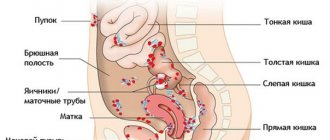
Bartholinitis is a disease characterized by inflammation of the Bartholin gland, located in the vestibule of the vagina. With this pathology, bacteria affect not only the excretory flow of the gland, but also its entire soft tissue. There are several types of the disease, each of them can be cured with its own method, this can be either drug treatment or surgical intervention. Before you figure out when surgery is needed for bartholinitis, how it goes, you need to know what type of disease.
Bartholinitis: true form
The penetration of bacteria into the parenchyma of the gland and the tissue that surrounds it leads to the formation of a true abscess of the Bartholin gland, while its parenchyma melts. The labia majora and minora are slightly swollen. The lymph nodes in the groin area become enlarged. During sexual intercourse, severe pain appears, but at rest, severe pain in the perineal area can also be observed. The woman feels pain when walking, her body temperature rises and remains within 37.5 degrees. If you look at a blood test, you can immediately notice an increased ESR and leukocytes.
You can distinguish true bartholinitis from false one by constant pain, swelling in the perineal area, immobility of the skin directly above the abscess and high body temperature.
There are several reasons that can provoke true form of bartholinitis:
- weak immune system;
- lack of personal hygiene;
- infectious diseases.
It is worth remembering that if, having immediately discovered an abscess, you seek help from a doctor, then you can get rid of the disease with the help of medication, but if this is not done, then surgery will be required.
When treating bartholinitis, the doctor recommends taking medications and using physical therapy. It is very dangerous to squeeze out an abscess, because in this case the infection can enter the circulatory system and this can lead to serious consequences, such as sepsis. Ultimately, everything can end in death, so you shouldn’t delay it and at the first symptoms you should consult a doctor.
https://youtu.be/c10VA1xAZXk
Reviews
I put off going to the gynecologist for a long time and couldn’t find the time due to my busy work schedule. A small lump on the labia did not bother me. However, the lump became larger and larger, and pain periodically occurred during sexual intercourse and hygiene procedures. On the advice of a friend, I went to the Lama clinic, where I see an excellent doctor, Zhanna Georgievna Muradova. At the appointment I learned that surgical intervention was necessary to remove a Bartholin gland cyst. The operation went quickly, the anesthesia did not cause any significant inconvenience. I returned home in the evening, and a few days later I started work.
Anastasia (Moscow, 2020)
During a regular examination by a gynecologist, they found a gland cyst on my labia. I didn't even notice it myself. The cyst was observed for a year, and when it reached the size of a cherry, I decided to remove it for cosmetic reasons. She started to bother my husband. The operation was done quickly. I arrived at the clinic in the morning and was already home by lunchtime. After the anesthesia there was a bit of a plague-like state, but I thought it would be worse. The next day the discomfort stopped, and after two weeks everything was completely restored. It’s right that I decided not to install a catheter; recovery with it takes longer. I recommend contacting the clinic. Everything is clear, fast and professional. Prices are strictly according to the price list and no markups.
Tatyana (Moscow, 2014)
At an appointment with Zhanna Georgievna Muradova, it turned out that I have a Bartholin gland cyst. Previously, I did not pay attention to the slight swelling, but my husband and I were going to have a baby, and I took it seriously. The doctor explained that the cyst can become inflamed during pregnancy, and this can harm the baby. In this case, you will have to remove the gland completely. At first I didn’t decide to have surgery, but I soon noticed that the lump had significantly increased in size. The operation went without complications. Thanks to the clinic specialists.
Marina (Moscow, 2014)
I discovered a fatty deposit on my labia myself and immediately went to my gynecologist at the Lama clinic, where I always undergo examinations. It turned out to be a cyst of the gland of the vaginal vestibule, and that an operation was needed to remove it. We agreed to observe for another month, but during this time it doubled in size. The operation was performed using a silicone implant to prevent relapse. A month later it was removed. I recovered very quickly. I'm satisfied with the operation. Many thanks to the doctors of the clinic.
Victoria (Moscow, November 2013)
I liked the attitude towards me at the clinic, and especially the professional abilities of Dr. Zhanna Georgievna Muradova. The gynecological problem, namely the removal of the cyst, was resolved quickly and without complications. Once again I want to thank Zhanna Georgievna and the entire Lama staff!
Marina (Moscow 2018)
I discovered a lump on my labia this summer. I read it on the Internet and decided not to treat the cyst until it started to hurt. Painful sensations appeared four months later, after which I turned to my gynecologist at the Lama clinic. I was scheduled for surgery to remove the cyst because internal inflammation had begun. The operation was performed under anesthesia, during which I did not feel anything. Afterwards, the anesthesia wore off within an hour, it was painful, but tolerable. The first day it hurt to walk, but on the second day everything was fine. After the operation, everything healed within two weeks, there was no relapse. It was right that I decided to have surgery and not delay it. I recommend contacting Muradova Zh.G.
Valentina (Moscow, 2013)
I consider myself lucky that I turned to Dr. Alina Valerievna Ervasova with my problem. I experienced great relief from the doctor’s tactful communication, and even more so after the most successful operation. I can say from my own experience that Alina Valerievna is a young, but at the same time experienced doctor. My sincere gratitude to Alina Valerievna.
Inna (Moscow 2017)
Articles on the topic
Bartholin gland cyst: symptoms of the disease
A Bartholin gland cyst is a tumor on the labia, the causes of which can be both infectious diseases and inflammatory processes of various natures. The symptoms of this disease are usually expressed at the location of the gland itself. With a glandular cyst, the labia become swollen, [...]
Marsupialization of Bartholin gland cyst
A Bartholin gland cyst is a tumor on the labia, which is an encysted accumulation of secretion produced by the Bartholin gland. Such a cyst is always caused by inflammation of the gland duct, which blocks the outflow of secretions. At the beginning of the development of the disease, it proceeds almost unnoticed and appears as a tumor [...]
Bartholinitis: false form or canaculitis
It will be very difficult to determine the initial stage of canaculitis, since the woman’s general health does not change in any way. The only thing that may appear is a small red spot located around the external opening of the excretory duct. This spot is surrounded by slightly swollen inflammation; if you press on it, you can see a small amount of pus protruding. It is this drop that is taken for analysis to determine the pathology.
If the excretory duct is blocked, this leads to a pseudoabcess of the gland. During this standing, the patient experiences slight swelling, hyperemia, and the skin over the swelling is mobile. The false form of the disease slightly protrudes the inner surface of the labia majora and at the same time blocks the entrance to the vagina. A patient with this form of the disease may experience an increase in body temperature to 37.5 degrees, and may also experience discomfort when walking.
This form of the disease can be easily treated with medications and physical therapy, the main thing is not to self-medicate and immediately go to the doctor.
Bartholinitis: acute chronic form
The chronic form of the disease can recur or, in simple words, repeat itself. The pathology is characterized by mild inflammatory processes, mild pain and a dense structure of the gland. If the disease is not treated for a long time, exudate in liquid form accumulates in the gland cavity. A tumor also forms, which is accompanied by a tumor without pain - a Bartholin gland cyst. In this case, surgery is necessary, and there is no way to do without it, but only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis and carry out all the necessary research.
Where to do it in Moscow?
To treat a cyst of the large gland of the vaginal vestibule in Moscow, we suggest you use the services of our specialized center for operative gynecology at the K-MED clinic for the following reasons:
- The latest equipment and materials : In our center for operative gynecology at the K-MED clinic, we use only the latest equipment. Operations are carried out in a modern operating room, which fully meets all approved standards.
- Experienced doctors : Our center has already existed for more than 15 years. Gynecology is one of the main areas of the clinic. Our clinic employs experienced gynecologists, candidates and doctors of science. During this time, we have already treated thousands of patients and performed hundreds of successful operations.
- Removal of a Bartholin gland cyst without pain : Usually this procedure is performed under anesthesia, which is selected individually for each specific case. However, at the request of the patient, it can be performed under local anesthesia or without it.
- Transparency of work : before treatment, the attending physician will fully tell you how the operation will take place, what will be done and what the expected result will be.
- Saving time : we value your time very much, so we will coordinate your appointment time with you in advance so that you do not have to wait. On average, an operation to remove a cyst takes about an hour, after which you will be in the clinic room for 2 hours, and then you can leave our clinic on your own, even while driving your own car.
During subsequent treatment, a consultation with a gynecologist-surgeon in our clinic is free of charge .
Get a free detailed consultation by calling (495) 434-34-44 or from 8 a.m. to 8 p.m. daily.
Our addresses : Moscow, Metro Yugo-Zapadnaya or Belyaevo / Konkovo, st. 26 Baku Commissars, no. 6; Moscow, metro station "Proletarskaya" st. Talalikhina, 2/1, bldg. 5.
Doctor's examination and confirmation of diagnosis
If suddenly unpleasant sensations appear in the perineal area or redness is detected, then you should not delay, you should immediately seek the advice of a doctor. The doctor uses the following diagnostic methods to confirm the diagnosis:
- Visual examination of the genital organs. This method can determine whether the patient has compaction, pain and redness. If a cyst is present, the doctor feels it in the form of a painless tumor-like formation.
- Afterwards, the secretion of the gland is examined under a microscope, so it is possible to determine the presence of pathogens that caused the pathology.
- In addition to the basic diagnostic methods, the doctor may also prescribe additional tests - a vaginal smear, which will help identify chlamydia, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, mycoplasmosis, ureaplasmosis, papilloma virus and many other infections that provoke bartholinitis.
How to treat a false form of the disease?
As soon as a small red spot appears on the labia, you should not delay going to the doctor; the initial stage of the disease is easy to treat and does not bring any inconvenience to the patient. Among the methods of therapy, the doctor recommends:
- Apply ice to the outer labia to relieve swelling. The procedure should be carried out like this: wrap an ice pack in a cloth and apply it to the inflammation. You need to keep the ice for at least 40 minutes. Afterwards you need to take a break for 20 minutes and put ice on it again for 40 minutes. It is also often recommended to use a 10% salt solution; it is believed that it absorbs excess moisture without destroying leukocytes. It is not difficult to prepare a solution; dissolve 2 tablespoons of salt in a liter of purified water, moisten a piece of cloth in this solution and apply it to the site of inflammation.
- The swelling is treated with disinfectant solutions such as potassium permanganate, miramistin, chlorophyllipt, chlorhexidine;
- Antibacterial drugs are used at elevated body temperatures;
- On the 3-4th day of therapy, the doctor recommends using physiotherapy: UHF and UV.
How is the true form of bartholinitis treated?
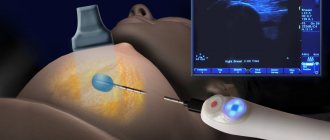
In case of bartholinitis, when the patient has already formed an abscess, surgery is needed. This is a simple opening and drainage procedure that can be performed under local anesthesia. In this case, the surgeon makes an incision along the inner surface of the labia in the place where the fluctuation is greatest. After all the pus has come out, which must also be taken for examination, the abscess formation cavity is washed with disinfectants and turunda with a hypertonic solution is injected. The turunda will need to be changed twice a day. In addition, the patient is prescribed antibacterial, sedative, and painkillers. Physical therapy is also recommended.
Postoperative period
Immediately after the operation, it is necessary to undergo a course of drug treatment, which will help alleviate the condition and prevent the development of complications. In the postoperative period, you need to follow these instructions:
- take antibiotics and anti-inflammatory medications,
- immediately after the intervention and for several days after that, apply cold to the wound surface. This will help relieve pain and swelling,
- treat the seam with an antiseptic up to 4 times a day,
- apply wound healing and anti-inflammatory dressings based on levomekol,
- a couple of weeks after the intervention, undergo a course of physiotherapeutic procedures.
For another month after removal of the cystic formation of the Bartholin glands, the following rules must be followed:
- maintain complete sexual rest,
- do not take baths, do not visit baths and steam rooms,
- wear loose cotton underwear,
- strictly adhere to the rules of personal hygiene.
Treatment of Bartholin gland cyst
If the patient has already formed a cyst, then in this case surgery is needed. But it needs to be carried out during the “cold” period, or, to put it simply, at a time when there is no exacerbation. But before starting therapy, it is necessary to accurately distinguish an abscess from a pseudoabscess. Indeed, it very often happens that it is a pseudoabcess that is identified in many patients. It is formed as a result of an inflammatory process in the duct of the large gland on the vestibule, when the accumulated secretion suppurates. If during this process the gland tissues are subject to the melting of pus and this process is accompanied by inflammation, then an abscess eventually develops. Opening a pseudoabscess can only lead to temporary relief until the contents come out without obstruction. But as soon as the ends of the wound stick together, pus begins to collect again, which is why immediately after opening the patient is recommended to start taking antibacterial medications. They also make lotions with Vishnevsky or Levomikol ointment to stop the development of suppuration and remove the focus that produces pus. If it was not possible to cure everything, and the pus has collected again, the abscess is opened again.
The abscess is opened under local anesthesia, the incision site is punctured, it is carried out parallel to the labia minora and it is better to do this outside of it. After a wide opening, the abscess must be drained using a gauze swab, which remains with the patient for a day, and then it is replaced with a rubber tube.
Surgical treatment
Treatment of Bartholin gland cysts is not always surgical. Indications for surgical intervention are the following:
- recurrent inflammation or abscess;
- the cyst is large (more than 3 cm) and is in the way;
- the cyst aesthetically excites the woman;
- there are concomitant oncological diseases of the labia and vulva.
If a woman once had inflammation of a Bartholin cyst, it is recommended to think about surgical intervention, since the likelihood of recurrence of the infection is high. The type of operation performed depends on the desired result and the capabilities of the doctor and medical institution.
Puncture
It is performed on an outpatient basis under local anesthesia. A syringe with a needle is used to puncture the cyst and remove the purulent contents. The manipulation takes five to seven minutes, but does not lead to a complete cure. This is rather a temporary measure for those who, for some reason, cannot undergo hospitalization and more serious manipulation.
After the puncture, you need to carry out dressings yourself, do sitz baths, and also take anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drugs as prescribed by your doctor. However, even in this case, the likelihood of relapse soon is high.
Instead of a puncture, sometimes an incision is made above the cyst and all its contents are removed. But if additional drainage is not carried out and the operation is left at this stage, the incision site will soon “stick together” and the cyst will recur.
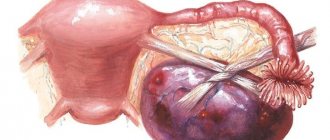
Removal of cyst and gland
This is one of the radical treatment methods. This intervention is carried out during the “cold period” to minimize the number of complications. The main advantage of the method is reliable protection against relapse - “no gland - no problems.”
This technique can be performed on any size cyst, unlike other modern techniques. But there is also a “other side of the coin”, and therefore such an operation is rarely used in European countries:
- blood loss - the Bartholin gland is surrounded by a large number of choroid plexuses, which are almost always affected when it is removed;
- frequent complications - in the postoperative period, hematomas of varying severity occur, which sometimes have to be additionally drained;
- change in the quality of intimate relationships - some women, after removal of the gland, note insufficient moisture in the vulva and vagina during sex;
- hospitalization is required - removal of the gland is carried out in the operating room; a hospital stay of at least two to three days is required.
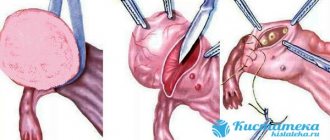
The operation is carried out in three stages.
- A skin incision is made. And the Bartholin gland cyst is desquamated; it is advisable not to open the formation, as the likelihood of postoperative complications is less.
- The gland itself is removed. Often this period is complicated by bleeding.
- The bed of the former cyst is sutured in layers . The anatomy of the genital organs is restored, and if necessary, drainage is installed for the outflow of secretions.
The healing period is at least a month. At this time, a woman needs to wash herself after each visit to the toilet, and should avoid sexual intercourse and physical activity. This is the only way to avoid complications after surgery.
Marsupialization
One of the effective methods with a relapse rate of no more than 20%. Can be performed in the “acute phase”. The operation is carried out as follows:
- the tissues above the cyst are cut - the contents are removed, the cavity is intensively washed with antiseptics;
- the walls of the cyst are sutured to the skin so that a new path for the outflow of secretions is formed.
- if necessary, drains are installed in the wound for better outflow of contents.
Marsupialization of a Bartholin cyst requires serious anesthesia, most often this is intravenous administration of drugs for general anesthesia. It is performed only in a hospital and requires observation of at least two to four hours and high-quality wound treatments. The recovery period is also about a month. The restrictions are similar to those for removing the gland.
Laser vaporization
Laser vaporization of a cyst is one of the effective methods. The procedure is in many ways similar to the usual opening and drainage of the cyst. Using laser energy, the cyst itself and part of the ducts are bloodlessly removed. The Bartholin gland remains intact, so the likelihood of relapse or the presence of pain and slight swelling after exercise remains.
Pros of the procedure:
- less painful - local anesthesia is used;
- no bleeding – the laser coagulates the vessels;
- quickly - the operation takes no more than 20 minutes, hospitalization is not required.
Disadvantages of cyst vaporization:
- expensive - not every clinic can afford a laser treatment machine;
- healing period - despite the advertised “rapid recovery”, tissues are completely regenerated only after two to three weeks;
- relapses - their frequency after such treatment is about 60-70%.
Word-catheter
The most promising technique is one that has long been widely used in foreign countries, but is still rarely found in the post-Soviet space. The operation takes place in four stages.
- An abscess or cyst of the Bartholin gland is opened.
- All contents are removed and the cavity is washed.
- A catheter is inserted into the resulting chamber.
- Its end is inflated to fix and ensure the outflow of contents.
The operation is performed under local or general intravenous anesthesia in a day hospital. The required observation in the postoperative period is two hours. Then the woman leaves and performs dressings on her own at home.
The catheter remains in the cavity of the former cyst for a month. During this time, a new channel for the outflow of secretions is formed. At the next doctor's appointment, the catheter is removed. The Bartholin gland remains intact, so the operation does not affect the quality of a woman’s intimate relationships. The risk of relapse is no more than 10% and is associated with careless handling of the catheter and its loss.
Piercing
Similar in nature to the Ward catheter is cyst piercing. Two holes are formed for the outflow of contents. Most often carried out during the “cold period”. The women's reviews are contradictory - for some, this technique helped get rid of the problem, while for others, a relapse occurred again.
Removal of a cyst for chronic bartholinitis
Today, there are two methods of surgical removal of the cyst: creation of an artificial duct of the gland (marsupialization) or complete removal of the Bartholin gland (extirpation).
Most often, with this pathology, doctors choose the most effective method - marsupialization. It is used in cases where the patient often experiences exacerbations of pathology, the formation of large forms of cysts that interfere with sexual and everyday life.
This operation allows you to form a non-sticking channel through which the secretion produced by the gland will be released unhindered.
The operation is performed under anesthesia; a small incision of about 5 mm is made in the cyst. The cavity is washed with a disinfectant solution, and then a catheter is inserted into it; a ball is inflated at its end, which prevents the catheter from falling out. The patient walks with such a catheter for about a month, after which it is removed. This time will be enough for a new duct to form for excretion. What is very important is that during the period when the catheter is inside, the patient is not prescribed any other therapy.
With this method, there are almost no relapses; most often they can appear if the patient is re-infected or the catheter falls out. But you can return it to its place without any problems; this method is much better than completely removing a large gland located in the vestibule of the vagina.
Removing the gland is a very serious and complex operation, and all this is due to the fact that the upper pole is attached to a large venous formation. Also, after removal of the gland, a woman’s natural hydration of the vaginal mucosa is disrupted. But there are situations when only such an operation can help.
Removal of the Bartholin gland is recommended when the patient experiences frequent relapses and it is not possible to form an artificial gland duct.
The operation is performed under anesthesia, an incision is made on the inside of the labia minora, after which the gland itself is removed with extreme care. The incision is then sutured using catgut.
After the operation has been performed, the patient is prescribed rehabilitation, which can take up to 10 days. At this time, it is recommended: phonophoresis, UHF, magnetic therapy, applications with medicinal ointments and other methods of therapy.
When a patient is being treated for chronic bartholinitis, she should avoid sexual intercourse so as not to infect her partner with the infection. Also, abstinence will protect the patient from relapse.
Briefly about cystic formation
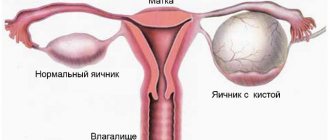
In the vestibule of the vagina there are special glands, the main function of which is to protect the vagina from infection and injury; in addition, it is these glands that secrete a special secretion that moisturizes the labia during sexual intercourse and washes away various pathogenic microbes and harmful particles from them. The glands are located in the lower third of the vestibule of the vagina. They are a paired, round-shaped organ that, in normal health, cannot even be felt, much less seen with the naked eye. The size of the glands does not exceed a couple of centimeters. The mouths of their excretory ducts are located on the inside of the labia minora.
If the ducts of these glands become clogged, the viscous viscous secretion they produce begins to accumulate inside, stretching the walls of the organ, which causes the formation of a cyst. This cyst-like formation has its own characteristics:
- the diameter of the capsule can reach up to seven to eight centimeters,
- most often this is a unilateral cyst, bilateral ones occur very rarely,
- not susceptible to malignancy,
- do not affect pregnancy and the fetus in the womb,
- do not disrupt hormonal levels,
- often recur, but are not inherited.
This formation occurs due to an infection entering the gland or a mechanical obstruction of the excretory duct. Infectious agents can be gonococci, chlamydia, ureaplasma, as well as opportunistic microflora that develops under the influence of certain factors (Escherichia coli, streptococci, staphylococci, etc.).
The following factors can provoke bartholinitis:
- decreased protective functions of the body,
- improper hygiene,
- tight, synthetic underwear and clothing,
- clogging of glandular ducts with lubricants,
- bacterial vaginosis,
- hypothermia,
- stressful conditions,
- rudeness during intimacy,
- a large number of sexual partners, which increases the chances of infection,
- skin injuries during epilation in the bikini area,
- gynecological manipulations and pathologies.
The main symptoms of the pathology include the visualization of a tumor on the labia, the size of a pea to a chicken egg, pain when walking and squatting, and discomfort during sex. Without adequate treatment, there is a high probability of developing an inflammatory process in the cyst, followed by suppuration and the onset of a true abscess.
Treatment after surgery
Very often, due to the fact that women do not turn to the doctor with their problems in time, most diseases develop into a chronic form, bartholinitis is no exception. Opening an abscess on your own can lead to serious consequences, as the wound can become re-infected. And such wounds take a very long time to heal, so it is better to leave the opening of the abscess and removal of the cyst to a doctor.
During the opening of the abscess, the surgeon frees the gland from pus, carefully treats the area affected by the operation and monitors the condition until the patient’s complete recovery. If the wound was opened at home, then most patients still turn to the doctor for help, since they cannot cope with the inflammation on their own. Therefore, in order to prevent complex complications, bartholinitis needs to be treated correctly and within the walls of the hospital.
After the operation, you should also follow some rules that will help prevent re-infection and allow the wound to heal faster. You need to take care of personal hygiene:
- You need to wash yourself 2 times a day, for this procedure you need to prepare a weak solution of potassium permanganate, a chamomile decoction or an antiseptic Citeal, purchased at a pharmacy, is also good. You can also use intimate hygiene products with antibacterial properties;
- You only need to wear loose underwear and it is better if it is made of natural material; also after surgery, when bartholinitis has been removed, it is better not to wear tight clothes;
- There is no need to use panty liners during wound healing, as bacteria can develop in them, which will lead to a new infection, but if you can’t do without them, then they need to be changed every 2-3 hours;
- during menstruation, pads should be changed every 4 hours and, if possible, washed before changing;
- During the healing period, you should refrain from sexual intercourse and masturbation.
In addition to personal hygiene, after surgery you will also need to use antiseptic drugs and antibiotics; such treatment will help the wound heal faster and protect against infection. After surgery it is recommended:
- treat the wound with iodine or brilliant green;
- place tampons with Chlorhexidine or Miramistin in the vagina at night;
- the wound should be washed and disinfected with Betadine solution;
- Vishnevsky ointment or Levomikol can be used only after all the pus has come out, these ointments are intended for healing and, if used too early, they can close the outlet through which the pus comes out.
In addition to the procedures described above, it is necessary to add antibiotics. After surgery, they will help the wound heal faster and protect against new infections. The antibiotic should be selected by the attending doctor, who will take into account the tests and select the correct drug depending on the infection that led to the formation of bartholinitis. Very often, antibacterial treatment is also prescribed to a sexual partner, so that in the future the infection will not be transmitted from him and will not lead to a relapse.