A cyst is one of the functional neoplasms that can occur in any organ, including the ovaries.
The disease is observed in women of different age groups, and often occurs without a clear clinical picture.
This neoplasm is characterized by independent regression, but one should not hope for such an outcome.
If the pathology becomes complicated, it is necessary to resort to surgical intervention, and in very severe cases, it may be necessary to remove the cyst along with the ovary.
The essence of pathology
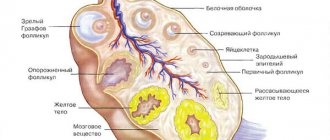
During the entire fertile period, a follicle develops and matures every month in a woman’s body, which at a certain moment bursts and an egg emerges, ready for fertilization.
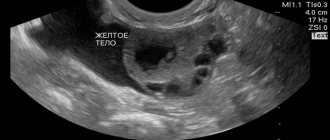
After this process, in the place where the follicle was, the gland remains for some time; it is called the corpus luteum because it contains a certain pigment that gives it a yellow color.
The function of the corpus luteum is the production of hormones that prepare the endometrial lining of the reproductive organ so that the fertilized egg attaches to it.
If pregnancy occurs, the corpus luteum continues to function during the first months; in the absence of pregnancy, the temporary gland is excreted from the body along with menstrual blood.
If the corpus luteum does not regress for some reason, a luteal cyst occurs.
In this case, as a result of deterioration of blood circulation, accumulation of serous or bloody fluid occurs.
Such neoplasms can be quite large in size, in most cases they reach 6-8 cm, but cysts with a diameter of 20 cm have been recorded.
NOTE!
This pathology does not occur often; it is diagnosed in 3-5%.
Doctors distinguish between a cystic formation that appeared during pregnancy and a formation formed from a follicle as a result of a malfunction.
The cystic formation can be right-sided or left-sided, and in its structure it can consist of one or more chambers that are connected to each other.
Most often, neoplasms are diagnosed on one side, which have one cavity containing yellow-red liquid contents.
A corpus luteum cyst is a harmless pathology that, as a rule, resolves within a few menstrual cycles..
This neoplasm never transforms into malignant.
Expert opinion
Shustova Olga Leonidovna
Obstetrician-gynecologist of the highest category
Corpus luteum cyst, despite its relative safety, can lead to various complications, among which it is especially dangerous. Such a complication requires immediate assistance from surgeons, and often the woman’s ovary is removed along with the ruptured cyst. In this regard, corpus luteum cysts should be under the supervision of a gynecologist and treated promptly and efficiently. A woman should understand that the clinical picture of the presence of a cyst is not always clearly expressed, and not ignore preventive examinations by a doctor.
Corpus luteum cyst of the ovary
Corpus luteum cyst is a neoplasm of the left or right ovary, the development of which occurs in the postovulatory period. A cystic lump appears as a result of the effect of luteinizing hormone (LH) on the reproductive system, which is why the pathology is often called a luteal cyst. LH is necessary for the formation of the corpus luteum, which produces progesterone. This hormone performs an important function: it is necessary to prolong pregnancy. Due to various factors, under the influence of LH, a cystic formation can form.
Symptomatic manifestations
If the cystic formation has increased to 5 cm or more, the woman may experience certain pathological signs:
- Pain and tingling sensations from the development of the cyst, but sometimes pain manifests itself in the entire lower abdominal area. Painful sensations are provoked by stretching of the tissue of the reproductive gland, and the pain becomes more pronounced during intimacy, physical strain, or during normal body bending.
- Problems with monthly bleeding. Menstrual bleeding may be delayed for a week or longer, although all the signs of the onset of menstruation are present - engorgement of the mammary gland, pulling sensations in the lower abdomen, and so on. Sometimes there may be a slight but lingering bleeding.
- In the second phase of the cycle, the rectal temperature rises.
- If the cyst puts pressure on the bladder, urination becomes more frequent.
One of the characteristic signs of a corpus luteum cyst is that symptoms appear in the second half of the menstrual cycle.
What is a neoplasm?
The cystic corpus luteum is a neoplasm located on one of the gonads. In medicine, the tumor is also called a luteal cyst.
It gets its name from the cellular pigment that gives it its yellow color. The neoplasm usually resolves on its own, which is why it is called functional.
The starting point in the development of the tumor process is regular cyclic changes in the female gonads, suggesting pregnancy.
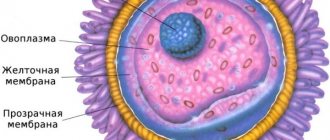
At the beginning of the cycle, follicle-stimulating hormone is produced, due to which the dominant Graafian vesicle grows and is selected. Next, it ruptures and the egg is released.
A glandular formation appears in place of the follicle. Its prerogative becomes the synthesis of the second phase hormone - progesterone.
This substance is necessary for implantation and pregnancy development.
A cystic corpus luteum is an overly large formation that synthesizes progesterone.
Normal sizes vary within 25 mm. If functional changes have a greater indicator, then we are talking about a cystic formation.
Gynecological statistics show that it usually does not exceed 6.8 cm in diameter.
Shortly before the start of a new menstrual cycle, the cyst on the right ovary (or left - it doesn’t matter) begins to go through the stages of regression.
The functional tumor disappears with bleeding, but in some cases the ovary with a large corpus luteum can persist for up to several months.
There is an officially unconfirmed pattern according to which luteal cysts of the right ovary are more common than those of the left.
This is explained by the fact that the right gland is better fed with blood through a large artery. Detection of a cystic corpus luteum in the left ovary occurs less frequently, since this gland is supplied with blood through the renal artery.
Causes
It must be said that the mechanism of formation of a corpus luteum cyst has not been fully studied.
It is believed that the main cause of the pathological process is a hormonal imbalance in the body, in addition, poor blood circulation in the female reproductive system plays a significant role in this.
There are certain risk factors:
- prolonged and uncontrolled use of certain medications that are designed to stimulate ovulation, as well as emergency contraception;
- the onset of menstruation too early;
- hereditary predisposition;
- endocrine pathologies, in particular thyroid diseases;
- malfunctions of the hypothalamic-pituitary system;
- a history of ectopic pregnancy;
- abortions;
- strong psycho-emotional stress;
- hard work;
- lack of normal working and rest conditions;
- dietary abuse, which leads to imbalance in the body;
- overweight or underweight;
- genital infections;
- inflammatory processes in the reproductive system.
Some scientists explain the increase in the development of cystic neoplasms in the reproductive system of women by neglect of the reproductive function of the body.
For many centuries, women gave birth to 6-10 children, which means they had fewer menstrual cycles and there were fewer ruptures of the ovarian membranes. Currently, a woman, at best, gives birth to 3 children, therefore, the number of menstruation and ruptures of the ovarian membrane increases tenfold.
Doctors consider this phenomenon to be a great stress for the body, which as a result cannot stand it and fails.
Treatment
To eliminate an ovarian corpus luteum cyst, it is necessary to take medications. In some cases, a wait-and-see approach is possible. If the size of the cyst is no more than four centimeters, then it is simply monitored using ultrasound. After three months it should resolve on its own.
- If an enlargement of the corpus luteum cyst occurs, anti-inflammatory therapy is indicated (local remedies: suppositories and vaginal tablets with antibacterial and antifungal components); physiotherapeutic treatment.
- Taking hormonal drugs (Regulon, Jess, Yarina, Norkolut, etc.) is indicated for concomitant menstrual irregularities and other gynecological pathologies. Utrozhestan and Duphaston are considered the best hormonal agents. These two drugs are progesterone analogues. With the introduction of synthetic progesterone, the production of luteinizing hormone by the pituitary gland is reduced, which leads to the cessation of the work of the corpus luteum.
- If the cyst is larger than four centimeters in size, it is removed surgically. The operation is usually performed laparoscopically.
- When there is a rupture of the corpus luteum cyst without bleeding or torsion, the remaining membranes of the formation, ovary and fallopian tube are removed.
- In case of bleeding with hemorrhagic shock, emergency surgery is performed (laparotomy and removal of the ovary).
- Traditional methods of treatment are not used: it is life-threatening.
If a corpus luteum cyst occurs during pregnancy, then the treatment methods remain the same. If timely measures are taken, the outcome for the expectant mother and child is favorable. If all doctor's recommendations are followed, the danger is minimized.
Read
Also:
- Calculate body mass index for women
- Laparoscopy of ovarian cyst
- What is an ovarian retention cyst, methods of treatment
- Endometrioid ovarian cyst
Why is pathology dangerous?
The yellow cyst itself does not have negative consequences; its complications are dangerous:
- Torsion of the legs. This phenomenon can be complete or partial. The hemorrhage that occurs can cause symptoms of an “acute abdomen” - colic, vomiting, and others. Painful sensations in this case do not go away in any position of the body. Urgent surgery is required.
- Delayed menstruation.
- Cyst rupture.
- Internal bleeding. This phenomenon occurs when a cyst ruptures. In this case, blood enters the peritoneum or pelvic region, causing weakness, lethargy or shock.
You need to know that complications can develop against the background of rapid growth of the tumor, as well as under the influence of provoking factors.
Education gap
Cyst rupture is a fairly serious complication; of course, this does not always happen, but this possibility should not be ruled out.
The reasons that can lead to cyst rupture are as follows::
- hormonal imbalance;
- excessive physical activity - heavy lifting, sports;
- trauma to the pelvic organs;
- too active sexual intercourse;
- problems with blood clotting;
- inflammation in the reproductive organs.
Symptoms of a rupture:
- an increase in temperature that cannot be brought down by taking antipyretics;
- sharp pain;
- the appearance of bleeding;
- disruptions in the process of bowel movements and urination;
- paleness of the skin;
- fainting;
- decreased blood pressure;
- symptoms of general intoxication.
Possible consequences
In most cases, the occurrence of a yellow cyst in the ovary does not endanger the woman’s health. Negative consequences are possible if the formation reaches a large size or if the doctor’s recommendations are not followed.
Leg torsion
This pathology rarely develops due to the absence of a stalk in this type of formation. Factors why torsion of ovarian corpus luteum cyst occurs:
- active sexual intercourse,
- heavy physical activity,
- sharp turns of the body,
- increased intra-abdominal pressure – often occurs due to constipation.
Twisting of the pedicle of the formation is accompanied by acute pain in the lower abdomen. A patient with such symptoms requires immediate hospitalization, otherwise it can lead to rupture of the cyst or disruption of the integrity of the ovarian tissue.
Gap
Rupture, or apoplexy of the formation, occurs quite rarely. This is explained by the rare occurrence of large corpus luteum cysts. In addition, rupture of cystic formations most often occurs during the period of ovulation or immediately before the release of the egg - this is explained by increased local blood circulation, and during this period the corpus luteum is not yet formed.
The factors that provoke cyst rupture are similar to the causes of torsion of its pedicle. With apoplexy, the patient experiences acute pain, accompanied by a drop in blood pressure, pale skin, cold sweat and the appearance of bloody discharge from the vagina.
Failure of the menstrual cycle
The monthly cycle with pathology often becomes irregular. With a single occurrence of a formation and its rapid elimination, it is possible to lengthen only one menstrual cycle. Subsequent menstruation will occur as usual, which is individual for each woman. Their normal frequency is 28-35 days.
The menstrual cycle is restored on its own after the condition of the ovary is normalized, sometimes this requires hormonal support with special medications.
Internal bleeding
This pathology occurs when the formation or the ovary itself ruptures. Internal bleeding is dangerous due to the occurrence of severe anemia and peritonitis - inflammation of the abdominal cavity as a result of blood and cyst contents entering it. In the most difficult cases and in the absence of medical care, death is possible.
Diagnosis of the disease
To diagnose a cystic formation, the doctor collects an anamnesis, finds out the patient’s complaints, and examines her in a gynecological chair.
If a tumor is suspected, a woman is referred for an ultrasound or laparoscopy.
To differentiate this disease from other pathologies, color Doppler sonography and analysis for the tumor marker CA-125 are prescribed, and measures are also given to exclude pregnancy, including ectopic pregnancy.
Non-surgical treatment methods
Conservative methods are used to stop the growth of the cyst, and to eliminate it by normalizing hormonal levels .
Drug treatment is also aimed at preventing complications. Hormonal medications, homeopathy, vitamins, and physiotherapy are prescribed.
Compliance with a special diet plays an important role in treatment. The patient should stop drinking alcohol, quit smoking, and eliminate stress and physical activity.
You may need to consult a neurologist who will prescribe antidepressants or sedatives . For example, Notta or Novopassit. To relieve pain, No-shpa, Ibuprofen, and Spazmalgon are prescribed.
In the presence of inflammation and infections, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory or antifungal therapy is carried out. The most commonly prescribed anti-inflammatory suppositories are Distreptase.
Pregnant women are recommended homeopathic remedies such as Apis . This drug restores hormonal balance, has a positive effect on the functionality of the ovaries and promotes the resorption of cysts.
Another homeopathic remedy is Berberis - it is prescribed for severe pain.
As for hormonal drugs, Duphaston is most often prescribed, which significantly reduces the size of the tumor and prevents the appearance of new cysts.
If cysts appear frequently, gonadotropic hormones are recommended - Goserelin, Danazol, Buserelin, Eligard.
For local treatment, suppositories are prescribed - Ichthyol, Longidaza, with Indomethacin.
For mild tumors, oral contraceptives are prescribed.
Conservative treatment is not carried out for 3 months; if no positive dynamics are noticed during this time, surgical treatment is prescribed.
Surgical intervention
Corpus luteum cyst is removed using laparoscopy or laparotomy .
In some cases, the technique for removing the cyst changes during surgery.
If signs of pelvioperionitis are detected, laparoscopy will not be able to fully cope with the problem; in such cases, the ovary must be completely removed.
But most often, laparoscopic removal is quite sufficient.
The cyst is removed, the cavity is sutured, and the organ tissue is preserved as much as possible..
Associated symptoms
An ovarian corpus luteum cyst can be present in the body without showing signs - its development is not accompanied by pain or other sensations, and can only manifest itself as a delay in menstruation.
The main symptoms of an ovarian corpus luteum cyst:
- discomfort or pain in the right or left lower abdomen,
- intensification or appearance of pain during physical activity, after sexual intercourse,
- delayed menstruation followed by heavy menstrual bleeding,
- increased frequency of urination - occurs rarely, with a large diameter of the cyst.
Over time, the formation can increase in size, which is manifested by an increase in the intensity of symptoms.
Folk remedies
As for traditional medicine , it is recommended to collect :
- liquorice root;
- mint;
- sweet clover;
- elecampane;
- eucalyptus;
- sagebrush.
Each plant is taken in equal proportions, mixed, a tablespoon of the mixture is poured into a glass of water and placed in a water bath..
After 15 minutes, turn off the heat and leave the product covered for 3 hours.
Drink 100 grams per day, add to water for sitz baths.
Pathology and pregnancy
With functional neoplasms , pregnancy, as a rule, does not occur, but with fibrocystic mastopathy, conception is quite possible .
This phenomenon should not bother a woman, since pregnancy is a means to treat mastopathy, regardless of the place of its formation and form.
CAREFULLY!
But ovarian cysts and pregnancy are not always compatible concepts. Mucinous and serous cysts are dangerous during pregnancy and must be removed.
As for the corpus luteum cyst, it does not pose a danger to pregnancy; moreover, in the first months of bearing a child, it will produce progesterone, which maintains the tone of the reproductive organ and prevents rejection of the fertilized egg.
As a rule, at the 12th week of pregnancy, the corpus luteum cyst will begin to regress and completely disappear by the 20th week.
Corpus luteum
Initially, you should understand what the corpus luteum is and what are the reasons for its formation in the body. So, it is a gland that develops in the ovary every monthly cycle. Its main function is considered to be the production of the hormone progesterone.
The corpus luteum begins to develop in the luteal (second) phase of the menstrual cycle. If fertilization is absent, then it stops developing and, accordingly, stops producing the hormone. If pregnancy has occurred, it continues to grow and function for another two or three months, which provides the body with the required amount of progesterone. This function is then taken over by the resulting placenta.
Other types of ovarian cysts
There are the following types of cysts that can be found in the ovary :
- dermoid - a benign neoplasm, which is characterized by extremely slow growth;
- endometrioid - benign neoplasm, more common in nulliparous young patients;
- polycystic ovary disease - enlargement of the organ due to the development of small atheromas;
- follicular – most often diagnosed in pregnant women and women of reproductive age;
- serous - a benign tumor with a certain cell structure;
- mucinous - very similar to the previous one;
- papillary - in half of the cases the formation is malignant.