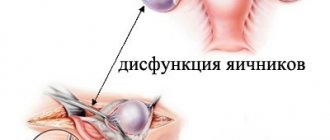
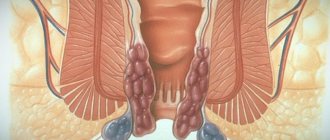
How the ovaries and tubes hurt
“...Your feet will freeze—the appendages ache! And now, after menstruation, the lower abdomen still hurts and my lower back is tight. Intimate life is also not happy - after intimacy, everything inside is “torn”. What should I do with all this, how can I get rid of inflammation?...” The situation given in the quotation from the patient’s letter is familiar to many women firsthand.
The appendages are the fallopian tubes and ovaries. They are located in the lower abdomen, above, to the right and left of the pubic bone. These organs are responsible for the growth and development of the egg, as well as for its release into the uterine cavity. Less commonly, the problem affects just the tubes; usually the infection spreads to the ovarian mucosa.
Inflammation of the ovaries in women can be caused by a wide variety of reasons, one or more. In combination with risk factors, they can cause the development of an infectious process in the pelvic organs. Such provoking agents may be:
- Genital tract infections,
- Hypothermia, stress,
- Change of sexual partner,
- Surgical abortions,
- Intrauterine manipulations,
- Violation of intimate hygiene rules.
Why can the ovaries become inflamed and hurt if you get a cold? The fact is that the bacterial flora of the female vagina contains pathogenic microorganisms in certain quantities. At the same time, their number and vital activity are controlled by the immune system. With a sharp and sudden decrease in protective reactions, which is precisely what is observed against the background of hypothermia, private stress and for other reasons, inflammation of the internal genital organs can form on its own, without the presence of an external source of infection. This mechanism for the development of inflammation of the appendages is usually observed in teenage girls and virgin girls.
Signs and symptoms of inflammation
In gynecology, there is inflammation of the left ovary, bilateral inflammation and inflammation of the right ovary. Symptoms and treatment of appendages in women depend on the form in which the process takes place. This can be acute, subacute and chronic. All of them are characterized by common symptoms, among which the most common are the following:
- Pain in the lower abdomen, lower back,
- Irregularities of the monthly cycle,
- Increased discharge
- Increased urination
- Increased body temperature
- Pain during sexual intercourse, weakness.
WHAT HAPPENS TO INFLAMMED TUBES AND OVARIES?
The mucous membrane of the tubes becomes swollen, thickens, the lumen narrows, they become difficult to pass through for eggs, which can cause the tubal form of female infertility.
The consequence of prolonged inflammation in the pelvis is adhesions. They are growths of connective, scar tissue on the mucous membrane; they fence off the area of inflammation from healthy cells. Subsequently, the adhesive process becomes an obstacle to the fertilized egg as it moves towards the uterus. And this is infertility, inability to get pregnant, ectopic pregnancy.
The process of formation of female sex hormones is disrupted, which leads to menstrual irregularities and unstable egg maturation.
Inflammatory diseases of the ovaries, untreated or insufficiently treated, after some time become chronic. Ultimately, this leads to adhesions in the pelvis and infertility. Therefore, given the variety of causes that cause pain in the lower abdomen and other symptoms indicating inflamed appendages, in order to avoid consequences, it is necessary to consult a gynecologist in a timely manner!
CONSEQUENCES OF OVARIAN INFLAMMATION:
- The likelihood of developing an ectopic pregnancy increases many times;
- Adhesions and obstruction of the fallopian tubes;
- Constant leucorrhoea, vaginal dysbiosis;
- Disorders of the menstrual cycle (delays, pain, bleeding);
- Infertility, risk of miscarriage;
- Cysts on the ovaries as a consequence of cold appendages;
- Bladder dysfunction;
- Purulent complications requiring surgical treatment;
- Frigidity, anorgasmia.
Treatment of appendages in women
If the disease is treated correctly, the acute symptoms disappear after a few days, but this does not mean that the procedures can be completed. If the causes are identified, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial and restorative therapy is prescribed, the process takes a lot of time, it cannot be interrupted, otherwise complications in the form of a chronic form of the disease are possible.
In general, the process includes a number of stages:
- treatment of inflammation of the appendages with antibiotics.
- physiotherapy, suppositories for inflammation of the appendages.
- if a chronic form and adhesions are detected, preventive physiotherapy for 1.5-2 years.
- if adhesions have formed (sticking together of the walls of the fallopian tubes and ovaries), an endoscopic dissection operation is required.
- sanatorium-resort and balneotherapy.
Grandmother's funds
Official medicine is not all the methods that can be used in the treatment of inflammation of the appendages. In this case, traditional medicine recipes can be used as auxiliary techniques.
For example, herbal tea helps a lot.
To do this, you need to prepare a collection of 20 g of meadowsweet grass, daisy and mantle, add 200 g of rose hips. Take 2 tbsp. l. crushed collection, pour 0.5 warm water, leave for 5 hours, bring to a boil, then cool and strain. The finished infusion should be drunk during the day, and the general course of treatment in this case is 2-3 weeks.
You can use a decoction for douching; to do this, you need to mix equal parts of horsetail and knotweed herb, yarrow and calendula inflorescences, wood mallow and white clear flowers. Chopped mixture in the amount of 2 tbsp. l. pour a liter of boiling water, leave, covered, for an hour, then strain and cool from body temperature. Douching needs to be done for a long time (4 weeks, possibly until complete recovery).
If a woman has a cold in her ovaries, the symptoms of inflammation or, as most people call it, “colds” of the appendages are pronounced and cause considerable discomfort. Even in childhood, girls are taught to wear warm pants in cool weather and never sit in cold weather. But it often happens that the disorder appears suddenly, and the woman is not even aware of the true causes.
Ovarian cold is an inflammatory process (oophoritis), which can spread to the fallopian tubes (), the uterus and, if left untreated, causes infertility. ARVI is not the main cause of this disease. During a viral infection, the body is weakened and susceptible to bacteria. Thus, gonococci, staphylococci, gonococci, and chlamydia provoke the development of ovarian colds in women. However, gynecologists have identified several more factors that contribute to the onset of the disease:
- constant stress, depressed mood, nervousness, hysteria;
- psycho-emotional fatigue, depression;
- lack of rest, lack of sleep, insomnia;
- unbalanced diet, lack of vitamins, overeating or, conversely, malnutrition;
- obesity/anorexia;
- previous acute viral diseases (flu, sore throat, etc.);
- taking antibiotics;
- chronic diseases of the pelvic organs;
- hypothermia;
- wearing tight, tight underwear;
- abortion;
- incorrect installation of the intrauterine device;
- surgical interventions;
- unprotected sex, frequent change of sexual partners.
Even the most ordinary swimming in cool water, taking a cold shower or wearing a wet swimsuit for a long time contribute to the development of ovarian colds.
Every woman as a child has more than once heard truthful “calls” not to sit on cold surfaces, for example on window sills, on benches or on a concrete floor in winter. After all, in this way you can get serious hypothermia and, as a result, flu, acute respiratory infections, cystitis, inflammation of the ovaries, appendages, bladder and other colds.
As a rule, the ovaries take part in the inflammatory process simultaneously with the tubes and other internal organs related to them. A cold usually results in dysfunction of these organs. Microbes of this infection can be brought into the ovaries from neighboring organs, as well as through lymphatic and blood vessels.
Acute inflammation of the ovaries can also be caused by cold feet during menstruation, a cold, or douching with cool or cold water after sex. In the acute stage of a cold in women, the pain is quite pronounced, especially in the lower
The main factors for genital colds in women
The causes of the disease are mainly various microorganisms and bacteria. For example, such as E. coli, staphylococci, gonococci, streptococci, tubercle coli and various fungi.
They penetrate the inside of the genital organs both due to poor hygiene, and due to everyday issues or illness of the sexual partner.
One of the main causes of the disease is a violation of their integrity. This can occur from strong friction from uncomfortable or tight clothing, from foreign objects being in the vagina for a long time, from swimming in bodies of water with infectious microorganisms, or from violating the rules of antiseptics and disinfection during surgery.
Inflammation of the genital organs is observed mainly in women of childbearing age and women with an active sexual life.
Unusual discharge, pain in the lower abdomen, general poor health - everything may indicate cold appendages. The disease is as dangerous as it can occur unnoticed. A woman dressed inappropriately for the weather, sat on a cold bench, got her feet wet and didn’t have time to warm them up - and problems on the female side begin.
In order for cold appendages to remain the only problem, without becoming the beginning of more serious female diseases that threaten, it is necessary to know their symptoms, respond to them in a timely manner and immediately consult a doctor for help.
Grandmother's funds
Signs and methods of treating cold appendages.
Every person at least once in his life was hypothermic, after which a cold and inflammation of internal organs occurred. The most dangerous and unpleasant condition for a woman is when she has a cold in her appendages, that is, the organs that perform the reproductive function in her body. Inflammation of the ovaries and fallopian tubes leads to severe complications and even infertility.
Inflammation of the appendages can manifest itself in two forms - acute and chronic. In the first case, we are talking about pronounced symptoms, when they appear, you should immediately consult a doctor. If the disease was not completely cured or was not treated at all, it becomes chronic. In this case, the symptoms are less pronounced, which is why the manifestations of the disease can be mistaken for signs of other diseases (appendicitis, cystitis, etc.)
The manifestations of the acute form of salpingoophoritis include the following symptoms:
- Delayed menstruation or acyclic bleeding. If a woman has a cold in her appendages, she may experience fluctuations in her monthly cycle and the appearance of bloody or bloody vaginal discharge that is not associated with menstruation.
- Acute pain in the lower abdomen (on one side with unilateral inflammation and on both sides with bilateral inflammation). Pain increases when performing physical activity, changing body position, lifting weights, or having sexual intercourse.
- Increase in body temperature to 38-39 degrees.
- General intoxication of the body, manifested in the form of weakness, chills, dizziness, nausea and vomiting.
- Difficulty or painful urination and bowel movements.
When the disease becomes chronic, we are talking about symptoms such as:
- Pain during menstruation.
- Slight increase in body temperature (about 37 degrees).
- Periodic dull or aching pain in the lower abdomen and in the sacral area.
- Atypical vaginal discharge.
- Decreased sexual desire.
https://youtu.be/WGN7PsBcz88
Complications of inflammation
One of the serious complications of inflammation of the appendages is infertility. Inflammatory processes affect the epithelial cells of the fallopian tube (one or both), after which their work is disrupted and this can lead to scarring of the tube. After this, the fallopian tube stops working completely.
If the inflammatory process is prolonged, the connective tissue in the ovaries grows. The ovarian capsules thicken and become very strong. In such cases, a rupture will not occur during ovulation, and therefore pregnancy will not occur.
In addition to damage to the tubes and ovaries, the inflammatory process also spreads to the peritoneum - the inner lining of the abdominal cavity. The body fights infection and stimulates the growth of connective tissue, resulting in adhesions that combine the sheets in the abdominal cavity. The presence of a large number of adhesions can disrupt intestinal motility and lead to pain, constipation or diarrhea. At the same time, the mobility of the fallopian tube will decrease, the organ will be tense and the egg will not be able to enter the uterus.
As a result, the inflammatory process will lead to a complex form of infertility, which requires long-term treatment. Ectopic pregnancy can also occur due to inflammation.
Important! Inflammation of the appendages leads to disruption of the entire reproductive system if it lasts for a long time or is chronic. If you do not consult a doctor in time, the inflammatory process will worsen
As soon as you notice symptoms of infection, contact your gynecologist immediately. We recommend you learn: Ovarian cyst Louise Hay
Signs and methods of treating cold appendages
Every person at least once in his life was hypothermic, after which a cold and inflammation of internal organs occurred. The most dangerous and unpleasant condition for a woman is when she has a cold in her appendages, that is, the organs that perform the reproductive function in her body. Inflammation of the ovaries and fallopian tubes leads to severe complications and even infertility.
Why does inflammation occur?
When a woman does not warm up well during the cold season, the risk of developing inflammatory processes increases. When hypothermia occurs, all the body's forces are spent on warming up, so its protective function is reduced. Viruses and bacteria can easily enter the body.
The infection can directly penetrate the woman's genitals and cause disease of the appendages. This form is called ascending. Or the inflammatory process penetrates to the ovaries and fallopian tubes through the blood and lymph from other organs in which the pathology has arisen.
In addition to hypothermia, there are other factors that increase the risk of developing inflammation in the appendages:
- stress;
- unprotected sex;
- hormonal imbalances;
- overwork;
- exhausting diets;
- bad habits.
Symptoms
If a woman has a cold in her appendages, she can recognize it by the following symptoms:
- Abdominal pain. Most often - in the lower abdomen, can be unilateral or bilateral. The intensity of the pain can be different: strong, sharp, aching, pulling. It can be constant or have a paroxysmal character.
- Lower back pain. Drawing and constant, as during menstruation.
- When pressing on the abdomen, the woman feels tension in the internal organs and pain.
- Increased body temperature. In mild forms, about +37.4 ºC, in severe cases - +38.5 ºC and above.
- Weakness throughout the body, chills, headache.
- Frequent and painful urination. Changes in the amount of urine (it becomes less) and its color (it may become darker, there may be blood impurities).
- Changes in the amount and structure of vaginal discharge. There are more of them, they acquire a serous, sometimes purulent structure. Intermenstrual bleeding is observed.
- Itching and burning occur in the genitals.
- Sometimes signs of dyspepsia occur: nausea, vomiting and diarrhea.
When inflammation of the appendages is indolent, a woman may not feel obvious symptoms of the pathology. To determine the presence of this form, you must regularly visit a gynecologist.
What to do if you have a cold in your appendages
If a woman notices symptoms of inflammation of the appendages, she needs to go to the hospital. There she will have to undergo an examination by a gynecologist, have an ultrasound of the appendages, take a vaginal smear and a general blood test.
Based on the results of these studies, the gynecologist can diagnose “salpingoophoritis” or “adnexitis” - this means that the ovaries and fallopian tubes are frozen.
In mild forms, the disease is treated on an outpatient basis. The acute stage of the disease with complications requires constant doctor supervision of the patient, so it is better to go to the hospital.
A woman with inflamed appendages must remain in bed, follow all doctor's orders and adhere to a diet.
The treatment methods prescribed by the doctor consist of:
- antibiotic therapy;
- symptomatic therapy;
- restorative therapy;
- physiotherapy.
Drug therapy
The gynecologist prescribes antibiotics after the causative agent of inflammation is identified. The most popular are:
- Azithromycin;
- Doxycycline;
- Gentamicin;
- Amoxiclav;
- Amoxicillin;
- Ceftriaxone;
- Ciprofloxacin;
- Tsifran;
- Sumamed;
- Tsiprolet;
- Nolitsin.
These drugs are prescribed in a course that lasts 7–14 days.
Antibiotics should be taken strictly following the instructions and recommendations of the doctor. If you do not complete antibiotic therapy, the disease can become chronic.
The following medications will help relieve the inflammatory process:
- Voltaren;
- Diclofenac;
- Nimesulide.
To relieve pain and swelling, the following is prescribed:
- Loratadine;
- Ketotifen;
- Diphenhydramine.
To make the fight against bacteria more effective, it is necessary to use suppositories:
- Polygynax;
- Terzhinan;
- Trichopolum.
To help a woman’s body recover faster, vitamins, dietary supplements, homeopathic remedies and hormonal contraceptives are prescribed.
Physiotherapeutic methods
After the acute process of inflammation has passed, the woman can begin treatment with physiotherapy.
The most effective methods are:
- electrophoresis;
- magnetic therapy;
- mud therapy;
- paraffin therapy;
- hydrotherapy
If inflammation of the appendages leads to an ovarian abscess, adhesions of the fallopian tubes, or accumulation of pus in the uterine cavity, then the patient will undergo surgical treatment.
Folk remedies
It is not recommended to treat inflammation of the appendages at home. However, there are folk remedies that will help a woman get rid of unpleasant symptoms faster:
- Inflamed appendages can be heated with rock salt, which relieves pain well. Before this, you need to heat it in a frying pan and wrap it in a towel. Before doing the procedure, you need to consult a doctor, since if there is an abscess in the female appendages, any heating is prohibited.
- Dried nut leaves need to be poured with boiling water and left for 4 hours. Drink the infusion 3 times a day, 1 tbsp. l.
- Appendages can be cured by douching with herbal decoctions. For this purpose, you can use chamomile, yarrow, string, sage, oak bark and calendula.
- You can brew 50 mg of coltsfoot, thyme and oak bark in 1 liter of water. Drink 3-4 times a day after meals.
A patient with cold appendages needs to adhere to the following diet:
- reduce the amount of salt consumed;
- remove sweet, fatty and smoked foods from the diet;
- during an exacerbation, do not eat protein;
- the diet should consist of fermented milk dishes, cereals, vegetables and fruits.
Possible consequences
Inflammations that arise because a woman has a cold in her ovaries can lead to the following consequences:
- adhesions and scars on the fallopian tubes;
- hormonal imbalances, menstrual irregularities;
- abscess and necrosis of appendages;
- removal of appendages;
- infertility.
To prevent such complications, a woman needs to undergo complete treatment under the supervision of a gynecologist.
Prevention
To prevent diseases of the appendages, you need to adhere to the following preventive measures:
- during the cold season, protect the genitals and legs from the cold;
- wear natural rather than synthetic clothing;
- maintain genital hygiene;
- avoid unprotected sex;
- eat right and spend time actively in the fresh air;
- eliminate bad habits from life.
https://youtu.be/AUsfwvUI4GE
Expectant mothers need to be especially careful. After all, pregnancy already reduces a woman’s immunity, so the body does not need unnecessary stress in the form of hypothermia.
venerologia03.ru
Symptoms
There are acute and chronic forms of inflammation.
The acute form of adnexitis is characterized by:
- Aching pain, sharp or dull, localized in the lower abdomen, sometimes radiating to the lower back. The pain syndrome will be more pronounced during menstruation;
- Pain during physical activity, during bowel movements, urination;
- Fever up to forty degrees, weakness and chills;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Discharge: profuse leucorrhoea, purulent discharge - depending on the causative agent of the infection;
- Cycle disorders due to ovarian dysfunction and hormonal imbalance;
- Decreased or complete absence of sexual desire, pain during intercourse.
In the chronic or latent form of inflammation of the appendages in women, the symptoms are less pronounced, the temperature may be low-grade, and lethargy and irritability are observed. Chronic inflammation of the appendages is dangerous because pathological processes occur in the body, weakening and destroying it, but due to sluggish symptoms, the patient is in no hurry to consult a doctor, which ultimately leads to serious complications.
You should not engage in self-diagnosis based on information from the Internet. You can write to a medical forum about the symptoms that worry you; this will provide some psychological relief, but will not cancel a visit to the gynecologist.
To make an accurate diagnosis, the results of an examination by a gynecologist are necessary - a manual examination helps to immediately determine the glands enlarged as a result of edema. A number of laboratory tests are also required. The diagnosis is clarified according to the data of an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs, computed tomography and MRI. They do urine and blood tests, and a vaginal smear for flora. If necessary, laparoscopy is prescribed in some cases. Having made a diagnosis, the doctor determines treatment. Symptoms and treatment, respectively, are individual in each case.
Ultrasound is often prescribed to diagnose the disease.
Treatment
Grandmother's funds
If a woman suspects that she has caught a cold in her appendages, she should immediately visit a gynecologist. The doctor will conduct the necessary examination and select an effective drug therapy regimen.
Acute adnexitis requires immediate treatment in a hospital setting. Patients with the chronic form can receive care on an outpatient basis.
To treat cold appendages, the gynecologist prescribes pharmaceuticals and physiotherapeutic procedures.
The use of folk remedies is allowed. If it is impossible to cure purulent appendages using conservative methods, their removal is recommended.
For acute or chronic adnexitis the following are prescribed:
- antibiotics;
- antihistamines (Tavegil, Suprastin, Fenistil);
- immunostimulants (Immunal, Cycloferon);
- anti-inflammatory suppositories (Indomethacin, Movalis, Terzhinan, Polizhinaks);
- vitamins (groups B, E, C).
Additionally, medications may be recommended to normalize sleep, improve emotional state, and relieve pain.
Antibiotics
Antibiotics are used to treat acute or unspecified forms of the disease. The list of drugs is quite wide, the choice depends on the type of pathology and pathogen.
To achieve a quick therapeutic effect, injections of Doxycycline, Gentamicin, Ceftriaxone, and Lincomycin are prescribed.
For uncomplicated chronic adnexitis, antibiotics are taken orally, in the form of tablets: Azithromycin, Metronidazole, Ofloxacin.
Surgical intervention is indicated for purulent forms of adnexitis if drug treatment does not produce a positive effect.
Laparoscopy is a low-traumatic removal of pus, treating the source of infection with antiseptic and antibacterial drugs, restoring the patency of the fallopian tubes by separating adhesions.
Adnexectomy is a traumatic operation to remove appendages with extensive purulent inflammation.
ethnoscience
Along with medications, cold appendages can be treated with folk remedies.
These are lotions, douching, decoctions for internal use, baths.
The recipes include medicinal herbs that soothe pain, have anti-inflammatory and healing properties: chamomile, cinquefoil herb, St. John's wort, field grass, coltsfoot, sweet clover, oak and linden bark, viburnum flowers.
Grandmother's funds
Treatment for colds of the ovaries should be carried out as early as possible, since its absence or untimely treatment can lead to infertility. This is explained by the fact that foci of inflammation sooner or later begin to affect the two appendages (), fallopian tubes (adnexitis) and spread to other organs of the abdominal cavity.
In most cases, treatment for colds of the ovaries includes:
- Painkillers. Relieves painful symptoms.
- Immunomodulators, vitamins. Designed to normalize the body's balance and maintain immunity.
- Antiviral drugs. Eliminate infection and prevent the spread of inflammation to nearby organs.
- Antibiotics. They fight the root cause of the disease and are most often prescribed only in advanced cases.
- Physiotherapy. Massage, electrophoresis, mud baths.
Treatment of ovarian colds also involves abstinence from sexual activity, diet and bed rest, proper rest and elimination of bad habits.
The acute form of inflammation in most cases requires hospital observation, the chronic form requires surgical intervention. But this can be avoided if diagnosis is carried out in time and the cause of infection is identified.
Only a doctor will tell you in detail how to treat cold ovaries at home. This could be taking pills, using vaginal suppositories, etc. If the patient wishes to use folk remedies, she should also consult a gynecologist.
Treating ovarian colds at home involves preparing herbal infusions or tea. Sometimes douches and tampons are used. The following tools have proven themselves to be effective:
- Herbal decoction for drinking. In a container, mix meadowsweet, daisies, mantle (20 grams of each). Add 200 grams of rose hips. Grind the resulting mixture in a blender (combine, meat grinder) and pour 0.5 liters of boiling water. Let it brew for 5 hours, then boil, cool and strain through cheesecloth. Drink the resulting decoction in small portions throughout the day. The course of treatment is 2 weeks.
- Herbal decoction for douching. To prepare, combine 1:1 millennium, calendula, knotweed, horsetail, mallow, and jasmine. Grind the collection. 2 tbsp. l. Pour 1 liter of boiling water over the resulting mixture and let it brew for one hour. Strain through cheesecloth and let cool. Douche for at least three weeks, after which undergo a gynecological examination.
You can use traditional methods of treatment only after consulting a doctor!
To relieve painful symptoms and reduce foci of inflammation, the following remedies and recommendations are also suitable:
- regular mud baths and taking potassium iodide;
- lubricating the lower abdomen with ichthyol ointment or using tampons based on it;
- mandatory presence of pumpkin, pumpkin seeds, juice in the diet;
- drinking a decoction based on corn cob fibers;
- complete refusal of sexual activity.
Important! At the first painful sensation in the lower abdomen, a woman should consult a doctor, and not self-medicate and take painkillers. Otherwise, the disease can lead not only to bilateral oophoritis, adnexitis, adhesions, but also to infertility.
There are many different types of colds. There is also a common cold among the genital organs. What disease is actually hidden behind this designation?
When treating acute adnexitis, hospitalization is necessary, ensuring physical and mental rest, prescribing a light diet, a sufficient amount of liquid (fruit juice, tea, alkaline drinks), and it is also necessary to monitor the excretory function. As a rule, to treat inflammation of the appendages, painkillers, anti-inflammatory, and desensitizing drugs are prescribed, but the main role belongs to antibiotics, and it is preferable to use antibiotics that have a long half-life and elimination period.
If the disease is severe and threatens the development of sepsis, then to treat inflammation of the appendages it is necessary to take antibiotics in various combinations, drugs that have a bactericidal effect on the anaerobic flora (orally or intravenously). For the purpose of intoxication, infusion treatment is used.
When determining purulent forms of inflammation, laparoscopy is provided, during which the pus is removed and the site of inflammation is irrigated using antibiotics and antiseptics. To cure acute adnexitis, puncture of the vaginal vaults is used, as well as local administration of antibiotics. If the disease is at such a stage that conservative treatment will not be effective, then surgical removal of the appendages is necessary.
After the acute symptoms of adnexitis are relieved, physiotherapy is prescribed (ultrasound, vibration massage, electrophoresis with potassium, magnesium, zinc on the lower abdomen), as well as the use of biostimulants. These methods reduce tissue exudation, have absorbable and analgesic effects, and help reduce the formation of adhesions.
If chronic adnexitis has worsened, then the same treatment as acute is provided. In addition, paraffin treatment, therapeutic mud (ozokerite), baths and vaginal irrigations with sulfide, sodium chloride mineral waters, as well as spa treatment in the stage of stable remission are effective.
If a woman has a cold like a woman, treatment should be early and timely. Otherwise, complications will develop that lead to scarring of the inflamed tissues and, as a result, the development of infertility.
The most dangerous state of the disease is the latent form. Due to its mild severity and absence of symptoms, the woman is in no hurry to see a doctor. However, the adhesive process can be started, making it impossible to conceive a child.
What to do if you have a cold like a woman? In severe cases, it becomes necessary to completely remove the inflamed appendages. This occurs with complicated purulent adnexitis.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=viQxnNvDCbc
But usually therapy is carried out in a hospital setting, where antibiotic treatment is used. Anti-inflammatory drugs, vitamins, immunostimulants, painkillers and antihistamines are prescribed as additional medications.
To prevent vaginal dysbiosis, antimycotic drugs are prescribed. As a local treatment, probiotics are used in the form of suppositories, and baths are made with antiseptics and anti-inflammatory drugs.
When severe symptoms subside, physical therapy is indicated. Often, when the appendages become inflamed, a disruption occurs in the menstrual cycle; in this case, hormonal agents are prescribed to restore it.
Treatment for colds of the ovaries should be carried out as early as possible, since its absence or untimely treatment can lead to infertility. This is explained by the fact that foci of inflammation sooner or later begin to affect the two appendages (bilateral oophoritis), fallopian tubes (adnexitis) and spread to other organs of the abdominal cavity.
How to distinguish inflammation of the appendages from other diseases
It is impossible to independently find out what kind of inflammation occurs in the body, because the symptoms may be similar. Only a gynecologist can make the correct diagnosis by conducting a preliminary survey and examination of the patient.
USEFUL INFORMATION: Utrozhestan during pregnancy until what week to take
Current examination methods:
- Blood and urine analysis.
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- Diagnostic laparoscopy.
Only after indicating the diagnosis, the gynecologist will prescribe a course of treatment, which includes: anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial and restorative therapy. The duration of treatment is determined by the doctor and should not be changed, even if there is a temporary improvement.
Prevention will help avoid inflammation of the appendages:
- Dress according to the weather. Avoid hypothermia of your legs and reproductive organs.
- Current methods of contraception. To avoid diseases that are sexually transmitted and lead to inflammatory processes, use condoms.
- Unwanted pregnancy. A medical abortion will significantly increase the risk of developing inflammatory processes and should only be done if absolutely necessary, if there is no other option.
We recommend you learn: How a hypoechoic formation develops in the ovary
What causes inflammation?
Many women are at risk of the disease without even knowing it, because... The disease can be provoked by actions and situations that seemingly do not relate directly to the appendages:
- Promiscuous sex life. Having a large number of sexual partners reduces the protective function of the cervix.
- Douching helps eliminate the beneficial microflora of the vagina, which allows infections to easily penetrate the uterus and appendages.
- Sexual intercourse during menstruation is dangerous because the cervix is dilated and it is easier for pathogens to get inside.
- Intrauterine device. The threads of the spiral extend through the cervix into the vagina, so through them the infection can enter the uterus and appendages.
- Inflammatory processes and operations on the pelvic organs. In cases where salpingoophoritis has not been completely cured, bacteria and viruses continue to live and multiply in the body, which can lead to a chronic form of the disease, which will worsen with decreased immunity.
- After any operation, the patient is prescribed antibiotics to prevent the development of pathogens.
In order to protect yourself from diseases of the appendages, you should reduce the number of factors that contribute to the entry of bacteria into the uterus.
Causes of inflammation
It must be said that doctors call the phrase “inflammation of the appendages,” familiar to most women, the term “andexitis.” But today this name is used very rarely, since the terms “salpingitis” - an inflammatory process of the fallopian tube and “oophoritis” - an inflammatory process of ovarian tissue have come into use. But these pathological processes are rarely observed individually and, as a rule, doctors deal with “salpingo-oophoritis”.
The process of inflammation in the uterine appendages and ovaries is caused by opportunistic and pathogenic bacteria. Under certain conditions they are pathogenic and cause this disease. The infection penetrates into the uterine appendages in the following ways:
- from the vagina and cervix;
- from other organs where the process of inflammation is present - the sigmoid colon, appendix;
- through lymphatic and blood vessels.
Factors contributing to the development of the disease are:
- promiscuous sexual intercourse;
- failure to comply with hygiene rules;
- childbirth with complications;
- stressful situations and hypothermia;
- appendectomy;
- weakening of the immune system, which is caused by various infections and diseases - HIV infection, diabetes and any other infectious diseases;
- medical interventions inside the uterus - removal or insertion of a device, curettage of the uterine cavity, abortion, etc.
Causes of a bladder cold
A woman wants to be beautiful and elegant at any time of the year, even in the cold.
At the same time, she is overcome by two desires - to be healthy and beautiful. I don’t want to wear warm underwear and heavy warm coats. If beauty wins, this is fraught with a hospital ward and serious illnesses. Female organs are very vulnerable, especially when exposed to cold. The main cause of the disease is the entry of bacteria into the urinary system. This leads to damage to the mucous membrane that lines the bladder.
Bladder cold in women
Getting cystitis is very simple - you catch a cold in your feet, and after a couple of days you have a whole bunch of its manifestations. All this leads to the fact that the woman has a slight cold in her legs, and her lower abdomen already hurts and other symptoms of cystitis are observed.
Treatment for this pathology should be selected by a doctor. It is usually comprehensive, aimed at restoring normal immunity and eliminating inflammation in the joints.
In some cases, larger joints, such as the knee and hip, are also affected. In such cases, there is redness in the area of the affected joint, swelling, severe pain and limited movement.
Arthritis is often accompanied by general symptoms, such as fever, chills, drowsiness, loss of appetite, etc.
With a weakened immune system, the digestive organs can also be involved in the process, which is why the woman’s bowel movements are disrupted, her back begins to hurt, and prolonged diarrhea is observed. Inflammation of the appendages often develops into a latent form, which occurs without visible symptoms, worsening during the cold season and before menstruation.
Causes
Often the cause of inflammation is infection that occurs through sexual contact.
However, sometimes inflammation appears as a result of the body’s protective reaction and has nothing to do with infections:
- If we talk about infectious causes of oophoritis, then first of all this happens after unprotected sex with a partner who himself has inflammation
- There is another reason for inflammation - physiological, so to speak. In women, unlike men, the rectum, vagina and bladder are located very close to each other. Therefore, if there is an infection in the body, say, E. coli, then the parasite can easily get from the rectum into the vagina and, making its way higher through the pipes, reach the ovaries.
- You can add one more reason - abortion. Quite often, abortions are complicated by oophoritis.
When the ovaries become inflamed, the entire area around them becomes inflamed, including the fallopian tubes.
Indirect reasons can also be identified:
- many stressful situations;
- lack of sleep;
- smoking;
- overwork;
- avitaminosis.
Traditional therapy
What to do for cold ovaries is usually decided by a gynecologist. Most often, doctors prescribe complex treatment with drugs, which lasts from 7 to 14 days. These can be tablets, IVs or injections.
For cold ovaries the following are prescribed:
- antibiotics;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- painkillers;
- vitamin complex.
In this case, the sick woman is prescribed bed rest, rest, as well as a special diet, which contains healthy food rich in vitamins.
In some cases, a girl may be prescribed physical therapy: treatment with ultrasound, UV irradiation, etc.
Do not reduce or change doses of medications, skip doses, or shorten the number of days. This will most likely lead to complications of the disease and provoke its chronic form.
Depending on the severity of the disease, infusion therapy is used. In a hospital setting, intravenous drip administration of saline solution, hemodez and glucose is used.
Antibacterial therapy forms the basis of treatment; drugs are selected depending on the type of pathogen and wide spectrum of action.
The most commonly used drugs are penicillins or cephalosporins. These include “Amoxiclav”, “Ceftriaxone”.
If anaerobic bacteria are present, then synthetic drugs nitroimidazoles will be effective. These are “Metronidazole”, “Trichopol”. They are capable of suppressing the vital activity of both gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms, as well as protozoa.
Regarding gram-positive bacteria, macrolites are effective drugs. They successfully eliminate infectious phenomena such as chlamydia and mycoplasma. Among the most popular drugs from this group are “Erythromycin”, “Azithromycin”, “Spiramycin”.
In order not to disturb the natural microflora inside the body, antifungal agents such as Nystatin and Diflucan should be taken along with antibiotics.
At the doctor's discretion, other antibiotics or even a combination of them may be used. If the drug is effective, it will be noticeable within 2-3 days. Typically, injections are used at the beginning of therapy, then you can switch to tablets.
If a woman has a cold like a woman, treatment with folk remedies is quite acceptable. Before starting such therapy, you should consult your doctor.
If a woman has a cold and the symptoms are pain in the lower abdomen, then this can be treated with a salt bath. This is done before the main procedures to relieve pain.
To do this, hot water is drawn into a bathtub or basin, in which salt is diluted. For 10 liters of water, take 1/3 of the pack. After this, you need to sit in the water for 15 minutes. At the same time, the room should be warm and there should be no drafts. After the procedure, you need to dry yourself well, put on dry clothes and immediately go to bed. It is advisable to do this bath every evening until the pain completely disappears.
For women's problems, it is recommended to drink white acacia as a decoction and also douche with it. This plant is good for many inflammations, including in the appendage area.
The infusion is prepared as follows:
- Pour a glass of boiling water over a teaspoon of dry plant.
- Cover the product with a lid and leave for 20 minutes.
- They drink tea 4-5 times a day.
- If desired, add honey to the drink.
Douching:
- For 1 liter of boiling water, take a tablespoon of raw materials.
- The product is placed on fire and boils for 5 minutes.
- Wait until the product becomes warm.
- Douching is carried out 2 times a day - morning and evening.
- The course lasts two to three weeks.
- It is recommended to combine the product with acacia infusion.
Sometimes women wonder: what to do if they have a cold like a woman during pregnancy? At this time, many medications are prohibited; this is where traditional therapy, which is safe for a growing baby, will help.
During periods of lull in the disease, it is worth using warming procedures. For example, dry heat on the lower abdomen and lower back, taking warm baths. In the acute period, when the main treatment is carried out, a woman should abstain from sexual intercourse.
You should not delay treatment, even if the disease does not manifest itself clearly. For prevention, you need to undergo an examination by a gynecologist at least once a year in order to know what symptoms and treatment of inflammation of the appendages occur in women.
Diagnostics
The diagnostic actions of such a disease can confidently be called a fairly important task. If you do not find and do not recognize the signs of adnexitis in the first stages, very serious and negative consequences may result.
To find certain symptoms and confidently recognize them, it is important to know some points that will help you diagnose the disease
First of all, take a pregnancy test and also see your doctor for a chairside examination. Thanks to such actions, the doctor will be able to determine the sensitivity of the cervix, as well as its appendages. Moreover, when examined on a chair, the specialist will feel the mobility of the organs and their shape.
Next, it is quite important to undergo a special examination in the laboratory. You will undergo a microscopy, which will help determine the cause of the disease and its causative agent.
Pay special attention to computer tomography, thanks to which you will receive a complete analysis of the disease, as well as the most complete characteristics and effective method of treatment. Thanks to such a comprehensive and extensive analysis, you will be able to obtain all the necessary information not only about the disease, but also about methods of its treatment
This option is currently very popular, since the personal experience of many women has tested its effectiveness, as well as its reliability.
Thanks to such a comprehensive and extensive analysis, you will be able to obtain all the necessary information not only about the disease, but also about the methods of its treatment. This option is currently very popular, since the personal experience of many women has tested its effectiveness, as well as its reliability.
With prolonged inflammation, you risk worsening the condition of the entire body, and the infectious process will spread to many organs. Moreover, after the disease enters the chronic stage, the body’s immunity decreases significantly, and the body’s fight against certain diseases simply stops.
If bacteria remain at the site of the inflammatory process for a long period, they can develop simple resistance to the antibiotics or other drugs you use, as a result of which the use of drugs will become useless. Thus, if a woman suffers from adnexitis, she can use various medications that are not even related to the treatment of this disease.
Thus, the above characteristics of the chronic variant greatly complicate treatment, as a result of which it is imperative to start it on time. The effectiveness of these actions is confirmed in 73% of sick women.
The acute version of this disease is characterized by treatment only with antibiotics. In addition, such medications are selected by a medical specialist, taking into account the sensitivity factor of the microflora. In other words, those antibiotics to which your body is sensitive are used. In the event that there is no time to wait for culture results, those drugs are prescribed that are characterized by a very wide spectrum of action.
If for a certain time, and in particular 72 hours after taking the drug, the doctor does not observe any improvement, the antibiotic is replaced. In this case, you should take tests again and clarify the woman’s diagnosis. If you neglect such situations, you risk your health.
If you are not being treated in a medical facility, but are using medications at home, you should be very careful. The fact is that at the slightest sign of abdominal pain during treatment, or other dangerous symptoms, you must immediately consult a doctor, since such moments are very dangerous and can lead to quite serious problems in the future
USEFUL INFORMATION: Hemostasiogram, what it is, how to take it, decoding of indicators
Inflammation of the appendages in women, symptoms and treatment is very relevant and important information for every woman. That is why it is important to know and understand the seriousness of diseases, their symptoms, as well as the full characteristics of treatment courses
Only in this case will you maintain your health and be able to continue to live with confidence in the future.
Traditional medicine
https://youtu.be/8BXznLyIaBU
To eliminate inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs, the following remedies can be used:
- salt heating. Heat regular salt in a frying pan, then pour it into a woven bag or towel. Apply a warm bag to the lower abdomen to warm the inflamed organs;
- decoction from boron uterus. Grind 1 tbsp. l. herbs, pouring 250 ml of boiling water over it. After a couple of hours, strain the infusion. Take 50 ml three times a day;
- paraffin therapy. Melt 300 g of paraffin in a water bath. Using a clean rag, apply it to your lower abdomen, then wrap yourself in a blanket.
What is adnexitis
Adnexitis is an inflammatory or infectious disease of the fallopian tubes and adjacent pelvic organs (primarily the ovaries). This disease is also called inflammation of the appendages. Most often, the cause of adnexitis is an ascending infection emanating from the vagina and cervix. In a large number of cases, adnexitis develops against the background of chlamydia. In 30-40% of cases, inflammation of the appendages can be caused by several bacteria simultaneously: gonococcus, gardnerella, Haemophilus influenzae and anaerobic bacteria such as peptostreptococci and bacteroides. Signs of adnexitis can vary from clinically asymptomatic to serious manifestations. The most common symptoms are pain in the lower abdomen and vaginal discharge. Adnexitis is most common in women under 25 years of age who have multiple sexual partners and practice unprotected sex. Symptoms of inflammation of the adnexa may be similar to appendicitis, cervicitis, endometriosis, urinary tract infections and pelvic tumors. Also, very often, ectopic pregnancy can be mistaken for inflammation of the appendages. If adnexitis is not treated on time, it can lead to such serious consequences as chronic pelvic pain and tubal infertility.
Adnexitis and pregnancy
Infection, both acute and chronic, has an extremely negative effect on the course of pregnancy. If you have untreated inflammation, it will definitely worsen during pregnancy, since a woman’s immunity decreases during pregnancy.
READ MORE: Stones and sand in the kidneys, symptoms in women, treatment
When planning a pregnancy, it is advisable to undergo a gynecological examination to exclude the presence of adnexitis.
If you discover this disease while pregnant, start treatment as soon as possible, and be sure to notify your doctor about your pregnancy. This is necessary because not all medications are suitable for pregnant women. Refusal to treat adnexitis during pregnancy can lead to its termination or infection of the child during childbirth (in this case, obstetricians insist on artificial birth - caesarean section).
Inflammation of the appendages
Often girls are faced with a diagnosis such as inflammation of the appendages. This disease is also known as adnexitis. It appears as a result of damage to the ovarian appendages by infection.
One of the common causes of inflammatory processes in the appendages is hypothermia. For example, if a girl sat in the cold for a long time or got her feet wet in the winter.
Also, inflammation of the appendages can be caused by bacteria that entered the woman’s body through sexual contact. Some of these are gonococci and chlamydia. Once the bacterium enters the body, it travels from the vagina to the fallopian tubes, where the environment suits its needs. In this area there is a cylindrical epithelium, which is considered the most favorable environment for chlamydia. These and other bacteria, being in the environment necessary for life, are able to resist immunity for a long time and multiply.
Important!
How to determine ovarian inflammation? Inflammation of the appendages can be detected by the following symptoms:
- Severe aching pain in the lower abdomen, especially felt during menstruation or a few days before it.
- Painful sensations during sexual intercourse and, as a result, lack of sexual desire.
- Violation of the MC.
- Increased body temperature, fatigue, mild weakness.
We recommend you learn: About ovarian inflammation and treatment
Vaginal suppositories
How can you treat colds of the epididymis?
If adnexitis develops, experts recommend using vaginal suppositories. They provide effective local treatment of inflammation and relieve pain.
The most effective drugs include:
- "Terzhinan" is a combined action drug that contains antifungal and antibiotic components. Helps suppress pathogenic anaerobic flora in the uterus and fallopian tubes;
- "Indomethacin" is an antibacterial suppository with a pronounced antiphlogistic and analgesic effect. Helps destroy pathogens and eliminate inflammatory processes;
- Movalis is one of the most powerful painkillers that has antipyretic and anti-inflammatory effects. Inhibits the synthesis of prostaglandins, which leads to the elimination of inflammatory processes in tissues.
What are appendages in the ovaries
Next to each ovary there are rudimentary formations: appendages, remnants of the tubules of the primary kidney and its duct, periovaries (appendages), vesicular appendages.
The ovarian appendages (supraovaries) are located between the layers of the mesentery of the fallopian tubes, lateral and posterior to the ovary. They contain a longitudinal duct and tubules flowing into it - transverse ducts, the blind end of which faces the exit from the ovary.
The periovary is a small formation that is located in the mesentery of the fallopian tube, next to the tubal end of the ovary. It connects blind divided tubules.
Stalk hydratide or vesicular appendage are vesicular formations that are fixed at the end of an elongated process and filled with colorless liquid. Some are attached lateral to the ovary, while others are located below the infundibulum of the fallopian tube.
Often girls have a question: “Are appendages and ovaries the same concepts or not?” As we have already found out, the appendage is part of the girl’s reproductive system and is located next to the ovary. Therefore, the answer is obvious - no, ovaries and appendages are not the same thing.
Diagnosis and treatment
In this case, you should not self-medicate. The disease is dangerous due to its complications. Consultation with a gynecologist should be fundamental and timely.
Diagnosis is carried out by manual examination, smear examination and ultrasound. For a complete picture, a blood test result is needed. The combination of all these studies allows the doctor to make the correct diagnosis and prescribe treatment. Additionally, a bacteriological analysis is required to determine the type of microorganisms. Therapy is carried out with vaginal or oral tablets. The following are used in treatment:
- antibiotics or their complex, depending on the severity of the condition;
- antiallergy drugs to prevent a reaction to an antibiotic;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- if the disease is accompanied by the release of pus, laparoscopic surgery is performed;
- Physiotherapeutic treatment methods are prescribed: electrophoresis, massage;
- in a critical situation, the only way to stop inflammation may be to remove the damaged organ.
If a woman has a cold in her appendages, this is manifested by severe symptoms that require immediate diagnosis and effective treatment. If the disease is not detected in a timely manner and you do not seek help from a qualified specialist, this can lead to serious and dangerous complications for the female body.
Ovarian cold refers to inflammatory pathological processes that spread to the uterus, fallopian labor and, if symptoms are ignored, leads to the development of infertility.
If cold ovaries are not treated, this can lead to the development of infertility.
One of the most common causes that provokes inflammation of the appendages is ARVI. This is explained, first of all, by the fact that during the development of a viral infection in the body, it weakens significantly and becomes susceptible to various bacteria. Thus, inflammation of the ovaries is provoked.
In addition to ARVI, the following pathologies can provoke the occurrence of an inflammatory process in the appendages:
- frequent change of sexual partners;
- unprotected sexual intercourse;
- systematic stressful situations, nervousness and depressed mood;
- surgical interventions in the organs of the genitourinary system;
- depressive states and psycho-emotional fatigue;
- incorrect and unprofessional installation of the intrauterine device;
- systematic lack of sleep or lack of proper rest;
- insomnia;
- abortion;
- constantly wearing tight, narrow underwear made of synthetic materials;
- avitaminosis;
- unbalanced diet;
- overeating or undereating;
- hypothermia;
- obesity;
- anorexia;
- chronic diseases of the pelvic organs;
- previous acute respiratory viral infections or influenza;
- taking antibacterial drugs.
As practice shows, even the most ordinary bathing in cool water can lead to cold appendages. Therefore, you should be careful about your health and, at the first symptoms of illness, seek advice from a doctor.
If a woman has a cold in her appendages, the following symptoms indicate the development of the inflammatory process:
- pain in the lumbar region, which can have varying degrees of severity;
- pain in the abdominal area, which mainly manifests itself in the lower part and can occur on one or both sides. The intensity of such pain can be completely different, and also appear periodically and have a paroxysmal nature;
- upon palpation of the abdomen, tension in the internal organs is manifested and pain is diagnosed;
- body temperature rises;
- systematic headaches appear;
- chills and weakness appear throughout the body;
- signs of dyspepsia occur, such as nausea leading to vomiting and diarrhea;
- changes are observed in the structure and quantity of vaginal discharge;
- Intermenstrual bleeding may occur;
- a burning sensation also occurs in the genital area;
- frequent and painful urination occurs;
- the color of the urine changes or impurities of blood or pus appear in it.
There are quite a few symptoms of cold appendages, one of the main ones is abdominal pain
If the symptoms of cold appendages appear in a sluggish form, then a woman may not even pay attention to the developing pathology, and mistake it for a simple malaise. This, in turn, can provoke a worsening of the situation and the development of serious complications. In order to prevent this, you should regularly visit a gynecologist and immediately seek qualified advice if even minor symptoms appear.
If a woman has symptoms indicating that the woman has a cold in her ovaries, she should immediately seek qualified medical help to make an accurate diagnosis and choose the most effective treatment.
First of all, in order to make a preliminary diagnosis and prescribe a number of additional studies, the gynecologist will conduct an examination using palpation. In this case, you should be prepared for the fact that the sensations during the procedure will be quite painful.
In addition to palpation, the patient must undergo a urine test, as well as a vaginal smear. Thanks to the results of the above studies, it becomes possible to identify the presence of certain viruses and bacteria in the female body.
The patient must first undergo a vaginal smear and urine test
But in most cases, these diagnostic procedures are not enough to make an accurate diagnosis, so the patient is also prescribed an ultrasound examination of the appendages and uterus, since such an examination is considered the most accurate and safe way.
If, after diagnostic procedures, it is revealed that a woman has a cold in her appendages, treatment in each individual case should be selected by the attending physician. Basically, therapy, depending on the stage and advanced stage of the disease, is carried out using medication, surgery or physiotherapy.
What to do if a woman has a cold in her appendages is up to the attending physician to decide. If diagnosed in a timely manner, then the woman is given comprehensive treatment with medications. Basically, this treatment is carried out over two weeks. Medicines are selected individually in each case and mainly include tablets, injections, and droppers.
As for medications, the following drugs are prescribed to treat the symptoms of colds:
- painkillers;
- antibacterial;
- anti-inflammatory;
- vitamin complex;
- drugs aimed at increasing immunity.
Among other things, during the treatment process, a woman must observe a pastel regime and adhere to a special diet, during which she should give preference to healthy and fortified foods.
The medications will be prescribed by the doctor, depending on the course of the disease.
In some cases, physiotherapeutic procedures may be prescribed as additional therapy, such as UV irradiation treatment, ultrasound treatment, magnetic therapy, acupuncture and others, depending on the form of the pathology.
Note! During treatment, it is strictly forbidden to change the dosage of the drug, shorten the duration of treatment, or skip a dose, as this can cause complications of the pathology, as well as its transition to a chronic form.
Unfortunately, it is not always possible to get rid of inflammation of the appendages in a conservative way. If the disease is diagnosed in an advanced stage, drug treatment has not brought results, and also when cysts or tumors are detected on the appendages, then surgical intervention simply cannot be avoided.
If the disease is diagnosed in an advanced stage, surgical intervention is necessary
Before choosing the most effective method of surgical intervention, certain studies are carried out, and after that, either laparotomy or laparoscopic method is selected. The difference between them is that with the laparotomy method an incision is made, and with the laparoscopic method a puncture is made.
Depending on which method of surgical intervention is used, the duration of the recovery period depends, which varies from five to ten days.
To prevent the development of ovarian inflammation, you must constantly adhere to the following recommendations:
- give up all bad habits;
- in the cold season, carefully protect your legs and genitals from the cold;
- refuse tight and synthetic underwear, and give preference to clothes made from natural materials;
- give preference to a healthy and balanced diet;
- spend more time outdoors and give preference to moderate physical activity;
- observe intimate hygiene every day, and completely avoid unprotected sexual intercourse;
- exclude promiscuity.
In the cold season, you need to dress warmly
Particular attention should be paid to your health during pregnancy, since during this period a decrease in immunity occurs in a woman’s body. That is why even minor hypothermia, as well as stressful situations, can lead to the development of ovarian inflammation.
Symptoms of inflammation of the appendages
Acute adnexitis
The clinical picture during the development of acute adnexitis is very characteristic, so diagnosis does not present any difficulties for the doctor. The disease always begins acutely with an increase in body temperature to 39 degrees; if there is purulent inflammation, the woman will be bothered by severe chills. Sharp, sharp cutting pains occur in the lower abdomen; they can be present on one side with unilateral inflammation of the appendages, or spread throughout the entire abdomen with bilateral adnexitis. The acute form of the disease in question will be characterized by irradiation of pain to the rectum, sacral region or lower extremities.
If you palpate the anterior abdominal wall at the very beginning of the disease, you will be able to determine its tension, intense pain and symptoms of peritoneal irritation. In some cases, problems with urination appear - it becomes painful and difficult. Without fail, the woman’s general health also deteriorates - there is nausea and vomiting, there is a complete loss of appetite, and obsessive headaches are bothering her.
Examination of the patient on a gynecological chair leads to the identification of serous-purulent (or purulent) discharge from the cervical canal. The doctor cannot clearly determine the size and contours of the appendages, their mobility is limited, and the woman will characterize the examination itself as painful. Laboratory blood tests will reveal an increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), an increased white blood cell count, and a high level of C-reactive protein.
Chronic adnexitis
Inflammation of the appendages can develop from an acute form to a chronic one; this is observed with poor quality treatment of the acute inflammatory process. Symptoms of chronic adnexitis include dull/aching pain in the lower abdomen radiating to the lower back and vagina. Palpation of the abdomen will be moderately painful, and the entire clinical picture will be somewhat blurred.
In the chronic form of inflammation of the appendages, the menstrual cycle is disrupted, patients complain of a lack of sexual desire, pain during sexual intercourse. When examining a woman in a gynecological chair, the doctor will note the presence of purulent discharge from the cervical canal, the area of the appendages will be painful on palpation, and their mobility will be limited.
IVF and female inflammation
Artificial insemination and embryo transfer is a complex and very responsible operation. After it, a woman must maintain complete peace of mind and lead a correct lifestyle.
Under no circumstances should you allow hypothermia, which can cause adnexitis. Inflammation after embryo transfer often causes involuntary termination of pregnancy.
Therefore, be careful and take measures so that the long-awaited expectation of the baby is not disrupted.
At the first signs of cystitis, you should definitely consult a doctor to prevent acute pyelonephritis. Even if the unpleasant symptoms disappear after a day, the pathogenic microflora will lead to inflammation the next time hypothermia occurs.
The doctor will give a referral for bacterial culture. Only after the result is antibacterial treatment prescribed.
To relieve pain, antispasmodic drugs and douching with disinfectant solutions are recommended. Recovery will begin in three to four days.
In the treatment of mycoplasma, antibacterial therapy is used after examination and passing the necessary tests. Physiotherapy, diet therapy and vitamin-mineral complexes are prescribed. Drugs that strengthen the immune system are prescribed without fail.
Antibacterial drugs and antibiotics are used to treat endometritis. In some cases, mechanical cleaning of the uterine cavity or separate diagnostic curettage is necessary.
Antiviral therapy and immunotherapy are used in the treatment of genital herpes. The effectiveness of treatment depends on timely consultation with a doctor
I caught a cold like a woman: how to treat it with medicinal herbs?
Medicinal plants are effectively used to treat inflammatory processes in the female genital organs.
How to understand that you have a cold in the bladder and what symptoms most accurately indicate this disease? Let's study the signs of the disease so that we can quickly begin treatment to avoid more dangerous and complex inflammatory processes in your body.
urination – frequent, with burning and pain, in small portions; false urges; urine – cloudy, with an unpleasant odor, sometimes mixed with pus and blood; general weakness in the body, aching joints; temperature rise to 38°C; pain in the lower back and lower abdomen.
Treatment of inflammation of the appendages, methods and drugs
Acute inflammation of the appendages in women has pronounced symptoms, so treatment should be aimed at relieving pain, eliminating the inflammatory process and increasing immunity.
Therapy for a chronic process takes longer - this is associated with a deterioration in the functioning of the affected organs and a general weakening of the body.
Drug treatment
Antibacterial drugs - Azithromycin, Ceftributen, Erythromycin, Metronidazole, Terzhinan (suppositories) can be prescribed. If the disease is acute, then it is better to take the antibiotic as an intramuscular injection - this way its action will be faster and more effective.
Anti-inflammatory drugs - Ibkulin, Indomethacin (suppositories), Ketoprofen, Ibuprofen. Necessary for relieving inflammation and reducing swelling of the ovaries and fallopian tubes. Some of the drugs contain analgesics.
USEFUL INFORMATION: Herb izmagen indications for use, medicinal properties, reviews
The suppositories used for inflammation of the appendages are made on the basis of medicinal plants that have an antiseptic effect and reduce inflammation in the tissues.
Painkillers - prescribed for acute inflammation, when the patient experiences severe pain in the lower abdomen.
In the treatment of chronic inflammation of the appendages, analgesics are not used, since the effect of anti-inflammatory drugs, which have a weak analgesic effect, is sufficient.
Physiotherapeutic treatment
Effective for chronic inflammation, used during periods of latent disease. Electrophoresis, which is carried out using magnesium, lidase and zinc, plays a major role in treatment.
For this purpose, vibration massage and medicinal baths with the addition of medicinal herbal extracts can be prescribed. Physiotherapy is intended to be an auxiliary method of combating pathology; it is not as effective as drug therapy.
Some women make the mistake of refusing courses of antibiotics and limiting themselves only to physiotherapeutic methods of treating the disease.
Surgery
If purulent foci are diagnosed, then treatment of inflammation of the appendages with antibiotics will not bring the desired effect. In such cases, surgical intervention performed by laparoscopy is indicated, which will allow the surgeon to manually remove the purulent exudate before it spreads throughout the entire abdominal cavity.
After surgery, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drugs are indicated. If the disease is in an advanced stage, then during surgery a decision may be made to remove the inflamed appendage.
Complications and consequences of the disease
Left untreated, chronic inflammation of the uterine appendages can cause infertility, ectopic pregnancies and ovarian dysfunction.
A constant inflammatory process in the pelvis can spread to the intestinal walls and other internal organs, and also cause a general decrease in immunity and weakening of the body.
After inflammation of the appendages, a woman retains her reproductive functions only if the stage of the disease was not advanced.
Full recovery in a hospital setting occurs in 10–20 days.
Concomitant treatment
When diagnosing inflammation of the appendages, treatment in women should be comprehensive: a combination of medications with physiotherapy, gynecological massage, osteopathy, and physiotherapy.
The main point in the treatment of inflammation is antibiotics. They are selected with a wide spectrum of action and maximum half-life. In addition, the woman herself needs to monitor her lifestyle (proper nutrition, abstinence from sexual activity, physical exercise, smoking and alcohol should be stopped).
The disease cannot be neglected, since the inflammatory process soon becomes chronic, which leads to infertility.
In addition to the prescription of antibacterial drugs, detoxification therapy is carried out (intravenous infusions of saline solutions, glucose, hemodez, rheopolyglucin and others in a volume of 2 - 3 liters).
READ MORE: Spinal cancer symptoms and manifestation stage 4
Relief of pain and reduction of the inflammatory process is carried out with the help of anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs in the form of tablets. These are Diclofenac, Ibuprofen, Ketarol and other drugs. Be sure to prescribe vitamins C and B, as well as allergy pills.
When relieving an acute process and in the treatment of chronic inflammation of the appendages outside of exacerbation, physiotherapy is widely used: copper and zinc electrophoresis according to the phases of the menstrual cycle, electrophoresis with lidase or iodine, ultrasound, high-frequency pulsed currents (CMT, DDT).
Also used in rehabilitation treatment are immunomodulators, autohemotherapy, injections of aloe, FIBS, Longidase, etc. For chronic adnexitis, sanatorium-resort treatment is indicated - mud, paraffin, medicinal baths and douching.
More on the topic: Why is inflammation of the appendages dangerous during pregnancy?
Why does the lower abdomen hurt?
WHY DOES THE BOTTOM OF THE ABDOMEN STILL??? Everyone knows that as soon as any tingling occurs in the lower abdomen, it means that the organ located in the abdominal cavity has malfunctioned. It is almost impossible to determine the cause of pain on your own; a thorough medical examination is required. Often the reason why colitis in the lower abdomen is difficult to determine even for a professional doctor, since the pain can occur on the right, and the source of pain is in the left side of the abdomen. Today…