Retroversion or retroflexion of the uterus is an abnormal structure of the main organ of the female reproductive system, which is popularly called a bend of the uterus. About 20% of patients in gynecological departments face this diagnosis, but despite this, a woman with any type of bend has every chance of becoming pregnant and bearing healthy offspring, but for this it is necessary to undergo a consultation with a gynecologist.
Below you can find complete information about the pathology: what it is, what are the causes and consequences of the bending of the uterine body, what signs can be used to determine the presence of pathology, what methods and how to treat the disease.
What it is
The uterus is a hollow pear-shaped organ that is located in the recess of the small pelvis parallel to the vagina. In this position, the uterus is firmly held by the ligamentous apparatus. This arrangement of the organ is optimal in order to provide sperm with the opportunity to freely move to the germ cells for fertilization.
If the uterus deviates away from its normal position, it is diagnosed as kinked or bent, this means that sperm may now have problems achieving their final goal, and women with this diagnosis very often experience prolonged and unsuccessful attempts to get pregnant.
It is quite difficult to identify the pathology; most often it is discovered during an in-depth examination, which is usually carried out by couples who have been making unsuccessful attempts to conceive a child for a long time.
The pathology does not produce specific symptoms; only in rare cases can it manifest itself in the form of too painful periods. But this sign may indicate the development of completely different problems with women’s health.
The bend may be a congenital anomaly, or it may be a secondary pathology that develops against the background of previous infectious diseases of the genitourinary system and surgical interventions.
https://youtu.be/Mg2FWUXPVk8
Retroflexion of the uterus and pregnancy
Women with retroflexion have difficulty conceiving: due to a violation of the anatomical location of the uterus, sperm cannot reach the part of the uterus where fertilization of the egg normally occurs. If favorable conditions are created, the uterus will change its angle and the woman will be able to get pregnant.
With unfixed retroflexion, the most suitable position for fertilization is knee-elbow. After sexual contact, you need to stand in the “birch tree” position or lie on your stomach for 15-20 minutes. Under the pressure of gravity, the uterus will reduce its curvature and it will be easier for sperm to enter the uterine cavity.
The prognosis for bearing a child with mobile retroflexion is favorable. Under the pressure of amniotic fluid and the weight of the growing fetus, the uterus gradually straightens. As the fetus grows, the muscles of the uterus begin to strengthen. Usually pregnancy proceeds without deviations. In some situations, after delivery, the uterus returns to its correct anatomical position. Despite this, the expectant mother must be under medical supervision and follow all the doctor’s instructions.
With a fixed bend formed due to the adhesive process, there is very little chance of conceiving, carrying and giving birth naturally. Before planning a pregnancy, it is recommended to undergo a preliminary examination and, if necessary, undergo comprehensive treatment.
What are the causes of the pathology
Most often, pathology can arise in the womb and does not even make itself felt for a long time. Acquired bending brings much more inconvenience and negative consequences for the female body, so its treatment should be taken very seriously. Let's consider the main causes of pathology:
- the formation of adhesions after surgery or previous infectious diseases in the organs of the reproductive system. After such interventions and diseases, an inflammatory process may begin, which activates the proliferation of connective tissue - the adhesive process. This, in turn, leads to deformation of the uterus or to a change in its location in the pelvic cavity;
- underdevelopment of the ligaments that support the uterus. For this reason, bends most often occur in girls aged 17-18;
- atrophied muscles. Such phenomena can occur in women during menopause, when hormonal levels change and other age-related changes occur in the body;
- deformation of other organs of a pathological nature. If the size of the intestines or bladder changes, the uterus may also move. The reason for this may also be the development of oncological tumors in the pelvic area.
A bend of the cervix can occur due to constant heavy physical labor or inflammatory processes caused by promiscuous sex life. In some cases, it is a consequence of early abortions or develops after the birth of a child with the manifestation of hidden pathologies.
Only a doctor can say exactly why the bend could have occurred and how to get rid of this pathology, so women who are planning a pregnancy should necessarily undergo appropriate treatment before conception.
Diagnosis of uterine retroflexion
Diagnosis of uterine retroflexion is based solely on tests and results of an examination performed by a gynecologist. It is usually carried out by palpation: the doctor inserts the fingers of one hand into the vagina, and with the other, through the abdominal wall, displaces the uterus itself. This method helps not only to identify uterine retroflexion, but also to absolutely accurately determine its type. Additionally, you can conduct an ultrasound examination and computed tomography of the pelvic organs, which will help confirm or refute the specialist’s concerns regarding the cause of the formation of a bent cervix.
Classification
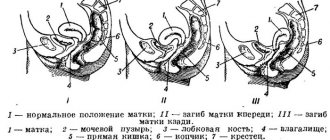
There are two main types of uterine tilt depending on the origin:
- congenital bend, which is formed in the womb;
- acquired bend, which occurs due to various reasons.
Depending on the position of the organ relative to its neck, the following forms of pathology are distinguished:
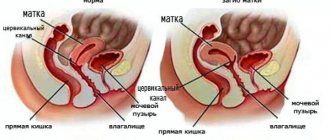
- anteflexion. This is the most commonly diagnosed condition in which the position of the uterus is closer to the central part of the pelvis, and its fundus is directed upward and forward. The cervix is curved downwards and anteriorly. The body of the uterus and the cervix form an obtuse angle. This is the most harmless form of pathology, which gives a great chance of natural conception and bearing healthy offspring;
- anteversion. With this type of pathology, a bend is detected anteriorly relative to the vagina, which also changes the position of the cervix;
- leteroflexion. In gynecology, this term refers to a change in the position of the uterus relative to the axis closer to the right or left ovary;
- retroflexion. With this type of pathology, the organ exhibits a strong posterior bend. If a woman has a retroflexed uterus, the likelihood of conceiving a child on her own is very low.
When the cause of the bend is weakness of the ligamentous apparatus, it is customary to assess the condition of the uterus by its mobility. In this regard, there are several more types of uterine bending, in which the uterus is defined as:
- motionless;
- with limited mobility;
- movable.
In the latter case, if the mobility is too active, the reproductive organ can not only tilt, but even twist around its axis.
Diagnosis of uterine retroflexion
To identify a bend of the uterus, after a preliminary conversation with the patient and examination of her complaints, a gynecological examination is performed in a chair. During a two-handed examination, the doctor determines the presence of abnormalities and assesses the mobility of the uterus. The diagnosis is made taking into account the results of the examination: when the position of the organ changes, fixed retroflexion causes sharp pain.
To determine the cause of a bent uterus, vaginal smears are examined for infection and ultrasound diagnostics of the uterus and pelvic organs is performed. If necessary, a histological analysis of scrapings from the uterine cavity and computed tomography are performed.
Based on the research results, the doctor determines the form of retroflexion and the cause of the pathological process, and also develops suitable therapeutic tactics.
Symptoms
Each type of uterine bending has its own characteristic symptoms, but there are certain signs of bending that most patients complain about:
- severe pain in the abdominal area during menstruation;
- weakness throughout the body;
- a sharp change in the amount of menstrual blood released;
- bloody lumps;
- bleeding not associated with critical days;
- pain during sexual intercourse;
- inability to have children;
- problems with the digestive and urinary system.
A woman should carefully monitor the amount of vaginal discharge, and if it changes sharply, she should definitely go to the doctor to find out what is causing it.
A characteristic sign of a fixed bend is intermenstrual spotting, and in the case of a mobile bend, formed after childbirth or sudden weight loss, constipation and pain in the lumbar region and lower abdomen may begin.
Why is bending dangerous?
If a woman has a curved uterus from birth, then it does not threaten her health in any way.
The only danger is the acquired form of the pathology, which is accompanied by severe pain during menstruation or during intimacy.
In order not to delay visiting a doctor if such signs are detected, it is important for every woman to know the dangers of a curved uterus.
- Firstly, it causes menstrual irregularities; not only the duration of the discharge changes, but also its nature.
- Secondly, the risk of developing inflammatory and hyperplastic processes in the endometrium increases.
- Thirdly, a uterus that is bent backwards or forwards puts pressure on the rectum or bladder, which affects their functioning and leads to difficulties with urination or defecation.
But the most severe complications are caused by bending for women of reproductive age who want to have a child. Because of this pathology, problems arise with conception, the process of bearing a child becomes more complicated, and difficulties arise during childbirth.
How to diagnose
If the symptoms of the pathology are pronounced, the bend can be determined at the next visit to the gynecologist. It is very important to correctly carry out differential diagnosis in order to exclude other diseases of the genital area. During a visit to a specialist, the following diagnostic techniques are used:
- ultrasound examination, which is carried out with a special vaginal sensor. On an ultrasound, the specialist sees the exact location of the body of the uterus relative to its cervix;
- patient interview. The gynecologist takes into account the woman’s complaints of pain during menstrual periods and having sex, a large amount of discharge between menstruation;
- palpation. The fact that the uterus is bent can be indicated by its immobility, which is caused by formed adhesions.
Only by accurately determining the form of the pathology can the doctor select adequate treatment.
How to treat
Treatment of a bent uterus should be carried out in a complex manner. Only the attending physician can tell you what to do in this or that case after carrying out diagnostic measures.
Under no circumstances should you treat yourself, as this can lead to serious consequences.
Drug therapy
When the uterus is bent, drugs from several pharmacological groups are prescribed at once, since there is no single drug that could cure the pathology:
- anti-inflammatory (Hexicon, Betadine, Flagyl, Terzhinan). They are needed in cases where the position of the uterus has changed due to the development of an inflammatory process in the ovaries or in the body of the uterus itself;
- antibiotics (Cefepime, Cefazolin, Cefuroxime and other medications from the cephalosporin category). Drugs in this group are prescribed in cases where the cause of inflammation and the development of pathology are infections of a bacterial nature;
- absorbable (Chymotrypsin, Logidaza). These medications help eliminate adhesions;
- hormones (Novinet, Mercilon). This type of hormonal-based medication is prescribed to women with congenital pathology to create the necessary hormonal levels for pregnancy;
- vitamins. It is recommended to take vitamin complexes, which include vitamins B, PP, C for general strengthening of the immune system;
- antispasmodics. To eliminate pain associated with the curved shape of the uterus, you can take No-shpu or Spazmalgon.
Physiotherapy
An effective method in the fight against uterine inclination is the use of physiotherapeutic procedures. UHF and mud therapy give good results. In case of adhesions, electrophoresis is prescribed, which does not eliminate them, but significantly softens them, due to which the uterus independently returns to its normal position. Electrophoresis additionally helps to improve the functioning of the intestines, which have been tightened by adhesions, and relieves pain.
To achieve a sustainable effect, it is recommended to combine several physiotherapeutic methods and undergo treatment courses lasting from several weeks to six months.
Massage
The use of gynecological massage for pathology is advisable if the cause of changes in the position of the uterus is inflammation, weakness of the pelvic muscles or ovarian dysfunction.
This treatment method is contraindicated in cases of congenital deformity, as well as in cases where the patient has infectious pathologies of the genitourinary system, menstrual irregularities, high body temperature and endometriosis.
This method can remove adhesions, strengthen the pelvic floor muscles and set the uterus in the correct position without the need for surgery.
The number and frequency of massages is determined by the doctor. During the procedure, the patient lies on a gynecological chair, and the specialist massages the vaginal walls with one hand and the abdomen with the other. Massage is not performed during menstruation or in the presence of inflammation.
Exercises
To consolidate the effect of the listed treatment methods, the doctor may recommend that the patient perform special therapeutic exercises, which are based on special Kegel exercises. They include several techniques:
- alternately tense your pelvic floor muscles. You need to do 10 contractions several times a day;
- Fully tighten your pelvic floor muscles and hold them tight for at least 10 seconds;
- do the “Wave” exercise. It involves the muscles around the anus, vagina and urethra. They need to be strained one by one, making a kind of “wave”.
Performing these exercises does not depend on the time of day or location of the woman; those around her may not even know that she is doing therapeutic exercises.
Excellent results can be achieved by performing exercises in different positions - lying down, standing on all fours or sitting.
ethnoscience
Treatment with folk remedies can really help get rid of uterine inflexion, but you can resort to using it only after consulting a doctor.
Many of the components that are included in traditional medicine recipes do not need to be prepared independently; they are sold ready-made in pharmacies, but they also need to be purchased only with the permission of a doctor.
At home, you can eliminate the inflammatory process that caused the bend of the uterus using this infusion for douching:
- mix 1 tablespoon. dry leaves of chamomile and sweet clover with 2 tbsp. lie marshmallow leaves;
- 1 table. lie pour the resulting mixture with a cup of boiling water;
- leave for a quarter of an hour;
- The resulting infusion should be douched twice a day.
You can take an infusion of acacia inflorescences, 1 table. lie which need to be filled with 60 ml of alcohol. This mixture is infused for about a week, and then taken 1 teaspoon. as a pain reliever. This medicine can also be diluted in a 1:1 ratio with boiled water and douched to relieve inflammation caused by bending.
Surgery
If the symptoms of the bend are pronounced, and the patient’s condition is rapidly deteriorating, the doctor may prescribe surgical intervention. Most often it is performed laparoscopically. In this case, all manipulations are done through several small punctures in the abdominal wall. During the operation, the uterus is placed in the correct position and adhesions are removed, but surgical intervention cannot remove the original cause of the development of the pathology, so specialists resort to this technique only in extreme cases. Without identifying and eliminating the root cause after surgery, cases of relapse of the pathology are very common; to prevent this from happening, you must follow all the doctor’s recommendations.
Treatment of uterine retroflexion
If the bending of the uterus is not accompanied by pathological symptoms and is not caused by inflammatory or tumor diseases, therapy is not carried out. If uterine retroflexion occurs as a result of one of these diseases, appropriate treatment is prescribed.
The tactics and treatment regimen are selected by the gynecologist, taking into account the possibility of reverse displacement of the uterus. With mobile retroflexion, the organ is reduced manually. Special gynecological pessaries can also be used, which are installed in the uterine cavity or vagina.
There are two types of pessaries:
- Supportive. Pessaries in the form of rings are placed on the cervix for fixation. Cup-shaped pessaries are used to drain vaginal secretions.
- Filling. They are used to eliminate changes in the position of the uterus, as well as to prevent prolapse of the bladder and rectum. Filling pessaries can be mushroom-shaped, cubic or thick ring-shaped.
- taking anti-inflammatory, antibacterial medications;
- vitamin therapy;
- prescription of hormonal drugs;
- mud therapy;
- carrying out physiotherapeutic procedures (electrophoresis, ultraphonophoresis);
- acupuncture;
- physiotherapy;
- gynecological massage.
The selection of a suitable device is carried out by the doctor, taking into account the degree of uterine curvature, the clinical picture of the pathology and the anatomical features of the patient.
Gynecological pessaries are also used to treat fixed retroflexion. Before installation, complex treatment is carried out, which may include the following therapeutic measures:
If the use of the above therapeutic methods does not produce the desired results, surgical intervention is indicated. The safest surgical method for combating uterine retroflexion is considered to be laparoscopy. The essence of the intervention is the excision of adhesions. The operation is performed using general anesthesia.