Why is laparoscopic incision surgery performed?
During laparoscopy, incisions are made on the ovaries with the following goals:
- Free a woman from infertility.
- Normalize the menstrual cycle.
- Stimulate ovulatory processes in the ovaries.
Indications for surgical intervention are various conditions in which a woman cannot conceive and bear a child. Most often, such procedures are undertaken:
- with polycystic ovary syndrome;
- if there is a cyst on the ovary;
- with some hormonal disorders.
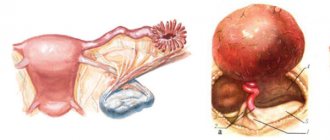
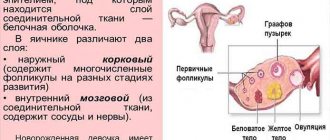
During the menstrual cycle, an egg matures in the ovarian capsule; this process takes place under the influence of various hormones.
When the time comes for ovulation, the capsule bursts, and the egg leaves the ovarian follicle and enters the fallopian tube, where fertilization occurs. If the capsule does not burst, the egg does not come out, ovulation does not occur, and therefore conception is impossible. Pathologies and cystic neoplasms of various types interfere with this process.
Laparoscopic surgery allows you to get rid of the disease and increase the chances of pregnancy, and the method of implementation significantly reduces the risks associated with surgery.
https://youtu.be/KJfU6bjdh8k
Consequences of the procedure: pros and cons
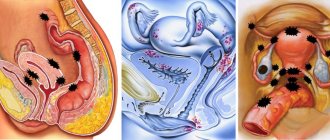
With polycystic disease, the egg maturing in the ovary cannot be released for fertilization, since the walls of the follicle are too dense. As a result, over time, many follicles form on the ovary, they fill with fluid and turn into cysts. The ovary also increases in size.
Important! The main advantage of cauterization is its minimal invasiveness.
Violation of the integrity of the follicles, cleansing of accumulated fluid and restoration of ovarian function is carried out through small incisions. The operation is performed under anesthesia using special instruments and equipment. 3 pinholes are made in the abdominal cavity, after which small sutures remain, which are quickly and painlessly tightened. Another plus is complete control of all manipulations. This is achieved through the use of a camera, which displays the image on the screen. Every movement of the specialist is under visual control.
As for the disadvantages, they are related to the very essence of the surgical operation. No one is immune from blood loss or damage to other internal organs. The likelihood of adhesions in the pelvis does not completely disappear. This operation also does not promise to completely get rid of polycystic disease.
The essence of the method of applying notches and the scheme for its implementation
The operation is performed in a low-traumatic manner, which allows you to obtain the desired result and minimize risks. The technique is to facilitate the process of ovulation. Doctors in their practice take the following actions:
| Sequence of manipulations | Description of the actions taken |
| First step | With the help of several punctures they get to the organs |
| Second step | Small incisions are made on the ovaries in places where translucent follicles are visualized or the membrane is removed to facilitate the onset of ovulation |
| Third step | Cauterize blood vessels with a coagulant to avoid bleeding |
Sutures are not placed on the surface of organs after incisions are made on the paired sex glands, as this can negatively affect ovulatory processes in the body. At the time of the operation, the surgeon must determine in which cases incisions are made and in which the membrane is removed:
- if the organ is covered with a dense membrane, then incisions on the ovaries will not contribute to the onset of ovulation, in this case the film is removed, completely removed from the paired sex gland, and then incisions are made;
- if the organ is not covered with a membrane, then it is enough to make a few notches to solve the existing problem.
The operation is performed under general anesthesia, but if there are contraindications to anesthesia, then preference is given to spinal anesthesia.
Before undergoing laparoscopic surgery, a woman will have to donate blood and urine for tests, and also undergo a number of diagnostic procedures.
Since the intervention method is considered low-traumatic, recovery takes several days. For its successful completion and pregnancy, a woman is recommended:
- After a successful operation, when the incisions are made on the ovaries, the woman is recommended to stay in the hospital for a day, under the supervision of a doctor. At this time, it is necessary to observe bed rest.
- After a day, you can leave the medical facility, having clarified the recommendations for further treatment with the doctor who operated on the patient.
Often, after surgical procedures, the patient is prescribed hormonal therapy. Taking such medications can increase the chances of a successful pregnancy.
Indications for use
The main reason for prescribing cauterization of the ovaries is the impossibility of follicles emerging from them.
The following pathological conditions can lead to this situation:
- Polycystic ovary syndrome - occurs due to a hormonal imbalance, leading to the fact that mature follicles do not burst, but continue to increase in size, turning into cysts. This happens due to the thick walls of the follicles. Subsequently, many cysts form on the uterine appendages, and the release of eggs is impossible. As a result, infertility occurs,
- Hormonal imbalance , in which the follicles do not respond to the effects of hormones, or the effect of these substances is too small. Due to this, their physiological rupture with the release of germ cells does not occur,
- Other chronic, vegetative or genetic diseases in which the release of eggs from the ovaries is impaired.
Important! Not all sick women can undergo cautery for health reasons. In case of extensive adhesions in the abdominal organs, cardiovascular, renal failure, sepsis, coma, intestinal obstruction, the cauterization procedure is completely contraindicated.
Consequences of notching and cutting
As such, the application of notches and incisions to the female ovaries does not have any serious consequences that are dangerous to life and health. It is well tolerated, and problems arise only if the doctor’s recommendations are not followed. Surgical intervention helps achieve the following results:
- normalize the menstrual cycle (bleeding occurs regularly, at the right time);
- pregnancy after incisions on the female ovaries occurs in the first 2-3 months after the intervention.
If for some reason pregnancy does not occur, then the operation of making incisions on the ovaries is repeated, and hormonal therapy is started.
Incisions on the ovaries made for polycystic disease or various cystic neoplasms allow a woman to hope for a successful conception. The procedure has good results, and the risk of developing consequences is minimal. For this reason, laparoscopy is successfully used in gynecology and not only for the purpose of treatment, but also for diagnosis.
Progress of the operation
Before cauterization, the patient is put under anesthesia, that is, she will be unconscious and will not feel anything. Control over the drugs administered for pain relief and the body’s reaction to them will rest with the anesthesiologist.
After treating the abdominal skin, the surgeon will make the required number of punctures in the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity. Through the holes formed in it, instruments, a laparoscope with illumination and a video camera, and a coagulator will be inserted inside. Before cauterization begins, carbon dioxide must be injected into the abdominal cavity for a better view of the operated area.
What are polycystic ovaries
A common hormonal disorder in women who are not yet past childbearing age is called polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS). It is characterized by the development of many small cysts - follicles filled with fluid. They contain undeveloped eggs located along the lining of each ovary. The consequence of this may be disruption of the menstrual cycle, problems with pregnancy, and the appearance of cysts in the genitals. Experts associate polycystic disease with changes in the levels of progesterone and estrogen, which help in the process of producing eggs.
Features of electrocautery
Electrocauterization of the ovaries restores the function of the gonads, malfunctions of which prevent patients from becoming full-fledged women capable of becoming pregnant and bearing a child.
As a result of cauterization and dissection of the surface of the organs with a hook or electrode, the follicular fluid of the cyst pours out through the holes made (in total, “cuts” are made from 7 to 20, the number depends on the stage and severity of the disease), the ovaries decrease in volume and begin to function correctly in the near future .
The recovery period after the intervention is quick, the risks of complications and adhesions are minimal.
Laparoscopy for PCOS
In almost all cases of the development of PCOS, doctors note in women a decreased sensitivity to insulin, a hormone that regulates the amount of glucose in the blood. When a large amount of this substance circulates in the circulatory system, the ovaries begin to increase the production of androgens (male hormones). The substance disrupts the function and structure of the ovaries. The hormone negatively affects ovulation, preventing eggs from developing normally.
Under the influence of androgens, the ovarian membrane becomes thicker, and a mature follicle cannot break through it. This prevents the release of an egg ready for fertilization. Unruptured follicles fill with a liquid substance and transform into a cyst. This is how a woman develops polycystic disease - an accumulation of several small formations. Laparoscopy for PCOS is usually performed to treat infertility. The advantage of the technique is the ability to eliminate the accompanying peritoneal factor - obstruction of the uterine tubes or existing adhesions.
Diagnostic laparoscopy
During the diagnosis of PCOS, the doctor examines and interviews the patient, while he notes external signs of pathology and enlargement of both ovaries. Using ultrasound, a specialist identifies several unruptured follicles up to 1 cm in size and prescribes diagnostic laparoscopy. During the procedure, the gynecologist takes a small piece of the ovary using a special instrument. Next, the sample is sent for histology. An endometrial biopsy is necessary for patients who experience bleeding outside of menstruation.
Decortication of the ovaries
Women with sclerocystic membranes are prescribed ovarian decortication. The doctor removes the transformed white surface of the organs with a scalpel or special scissors, the follicles are pierced with a needle, and their edges are sutured with special threads. This procedure helps remove the factor that prevents ovulation. The material that was removed from the ovaries is sent for histology. This type of laparoscopy is performed not only for therapeutic purposes, but also for diagnostic purposes.
Notches on the ovaries
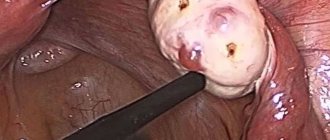
For patients with polycystic disease, to restore reproductive function, small incisions are made on the ovaries, thanks to which the functions of the organ are restored. During the process of cauterization, the ovary is fixed with special clamps and, using a laser or coagulator, incisions up to 1 cm deep are made on its shell. In this case, the surgeon makes incisions in places where translucent follicles are visible, thereby ensuring their rupture when the egg matures.
Laparoscopy: reviews for PCOS about long-term consequences
Much less often, in situations requiring repeated surgical intervention with penetration into the abdominal cavity, adhesive disease occurs in women who have undergone laparoscopic surgery. And this is observed in 90% of cases compared to laparotomy operations. Statistics also point to the fact that the incidence of postoperative inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs is much lower than with open approaches during operations on the abdominal organs.
It can be said unequivocally that there are many more advantages to such a minimally invasive method of surgical intervention, and always when choosing an access and surgical technique, the surgeon must weigh the pros and cons and make the right decision that will most appropriately meet the clinical situation in a particular case and goals and the objectives of the operation itself. Since not in all situations in surgical practice, minimally invasiveness is crucial, which should also be taken into account when choosing patient management tactics.
Preparation
The primary preparatory measure for the removal of polycystic ovary syndrome is passing all the necessary tests, including:
- general urine/blood test;
- fluorography;
- blood biochemistry with determination of the amount of bilirubin, protein, sugar;
- electrocardiogram;
- vaginal smear for microflora;
- blood for hepatitis, HIV, syphilis;
- coagulogram.
Laparoscopy for polycystic ovary syndrome is performed only if all results are normal, otherwise there is a high risk of complications. If there are any health problems, the operation is postponed to undergo a course of treatment. There is no specific recommendation regarding the day of laparoscopy: the procedure is carried out on any day of the cycle, with the exception of menstruation itself. When the patient is approved for surgery, she is sent to the hospital, where an ultrasound and ECG are additionally performed.
In the evening, the day before surgery, you should avoid eating after 19:00. Laparoscopy is performed exclusively on an empty stomach, and you cannot even drink after 22 hours the day before the operation. Such measures are necessary to reduce the risk of stomach contents entering the respiratory tract while a woman is under anesthesia. Doctors at the gynecology department ask patients to do an enema and shave their pubic area on the eve of the procedure. In the morning before laparoscopy, cleansing is repeated. In some cases, a one-time evening dose of a laxative is additionally prescribed.
Preparatory stage before surgery
After the doctor has prescribed ovarian cautery, he and the patient must choose a date for it. Before the appointed date, the woman must undergo a full examination, including:
- Submission of biological materials for analysis (blood to determine the content of formed elements, Rh factor and group, the presence of antigens and antibodies to viral hepatitis, HIV, syphilis, urine, feces for helminth eggs);
- Carrying out instrumental diagnostics (fluorography, electrocardiography, ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs, uterus and its appendages);
- Taking smears from the vagina for microflora.
How to do laparoscopy for polycystic ovary syndrome
The operation, unlike laparotomy, is performed not by cutting the abdominal tissue, but by making three small holes with a diameter of up to 1 cm. Three manipulators are passed through them to the internal organs. One of the tools is equipped with a flashlight and a camera, while the rest are needed to fix and remove cysts. During the operation, the doctor is guided by the image received on the screen. After successful completion of laparoscopy, the doctor removes instruments from the peritoneal cavity and applies sutures or simply seals the holes on the outer surface of the abdomen.
Features of preparation for surgery
Preparation for ovarian laparoscopy includes laboratory tests of blood and urine, chest x-ray, biochemical blood test, electrocardiogram and ultrasound of internal organs. If necessary or in particularly complicated cases, MRI or CT is required. The examination is carried out only if removal of the uterus and ovaries by laparoscopy is planned in advance. If urgent intervention is necessary, it is not required.
In addition, as preparation before surgery, you must follow the following recommendations from doctors:
- A few days before the proposed intervention, it is necessary to exclude psycho-emotional and physical stress. They can affect blood pressure and heart function during and after the procedure.
- Before surgery, it is better not to eat foods that cause increased gas formation. Food should be easily digestible so that it does not create additional stress on the body.
- The day before the intervention, the patient must go to the hospital. In the evening, the patient is allowed to drink a glass of kefir, sweet tea, or yogurt.
- During laparoscopy, you cannot eat anything at all in the morning. Breakfast is allowed if the operation is rescheduled for the evening.
- It is important to cleanse the intestines before surgery. Nowadays laxatives and microenemas are used for this purpose.
- When removing a tumor, cyst, or foci of endometriosis laparoscopically, it is necessary to prevent any complications in those people who are prone to them. Purulent processes are prevented by antibiotic therapy, and the formation of blood clots should also be avoided. Before removal surgery, specialists bandage the lower limbs with an elastic bandage.
If you need to operate on the ovaries, you can do this on any day of the cycle, except for the time of direct menstrual bleeding. The discharge may be too heavy. There is also a risk of bleeding that will be difficult to stop.
What laparoscopy is is already clear, but not everyone knows that its duration ranges from 20-90 minutes. It all depends on how complex the pathology is.
Recovery after laparoscopy
Recovery of tissues and organs occurs 2-6 weeks after surgery. Rehabilitation after laparoscopy for polycystic ovary syndrome requires strict adherence to medical instructions. These include:
- you cannot have sexual intercourse for 1 month after surgery (except for oral);
- Serious physical activity and hard work are prohibited for 4 weeks after laparoscopy (the maximum load allowed for lifting is 3 kg);
- You should not eat salty, hot, spicy foods;
- alcohol is prohibited;
- you should undergo a rehabilitation course of physiotherapy to speed up wound healing;
- It is recommended to take vitamin and mineral preparations such as Supradin, Vitrum, etc.
Period
Minor bloody or mucous discharge may be observed for 5-15 days after laparoscopy. The reason for contacting a gynecologist is their increased duration or abundance. After laparoscopy, the menstrual cycle does not go astray, but remains the same. Sometimes menstruation is slightly delayed after surgery, but, as a rule, no longer than a few days. Do not worry if the duration or nature of your periods changes - this is a normal reaction of the body to surgical treatment.
Nutrition
After surgery to remove polycystic disease (within 7-8 hours), the intake of still water is allowed, after which the woman is prescribed a light recovery diet. In the next 2-3 days, you are allowed to eat exclusively liquid or puree foods. Suitable products for this period will be:
- low-fat natural yogurt;
- chicken bouillon;
- pureed lean meat;
- boiled rice;
- steamed fish.
Starting from 4-5 days after laparoscopy, you can eat as you are used to, but it is better to exclude pickles, hot, spicy foods and alcohol from your diet. After surgery, the woman’s body recovers within 0.5-1 year and again acquires the ability to conceive a child. In this case, ovulation can begin as early as 2 weeks after laparoscopy (this can be determined by measuring basal temperature).
The cost of surgical intervention depends on the stage of polycystic disease, the presence/absence of complications or concomitant pathologies and the choice of medical institution. The operation cannot be called inexpensive - the price of the procedure starts from 7 thousand rubles. How much does laparoscopy cost during pregnancy? The cost of removing polycystic disease in this case is much higher, with the lower limit being 10-12 thousand rubles.
Ovulation after ovarian cauterization
Any surgical intervention in the functioning of internal organs can provoke disturbances in their functioning. So, after cauterization of the ovaries, the menstrual cycle may be disrupted. Your period may not come as scheduled. This is considered normal. In the first month after surgery, a woman is recommended to have an ultrasound scan every 2 weeks to monitor the condition of the ovaries.
If the operation is successful, ovulation occurs within 2-3 weeks. The egg is successfully released from the ovary and is ready for fertilization. Ovulation usually occurs while taking special medications.
Important! Doctors recommend refraining from open sexual intercourse in the first cycle after surgery.
If the leading specialist did not give recommendations on taking medications, and ovulation occurred on its own, this is a good sign indicating that cauterization is effective and there is a good chance of getting pregnant.
Reviews
I had a laparoscopy at a private gynecology clinic to treat my infertility. On the second day after the procedure, I was able to return home. I managed to get pregnant only after 3 years, so the operation is unlikely to have helped - it only comes with a one-year warranty. A friend underwent the same procedure and became pregnant in the third month.
My reasons for laparoscopy were persistent discomfort in the lower abdomen. The doctor said that this is not a good symptom and that surgery needs to be done. Everything went well - during laparoscopy, torsion of the cyst stalk was discovered. It was quickly removed, and the pain disappeared.
Found an error in the text? Select it, press Ctrl + Enter and we will fix everything!
Why are incisions made on the ovaries?
The doctor makes incisions on the ovaries during laparoscopy. This operation is indicated for women who have a cyst or those who cannot become pregnant. Laparoscopy is rightfully recognized as the “gold standard” in the diagnosis of infertility.
How can notches on the ovaries help you get pregnant? In order for the patient to ovulate, the egg must mature along with the follicle. For some reason, the follicle membrane interferes with its growth, which prevents the egg from maturing and being released. During laparoscopy, the doctor makes an incision in the follicle, so it can ripen unhindered, and the girl’s cycle is restored.
The lack of conception is affected by hormonal changes in the body. During certain phases of the menstrual cycle, the concentration of some hormones in the female body increases, while others decrease. Thanks to this balance and cyclicality, menstruation is stable and occurs at regular intervals. If a girl develops a cyst or has hormonal imbalances, a dense protein shell forms on the follicle, which prevents ovulation. The notches on the ovaries help the system to “reboot” and begin to function normally. We recommend you learn: About anesthesia for laparoscopy of ovarian cysts
Progress of the procedure
This operation is performed in a hospital under general or local anesthesia. On the day of the procedure, it is advisable that the patient already knows basic information about ovarian cautery: what kind of procedure it is, how long it lasts, etc. This will help to avoid excessive anxiety.
The anesthesiologist will monitor the slightest changes in the woman’s body during the operation.
After the anesthesia takes effect, the surgeon lubricates the woman's abdomen with an antibacterial solution. Next, using a special gun, he performs a puncture of the anterior abdominal wall with a diameter of 1 cm. A rigid metal tube is subsequently inserted into it, and a laparoscope is inserted through this tube.
Then the specialist makes 2 more punctures with a diameter of about ½ cm in the iliac abdomen (they should be on the sides of the main hole). To facilitate access to the ovaries and improve visibility inside the abdominal cavity, carbon dioxide is injected into it.
After this, the gonads are fixed in the most convenient position with special forceps. Using a coagulator in the form of a thick needle, 15-20 incisions are made on the surface of the ovary. The depth of each of them is 4-5 mm, and the width is 2-3 mm.
All incisions are made in the projection of cystic formations. The accumulated liquid comes out of the holes.
After completing these steps, the procedure is carried out in a similar way on the second ovary.
The surgeon sees all his actions during the operation on the monitor
There is such a variation of this manipulation as electrocauterization or, which is the same thing, diathermocauterization (incisions are applied to the ovary with an electrode, i.e. the cysts are destroyed with a high-frequency current).
After diathermocautery, the ovary is significantly reduced in size, and its dense capsule is destroyed. Thanks to this, the eggs will be able to mature normally again and leave the follicles. When all the main work is done, the specialist releases carbon dioxide from the patient’s abdominal cavity and applies stitches.
The duration of the operation is about 40 minutes.
Important! Cauterization is so effective that many women regain the ability to conceive within the first month after it. However, doctors advise thinking about pregnancy only for 2-7 months.
Consequences
After the patient has incisions made on the ovaries, she needs to rest more on the first day and, if possible, stay in bed. Laparoscopy has no negative consequences, so the woman can return to her usual lifestyle the very next day after the operation.
Many girls are worried about how soon they can get pregnant after this procedure? Doctors say that healing occurs very quickly, the menstrual cycle is restored in the shortest possible time. Thus, the patient will be able to become pregnant a few months after the operation.
It should be noted that after laparoscopy, a woman must register with a gynecologist. In some cases, the doctor may admit the patient to the hospital for close monitoring. To restore hormonal levels, a woman is prescribed medication.
The chance of becoming pregnant within a few months after ovarian laparoscopy is 80%. In very rare cases, cutting the ovaries does not help a woman become pregnant. Then the gynecologist may prescribe a repeat procedure for her. The most important thing is not to despair ahead of time. Each woman’s body is individual, so it needs a certain amount of time to recover. In some patients, pregnancy can occur even a year after ovarian laparoscopy.
We recommend you find out: Are your periods regular after ovarian laparoscopy?
Rehabilitation period
After the operation, the patient is placed in a hospital for approximately 3-7 days, where her condition is monitored by doctors. On the second day, the woman is allowed to take food in liquid form. After discharge from the hospital, the patient must follow the following clinical recommendations:
- give up cigarettes and alcohol;
- adhere to a certain diet (necessary to restore intestinal functions);
- take vitamin complexes, immunostimulating medications and hormonal agents;
- avoid physical overload.
To avoid secondary infection, puncture sites should be treated with antiseptic compounds.
In the first month after surgery, women are advised to move more. Food should be taken in small portions 5-6 times a day. In order to prevent infection during the rehabilitation period, it is necessary to avoid sexual contact and be sure to follow the rules of intimate hygiene.
It takes about one month to fully restore the body after cauterization. The duration of the rehabilitation period directly depends on the individual characteristics of the patient’s body.
After surgery for polycystic disease, menstruation may be delayed. The menstrual cycle is restored within several months. The duration of this period is different for each woman.
Laparoscopy, incisions on the ovaries
Hello everyone. Please share your information. On July 16, they did a laparoscopy, incisions on the ovaries, tubal patency, and took some kind of analysis from the uterus. The doctor said that the tubes are well passable (no adhesions), the location of the uterus is good, the ovaries are good, but they made incisions as they wanted. On day 7, the stitches were removed and sent home. The only thing that worries me is the month of sexual rest. My husband works shifts and he’s leaving in a month, meaning we won’t even try this month and we’ll miss the next month. Our chances are zero. Please tell us who, after such an operation and after how long, began to be sexually active and what the consequences were
Woman.ru experts
Find out the opinion of an expert on your topic
Svetlana Borisova
Psychologist. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Elena Vladimirovna Akchalova
Psychologist, Clinical psychologist. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Boyko Inessa Borisovna
Psychologist, Online consultant. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Kuzmin Ivan Ivanovich
Psychotherapist, Supervisor. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Svetlana Kazakova
Psychologist. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Antakova Lyubov Nikolaevna
Psychologist, Consultant. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Olga Matvienko
Psychologist, Art therapist. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Baranova Yulia Germanovna
Psychologist, Consultant. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Tropina Natalya Vladimirovna
Psychotherapist. Specialist from the site b17.ru