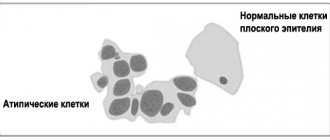
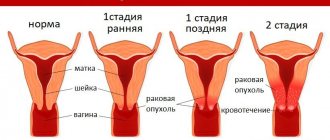
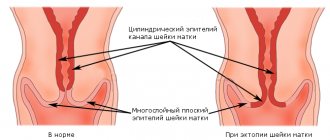
What is cervical dyskaryosis?
This is a pathology during which changes occur in the cellular composition. The nucleus becomes larger than the cytoplasm. In a normal state, everything should be the other way around.
Timely detection of cell degeneration can protect a woman from cancer. If you do not contact a specialist at the initial stage, then there will be a large number of affected cells, and this is how cancer begins.
What it is? This is a precancerous condition that can be cured and prevent serious consequences.
In the photo you can see the uterine cervix with dyskaryosis, cancer and in normal condition.
https://youtu.be/VvEJ9n9oQ1M
The essence of the disease and some statistics
Cervical dysplasia is a pathological process characterized by changes in the structure of the cells of the mucous membrane of the cervix, expressed by thickening, proliferation, impaired maturation of epithelial cells and their rejection by cervical cells. Many people confuse cervical dysplasia with erosion, but these diseases have a significant difference: with erosion, only the integrity of the mucous membrane of the cervix is damaged, and with dysplasia, deeper layers are affected. The frequency of diagnosing cervical dysplasia is 1–2 cases per 1000 women.
Causes of the disease
This disease can be caused by various factors. This:
- disturbance of vaginal microflora;
- vaginal candidiasis;
- bacterial infections;
- human papillomavirus (HPV);
- STD.
If you have chlamydia, trichomonas, herpes and gonococci, you should also be on guard. Women who suffer from hormonal imbalances are also susceptible to this disease. The risk group includes pregnant women and women experiencing menopause.
Secondary causes include:
- early sexual life;
- frequent change of partners;
- poor quality nutrition;
- bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol);
- frequent abortions, unsuccessful cleansing;
- the use of birth control pills that affect hormonal levels;
- rudeness of the partner during sexual intercourse;
- endometriosis;
- myoma;
- cervical injury.
Interpretation of cytological examination results
The most common at present is the Bethesda classification (The Bethesda System), developed in the USA in 1988, to which several changes have been made. The classification was created to more effectively transfer information from the laboratory to clinical doctors and ensure standardization of treatment of diagnosed disorders, as well as follow-up of patients.
The Bethesda classification distinguishes squamous intraepithelial lesions of low grade and high grade (LSIL and HSIL) and invasive cancer. Low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions include changes associated with human papillomavirus infection and mild dysplasia (CIN I), high-grade - moderate dysplasia (CIN II), severe dysplasia (CIN III) and intraepithelial carcinoma (cr in situ). This classification also contains indications of specific infectious agents that cause sexually transmitted diseases.
To designate cellular changes that are difficult to differentiate between reactive states and dysplasia, the term ASCUS - atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance (squamous epithelial cells with atypia of unclear significance) has been proposed. For a clinician, this term is not very informative, but it directs the doctor to the fact that this patient needs examination and/or dynamic monitoring. The Bethesda classification has now also introduced the term NILM – no intraepithelial lesion or malignancy, which combines normal, benign changes, and reactive changes.
Since these classifications are used in the practice of a cytologist, below are parallels between the Bethesda classification and the classification common in Russia (Table 22). Cytological standardized report on material from the cervix (form No. 446/u), approved by order of the Ministry of Health of Russia dated April 24, 2003 No. 174.
The reasons for receiving defective material are different, so the cytologist lists the types of cells found in the smears and, if possible, indicates the reason why the material was considered defective.
Cytological changes in the glandular epithelium
| Bethesda Terminology developed in Bethesda (USA, 2001) | Terminology adopted in Russia |
| ASSESSMENT OF SWIM QUALITY | |
| Full material | The material is adequate (a description of the cellular composition of the smear is given) |
| The material is not complete enough | The material is not adequate (a description of the cellular composition of the smear is given) |
| Unsatisfactory for evaluation | Cellular composition is not enough to confidently judge the nature of the process |
| Satisfactory to evaluate, but limited by something (identify reason) | |
| Within normal limits Metaplasia (normal) | Cytogram without features (within normal limits) - for reproductive age Cytogram with age-related changes in the mucous membrane: - atrophic type of smear - atrophic type of smear with leukocyte reaction Estrogenic type of smear in a postmenopausal woman Atrophic type of smear in a woman of reproductive age |
| BENIGN CELL CHANGES | |
| Infections | |
| Trichomonas vaginalis | Trichomonas colpitis |
| Fungi morphologically similar to the genus Candida | Elements of Candida fungus detected |
| Cocci, gonococci | Diplococci located intracellularly were found |
| Predominance of coccobacillary flora | Flora coccobacillary, possibly bacterial vaginosis |
| Bacteria morphologically similar to Actinomyces | Flora of the Actinomycetes type |
| Other | Flora of the type Leptotrichia |
| Flora – small sticks | |
| Flora – mixed | |
| Cellular changes associated with Herpes simplex virus | Epithelium with changes associated with Herpes simplex |
| Possibly chlamydial infection | |
| Reactive Changes | |
| Inflammatory (including reparative) | The changes found correspond to inflammation with reactive changes in the epithelium: degenerative, reparative changes, inflammatory atypia, squamous metaplasia, hyperkeratosis, parakeratosis, and/or others. |
| Atrophy with inflammation (atrophic | Atrophic colpitis Atrophic type of smear, leukocyte reaction Mucosal epithelium with hyperkeratosis Mucosal epithelium with parakeratosis Mucosal epithelium with dyskeratosis Reserve cell hyperplasia Squamous metaplasia Squamous metaplasia with atypia |
| Radiation changes | Epithelium of the mucous membrane with radiation changes |
| Changes associated with the use of intrauterine contraceptives | |
| PATHOLOGICAL CHANGES IN THE FLAT EPITHELIUM | |
| Squamous epithelial cells with atypia of undetermined significance (ASC-US*) Squamous epithelial cells with atypia of undetermined significance not excluding HSIL (ASC-H) | The changes found are difficult to differentiate between reactive changes in the epithelium and dysplasia. Cells were found that were difficult to interpret (with dyskaryosis, enlarged nuclei, hyperchromic nuclei, etc.) |
| Changes in squamous epithelium (non-tumor, but worthy of dynamic observation) | |
| Low grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (LSIL): human papillomavirus infection, mild dysplasia (CIN I) | Epithelium of the mucous membrane with signs of papillomavirus infection. The changes found may correspond to mild dysplasia. |
| High-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL): moderate, severe dysplasia and intraepithelial carcinoma (CINII, CIN III) | The changes found correspond to moderate dysplasia. The changes found correspond to severe dysplasia. The changes found are suspicious for the presence of intraepithelial cancer. |
| Invasive cancer | |
| Squamous cell carcinoma | Squamous cell carcinoma Squamous cell carcinoma with keratinization Small cell squamous cell carcinoma |
| Glandular hyperplasia The changes found correspond to endocervicosis | |
| Atypical glandular epithelial cells (possible assumptions): – Unclear significance (AGUS); – suspicious for neoplasia; – endocervical adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS); – adenocarcinoma | Glandular hyperplasia with atypia of the dysplasia type (I, II, III) Adenocarcinoma |
| Endometrial cells are cytologically benign (in a woman in menopause, etc.) | |
| Endometrial adenocarcinoma Adenocarcinoma of another location Adenocarcinoma without additional characteristics | Adenocarcinoma, possibly endometrial adenocarcinoma Adenocarcinoma NOS (not otherwise specified) |
| Other malignant tumors (if possible, determine the nosological form) | |
| Assessment of hormonal status | |
* whenever possible, ASCUS should be defined as similar to reactive, reparative or precancerous processes;
** changes associated with exposure to human papillomavirus, previously designated as koilocytosis, koilocytic atypia, condylomatous atypia, are included in the category of mild changes in squamous epithelial cells;
*** If possible, it should be noted whether the changes relate to CIN II, CIN III, whether there are signs of cr in situ;
****hormonal assessment (carried out only on vaginal smears): – the hormonal type of smear corresponds to age and clinical data; – the hormonal type of smear does not correspond to age and clinical data: (decipher); – hormonal assessment is impossible due to: (specify the reason).
Symptoms
There are no symptoms for this pathology. A precancerous condition can be detected by examining the female genital organs in a gynecological chair.
It should be noted that dyskaryosis of the uterine cervix often occurs with various diseases. These include:
- colpitis;
- cervicitis;
- chlamydia;
- gonorrhea;
- the occurrence of genital warts.
If an infectious disease occurs, the woman will feel itching, burning, and discharge with an unpleasant odor will be visible on her underwear. Usually it is with these symptoms that a woman comes to her appointment. Upon examination, the doctor finds a completely different reason that needs to be dealt with.
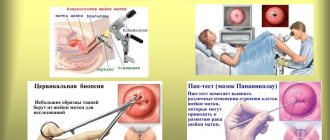
A gynecological examination alone is not enough to establish a residual diagnosis. The patient is required to undergo tests. You need to take a PAP smear. This cytological examination reveals atypical cells. HPV can also be detected here. In addition, a histological examination should be performed. Tissue samples taken will help determine the diagnosis.
The lady also undergoes colposcopy. The picture will increase several times, and the specialist will be able to examine the entire affected area in detail. The doctor will immediately treat the tissues with a special solution, as a result of which we can say with confidence whether any abnormalities are present.
Diagnosis of dysplasia
The clinical picture has no characteristic signs and, as a rule, is asymptomatic. The complaints are due to related
gynecological diseases. When viewed in mirrors
You can observe ectopia of the cervix of various sizes, white spots of leukoplakia, papillomas, and even a visually unchanged cervix.
One of the diagnostic methods is colposcopy (examination of the cervix using a microscope), in which the picture can also be very diverse - from ordinary ectopia to leukoplakia, silent iodine-negative areas, areas of atypical transformations of squamous epithelium.
Discaryosis
A mandatory test is to take a cytological smear from the cervix
, where cells with dikaryosis are detected.
Dyskaryosis
is a borderline condition in which cell atypia is expressed mainly in the cell nuclei, while in cancerous conditions changes are found in both the nuclei and the cytoplasm. If dyskaryosis is detected, a histological examination is indicated, which allows a final diagnosis. To do this, a targeted biopsy of the cervix and diagnostic curettage of the mucous membrane of the cervical (cervical) canal are performed. The results of histological examination make it possible to determine the degree of changes in the cervical epithelium and outline the nature of treatment measures.
Treatment
Treatment of the cervix will be prescribed after a complete diagnosis. Only after the test results are known and the degree of pathology is determined, the gynecologist has the right to prescribe appropriate therapy. If a woman is carrying a child, treatment will have to wait, since the medications used can harm the baby.
Vaginal suppositories
In case of moderate or mild pathology, when the affected cells are single, the treatment is conservative. The woman will be treated at home. It is recommended to take immunomodulators, vitamin complexes, and a balanced and nutritious diet. Special vaginal suppositories are prescribed. They restore the vaginal microflora and enable tissues to recover as quickly as possible. Administration should be done in a lying position. After the procedure, it is not advisable to get up for half an hour. If a vaginal capsule or suppository was prescribed once a day, then it should be used before bedtime so as not to get up after its administration.
Justified use:
- "McMirror." Prescribe one suppository once a day. The course of treatment is a week.
- "Lactonorma". Administration is carried out using an applicator or manually. Depending on the situation, a capsule is prescribed once or twice a day. Duration of use is 1-2 weeks. If necessary, the course is increased.
- "Acylacta". Inserted into the vagina twice a day. The first administration is carried out in the morning, after which you need to not get up for half an hour so that the composition can dissolve. The course of treatment is a week.
- "Lactozhinalya". The capsule is moistened before use so that it quickly dissolves in the vagina. It is recommended to use it once a day for two weeks, or twice a day for a week.
The duration of use and dosage of a particular drug may be changed depending on the situation. Everything is individual for each patient. Only a doctor can prescribe; self-medication is unacceptable. If, after the completed course of treatment, pathologically changed cells remain in the repeated smear, then colposcopy is performed.
Colposcopy
A special device, a colposcope, helps to see pathologically changed areas in an enlarged size. Also, during the examination, the doctor makes special tests. Treating the suspicious area with iodine or vinegar solution, he will monitor their further condition. If the tissue is healthy, it will darken; if not, it will remain the same color. If necessary, a biopsy is taken immediately. A tissue sample can only be taken if there is no inflammation.
Conization
If the cervix is severely affected, that is, dyskaryosis is of the second or third degree, conization should be done immediately. In this operation, the surgeon removes an area of tissue using a scalpel or laser knife. Afterwards, the resulting material is sent for histological examination.
You can also cure dyskaryosis using cauterization with a radio wave, liquid nitrogen or laser.
For mild cases, therapy is not prescribed. The gynecologist will only observe the ongoing process and take oncocytological analysis every six months. Often the pathology goes away on its own.
After surgery, you need to visit the hospital to prevent relapse. After three to four months, the woman needs to appear and have a cytological smear. In the future, this must be done every quarter for 12 months. Afterwards, routine examinations are carried out every six months in a gynecological chair using mirrors.
To avoid developing the disease in the future, you should:
- eat well;
- take more vitamins;
- carry out sanitization of the genital organs in a timely manner if any infection occurs;
- stop smoking;
- use condoms during casual sex;
- visit an obstetrician-gynecologist’s office every six months for a preventive examination;
- have a permanent partner.
Degrees of dysplasia: 1st – mild, 2nd – moderate, 3rd – severe
Depending on the prevalence of the pathological process, dysplasia is classified into mild, moderate and severe.
Mild dysplasia (grade 1)
characterized by proliferation of the deepest layers of squamous epithelium (its lower third) - basal and parabasal, while the cells of the upper part of the layer are mature, differentiated and retain their normal structure.
For moderate dysplasia (grade 2)
the involvement of the lower two-thirds of the epithelial layer in the pathological process is noted.
With mild and moderate dysplasia, cell atypia is not observed.
Severe (grade 3) dysplasia
differs in the following features: maturation and differentiation of cells is maintained only in the surface layer of squamous epithelium, cells with atypia appear.
Thus, in the modern morphological classification, there are 3 degrees of dysplasia: degree 1 - mild, degree 2 - moderate, degree 3 - severe. To date, it has been established that all these conditions are successive stages in the development of one malignant process.
Consequences and complications
If a woman seeks medical help in a timely manner, the outcome is positive in 95%. After radical treatment, relapses occur in 7-8% of cases. The reason for this is the inexperience of the specialist who did not remove the entire affected area or the presence of the human papillomavirus. All the other ladies lead the same lifestyle and can even conceive a child. Pregnancy should be monitored at all times, since after conization of the uterine cervix, problems with bearing the fetus are possible.
60% of women who do not treat dysplasia become victims of cancer. The degeneration of cells into a malignant tumor entails difficult treatment. This includes long-term chemotherapy and radiation. It is not a fact that even after this the lady will live more than five years.
Dyskariosis
Dyskaryosis is an abnormal condition of a cell when its nucleus has a number of signs indicating an early stage of the cell’s degeneration into a malignant tumor, while the cell cytoplasm remains completely normal.
Observed, for example, in squamous and columnar epithelial cells of a smear obtained from the cervix. This is how modern doctors write about it. However, I would like to note that there is no such diagnosis in the Great Medical Encyclopedia. Dyskaryosis is not a diagnosis, it is a term and nothing more.
Let's define the concept - Diagnosis. What is it and what is it eaten with? Here is a definition of the concept of Diagnosis from the Great Medical Encyclopedia:
The diagnosis presupposes the commonality of principles and methods of diagnosis, treatment and prevention of certain groups of diseases, but does not exclude reasonable deviations in specific conditions. According to this generally accepted approach, the leading principle in the construction of D. is the nosological principle, i.e. the diagnosis must contain the name of a specific disease (injury), reflecting its essence. Other elements of clinical diagnosis clarify this essence (according to etiology, pathogenesis, functional disorders, etc.) or give an idea of the course, complications of the disease, etc. Thus, in clinical D., in a number of cases, periods of exacerbation or remission of the disease (for example, peptic ulcer disease, chronic bronchitis), its stage (for example, in hypertension, sarcoidosis) are indicated; in the presence of an inflammatory process, its phases (active, inactive) and degree of activity; The course of the disease is characterized (acute, subacute, protracted or chronic).
When formulating Dagnosis, the main disease is indicated in the first place, complications of the main disease in the second place, and concomitant diseases in the third place. The main disease is considered to be a disease (injury), which itself or through a complication associated with it was the reason for seeking medical care or hospitalization or death of the patient. It must correspond to the nosological form (for example, cholelithiasis) and be formulated according to the nosological classification of diseases, and not as a syndrome (for example, obstructive jaundice) or a list of symptoms (for example, vomiting, abdominal pain). It is unacceptable to express the underlying disease using a group concept, for example, “nephritis” instead of “acute glomerulonephritis” or “acute pyelonephritis,” etc. A complication is a secondarily occurring pathological condition or pathological process that is pathogenetically related to the underlying disease. Concomitant diseases are considered to be diseases that the patient has, which are independent, etiologically and pathogenetically not related to the main disease of the nosological form, and have their own nomenclature classification.
Based on what is written above, we come to the conclusion that dyskaryosis can be used as a term for one of the results of a patient’s examination when making a diagnosis, but not as an independent diagnosis. To make it more clear, this is like the term “low hemoglobin” for anemia or other diseases.
Unfortunately, people are too accustomed to trusting doctors, not thinking at all that they can fool them for their own benefit. At best, they may be wrong. A striking example of this is the hype around swine flu. They scared people - they made money.
Let's continue further.
14:21 23-11-2004 / Veronica...
Good afternoon, I had a medical examination at work, the result of the smears was bad - an inflammatory process, dyskaryosis. The gynecologist prescribed the following treatment - 10 days of douching with oak and chamomile bark and a suppository with syntomycin, then 10 days of a suppository with methyluracil. I am 54 years old, at the age of 50 I had my uterus and cervix removed (fibroids), I do not feel any signs of menopause. What is the health prognosis, will it really be cancer?
Answers
# 10:55 11/24/2004 Tatyana Borisovna Malanova
No, it’s a banal inflammation of the vaginal mucosa. Don't worry.
Have you carefully read what is written in bold? Now imagine the condition of a person who was told that he may have cancer in the “female line”, and of those organs that have already been removed! What can you call it? In a state of fear for his life, a person is ready to do anything. Now imagine how many women have been given a non-existent diagnosis and what condition they are in. These doctors have no conscience. I respect medical professionals, but not like this. Unfortunately, there are very few real medicines left and they are difficult to find, just like a good healer.
Almost all sources refer to the human papillomavirus, or more precisely, some of its strains, which can lead to cancer. Actually, this virus mainly causes hanging moles and warts, but this is already “cosmetics”, although unpleasant and can have its consequences. And now I want to understand what the connection is between this virus and dyskaryosis, but I just can’t.
Below is the full article by one of the doctors:
Precancerous diseases of the cervix
Precancerous diseases of the cervix are called dysplasia. The term was approved at the WHO session in 1972 and is a morphological concept, that is, such a diagnosis can only be made as a result of cytological or histological examination. Dysplasia is characterized by impaired maturation and differentiation of squamous multilayer epithelial cells covering the cervix. At the same time, basal and parabasal cells with polymorphism appear at different levels of the multilayered squamous epithelium. In addition, dysplasia is characterized by hyperplasia, hypertrophy, hyperchromia, increased mitotic activity, and an increase in the nucleus-cytoplasm ratio (the nuclear-cytoplasmic index increases to 0.7). In the cervical canal with dysplasia, pronounced hyperplasia of reserve cells is observed.
Depending on the severity, there are three main forms of dysplasia: mild, moderate and severe. With mild dysplasia, there is a moderate proliferation of epithelial cells of the basal and parabasal layers, while the cells retain their normal structure and polarity of location. In individual cells of the basal and parabasal layers, the phenomena of dyskaryosis are observed. With moderate dysplasia, the pathological process involves from 1/2 to 2/3 of the thickness of the epithelial layer. The phenomena of dyskaryosis are observed in many cells; proliferating cells are present in all layers of the epithelial layer. Severe (severe) dysplasia is characterized by a random arrangement of cells of the basal and parabasal layers, which occupy almost the entire thickness of the MPE. Nuclear hyperchromatosis is pronounced, the nuclei are large, and mitoses are common. The phenomena of dyskaryosis are observed in almost all layers of the epithelial cover. Normal cell maturation and differentiation occur only in the most superficial part of the epithelial layer, which distinguishes this condition from Ca in situ.
There is no specific clinical picture for dysplasia. Half of the patients have no complaints at all, while in the rest the symptoms are due to concomitant gynecological diseases.
Visually, when examined in mirrors and during colposcopy, the so-called atypical mucous membrane can be detected, which occurs in 3.5 to 16.2% of the total number of colposcopic examinations (J. Holtorf, 1958; V. N. Kustarov, V. A Linde, 2002). In this case, the mucous membrane of the cervix may have iodine-negative areas, various variants of dyskeratosis (leukoplakia, mosaic, punctation), papillomatous and condylomatous changes. Moreover, over time or as a result of treatment of inflammatory diseases, correction of hormonal disorders, the condition of the mucous membrane of the cervix may change, and some elements may transform into others. At the same time, dysplastic processes of the cervix may become less pronounced or disappear completely. In this regard, a wait-and-see approach is acceptable, monitoring the dynamics of the process for mild and moderate dysplasia, for which the possibility of regression is quite high with conservative treatment. With severe dysplasia, the likelihood of developing cervical cancer significantly increases, which requires active management tactics for patients with this pathology. In this case, wait-and-see tactics with repeated cytological examination of smears are unacceptable. The main method of treatment for severe dysplasia is removal of the cervix, followed by a thorough histological examination of the resulting material.
L. Cysloparova
You see how scary and clever everything is, or rather abstruse! I continue to adhere to my opinion that the more abstruse and incomprehensible words in a person’s speech, the more deceitful the speech and the person himself are. In her article, the following words were key for me: “There is no specific clinical picture for dysplasia. Half of the patients have no complaints at all, while in the rest the symptoms are due to concomitant gynecological diseases.”
And if you translate everything into Russian, then everyone is free to lie as it benefits him.
Now let's return to the definition of the concept - dysplasia. What kind of horror is this?
Dysplasia and I (dysplasia; Greek dys- + plasis formation, formation) is the general name for disorders of the development of organs or tissues during embryogenesis and in the postnatal period.
That is, these disorders already appear at the time of fetal development.
Diagnosis - Cervical Dysplasia - no! There are various other dysplasias, a whole list, they are mainly associated with diseases of the bones and brain! It was invented so that you Women would pay the loot. As Bogdan Titomir said: “People are eating.”
Indeed, there are two types of medicine, one for suckers (pills and other crap), the other is elite. Unfortunately, not everyone can use the elite one and not everyone is ready. It's easier to take pills.
The choice is always yours.
- < Abstract: Pathology of childbirth and obstetric care - Bank of abstracts, essays, reports, coursework and dissertations
- Hip fracture: treatment. Rehabilitation after a fracture >
Conclusion
Cervical dyskaryosis is a precancerous condition that should not frighten a woman or confuse her. If you seek the help of a professional on time, then within a few months you can live as before and not be afraid of dire consequences. Now there are a number of techniques that quickly and permanently relieve a woman from this pathology. If the disease is in a mild stage, then there is no need to treat it at all, but it is important to be constantly monitored by a gynecologist. At the first deterioration, appropriate treatment is prescribed. But usually everything goes away on its own.
Those ladies who neglect treatment may get cancer in the near future, resulting in a short life span and death.
Treatment of dysplasia
Doctors often dispute the need to treat stage 1 lesions, hoping that pathology of this degree can go away on its own. Doctors who disagree with this opinion recommend drug support to their patients, focused on stabilizing hormonal levels.
The main task of doctors when managing a patient with mild dysplasia is to prevent the progression of a dangerous lesion to grade 2. Moderate dysplasia is always treated. At this stage, a complex impact is necessary:
- the use of drugs that increase local and general immunity;
- application of radio wave treatment methods;
- carrying out cryodestruction or electrocoagulation.
The drug Isoprinosine is often used to provide antiviral therapy. The drug is active in the fight against the papilloma virus and suppresses the mechanism of HPV nuclear division. Radio wave treatment is the safest and most painless, preventing the formation of scars and other defects on the mucous membranes. The methods are often used in nulliparous women.
Treatment of severe dysplasia often requires surgical intervention using diathermoexcision using a specific electrode. Electroconization is also carried out using the Surgitron radio wave apparatus or knife amputation.
The effectiveness of the therapeutic technique largely depends on the diagnosis and timely treatment of local infectious and inflammatory processes localized to the cervix. After the operation, the doctor must monitor the dynamics of the recovery processes.
An innovative method of treating dysplasia - FTD
Modern methods of therapy can reduce the likelihood of dysplasia turning into an oncological process. These include the method of photodynamic therapy. The method allows you to get rid of cervical dysplasia quite quickly.
PDT involves the introduction of a special photosensitizing substance into the human body. The product entering the body increases the photosensitivity of cells and triggers a chemical reaction. By applying a laser pulse, a reaction is triggered to activate the selective destruction of atypical cells containing a special substance. Healthy tissues are not destroyed, which is what makes the technique unique.
Attention! A similar treatment method is used at different stages of dysplasia. Doctors consider it as a breakthrough in the treatment of precancerous conditions.
Photodynamic therapy is also actively used for the treatment of oncology. List of main advantages of FTD:
- a gentle action that allows you to destroy dysplasia, fully preserving the reproductive function of a woman;
- painlessness of the procedure;
- adaptability for patients of different age categories, the technique is applicable for elderly people;
- possibility of repeated manipulation;
- no systemic complications.
An equally important condition that increases the popularity of the method is that the patient can return to their usual lifestyle as early as 6 weeks after using the method. The cost of treatment ranges from 30 to 50 thousand rubles.
Surgery
Conization is a surgical intervention that ensures complete removal of the lesion. The lesion is removed in the form of a cone - hence the name of the technique. This method is classified as a simplified type of surgical intervention; the features of the anatomical structure are taken into account, therefore the method is considered as gentle. After the procedure, no scars remain on the surface of the cervix. A woman can become pregnant, successfully carry to term and give birth to a healthy child.
Attention! Surgical practices are rarely used to correct mild to moderate dysplasia. For minor lesions, preference is given to gentle methods.
Excision is a surgical treatment technique that involves removing some parts of the cervix. It belongs to the category of low-traumatic methods and is provided by vaginal access. During such an operation, it is possible to take a biopsy sample for further microscopic examination. This condition allows one to evaluate histology and give a prognosis.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is a common treatment for cancer. The method is highly effective, but the use of drugs with a wide spectrum of activity has contraindications and often provokes adverse reactions. Due to the risk of complications, the method is used to treat precancer, that is, severe dysplasia. In the early stages of lesion development, this method is not used.
Traditional methods
Cervical dysplasia: how to treat with folk remedies
Despite the fact that gynecologists have a negative attitude towards traditional medicine methods, most women still use them. Some representatives of the fairer sex choose their own remedies, but there are also those who turn to herbalists for help.
Treatment with folk remedies is not recommended as a separate independent therapy for the disease. The use of natural resources in treatment gives favorable results in combination with other methods. Treatment at home should be started after diagnosis, provided there is no oncological process.
When diagnosed with cervical dysplasia, treatment with folk remedies consists of using decoctions, infusions and tinctures made from natural ingredients. In most cases, plants such as celandine, boron uterus, chamomile and many others are used.
The use of celandine in the treatment of cervical dysplasia is justified by its composition. The juice of the plant contains about 30 alkaloids, the most important being chelidonine. Celandine is used only for douching or use with tampons. The decoction for douching is prepared independently and used no more than 2 times a day.
Aloe leaf juice is often used to treat dysplasia. The collected juice from aloe leaves is used to wet tampons. The procedure should be carried out 2 times a day.
In addition, suppositories with propolis or tamponing with propolis oil will help slow down the development of dysplasia. The boron uterus, which has many medicinal properties and is widely used in the treatment of gynecological diseases, copes well with this task.
When there is cervical dysplasia, traditional methods of treatment are auxiliary therapy to stop the pathological process.
Basic conditions for radio wave therapy
- there is no data (cytological-endoscopic screening) indicating cervical cancer;
- treatment should be carried out by a specialist who knows the basics of colposcopy.
In case of grade 3 dysplasia, the issue of dysplasia treatment is decided together with an oncologist-gynecologist. Recently, surgical treatment of dysplasia . Amputation of the cervix according to Sturmdorff is indicated for patients in whom dysplasia is combined with cervical elongation during uterine prolapse.