the distinctive feature of which is the content of the active form of folic acid - levomefolate. This form of vitamin B9 is quickly absorbed by the human body.
A monophasic contraceptive contains drospirenone as a gestagen, a substance that does not have mineralocorticoid activity and does not lead to weight gain or edema. Like other COCs, Jess Plus is taken for six months with subsequent monitoring of effectiveness.
Folic acid and other B vitamins
The treatment regimen for PCOS, depending on the initial data, includes vitamin complexes and is based on B vitamins. Both combination drugs (Milgamma, Neurobeks Neo) and single drugs (folic acid) are used.
B vitamins have a positive effect on metabolism, the state of the nervous system and psyche, and stabilize the production of hormones. When planning pregnancy against the background of polycystic disease, it is advisable to take folic acid in advance. The drug will have a beneficial effect on the reduction of androgens and prevent pathology of the neural tube in the fetus. Folic acid is taken 400 mg per day as part of the treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome.
Time factor
A popular complex of vitamins for polycystic ovarian changes is Time Factor. The drug consists of three types of capsules, consisting of vitamins and microelements necessary for the treatment of gynecological pathologies. The complex consists of folic acid, iron, nicotinamide (vitamin PP or B3), vitamin E, C, magnesium and zinc. Capsules are taken in different sequences during the menstrual cycle.
The time factor allows you to normalize the hormonal regulation of the phases of the menstrual cycle in polycystic disease.
Ovariamine
Among biologically active food additives, the most popular for polycystic ovarian pathology is Ovariamin, which is a complex of dried cattle ovaries. The drug contains a concentrate of proteins necessary to normalize ovarian function; in addition, taking the dietary supplement improves the quality of eggs.
Veroshpiron
Women with contraindications to taking contraceptives are prescribed spironolactone (trade name Veroshpiron). This drug is a diuretic, but its mechanism of action also has an antiandrogenic effect. Use 25 mg 2 times a day.
Important! Pregnancy while taking Veroshpiron is contraindicated, since the drug negatively affects the development of the male fetus.
The drug is not prescribed to patients with low blood pressure. During treatment, it is necessary to monitor renal parameters.
Klostilbegit
Women planning pregnancy due to PCOS are prescribed medications that induce ovulation. Often, Clostilbegit or Clomiphene are prescribed to initiate ovulation. The drug is an outdated inducer, has a lot of disadvantages and side effects, so it is not recommended to use it more than 3 times for polycystic ovary syndrome. But traditionally, if there is no effect, Clostilbegit is prescribed 5 times with increasing dosage.
Important! Before ovulation induction, it is necessary to assess the patency of the fallopian tubes and the quality of the partner's sperm.
Clostilbegit leads to the growth of the dominant follicle due to the suppression of estrogens, while the quality of the endometrium suffers, which undergoes negative changes in polycystic ovarian pathology. It should be taken into account that when stimulating ovulation with Clostilbegit, it is necessary to prescribe estradiol-based agents for endometrial growth.
The initial dose is 50 mg. This amount is taken from days 5 to 9 of the cycle. Follicle growth is monitored by ultrasound, and after ovulation, Duphaston or Utrozhestan is prescribed. If the effect does not occur, then the dose is increased to 100 mg and then to 150 mg.
Factors contributing to the development of resistance to treatment with Clomiphene:
- age over 30 years;
- BMI more than 25;
- ovarian volumes according to ultrasound are more than 10 cm³;
- the amount of luteinizing hormone is more than 15 IU/l;
- the amount of estradiol in the blood is less than 150 pmol/l.
Suppositories for polycystic ovary syndrome
The only hormonal drug in the form of suppositories that can be used in the treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome is Utrozhestan. But these vaginal capsules in the treatment regimen for the disease are more often used when planning pregnancy against the background of polycystic disease.
There is no local treatment for polycystic disease; however, with concomitant inflammation of the vagina and cervix, antimicrobial and immunomodulating suppositories are used.
Against the background of disruption of hormonal regulation of the cycle in polycystic disease, the composition of the vaginal flora changes, so infections occur more often. Depending on the causative agent of the infection, various suppositories are used:
- combined (Terzhinan, Polygynax);
- antibacterial (Betadine, Hexicon, Trichosept);
- for thrush (Ginofort, Pimafucin, Clotrimazole);
- antiviral immunomodulators (Genferon, Viferon).
Treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome with herbs
As part of the treatment of polycystic ovaries, the regimen can be supplemented with herbs. Herbal remedies can only be prescribed by a doctor, as they interfere with hormonal levels and can cause harm if used independently. The most effective and popular are red brush, hogweed, leuzea, peony, and sage.
Attention! Herbs with antiandrogenic properties: mint, rose hips, nettle and dandelion roots.
Herbs are taken in courses of 1-1.5 months, two to three times a year.
Forum Detki.kz
ovarian cyst
Zhanara 10 Jan 2007
Doctor RNITsOHMR 22 Feb 2007
1. The question of further treatment should be decided depending on the size of the cyst and the hormonal treatment carried out before (duration and type of treatment). 2. It is advisable to address this problem to the Scientific Center for Obstetrics, Gynecology and Perinatology in Almaty, Dostyk Avenue 125.
Sincerely, Ravil Kamilievich Valiev
Leyla March 21, 2007
Elena March 24, 2007
Doctor RNITsOHMR April 03, 2007
Issues of hospitalization in the paid department of NCAGIP are resolved by the hospitalization department. The price list can be found in the reception department of the National Center for Gynecology and Pediatrics and the clinic. This operation can be performed by almost any doctor in the gynecology department or a paid department.
Sincerely, Ravil Kamilievich Valiev
Leyla Apr 18, 2007
Leyla Apr 19, 2007
Doctor RNITsOHMR April 21, 2007
Ovariamin is obtained from the ovaries of cattle and is a complex of proteins and nucleic acids that have high antioxidant activity and include physiological concentrations of minerals, trace elements and vitamins in an easily digestible form. First of all, Ovariamin is a biologically active food additive - it is not a drug. Ovariomin has not undergone clinical testing in the conditions of NCAGiP - it is difficult to judge the results of action. A contraindication is individual intolerance to the components of this biological supplement.
Sincerely, Ravil Kamilievich Valiev
Lena May 12, 2007
Doctor RNITsOHMR May 17, 2007
The statement that you will not be able to have children is not substantiated. An examination is required.
Sincerely, Aimbetova Aliya Robertovna
Leyla May 22, 2007
Why is polycystic ovary syndrome dangerous?
Polycystic ovary syndrome has consequences affecting various organs and systems. If left untreated, the following may develop:
- persistent infertility;
- arterial hypertension;
- steatohepatitis and fatty hepatosis;
- depression;
- obstructive sleep apnea.
Complications are associated with a gradual increase in cholesterol, triglycerides, low-density lipoproteins, as well as impaired glucose utilization. Permanent hormonal changes lead to disruption of the functioning of other systems and organs.
The main techniques used in the treatment of the gonads
Most often, the following methods are used in complex treatment:
- Magnetotherapy. In this case, only a low-frequency magnetic field is used. In the primary type of disease, the effect is only on the collar area. With its help, the activity of the pituitary gland, as well as the hypothalamus, is regulated, which leads to an improvement in ovarian functionality.
- Galvanophoresis using lidase. Under the influence of a galvanic current supplied at low voltage, the drug reaches the gonads without entering the epidermis. Lidaza is able to activate the activity of the gonads, while improving blood flow and metabolic processes.
- Hydrotherapeutic activities. In this case, both sodium chloride baths, which have a water temperature of no more than 36°C, and pine baths can be used. In frequent cases, sea baths are used. They can improve blood circulation in the reproductive system, as well as have an anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect. With their help you can achieve a calming effect. For these purposes, a circular shower or Charcot shower is sometimes prescribed.
- Galvanophoresis using vitamin B1. The procedure is performed endonasally. As a result, there is an effect on the hypothalamic-pituitary system, with the help of nerve impulses emanating from the nasal cavity. In this case, patients experience an improvement in metabolic processes, as well as in neuro-reflex regulation.
- The use of paraffin therapy, as well as mud therapy. These natural materials are applied to the appendages and abdomen. With their help, metabolic processes are improved and the ovarian tissue softens.
Electrophoresis, as well as the use of laser and ultrasound therapy also have a positive effect.
Is it possible to exercise if you have polycystic ovary syndrome?
Physical activity is considered a prerequisite for the treatment of polycystic ovarian pathology. Moderate loads can increase the sensitivity of receptors to insulin, which will ultimately lead to the normalization of carbohydrate metabolism or reduce blood glucose levels, and against the background of weight loss, hormonal levels will stabilize. Physical activity for PCOS can effectively combat depression and neurosis.
Intense professional sports, which contribute to hyperandrogenism, are not recommended. You should resort to moderate exercise in the form of regular exercise in the pool, water aerobics, dancing, and gymnastics.
Treatment with hormones
Ovarian cysts in women can be of different types. A situation is considered dangerous if the formation affects both ovaries, as well as PCOS (polycystic ovary syndrome). Treatment methods directly depend on the nature of the disease, severity, severity of symptoms, etc. Treatment of the ovary with medication should be carried out under the strict supervision of a doctor who can adjust the therapy if necessary.
An integrated approach is important here. The patient is recommended not only to take pills for ovarian cysts, but also to drink vitamin complexes, improve nutrition, alternate between activity and rest, and avoid stress.
COCs and their meaning
Combined oral contraceptives, or COCs, are an excellent prevention for ovarian pathologies. They are also used as a therapeutic measure at the initial stage of the disease. It is better to remove large seals immediately, eliminating the risk of complications.
Treatment of ovarian cysts with COCs should be carried out according to certain rules: medications should be taken according to the schedule, every day at the same time. The first day of admission is the beginning of the menstrual cycle.
The most effective oral contraceptives:
- "Marvelon";
- "Janine";
- "Diana-35";
- "Klayra";
- "Rigevidon".
“Dimia” has also proven itself well for ovarian cysts.
While taking COCs, it is necessary to reduce the effect on the central nervous system. Lifestyle adjustments are an important factor for the patient’s recovery.
For ovarian cysts, treatment without surgery involves significant financial costs, since hormonal drugs are not cheap. For one package of tablets you will have to pay from 400 to 1300 rubles.
Cyst and gestagens
Conservative treatment includes taking gestagens. These medications block the pituitary gland and replace the natural hormone with an artificial analogue. As a result of such changes, the tone of the uterus decreases, and the endometrioid compaction of the ovary resolves. The dosage and course of treatment are determined by a doctor who understands how to cure an ovarian cyst without surgery.
The most effective drugs in this group are:
- "Dinazol";
- "Danol";
- "Norkolut";
- "Cyclodinone";
- "Mastodinon" and others.
What will be more effective, treatment or surgery for a tumor on the ovary, can only be determined after a thorough medical examination. With multiple capsules, surgical intervention is not necessary, since developing formations will put pressure on the pelvic organs, causing their dysfunction.
Birth control pills
An ovarian cyst is not considered a dangerous disease in gynecology, but if it is not treated with medication, it can cause serious complications. The modern methods of drug treatment used are aimed at stabilizing hormonal levels, because it is the imbalance of hormones that causes the appearance of formations.
Birth control pills help improve the condition of the endocrine system and restore hormone levels in the female body. The active components promote the self-resorption of drug capsules. A noticeable improvement in the condition is observed after taking Logest, Qlaira and Lindinet 20. “Janine” has an excellent contraceptive effect. Doctors often prescribe “Jess” for ovarian cysts; it has an excellent therapeutic effect.
Is it possible to cure polycystic ovary syndrome forever?
It is possible to completely get rid of polycystic ovary syndrome if it occurs secondary, in particular, with hypothyroidism, hyperprolactinemia, after removal of hormone-producing tumors. In other cases, it is impossible to completely cure polycystic disease. To alleviate the course of the disease, the onset of pregnancy and its successful pregnancy, it is necessary to fight excess weight, follow a diet and exercise. PCOS can be stopped and corrected with the help of hormonal drugs.
Instructions: admission rules
You need to take COC Jess Plus every day at the same time, without taking a break between packs.
Because The Jess Plus package contains 28 tablets (24 active and 4 vitamin), so there is no need to take a break from taking it: as soon as one blister runs out, we start a new one the next day.
When can you not use protection?
The most popular question on the Internet related to OK Jess Plus is “How long can you wait without protection?”
So when does the contraceptive effect occur?
If you have not taken OK before (how to take it for the first time):
- You start taking Jess Plus on the first day of your cycle. In this case, after your period, you may not need to use additional protection during sexual intercourse.
- If you started taking OK on the 2-3rd day, then you also don’t have to use protection.
- If you started taking OK after the 3rd day of your cycle, we recommend using additional contraceptives for another week.
You should start drinking the second package of Jess Plus immediately without interruption.
If you are switching from other OCs, you need to finish the package of the previous COCs. If there were 21 tablets in the pack, then you need to take a break for 7 days, and on the eighth day start taking Jess Plus. If the pack contained 28 tablets, then upon completion you need to start taking Jess Plus immediately without a break.
Analogues Jess and Jess plus - read.
After an abortion (in the early stages), you can start taking it immediately - no additional contraception is needed.
After an abortion (in the second trimester) or miscarriage, treatment begins on days 21-28.
ATTENTION! During lactation (breastfeeding), taking COCs is not recommended.
Jess Plus and smoking are incompatible. Especially after 35 years.
Jess plus and alcohol. The compatibility of these two substances is questionable. Yes, the instructions do not say that alcohol is prohibited while taking Jess Plus. Just as it is not said whether you can drink alcohol with Jess Plus.
When taking them together, be prepared for the consequences. COCs already thicken the blood, affect blood pressure and put a lot of stress on the liver. Plus, under the influence of alcohol, you may simply forget to take your pill on time. 1-2 glasses of wine from time to time may not be scary, but you should not abuse alcohol while taking OK. This may lead to health problems. Therefore, think before drinking alcohol while taking Jess Plus.
Jess plus and menstruation - read.
Skipping a pill
If you forget to take a pill, you need to proceed according to the following scheme:
- If no more than 12 hours have passed since you missed the pill, take the drug as soon as possible. The next tablet will need to be taken as per your regular dosing schedule.
- If more than 12 hours have passed since you missed a pill, then take the pill immediately (you will take the rest according to your regular schedule). You will also need to exclude pregnancy. Plus, you will need to use additional contraception for seven days.
- If you miss more than one tablet (2 or 3), withdrawal bleeding may occur. The first thing you need to do is rule out pregnancy (do a test or go to an appointment with a gynecologist) and take a pill, because You cannot take a break in the middle of taking OK. Use additional contraception for a week.
ATTENTION! Diarrhea or vomiting less than 5 hours after taking the OC is equivalent to missing a pill. In this case, proceed as if skipping.
If you miss inactive pills, nothing bad will happen. But you must start taking active pills on time, namely on the first day of the next cycle (on the 29th day from the start of the previous package).
If you take an extra pill, there is nothing to worry about. Continue taking it as usual.
Cancel Jess Plus
You can stop taking COCs only after you have finished taking all active tablets from the blister. It is not advisable to stop taking Jess Plus halfway through the pack, because Hormonal disruption and deterioration of health may occur due to the side effects of a sudden interruption of the course. You can abruptly stop taking OCs only with a doctor's prescription and only in exceptional cases.
ATTENTION! When taking COCs, visit your obstetrician-gynecologist at least once every six months.
Basic drugs
When choosing a drug for the treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome, it is necessary to take an individual approach. The gynecologist must take into account the woman’s hormonal characteristics, leading symptoms, age and desire to have children.
Veroshpiron
Polycystic ovary syndrome is often associated with excess production of male sex hormones. The drug Veroshpiron helps reduce the production of these biologically active compounds and deactivate androgens.
It allows you to eliminate the symptoms characteristic of the disease:
- increased male pattern hair growth;
- excessive greasiness of hair and skin;
- the occurrence of acne.
It is impossible to completely get rid of the disease with the help of the drug - its action is aimed only at eliminating the leading symptoms.
Siofor
Studies have shown that polycystic ovary syndrome can be triggered by an increased concentration of insulin in the blood. This phenomenon leads to shifts in carbohydrate metabolism and negatively affects the growth of follicles.
Siofor contains the active substance metformin. It normalizes blood sugar and blocks the production of male hormones.
As a result, lipid and carbohydrate metabolism improves, appetite decreases and weight returns to normal. The menstrual cycle is restored and becomes regular, which increases the chances of pregnancy and successful pregnancy.
Belara
Belara is a contraceptive oral contraceptive that has antiandrogenic properties.
This means that the drug suppresses the production of androgens, which interfere with the normal maturation of follicles and the release of eggs.
Treatment with Belara is quite long-term - at least for a year.
Glucophage
The properties of Glucophage are similar to those of Siofor, since the active ingredient of the drug is the same metformin.
This substance helps lower blood sugar levels, which allows you to achieve a balance between male and female sex hormones.
Cyclodinone
A herbal-based drug intended to normalize the menstrual cycle.
Cyclodinone for polycystic disease is used to treat women who complain of discomfort in the mammary glands.
The symptom is often a consequence of the activity of the enzyme prolactin. Cyclodinone reduces prolactin synthesis and improves a woman's condition.
The drug does not affect the pathogenesis of the disease and is used only for symptomatic treatment.
Jess is part of the group of oral contraceptives with a low content of hormonal components.
It has a mild hormonal effect, improves the condition of the skin with polycystic disease, normalizes hormonal balance and does not contribute to weight gain.
Ovariamine
Ovariamine does not contain hormones and is used only as an auxiliary drug for polycystic disease. The action of the drug is aimed at maintaining ovarian function and stimulating estrogen production.
Ovariamin is indicated for menopausal women - it not only helps fight cysts, but also smoothes out the course of menopause.
Cyclovita
The vitamin-mineral complex called “Cyclovita” was developed taking into account the characteristics of female physiology.
It contains 12 vital vitamins and 5 minerals. These organic compounds play a key role in regulating the functions of the reproductive system.
Taking the medication allows you to normalize the menstrual cycle, reduce the manifestations of premenstrual syndrome, and also support the functioning of the ovaries in general.
Utrozhestan
Utrozhestan is a synthetic analogue of the natural hormone progesterone. The drug is prescribed to women who have a lack of their own biologically active substances.
The medication can only help regulate the menstrual cycle by completely eliminating the endometrium, but it cannot help get rid of polycystic syndrome.
Diana is 35
The combined drug acts in two directions:
- normalizes hormonal levels;
- serves as a prevention of malignant neoplasms of the mammary gland.
Diane 35 demonstrates a powerful antiandrogenic effect. After completing the course of treatment, women have an increased chance of natural ovulation and successful conception.
Yarina
Yarina refers to monophasic low-dose contraceptives.
Yarina contains drospirenone - this substance is similar in structure and biological properties to the female hormone progesterone.
The drug is prescribed for a deficiency of female sex hormones, and also as a supporting agent in the treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome.
The drug Yarina Plus has another useful property - it reduces the risk of anemia.
Folic acid
According to laboratory studies, folic acid (vitamin B9) has the potential to cure ovulatory infertility that occurs as a result of polycystic disease.
It is enough to take 400 mcg of synthetic vitamin B9 per day to increase the chances of successful conception.