Resistant ovarian syndrome is a gynecological disease that occurs in young women under 35 years of age. The pathology is quite rare and is characterized by infertility and amenorrhea. To make a correct diagnosis, diagnostic methods such as ultrasound, various kinds of hormonal tests, and biopsy are used. This condition is mainly treated with hormonal therapy. Unfortunately, in most cases, such therapy does not bring the desired result, and therefore the chances of getting pregnant are not high. And often the only opportunity to have a child is to resort to the help of reproductive medicine.
Causes
Resistant ovarian syndrome has ICD code E28, which is also commonly called Savage syndrome in medicine. The reasons for its occurrence are not fully known, so it is still considered a little-studied phenomenon in the practice of doctors. It is possible that the formation of pathological anomalies is associated with disorders at the genetic level that have arisen in the receptor apparatus of the follicles.
There is also a theory that Savage syndrome occurs due to autoimmune diseases/disorders, since antibodies that can block the sensitivity of FSH receptors in paired female gonads are often found in the blood of the fairer sex.
According to statistics, Savage syndrome very often appears against or simultaneously with the following diseases:
- Hashimoto's disease;
- myasthenia gravis;
- diabetes;
- hyperthyroidism;
- hypoparathyroiditis;
- manifestation of platelet purpura;
- tuberculosis;
- sarcoidosis;
- hemolytic anemia;
- primary immune thrombocytopenia.
Treatment of the syndrome
Therapy for this disease poses significant difficulties, since its pathogenesis has not been established. Restoration of reproductive function can occur in an extremely limited number of cases.
Treatment is carried out comprehensively, involving doctors from various specialties, primarily a gynecologist and an endocrinologist.
Until now, there is debate in medicine about the advisability of hormone replacement therapy using gonadotropic hormones. There is an opinion that their introduction into the body can help remove the blockage from receptors in relation to hormones that stimulate follicle growth. In clinical practice, there are quite a lot of cases of restoration of fertility after taking it, but there is no reason to talk about the absolute effectiveness of such treatment.
Proponents of the autoimmune theory of the occurrence of resistant ovarian syndrome propose the following treatment regimen for the pathology:
- prescribing drugs to artificially suppress immunity, for example, glucocorticoids;
- replacement therapy with female sex hormones;
- purification of blood plasma from antibodies.
Physiotherapeutic procedures are indicated as additional therapeutic measures, for example, intravaginal ultraphonophoresis, acupuncture, spa treatment, and taking vitamin complexes containing vitamin E.
Among hormonal drugs, Femoston is usually prescribed, which is considered the gold standard for the treatment of hormonal disorders associated with ovarian dysfunction.
Expert opinion
Daria Shirochina (obstetrician-gynecologist)
Since the treatment of resistant ovarian syndrome is carried out with potent drugs aimed at correcting hormonal levels and immune status, independent selection of drugs is strictly contraindicated, since this can lead to serious negative consequences.
Other drugs used in the complex treatment of pathology include drugs usually used to relieve the symptoms of menopause, for example, Klinonorm, Klimen, Kliogest and others.
To normalize the condition, a woman is recommended to review her diet by including more foods high in vitamin E and lecithin in her daily diet: nuts, legumes, cauliflower, caviar.
Various herbal infusions with an analgesic effect, for example, a decoction of peppermint, chamomile and valerian root, can complement the therapeutic effect. Taking any remedy based on traditional recipes requires consultation with a doctor.
https://youtu.be/cOcgsxMEPi0
Risk group
There are also a number of factors that can lead to Savage syndrome, the main ones include:
- taking immunosuppressive drugs for a long period of time;
- treatment using radiotherapy methods;
- use of antitumor drugs;
- surgical interventions affecting the ovaries.
The following factors often lead to the manifestation of pathology:
- previous viral infection;
- stress and psycho-emotional stress;
- exhaustion;
- taking antibacterial drugs from the sulfonamide group.
Signs of Resistant Ovarian Syndrome
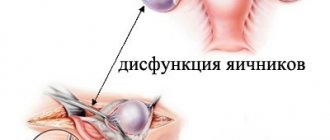
Resistant ovarian syndrome, the symptoms of which are similar to some other diseases, is difficult to recognize only by the first signs. To make a diagnosis, the doctor prescribes additional diagnostics based on the medical history obtained. The main symptom of Savage syndrome is irregular menstrual flow, and then the complete absence of menstrual periods in young women under 35 years of age. The absence of menstrual flow in this case is characterized by the exclusion of symptoms characteristic of menopause (increased sweating, rapid pulse, feeling of heat, etc.). The physique of patients suffering from resistant ovarian syndrome is no different from ordinary women; they also have physiologically correctly developed organs of the genitourinary and reproductive systems. Fibrocystic mastopathy is often found in the mammary glands of women with this pathology. Women often have a genetic predisposition to this pathology associated with the female genital organs and organs of the reproductive system. When collecting anamnesis, patients often do not tell about the presence of various autoimmune diseases, frequent infectious diseases, or previous abortions. Resistant ovarian syndrome is characterized by all of the above except the typical signs of menopause.
Prevention
Since the true cause of the disease is unknown, there is no specific prevention. However, taking into account the factors that provoke the disease, the following measures to prevent the disease can be formulated:
- prevention of acute infectious diseases, in particular, timely vaccination against influenza;
- promptly consult a doctor if bleeding, hair loss, constant slow or rapid heartbeat, mental changes, unexplained weakness and other signs of autoimmune diseases appear;
- effective treatment of ovarian diseases, with the goal of preserving as much of their normally functioning tissue as possible;
- annual preventive examination by a gynecologist;
- maintaining a healthy lifestyle, which in many cases helps maintain the overall good condition of all organs and systems and prevent serious illnesses.
Diagnosis of resistant ovarian syndrome
When the first symptoms of EOC appear, you must seek medical help from a specialist who, after carefully studying the clinical picture of the disease, will be able to make the correct diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment. The doctor collects anamnesis, asking the woman about genetic diseases, the duration of the menstrual cycle, its regularity, previous sexually transmitted diseases, abortions and miscarriages. If resistant ovarian syndrome is suspected, diagnosis may consist of the following studies:
- Ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs.
- General blood and urine analysis.
- Ultrasound of the female genital organs.
- Blood test for various hormones.
- Gynecological examination of a woman.
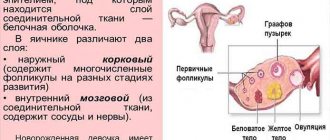
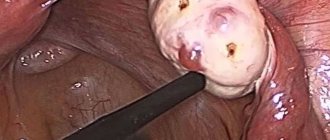
During the examination, the patient is prescribed histology. Diagnostic laparoscopy is often used, with the help of which follicles can be seen in the ovaries. Sometimes doctors prescribe CT and MRI. Sonographic signs of resistant ovarian syndrome (such as a decrease in uterine parameters) are not always able to help in making a diagnosis. Therefore, in such cases, a biopsy and histological examination are prescribed. For patients over 40 years of age, annual mammography, pelvic ultrasound, densitometry (to exclude osteoporosis), and blood tests for cholesterol and lipoproteins are recommended.
Symptoms
The disease is most often detected in patients under 35 years of age and is characterized by the fact that the ovaries cannot function normally. Its symptoms include amenorrhea and infertility.
Manifestations of SRS:
- Hot flashes are sometimes the main symptom of the pathology, but they are of low intensity and are not accompanied by vegetative problems (weakness, nausea, dizziness), which makes it possible to differentiate EOC from ovarian wasting syndrome.
- Amenorrhea. The first menstruation begins on time. However, after a while, your periods weaken or stop coming. Most patients experience discharge similar to menstruation, which is irregular and occurs quite rarely.
- Oligomenorrhea, when the interval between menstruation is more than 40 days or the bleeding itself lasts no more than two days. In this case, the patient has up to 8 cycles per year.
- Hormonal abnormalities:
- insufficient production of estrogen, manifested by redness and thinning of the mucous membrane of the external genital organs,
- laboratory: increased concentration of gonadotropins (FSH and LH), normal prolactin levels and estradiol deficiency.
Rarely, ROS occurs before puberty. In this case it is observed:
- absence of menstrual bleeding,
- defective formation of secondary female sexual characteristics,
- primary infertility.
Treatment
Prescribing treatment is complicated by the fact that the causes of the pathology are not fully known. In most cases, doctors resort to drug treatment. Women are prescribed two or three phase hormone replacement therapy. Its main goals are aimed at restoring the state of estrogen deficiency, normalizing the regularity of women's days, and reducing the amount of gonadotropins. As methods of contraception, young patients are prescribed Estradiol with Dydrogesterone, Norethisterone, Medroxyprogesterone or Cyproterone. Among drug treatments, acupuncture is popular. With the help of special acupuncture needles, a positive effect is exerted on the prescription regions of the ovaries. Ultraphonophoresis with vitamin E also has a positive effect. Homeopathy is powerless in this case.
Forecast
Unfortunately, the prognosis for natural pregnancy in a normal cycle is disappointing. Often such patients already have children born at an early age in a completely natural way. However, after the manifestation of ovarian receptor disorders, the chances of spontaneous pregnancy drop sharply.
With quick and timely treatment, natural pregnancies occur while taking HRT, but more often it happens to resort to IVF programs, often with a donor egg.
https://youtu.be/IfhXAqWJkNs
Pregnancy
Conceiving with resistant ovarian syndrome, pregnancy in most cases is only possible with the help of IVF. For in vitro fertilization, donor eggs are used. A long or short protocol is prescribed only after a thorough examination. Medicine also knows cases of natural fertilization with resistant ovarian syndrome, but they are extremely rare.
Diagnostics
The main direction in terms of diagnostic studies is the exclusion of organic pathology. That is, the emphasis is on differential diagnosis. Collecting anamnesis and complaints is half of a correct diagnosis. It is almost impossible to establish objectively the manifestations of pathology. Only with a long course of the disease does the gynecologist, during a vaginal examination, see the signs of hypoestrogenemia, which were discussed above.
General urine and blood tests do not show any specific changes. Biochemical research too. An ultrasound of the pelvic organs is prescribed. Ultrasound examination showed that the ovaries were enlarged in size. No more changes typical for paralyzed ovarian syndrome are detected with this method. The follicles are visible and their sizes range from 5 to 6 mm. Their structure has not been changed. The uterus is not enlarged. The endometrium is usually thinned due to depletion of estrogen content.
Laparoscopy allows you to clearly see the external parameters of the pelvic organs. There are many “translucent” follicles in the ovaries, but their sizes do not exceed 0.6 cm, which indicates their immaturity. A mature or dominant follicle cannot be detected. But hormone tests play a decisive role in diagnosis.
At the beginning, their initial level is determined. Refractory ovaries are characterized by an increase in the content of gonadotropic hormones in the blood - follicle-stimulating and luteinizing. In turn, estrogen and estradiol are reduced. Prolactin levels are consistently normal. The first test is a gestagen test. It should be negative for refractory ovarian syndrome. The clomiphene test is also negative. It excludes the hypothalamic level of pathology. The test with estrogen and gestagens is positive. In response to the introduction of sex hormones, the concentration of gonadotropic hormones in the blood decreases. This once again confirms that the ovaries are to blame for the pathogenesis of amenorrhea and infertility. That is, the pathology is not pituitary, not hypothalamic.
Consequences and prognosis
Insensitivity to hormonal stimulation in resistant ovarian syndrome has a negative impact on a woman's health. When such disorders occur, patients are faced with irregular menstrual cycles. Possible complications include infertility, which is difficult to treat. The diagnosis of infertility is perceived by patients as extremely difficult and painful; many become depressed and no longer see the meaning in life. Serious consequences include the possible development of malignant oncological diseases affecting the female organs of the reproductive and genitourinary systems. With timely diagnosis of the syndrome and properly selected treatment, the menstrual cycle can be restored.
Causes of Savage syndrome
As a result of the disease, the appendages stop “responding” to gonadotropic stimulation and do not produce sex hormones.
The reason why ovarian resistance occurs has not been reliably established. It is believed that the pathology develops due to autoimmune damage to gonadotropin receptors. This position is partially proven by the fact that EOC often occurs in combination with the following deviations:
- thrombocytopenic purpura,
- weakness of the muscular system due to autoimmune damage,
- diabetes mellitus,
- hemolytic anemia (autoimmune nature).
Antibodies are found in the blood of patients that block receptors that respond to gonadotropins in the ovaries. There is an opinion that ROS develops as a result of a change in the structure of the FSH molecule or its inactivity.
Pathology may be due to the reasons listed below:
- undergoing radiation therapy,
- taking pills that suppress the immune system and cytostatics,
- surgical interventions on the appendages.
The impetus for the development of SRY are:
- infections affecting ovarian tissue,
- taking large doses of sulfonamides,
- stressful situations.
Recommendations
There are no preventive measures that can completely eliminate the occurrence of ovarian pathology. There are a number of rules that can reduce the risk of its possible development:
- It is necessary to lead a healthy lifestyle, play sports, and give up bad habits.
- Avoid the occurrence of infectious diseases. To do this, you should strengthen the immune system: take vitamin complexes, harden yourself.
- Using condoms during sexual intercourse with untested sexual partners will help prevent the development of sexually transmitted diseases.
- When the first signs of sexually transmitted diseases appear, you should immediately contact a specialist and begin treatment.
- Avoid stressful situations and nervous tension, alternate between work and sleep.
- If there is a hereditary predisposition to the pathology, you must inform your doctor about this and regularly undergo the diagnostics prescribed by him.
Video: Resistant ovarian syndrome