What are follicles in the ovaries in women?
Understanding the purpose of the dominant follicle, as well as how it can be tracked, a woman will be able to avoid health problems in the reproductive system.
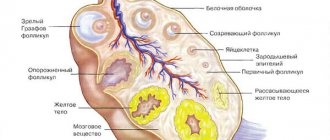
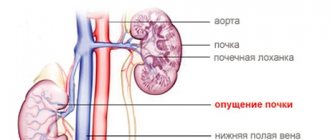
A dominant follicle is one of the main signs of the onset of the ovulatory phase of a particular woman’s menstrual cycle. By follicle, gynecologists mean the structural part of the ovary (one of the organs of the female reproductive system). Normally, it should consist of an egg, and also be surrounded not only by an epithelial layer, but also by a double layer of connective tissue.
The main components of follicles are:
- Oocyte This is a form of genetic material that is an immature egg, or the main cell of the female reproductive system, which plays a key role in the reproduction of its owner. An ovarian follicle should normally contain a single oocyte. It is a kind of cell nucleus that matures during the process of ovulation and participates in the direct process of fertilization - in the ovulatory phase of the menstrual cycle, the dominant follicle ruptures, and the egg - oocyte, located inside at this moment, prepares for fertilization. If at this time the sperm penetrates closely into the mature oocyte, in the normal course of the further process, pregnancy will occur.
- Glycoproteins. Proteins consisting of 2 components located around the oocyte. They form the second layer of the follicle.
- Granulosa cells. Protective, third layer of the follicle, enveloping glycoproteins.
- Basement membrane. This is the name of a thin acellular layer designed to separate the connective tissue from the epithelium in the ovarian follicles.
- Theta cells. Outer layer of follicles.
The main functions of follicles include:
- support function;
- regulatory;
- trophic.
Analysis of the dynamics of follicle maturation (folliculometry) allows doctors to:
- help the patient in planning pregnancy by predicting the most favorable days (from a physiological point of view) for conception;
- diagnose diseases the signs of which are the absence of ovulation (for example, polycystic disease);
- evaluate the progress of hormonal therapy in the treatment of primary infertility.
What it is?
A follicle is a structural component of the ovary in which an egg matures, surrounded by epithelium and layers of protective connective tissue.
Structure
The follicle consists of an oocyte - a spherical cell with a diameter of 25 microns, surrounded by follicular and granulosa cells and protected by membranes. The oocyte contains a nucleus (germinal vesicle) and a nucleolus.
Did you know? Few people know that the largest cell in the human body is the egg.
Its dimensions are 600 times greater than the size of a sperm , the smallest human cell.
Functions
The main purpose of the follicle is to protect the egg from external influences for its comfortable maturation. In it, the female reproductive cell is in a not yet fully developed state.
And its timely and correct maturation is very important, since it is this process that affects the maturation of the fetus, the occurrence of abnormalities during pregnancy and labor. Normally, each woman matures one follicle per month.
Follicle maturation
The maturation of the follicle can be recognized not only by folliculometry, but also by assessing the general condition of a particular woman.
Menstruation cycle
The most common signs of approaching ovulation, accompanied by the release of a dominant follicle, are:
- dull pain in the lower abdomen that does not go away even after taking painkillers;
- tingling in the left or right side of the lower abdomen, in the area of the ovary (the discomfort is usually minor, and both arises and goes away on its own);
- an increase in the amount of mucous discharge from a woman’s vagina, as well as changes in their appearance and consistency (discharge becomes more abundant, thicker, and also changes color to a more cloudy one with a whitish tint);
- decrease in rectal body temperature (specifically on the day of ovulation, that is, rupture of the dominant follicle, the basal temperature is as low as possible, and the very next day it begins to rapidly increase to normal - 37 degrees Celsius);
- an increase in the concentration of the hormone LH in a woman’s blood.
The process of follicle maturation can be divided into 3 main stages:
- A gradual increase in the size of all follicles located in a woman’s ovaries (the dominant follicle is characterized by growth of approximately 2 mm per day).
- Suspension of growth of all follicles except the dominant one. The dominant one continues to grow until its size reaches approximately 20 mm in diameter.
- Rupture of the follicle followed by the release of an egg that has matured at this point. At this moment, ovulation occurs - a key moment in the menstrual cycle.
Pathological conditions associated with follicles
There are many conditions in which the number of follicles, the speed and degree of their maturation shift from normal to pathological. This most often manifests itself as infertility, and these disorders themselves can lead to other disorders of the reproductive system.
Multifollicular ovaries
This is the term most often used by ultrasound doctors to describe the picture they see on the monitor of their machine. This term means that the ovaries have too many follicles (another name is multifollicular), each of which does not develop into a dominant one. This is not a disease, but a symptom of it. The disorder itself, that is, the reason contributing to the appearance of multifollicularity, can be different:
- Long-term use of hormonal contraceptives and the first three cycles after stopping their use (scientifically, this is ovarian hyperinhibition syndrome, and in this case the condition is reversible and most often disappears on its own);
- adolescence until the cycle stabilizes (this is also not a dangerous situation, you just need to wait until the hormone levels become normal);
- resistant ovarian syndrome - a condition in which the reproductive organs respond poorly or not at all to normal concentrations of gonadotropins;
- insufficient secretion of gonadotropic hormones by the pituitary gland, especially luteinizing hormones, as a result of which many antral follicles (small follicular ovaries), as well as thin endometrium and a decrease in the size of the uterus are detected on ultrasound.
Some of these conditions do not require intervention, but only observation over time, while with resistant ovarian syndrome or reduced secretion of gonadotropins, a woman needs serious treatment with hormonal drugs under the guidance of specialists: a gynecologist and an endocrinologist. No folk remedies can cure these conditions.
An ultrasound revealed I had small follicles. Is it dangerous? Angelina, 24 years old
Angelina, small follicular ovaries are usually characteristic of a hormonal disorder in which the pituitary gland produces too little luteinizing hormone. This is a reversible condition, but may require years or even lifelong treatment with special medications. Contact your gynecologist and endocrinologist with your ultrasound results.
Persistent ovarian follicle - what is it?
This is a pathological condition in which normal ovulation does not occur on time. The follicle continues to exist longer than expected, its wall does not rupture and the egg cannot enter the uterine cavity.
The causes of this condition are most often associated with hormonal disorders: reduced estrogen synthesis, prolonged increase in the production of luteinizing hormone, or the absence of a preovulatory surge in its level. Also, persistence often occurs when there is a malfunction of the hypothalamic-pituitary system, thyroid gland, etc. If the follicle does not burst in time, a follicular cyst may develop.
Symptoms of follicle persistence are as follows:
- prolonged amenorrhea (absence of menstruation) while the pregnancy test is negative;
- dysmenorrhea – lengthening of the monthly cycle to 50 days;
- algodismenorrhea - painful menstruation with heavy bleeding with clots;
- infertility.
https://youtu.be/4U1gul5MFGU
The role of dominant follicles
The dominant follicle is a structural element of the ovary, which plays one of the main roles in the onset of ovulation within a particular cycle, regulates the female hormonal system, and also determines the further fertilization of the egg released into the uterine cavity during the rupture of the follicle.
The maturation of follicles in itself, without drug intervention, in particular hormonal therapy, cannot be controlled.
When planning pregnancy, as well as therapy aimed at normalizing the functioning of the reproductive system, it is important for a woman to monitor the absence of factors that interfere with the normal functioning of the organs of the reproductive system:
- The use of oral contraceptives is OK, for several years without interruption. Most often, OCs are available in tablets. Doctors prescribe the hormonal drugs in question for a course, the duration of which usually does not exceed 5-6 months. After the specified amount of time, the body must be given a rest - 1-2 months - after which, in the absence of contraindications, oral contraceptives should be resumed. Regardless of the period of taking the type of pill in question, if any discomfort or negative changes in appearance occur, the woman should immediately contact a gynecologist to select another drug. It is strictly prohibited to stop taking hormonal medications on your own in the middle or beginning of the menstrual cycle.
- Disorders of the thyroid gland. Such pathologies can arise due to indiscriminate use of drugs containing iodine, which can provoke an excess or, conversely, a critical underestimation of iodized production acid.
- Excessive concentration of prolactin in the blood. The lactogenic hormone, necessary for physiological changes during the period of restructuring of the female body after childbirth, inhibits the development of follicles.
- Hormonal disruptions that occurred for secondary reasons (for example, adolescence, the onset of sexual activity, and so on).
Persistent follicle
The question of what a persistent follicle is is asked by those who have had a similar diagnosis. Pathology means that the formation of the dominant element occurred as it should until the very moment when it was supposed to burst. This did not happen and the egg, accordingly, is not released. Regardless of where the appearance of a persistent follicle was diagnosed on the right or left ovary, ovulation does not occur. The cause of the disease may lie in hormonal imbalances in a woman, in cases where the male hormone is present in excess. If you do not intervene in such a process in a timely manner, then the development of infertility is possible.
The essence of treatment comes down to hormonal therapy.
At the initial stage, medications are taken that will suppress male hormones in the body.
The second stage involves the introduction of hormones intramuscularly. In addition, it is necessary to carry out massage procedures, laser therapy, and ultrasound effects on the pelvic organs.
What does the appearance of a dominant follicle in the left and right ovary indicate?
In some cases, during folliculometry, the doctor cannot determine the dominant follicle, despite the absence of health problems in a particular patient, as well as secondary factors inhibiting the process of her approaching ovulation.
It can be explained like this:
- a physiological feature due to which the follicle matures extremely slowly, not having time to reach its maximum size before the end of the menstrual cycle;
- development of the follicle to the desired size without subsequent rupture (most often this is also a particular feature of a particular person);
- “freezing” of the follicle at one of the initial stages of its maturation (can occur if on the day of the menstrual cycle, when the development of the dominant follicle stopped, the woman experienced severe stress);
- up to 1-2 menstrual cycles per year can be anovulatory (during such periods, the woman’s reproductive system “sleeps”, which means conception will be impossible);
- the onset of premature menopause (with such hormonal changes, an insufficient amount of hormones is produced, which is why there may be no follicles in the ovaries at all).
The physiology of a healthy woman provides for the maturation of follicles alternately in the right and left ovaries. Despite this, statistics from gynecologists and reproductive specialists indicate that in 90% of cases the dominant follicle is found in the right appendage.
This may be explained by the fact that the right side of the human body has greater efficiency, due to which the blood supply in it is many times greater compared to the left. Dominant follicles formed in both ovaries are also not a pathology. With this development of events, the chance of a multiple pregnancy increases to 95%.
Role and functions of follicles
Each woman has a certain number of eggs laid during the embryonic period. When a girl is born, the follicles in the ovaries stop forming. How many follicles should there be in the ovaries? The number can reach 500 thousand or more; during the entire reproductive age, about 300-500 pieces have time to fully mature. All other follicles die. At the age of 18-36, about 10 elements gradually mature every month. By the time of ovulation, 1 follicle remains, which releases an egg ready for fertilization.
The main functions of the follicle:
- protect the egg from destruction,
- stimulation of estrogen synthesis.
Follicle-stimulating hormone stimulates the growth of several follicles in the initial phase of the cycle. The maturation of the capsule with the egg is completed by the middle of the cycle. The walls of the follicle stretch under the influence of an increase in the volume of fluid filled with salts, proteins and other substances necessary for the development of the egg.
When ovulation occurs, the capsule ruptures and the egg is released into the fallopian tube. There she can be fertilized by sperm. Complete maturation occurs in only one follicle per cycle. Others take an active part in the synthesis of estrogens.
How and with what to treat the pancreas during an exacerbation?
Read useful information. Learn about the causes of increased progesterone during pregnancy and the features of correcting the deviation from this article.
Norm of follicles by day of the cycle
The development of follicles depends not only on the initial health of a particular woman, but also her age, as well as the characteristics of the actual condition (pregnancy, menopause).
| Features of a woman's condition | The period of the follicular phase and features of the condition of the follicles, which is considered the norm for it |
| A woman aged 20-30 years with no serious pathologies | On the 1st day of the menstrual cycle (the beginning of the follicular phase), at least 15-20 small follicles of the same size are found in the ovaries of a healthy woman. Their diameter during this period is no more than 0.5 mm. After 3-4 days, a dominant follicle (size about 2 mm) should normally appear in one of the ovaries. The growth of the dominant follicle rapidly increases so that by the middle of the menstrual cycle (the end of the follicular phase and the beginning of the ovulatory phase) its size should reach 20 mm. |
| During pregnancy | Since the main purpose of ovulation occurring in the ovaries is the implementation of conception followed by pregnancy, during the period of bearing a child, the ovaries of the expectant mother “sleep”. This means that multiple small follicles in the appendages are in their original state throughout the entire 9 months, and ovulation does not occur. In a small percentage of cases - no more than 3% of the total, ovulation can be observed in the initial stages of pregnancy, which is not a pathology. In this case, the development of events follows a similar pattern described in the first paragraph. |
| During menopause | After the onset of menopause, no follicles are identified in the ovarian cavity (96% of cases). In some exceptions, if there are follicles in the appendages, they do not develop, remaining in their original number and size, which is the reason for the absence of ovulation, and in some cases, menstruation. |
In girls who have not yet reached childbearing age (no menstruation), ovulation, like the dominant follicle, cannot be diagnosed. All follicles in children are in a static state of minimal size. After the onset of menstruation, follicle maturation occurs according to the pattern described above, characteristic of healthy women aged 20-30 years.
After 40 years, minor changes may be observed in the female body due to upcoming hormonal changes.
Deviations from the norm
If the quantitative composition of follicles in the ovary exceeds 10, this is considered to be a violation. Such a pathology can be diagnosed only by ultrasound results. Moreover, their number does not change at all over the course of the cycle. During an ultrasound examination, a large number of small bubbles are noted. If their number increases several times, the woman is diagnosed with polycystic disease. Polycystic disease is characterized by the formation of multiple follicular formations along the periphery.
Polycystic disease can interfere with the formation of a dominant element, the ovulation process and conception. The development of such problems can provoke nervous disorders and stress. In this case, polycystic disease does not require special treatment, and the deviations will easily return to normal.
However, in some cases, underdevelopment of follicular elements requires special therapy. These include the following:
- if oral contraceptives were chosen incorrectly;
- if endocrine problems occur;
- when gaining excess weight or, conversely, sudden weight loss.
If the follicles in the ovary are higher than normal, this does not necessarily mean that polycystic disease has developed or is a signal of any illness. It is likely that the reason for this was overwork, stress, and constant emotional overstrain. In this case, after the first ovulation their number returns to normal.
Since obesity can provoke follicular failure and lead to an imbalance in the functioning of the ovaries, women are advised to monitor their diet and pay due attention to physical activity.
Every woman must regularly visit a gynecologist-endocrinologist. This will allow you to promptly identify the pathology and promptly begin to treat it.
Only a gynecologist can determine why the follicles in the ovaries are formed abnormally from the norm after undergoing certain tests and a special examination.
What parameters do follicles have before ovulation?
A dominant follicle is a follicle whose size exceeds the diameter of other cells by at least 1.5-2 times . Gynecologists determine the normal course of a woman’s menstrual cycle using generally accepted indicators that illustrate changes in the size of the follicles, as well as their growth rate.
By the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle, gynecologists mean the period from the first day of bloody vaginal discharge until the onset of ovulation. With an average cycle length of 28 days, the follicular phase lasts the first 2 weeks.
| Period of the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle | Condition of follicles considered normal |
| 1 day from the start of bleeding | The ovaries contain at least 20 minimum-sized follicles with an immature egg inside each. The diameter of the follicles during this period does not exceed 0.5 mm. Due to the increase in the concentration of hormones, in particular LH and FSH, the follicles begin to increase in size. |
| 4–5 days from the start of bleeding | In one of the ovaries a dominant follicle is found - preantral, the size of which is at least 2 mm. Menstruation ends or the discharge becomes scarce, due to which the endometrium begins to actively increase. |
| One week from the start of bleeding | The dominant follicle in one of the ovaries matures to a size of 5 mm, after which a cavity is formed inside it for the subsequent accumulation of follicular fluid and other changes that occur in the body as ovulation approaches. |
| 13-14 days from the start of bleeding | The dominant follicle increases to 20 mm in diameter, which is why its walls rupture, thus releasing the egg that has matured by this time. The egg is “sucked” into the opening of the fallopian tube with the help of fimbriae (special tissue processes located in the fallopian tubes). |
Lack of follicles
However, sometimes it happens that the follicular structures on the ovaries are completely absent. The reason for this lies in the early onset of menopause or failures in the functioning of the ovaries. In this case, the doctor prescribes hormonal treatment. You can find out about the presence of such a problem by irregularities in the menstrual cycle.
The body of the fairer sex must produce a certain number of follicles. If there are more or less of them, this is always considered a deviation. Sometimes everything can end in the development of infertility. Therefore, when faced with menstrual irregularities, a woman should immediately contact a doctor to determine the cause and prescribe the necessary treatment.
How is the day of ovulation calculated using ultrasound?
The dominant follicle is a structural element of the ovary, the size of which can only be determined using ultrasound. If a woman is at the planning stage of pregnancy or undergoing hormonal therapy, ultrasound should be performed dynamically, 2-3 times over 5-7 days.
Folliculometry, displaying the real diameter of the dominant follicle, will allow the gynecologist to determine the exact day of the menstrual cycle, as well as calculate the date of upcoming ovulation.
Folliculometry is carried out in accordance with generally accepted standards:
- the first ultrasound as part of folliculometry should be performed 7-10 days after the first day of menstruation;
- the second and subsequent ultrasounds are recommended to be performed every 2-3 days until the day of ovulation is accurately determined;
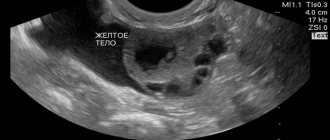
- in addition to observing the development of the dominant follicle as part of folliculometry, the gynecologist also describes the condition of the corpus luteum;
- if the dominant follicle is not determined within the specified time frame, it is recommended to continue folliculometry until the end of the menstrual cycle (until the next bleeding begins).
All studies carried out to calculate ovulation must be carried out by one ultrasound specialist, using the same ultrasound machine. This will minimize the risk of a doctor making a mistake (due to an error in the device), and will also increase the likelihood of making accurate calculations.
Evaluation of follicles by a specialist
AMH hormone is normal in women of reproductive age
| Age | Reference normal values, in ng/ml |
| 18-25 years old | 0,96 – 13,34 |
| 26-30 years old | 0,17 – 7,37 |
| 31-35 years old | 0,07 – 7,35 |
| 36-40 years old | 0,0,3 – 7,15 |
| 41-45 years old | 0,00 – 3,27 |
| {amp}gt;=46 years | 0,00 – 1,15 |
| Low AMH levels | Anti-Mullerian hormone levels are a reliable barometer for assessing the state of ovarian reserve in women. A low level indicates that ovarian reserve is rapidly declining. By determining the level of AMH, the quality and quantity of fertilized eggs is determined when diagnosing infertility. |
| Low AMH and pregnancy | AMH indicator of the state of the ovarian reserve. A depleted ovarian reserve leads to problems associated with pregnancy and infertility. If the number of eggs in the ovarian reserve drops, your chances of getting pregnant decrease. |
| Symptoms of low AMH | There are no obvious symptoms. But irregular periods or stopping of the menstrual cycle is something that women with low AMH commonly experience. A blood test is the most effective way to assess AMH levels. |
| Causes of low AMH | 1. Hormonal imbalance. 2. Age. 3. Endometriosis. 4. Genetic factor. 5. Environmental influence. 6. Unknown (idiopathic). |
When is folliculometry required?
Folliculometry is prescribed by a gynecologist or reproductive specialist to a woman if there is one or more indications from the list below:
- Carrying out hormonal therapy. The maturation of the follicle will help to suggest whether a particular woman needs to take an additional dose of hormonal drugs or, if necessary, on the contrary, reduce it.
- Determining the cause of primary infertility. In this case, folliculometry is advisable in conjunction with hormonal studies, as well as regular examinations by a gynecologist.
- Determining the cause of an irregular menstrual cycle. The presence of monthly ovulation indicates the normal functioning of the organs of the woman’s reproductive system.
- Mandatory examination before prescribing the procedure for in vitro fertilization (IVF).
- Assessing the effectiveness of stimulation aimed at maturing the dominant follicle and initiating subsequent ovulation.
It is not advisable to prescribe folliculometry yourself, since in some cases a qualified gynecologist can diagnose the patient and also prescribe concomitant treatment based on more significant symptoms and laboratory results.
What are the normal sizes on different days of the cycle?
The follicle is measured during a special study - folliculometry. Folliculometry must be carried out several times in a row on certain days of the cycle. The data obtained is compared with the norm of a 28-day cycle:
- Days 1-4 - do not exceed 4 mm.
- 5th - reach 5-6 mm.
- 7th - the dominant is determined to be 9-10 mm.
- 8th - the dominant reaches 2 mm.
- 9th - 14 mm.
- 10th – dominant 16 mm. The rest are starting to decline.
- 11th - 18 mm.
- 12th – 20 mm.
- 13th – 22 mm.
- 14th – ovulation: the follicle, which has grown to 24 mm, bursts.
When comparing folliculometry results with normal values, the duration of a woman’s natural cycle must be taken into account.
Possible problems
A dominant follicle is one of the signs of the normal functioning of the organs of the female reproductive system. Its untimely maturation may indicate serious pathologies requiring immediate medical intervention.
The most common problems in women's health, the presence of which can be assumed by the diagnosed absence of ovulation, are:
- atypical duration of the menstrual cycle (when its duration is less than 21 days or more than 31 days);
- various functional disorders in the functioning of the ovaries (most often arising due to problems with the production of hormones by the hypothalamus and pituitary gland);
- secondary hormonal disorders arising from diseases of the thyroid or pancreas;
- congenital pathologies;
- polycystic ovaries (with this disease, the ovaries increase in size, their walls become as dense as possible, through which the follicles cannot pass, and the dominant follicle is absent in both the right and left ovaries);
- pathology of the cervical canal (diagnosed in the presence of qualitative changes in the uterine mucus);
- erosion of the uterine cervix (the need for treatment should be determined by a number of additional examinations, for example, colposcopy);
- pathology of the fallopian tubes (obstruction, disruption of integrity or local damage);
- unruptured follicle syndrome (considered one of the congenital pathologies);
- endometriosis;
- pathologies of the physiological structure of the uterus;
- psychosomatics.
Features in the left ovary
Since the formation of a dominant oocyte followed by the appearance of a corpus luteum in its place is a physiological process, there are no significant differences from ovulation in the right ovary.
The localization of the dominant follicle in the left ovary is a normal variant.
- ovulation in the left ovary occurs less frequently due to its smaller size and number of eggs;
- if there is a dominant in the left and right organs, the chance of conceiving twins simultaneously increases;
Can "dominant" be empty?
A dominant follicle is considered empty if there is no follicular fluid and no oocytes. Despite the fact that the frequency of diagnosis of empty follicle syndrome varies from 0.3% to 8%, determining the causes of the condition in question is difficult in 90% of cases.
The most common reasons for the development of the condition in question are:
- untimely stimulation of ovulation;
- ovarian dysfunction (eg, multifollicular ovaries, polycystic disease, ovarian failure);
- genetic mutations or a woman’s congenital predisposition to infertility;
- the body's reaction to a specific drug treatment (for example, intolerance to a certain hormonal drug);
- the presence of external factors that negatively affect the development of follicles and the functioning of the organs of the reproductive system as a whole;
- jumps in the level of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG).
It is generally accepted that a follicle whose size indicates the beginning of the ovulatory phase of the menstrual cycle, in which the probability of fertilization of the egg is greatest, is dominant. It is necessary for every woman to understand what it is, as well as what dysfunctions such a pathology can provoke, regardless of whether she is planning a pregnancy in the near future.
Otherwise, by ignoring the symptoms of the anovulatory cycle, the girl risks starting treatment untimely, which in the future can lead to irreversible consequences, for example, infertility.
https://youtu.be/ijdqjrAXMY4
What does an ultrasound show?
Capsules with eggs can be easily detected on the screen during ultrasound diagnostics from the fifth day of the cycle. In the future, their dimensions increase. On the 7th day of the cycle, you can see which of them is dominant.
Upon examination, empty follicle syndrome can be detected. This means that the ovary is not able to provide the release of the sex gland. Such a woman needs to get rid of infertility.
Ultrasound is completely safe for the body.
Types of follicles
There are four types of follicles. These types differ depending on the stage of maturation of the structural component of the ovary.
Primordial
A follicle that is at rest is called primordial. Its dimensions are such that they cannot be examined with the naked eye - approximately 50 microns. It is flat in shape. Consists of an oocyte and 1-2-layer epithelium.
Their development begins in girls with the onset of puberty. After the pituitary gland begins to produce follicle-stimulating hormone, 5 to 15 primordial components mature.
Primary
After maturation, primordial follicles become primary or preantral. They already reach sizes of 150-200 microns and take the shape of a cube. The grown oocyte is now covered with granulosa cells in two or three layers and a membrane formed from connective tissue.
Secondary
Subsequently, a secondary or antral follicle with a diameter of 500 microns is formed. It has a double shell and also contains liquid with estrogen.
Mature
When mature, a mature or preovulatory (tertiary) follicle grows from 0.1 to 1.6-2 cm. At this time, it is also often called the “Graafian vesicle.” It consists of another shell and small cavities with cells, vessels and a membrane.
How many follicles should there be for conception?
In order for a woman to become pregnant, the egg must mature completely. How many follicles should there be to conceive? At the stage before fertilization, it is necessary to have one - high-quality dominant development. He should be ready to ovulate. If an ultrasound examination reveals two such formations, and they both undergo fertilization, twins will be born.
- Throat abscess disease
- The use of Fluconazole for thrush
- How to grow eyelashes
What could go wrong
The process of egg development does not always occur normally. A situation may occur when in a particular menstrual cycle there are no follicles in the ovaries. What does it mean? In this case, the egg does not mature, which means conception naturally becomes impossible. In addition, the menstrual cycle fails, and there is a lack of menstruation on time.
The absence of follicles can be either a temporary phenomenon or a sign of infertility. This is also one of the symptoms of the onset of menopause, when the resource of germ cells laid down in the prenatal period is depleted, or their maturation fails.
In the absence of a maturing follicle, a woman experiences an increase in testosterone
Disorders associated with the maturation of an empty follicle are also often observed. In this case, pregnancy is also impossible.
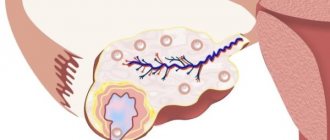
A slightly different situation is that the growing follicle in the ovary does not burst or does not open completely, that is, it becomes persistent. Such a violation also provokes cycle disorders, and the accumulated fluid in the sac can transform into a follicular cyst. Over time, when the process normalizes, the cyst resolves on its own, but with frequent failures of this kind, polycystic ovary disease develops.
Follicular ovarian cyst