When gynecologists, after an ultrasound, tell their patients that they have fibroids, this greatly alarms and frightens even the most trained and educated women in the field of gynecology. There is no need to be afraid of such a diagnosis; after the next menstruation, you should visit the doctor again and undergo an ultrasound examination with a Doppler sensor. Only after confirming the preliminary diagnosis, you need to spend time searching for information about this problem.
Let's try to cover the topic of what uterine fibroids are, symptoms and signs of the disease, and also briefly go over the methods of its diagnosis and treatment.
Why does it appear
Fibroids are the most common problem for women aged 30 to 45 years, this uncontrolled growth of muscle tissue most often occurs due to hormonal imbalance, but there are other causes of the disease that cause similar tissue changes:
- there is no regular intimate life, especially when it comes to women over 25 years old. Without regular orgasms, stagnation occurs in the pelvic organs;
- if a woman has never given birth after 30 years;
- genetic predisposition;
- chronic diseases of the reproductive system (endometritis, endometriosis, adenomyosis, adnexitis, etc.);
- a sedentary lifestyle, leading to problems with excess weight, even obesity;
- damage to the walls of the uterus during curettage, gynecological operations, surgical abortions, difficult childbirth, etc.;
- metabolic problems, hypertension, thyroid dysfunction, diabetes and other diseases of the endocrine system;
- stress that causes suppression of the activity of the adrenal glands, ovaries and thyroid gland.
Since the development of fibroids directly depends on hormonal levels, this disease is not diagnosed in girls before puberty and in women who have entered menopause.
Interestingly, it very often happens that a tumor formed at a young age, with changes in hormonal composition during menopause, resolves on its own.
Fibroids - what is it?
Fibroids are a benign tumor that forms in the myometrium, the muscular layer of the uterus. It is considered a common pathology and, according to various sources, accounts for 12 to 25% of all gynecological diseases.
Attention! The pathology does not relate to oncological diseases - there were no cases of degeneration of uterine fibroids from a benign neoplasm into a malignant cancer tumor during the entire period of tracking this disease.
According to many experts, these figures are too optimistic, and the real prevalence of the disease may be more than 70%. The main risk group is women of late reproductive age - 30–35 years and at the onset of menopause.
Unlike fibroids, which are composed of connective tissue, fibroids, or fibroids for short, are chaotically intertwined nodes consisting of smooth muscle tissue.
Types of fibroids
Depending on the nature of the manifestation and the location of the source of the disease, uterine fibroids have several types. Based on the number of tumors, fibroids are classified into:
- Single.
- Multiple is the most common manifestation of pathology.
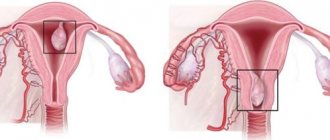
Based on the location of the tumor nodes, fibroids are divided into:
- Submucosal - the nodes are located in the submucosal membrane - the endometrium. Rarely seen.
- Interstitial, intramural - neoplasms form in the muscle tissue of the uterus.
- Subserous - nodes form on the outside of the uterus.
- Intraligamentous - tumors that form in the interligamentous tissues.
- Cervical – fibroids are located in the cervix.
The most common types are muscular or interstitial fibroids - according to some data, the incidence rate reaches 61%. The prevalence of tumors developing on the outside of the uterus (subserous fibroids) that develop in the abdominal cavity reaches 35%.
Reasons for development
To date, the mechanism of development of uterine fibroids has not been fully studied. However, most experts believe that the main cause of this pathology is associated with a woman's hormonal imbalance. An increase in estrogen increases the risk of developing pathology. It is for this reason that the disease is practically not diagnosed in girls before the onset of menstruation and in women after menopause. Negative factors in the development of the disease also include:
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Diseases of the genitourinary system that cause inflammation.
- Adenomyosis is a proliferation of the submucosal lining of the uterus.
- Pregnancy, frequent abortions.
- Sedentary lifestyle, muscle inactivity, obesity.
- Diseases of internal organs and endocrine system.
- Diabetes.
Studies have shown that most often, signs and symptoms of fibroids appear in those women who have relatives who have previously encountered this problem. This fact proves the hereditary factor in the development of pathology.
Proof of the hormonal origin of the disease is the fact that fibroids practically do not develop in young girls who have not reached puberty. It is also noted that after a decrease in estrogen in the blood, tumors decrease or resolve completely - this usually happens after menopause.
Attention! The opinion about the negative impact of sexual dissatisfaction in women on the development of the disease is not based on scientifically proven facts. Rather, dissatisfaction with sex life is often associated with hormonal imbalance.
A sedentary lifestyle, poor nutrition and the resulting consequences: obesity, physical inactivity and muscle atrophy. Hypertension and the development of diabetes mellitus also lead to disruption of the hormonal cycle and increase the risk of developing pathology.
Numerous, traumatic births or frequent abortions, absence of pregnancies, diseases of the genitourinary system with accompanying inflammatory processes are also negative factors and are prerequisites for the development of pathology.
What is the danger
Previously, it was assumed that over time, fibroids could develop into cancer, but science has proven that the tissues of malignant and benign tumors have completely different origins. In extremely rare cases, cancer can be a complication of fibroids, but not its degenerated form.
Despite the fact that fibroids are a benign formation, they can cause persistent infertility, so you should not treat them negligently; this is a disease that requires attention and treatment, otherwise the consequences will be disastrous.
Related article: consequences of uterine fibroids
Cost of examination, diagnosis and treatment of uterine fibroids
The Clinic of JSC “Medicine” offers services of primary examination, diagnosis and treatment at prices, which can be found in the table below or in the corresponding section of the clinic’s website.
The total cost of treatment is determined after an initial examination and selection of the most effective course of treatment. Specialists of JSC "Medicine" (clinic of academician Roitberg) in Moscow use the most effective techniques, modern high-precision diagnostic equipment, safe materials and effective drugs.
Types of uterine fibroids
To assess the size of fibroid development in official medicine, a comparison of the tumor with the size of the uterus during pregnancy is used, for example, 7 weeks, 25 weeks. Classification of neoplasms is carried out according to various parameters:
- by location - subserous, intramuscular, submucosal and adjacent location options;
- by location - in the body of the uterus, cervical fibroids, in the isthmus or fundus of the uterus;
- by size of fibroid nodes - large, medium and small sizes;
- according to the intensity of growth - true and false;
- according to morpho-histochemical characteristics - simple or expanding.
Symptoms of uterine fibroids in the early stages
Uterine fibroids are considered a widespread problem in gynecology. It makes up a quarter of all benign diseases of the genital organs and occurs in almost half of women of reproductive age. Based on the high prevalence of the disease, its early detection becomes extremely important. Indeed, in this case it is much easier to cure the pathology.
Causes and mechanisms
To date, there is still debate regarding the origin of fibroids. But many aspects of their development have already been established. It is known that hormonal disorders play a key role in the appearance of pathological lesions. They occur both at the level of the hypothalamus and pituitary gland (synthesis of gonadotropins) and in the ovarian system (overproduction of estrogens). The metabolism of sex hormones also changes in tumor tissues, which triggers cell proliferation.
In addition, immune factors play an important role in the mechanism of disease occurrence. The tumor develops under the influence of growth factors - special cytokines - and against the background of a decrease in the overall activity of protective systems that prevent the appearance of pathological cells. Provoking factors also include:
- Menstrual dysfunction.
- Infectious and inflammatory processes.
- Endocrine disorders.
- History of frequent abortions.
- Emotional stress.
- Hereditary predisposition.
Most often, the disease is detected in women from 30 to 50 years old, who have active hormonal processes involving estrogen. And in menopause, the development of fibroids is extremely rare. A tumor does not form in young girls who have just crossed puberty.
Classification
Myomatous nodes are rarely single; as a rule, the tumor has several small foci. Most often they are located in the body of the uterus and only 5% of observations confirm the process of cervical localization. Based on the direction of fibroid growth, they can be:
- Submucosal (submucosal).
- Intramural (intermuscular).
- Subserous (external).
The tumor always grows from the middle layer of the uterus - the myometrium. But according to its histological structure, it may contain more muscle tissue (leiomyoma) or connective tissue (fibromyoma). Taking into account morphogenetic features, simple and proliferating tumors are distinguished. They differ in the degree of cellular changes and growth rates. If we talk about submucous fibroids, the classification includes the following types:
- 0 – having a stalk and growing from the outer shell.
- I – on a wide base, immersed in the wall by less than 50%.
- II – more than half of the volume is occupied by the intramural component.
Thus, at an early stage, fibroids are small in size, most often localized in the body of the uterus, are generally multiple in nature and can grow in different directions relative to the muscle layer. All of these points should be reflected in the diagnosis, because the course of treatment correction directly depends on this.
The classification of fibroids takes into account the location of the tumor and the direction of growth, the size and number of nodes, and their histological structure.
Symptoms
The clinical picture of the tumor is extremely varied. It all depends on its location, size and type of growth. But in the early stages, symptoms of uterine fibroids are extremely few. In most cases, it occurs without any obvious signs at all. Exceptions are cases with submucosal nodes, when even small lesions can manifest certain signs. Most often, women with submucosal fibroids note the following symptoms:
- Long and heavy periods.
- Intermenstrual bleeding.
- Pain in the lower abdomen.
- Problems with bearing a child and infertility.
Myomas located submucosally significantly change the nature of menstruation. Due to the deformation of the underlying covering, the mucous membrane is rejected unevenly, which lengthens the cycle and leads to heavy discharge, including intermenstrual discharge. Knots can make this period painful, because they interfere with the normal contraction of the muscle layer. Submucosal tumors can be an obstacle to conception and bearing a child, but most often this happens a little later, when they reach a larger size.
Small subserous and intramural tumors are difficult to notice in the early stages because they do not produce significant symptoms. And only with an increase in size does heaviness appear in the lower abdomen, and if the nodes are comparable to a pregnancy of 12 weeks or more, then the function of neighboring organs is impaired. Then the woman notices increased urination, bloating, and constipation.
Additional diagnostics
Small fibroids, especially submucosal and intermuscular fibroids, cannot be identified during a gynecological examination. Therefore, additional methods are extremely important for diagnosis. For a woman who is suspected of having a benign tumor of the uterus, the following studies are indicated:
- Ultrasound of the pelvis.
- Hydrosonography.
- Hysteroscopy.
- Metrography.
- Diagnostic curettage.
The doctor determines which methods to use in a particular case. He evaluates the clinical symptoms and makes an assumption about the location of the tumor and the direction of its growth. But the results of additional studies allow us to fully establish the diagnosis and clarify the nature of the fibroids.
Early diagnosis of fibroids is an important component of preventive measures and is relevant for all cases of pathology.
Treatment
The tactics of therapeutic correction directly depend on the characteristics of the tumor. Small fibroids that are in the early stages of their development are subject to conservative therapy. Its goal is to stop the growth of nodes and their regression, restoring normal relationships in the hypothalamic-ovarian-uterine system.
Traditional therapy
In some cases, doctors adhere to a wait-and-see approach. it is used for asymptomatic fibroids that do not cause discomfort to the woman. Such patients should be regularly (twice a year) examined by a gynecologist with ultrasound monitoring. They are shown more preventive measures aimed at optimizing their lifestyle:
- A diet with limited smoked, fried, spicy foods, carbohydrate and fatty foods.
- Exclusion of thermal procedures (insolation, visits to baths and saunas, hot baths).
- careful attitude towards physiotherapy and massage.
And although the question of the advisability of drug correction for asymptomatic fibroids is still relevant, most doctors are of the opinion that the earlier treatment is carried out, the better. The basis of therapy is hormonal drugs. Some of them are analogues of natural regulators, while others are their antagonists. Likely representatives of such treatment would be:
- Antigonadotropic (Danoval, Vero-Danazol).
- Gestagens or progestins (Duphaston, Microlut, Implanon).
- Gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists (Decapeptyl).
In addition to systemic medications (tablets, capsules, injections), local forms are also used. These include, for example, the Mirena intrauterine system, which releases the drug levonorgestrel. This allows you to achieve a local effect without reactions from other organs.
Folk remedies
Many women wondering how to treat uterine fibroids opt for unconventional methods. Currently, various traditional medicine recipes are gaining popularity, for example, the following:
- Tincture of propolis, walnuts, celandine herb.
- A decoction of flax seeds, aloe juice.
- Infusion of boron uterus, nettle leaves, burdock, St. John's wort and calendula.
But such means must be used very carefully. Firstly, their effectiveness has not been proven by any research. Secondly, no one can say how the body will respond to the specified treatment, because allergic reactions and individual intolerance are likely. Thirdly, neglect of traditional therapy leads to the progression of fibroids. Therefore, traditional methods can only be used as a supplement and after consulting a specialist.
It is extremely important to identify uterine fibroids at the initial stage, when there are no clinical symptoms or they are very scarce. But this is only possible with regular examination by a gynecologist. All women of reproductive age should remember that early consultation with a doctor greatly facilitates the correction of pathology. A small tumor can be treated conservatively, but large nodes require surgical intervention.
Similar articles
flovit.ru
How to recognize fibroids
Most often, the disease develops without symptoms, and at stages 1-2, the presence of fibroids can only be determined by the results of a microscopic examination. Without preventive examinations, a woman may feel the first signs of the presence of myomatous formations only after 5-8 years from the onset of development. The 3rd stage of the disease is already felt during a medical examination when palpating the abdomen.
More information about the presence of a fibroid node in the uterus and what stage of development it is at can be obtained from an ultrasound examination. Sonographic signs of the disease will be as follows:
- in the structure of the myometrium there are formations with medium and low echogenicity;
- changes in the contours of the uterine cavity and endometrium may occur with submucosal and interstitial nodes;
- with dense nodes, the lumen of the bladder or rectum is deformed;
- the higher the percentage of connective tissue in the nodes, the higher its echogenicity;
- If calcium is deposited in nodules, it will appear as small hyperechoic inclusions with acoustic shadows at the back.
For female organs, ultrasound using a Doppler sensor is the most informative in making a diagnosis of uterine fibroids.
Self-examination
At home, fibroids cannot be detected in any way (either by touch or visually), but if some symptoms appear, you can simply come for an examination to a doctor as a preventive measure. The first signs of uterine fibroids will be uncharacteristic of this particular disease, so they can easily be confused with the symptoms of another disease. These include:
- constant causeless fatigue;
- general weakness;
- hemoglobin drops;
- I often want something “small”;
- migraine-like pain;
- difficulty with bowel movements;
- tides;
- heaviness and pain in the lower abdomen;
- heavy and painful menstruation;
- bleeding in the middle of the menstrual cycle.
General manifestations
With small fibroids, there are practically no symptoms, but as soon as the size of the tumor begins to increase, it immediately makes itself felt. Symptoms of uterine fibroids in the early stages include the following:
- menstrual irregularities (heavy periods, their delay, bleeding between periods). An increased volume of monthly blood indicates poor contraction of muscle tissue in the uterus, and in the case of intermenstrual bleeding, bleeding of the walls of the uterus itself occurs due to tumor irritation;
- painful sensations. The main localization of pain with myomatous tumor is in the sacrum or lower abdomen. It occurs suddenly when blood flow in the nodes is disrupted. If the formation is large, but the increase occurs slowly, then the pain is nagging and mainly appears during menstruation. The development of a tumor in the mucous membrane causes cramping pain. In the early stages, pain rarely occurs; it usually accompanies secondary signs of the disease;
- problems with nearby organs, in particular the rectum and bladder. They feel pressure as the tumor grows in their direction. As a result, constipation and frequent urge to urinate. For such symptoms, the following doctors should be consulted: gynecologist, gastroenterologist and urologist;
- anemia. Anemia develops as a result of excessive blood loss, accompanied by headache, weakness, pale skin and dizziness;
- heart pain. They are a consequence of a decrease in the tone of the heart muscles due to the growth of fibroids. A severe form of the disease causes increased venous pressure. Consultation with a cardiologist is required;
- infertility. With submucosal localization of fibroids, obstruction of the fallopian tubes may occur, which prevents sperm from accessing the egg;
- the belly increases. This is a sign of excessive enlargement of the myomatous tumor, while the patient’s weight does not change significantly.
The main symptoms are listed above, but general weakness and high temperature are secondary signs of fibroids, the cause of which is intoxication of the body caused by necrotic processes in the tumor tissue due to twisting of the nodes and the entire formation as a whole.
Symptoms and signs by form
Based on the location of the nodes, fibroids can be recognized by the following signs:
- subserous - located on the outside of the uterus under the membrane that separates the organ from the abdominal cavity. This type is not characterized by an enlarged abdomen, but constipation, problems with urination, discomfort in the lower abdomen, hemorrhoids and cramping pain may occur;
- intramuscular - located in the thickness of the uterine wall, accompanied by pain, heavy menstrual flow, bleeding and constipation may appear. Typical for women of childbearing age;
- submucosal - localized in the inner part of the uterus and extends into the lumen of the organ. This type grows quickly, is accompanied by prolonged bleeding, general weakness, inability to have children, and lower back pain;
- cervical - forms on the cervix, it happens very rarely. Does not cause problems with menstruation, but affects the ability to get pregnant and causes pain;
- fibroids in the interligamentous space. It forms asymptomatically, as it develops, it puts pressure on neighboring tissues, causing stagnation of feces and frequent “small” trips;
- pedunculated - this is not a separate type, a subtype of the formations presented above, since fibroids can be on a narrow and wide base, both inside the uterus and in the outer part.
As soon as a chain of such symptoms appears, you need to urgently contact a gynecologist to make a diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment.
Symptoms during pregnancy
It is hormonal imbalances in expectant mothers that most often cause fibroids to occur in women during pregnancy. The course of the disease should be monitored by a doctor, although with a small size of the formation, fibroids do not have a significant effect on the development of the fetus. When fibroid nodes are located far from the placenta, and this is in most cases, the pregnancy process is not disrupted, but sometimes the formation can cause the following complications when carrying a child:
- inflammation;
- the tone of the uterus increases;
- spontaneous abortions in the early stages and premature births;
- placental abruption;
- oxygen starvation of the fetus.
It is important to identify fibroids early in pregnancy to reduce the risk of miscarriage and premature birth.
Signs of menopause
If, before the onset of menopause, uterine fibroids did not show any symptoms, then there is a high probability that it will resolve on its own without additional medical help, this is due to hormonal changes characteristic of this period. It is important not to let the disease take its course in order to prevent malignant degeneration of myomatous nodes.
Myoma is highly likely to go away without a trace if menopause occurs without problematic symptoms and complications.
Causes of uterine fibroids in women
The development of fibroids is a consequence of hormonal imbalance in a woman; this is considered the main cause of uterine fibroids. Therefore, most often, fibroids form in young women, and can resolve on their own during menopause, at a time when estrogen levels noticeably decrease. So, the main causes of uterine fibroids:
- Hereditary disposition
- Hormonal disorders
- Adenomyosis
- Inflammatory gynecological diseases, as well as metabolic disorders, diabetes mellitus, chronic diseases of internal organs
- Prolonged or constant stress - depressing the functioning of the ovaries, adrenal glands, and thyroid gland
- Sedentary lifestyle, obesity
- Frequent abortions (consequences), use of intrauterine devices
- Lack of orgasm during intercourse
Let's look at some of the causes of uterine fibroids in more detail:
Excess estrogen, lack of progesterone
Uterine fibroids are considered a hormone-dependent tumor, so they practically do not occur in girls before the onset of puberty, that is, before the first menstruation and in postmenopausal women. When the local regulation of hormones that nourish this organ is disrupted, when their level increases, fibroid growth occurs. Moreover, many researchers argue that it is not just the high level of estrogen that is “to blame” for her growth, but an estrogen imbalance, which cannot be established with a single analysis; for this, the woman’s full hormonal status must be determined. Also, chemicals such as xenoestrogens, which are present in the body, have an estrogen-like effect, and their increase can affect the development of endometriosis and uterine fibroids.
Number of pregnancies, births, abortions
When determining a woman’s hormonal status, they take into account when the first menstruation began, the number of interrupted and full-term pregnancies, the duration of lactation and other factors. Women who have given birth to at least one child are less likely to develop fibroids.
Women's nutrition
An increase in estrogen levels is caused by metabolic disorders, obesity, and even just constant consumption of refined foods, lack of fiber, and excess saturated fatty acids in a woman’s daily diet. It has been proven that excess weight, or more precisely, excess fat mass in relation to lean body mass, is also a factor contributing to the excessive formation of female sex hormones, since fatty tissue promotes the transition of androgens to estrogens, which increases the risk of breast cancer, endometriosis, and uterine fibroids.
Vegetarians have a much lower risk of developing hormone-dependent diseases of the female genital organs. A diet containing mainly vegetables, cereals, fruits, fermented milk products with a low amount of fat reduces the risk of developing fibroids. Every extra 10 kg. weight increases the risk of its development by 20%. An interesting observation is that most women with elevated estrogen levels are well-fed, very energetic, healthy, look younger than their age, and are very feminine.
Lack of orgasm during sexual intercourse
Lack of harmony in intimate life, lack of orgasm during sexual intercourse, when the rush of blood after sexual arousal does not go away, but stagnates in the pelvis, this causes vascular tension and venous stagnation (one of the causes of pain during sex). If a woman does not experience satisfaction from sex for a long time, this can provoke hormonal imbalance and the development of fibroids.
Diabetes mellitus and hypertension
Women with metabolic disorders and those suffering from early hypertension, that is, before 35 years of age, also have a high risk of developing fibroids. This tendency can be indicated by a woman’s figure, if it resembles an apple and fat deposits are concentrated in the waist area, this is a greater risk of fibroid growth than with a pear-shaped figure, when accumulations of excess fatty tissue are mainly in the hips.
- Urban women have a higher risk of developing fibroids than women living in rural areas
- Use of oral contraceptives
- Damage to the genital organs, inflammatory diseases
Research shows that traumatic births, frequent medical abortions, diagnostic curettages, and inflammatory diseases of the genital organs contribute to hormonal disruptions and are a trigger for the occurrence of uterine fibroids.
Diagnostics
The first stage of diagnosis is a gynecological examination; it allows you to determine the presence of fibroids by the increased size of the uterus, compaction and deformation of its walls. To clarify the diagnosis and intensity of growth of uterine fibroids, the following studies may be prescribed:
- blood serum analysis for tumor marker CA125, ESR;
- Ultrasound of the genital organs for visual assessment of the contours and size of the formation;
- Hysteroscopy helps determine the condition of the endometrium and fallopian tubes. During the procedure, a biopsy of nodal tissue is taken and their cytological and histological composition is assessed;
- MRI is done to visualize the uterus volumetrically and clarify the correct diagnosis;
- Laparoscopy. During the procedure, which is carried out strictly as directed, small nodes can be removed immediately.
Reproductive system in women
External and internal genitalia in women are necessary for procreation and hormonal regulation of the body.
The female reproductive system is formed by the mammary glands and pelvic organs. In the ovaries, the formation of germ cells and the release of hormones necessary for the development of the female body occur. The mature egg is transported to the fallopian tube, where fertilization occurs after sperm penetrate the reproductive system. Then the germ of a new organism penetrates the uterine cavity, penetrates into the inner lining of the organ and receives everything necessary for further formation. Accessory structures, such as the gonads, are responsible for maintaining reproductive function. The uterus is a hollow organ designed for the development of the fetus. This anatomical structure is located next to the bladder and rectum. With the help of the cervix and vagina, the organ communicates with the external environment for the penetration of male cells during sexual intercourse. The uterus is also connected to the fallopian tubes, which ensures the introduction of the embryo of a new organism. The main stage of organ development occurs during a woman’s puberty, when hormones stimulate the final formation of the reproductive system. At this time, girls begin menstrual cycles, characterized by renewal of the inner layer of the uterus and the release of a mature germ cell into the fallopian tube.
Structure of the uterus:
- The mucous membrane (endometrium) is the internal lining of the organ, mainly consisting of tubular glands. The endometrium is necessary for the implantation of the embryo and the subsequent maintenance of embryonic development. If, after the release of a mature egg into the fallopian tube, fertilization does not occur, the endometrium is destroyed and renewed. Destruction of the endometrium during menstruation is manifested by uterine bleeding.
- The muscular (median) membrane, consisting of three layers of smooth muscle. Contractions of the uterine muscles are necessary to remove the destroyed endometrium and childbirth. In addition, the muscular structure of the uterus helps the organ stretch as the new organism grows.
- The outer shell of an organ, consisting of connective tissue. This section of the uterus is connected to the abdominal covering.
The uterus is a constantly renewing organ. Before the onset of menopause (up to about 50 years), characterized by changes in hormonal regulation of the body, women menstruate monthly. This physiological process indicates the ability of the female body to procreate. Unfortunately, hormonal changes during the menstrual cycle often lead to the development of pathologies of the reproductive system.
How to treat uterine fibroids
The method of treating fibroids depends on the severity of the disease, the size and location of the formation. If the tumor does not exceed 1-2 cm in diameter, then drug therapy is preferred, otherwise surgery is prescribed, especially if there is severe pain and bleeding.
Conservative treatment
When the tumor is small and does not cause the patient any discomfort, the doctor may limit himself to prescribing a diet and regular ultrasound examinations. When the patient experiences pain and the tumor reaches medium size, hormonal medications are prescribed. Such medications cannot eliminate fibroids completely, but only weaken their symptoms.
The most commonly prescribed drugs are:
- GnRH agonists. They act only during use, with prolonged use they cause osteoporosis, and when you stop taking them, the nodes resume their growth;
- oral contraception is prescribed to relieve pain and bleeding (Rigevidon, Novinet);
- antiprogestogens to reduce tumor size and relieve symptoms;
- antigonadotropins to relieve symptoms. Prescribed extremely rarely due to the large number of side effects.
Surgery
When fibroids are large and develop rapidly, which is accompanied by heavy blood loss and tissue necrosis, surgical intervention may be prescribed. If a woman is past reproductive age, complete removal of the uterus is recommended. In this case, the size for the operation is the main factor, since the need to preserve reproductive function is eliminated.
Myomectomy
If the patient plans to have children and the fibroid can be removed using minimally invasive techniques without excision of the entire organ, then a myomectomy is prescribed, one of the following types:
- embolization (the procedure is performed through the femoral artery);
- laparoscopy (manipulation is carried out through punctures in the abdomen);
- hysteroscopy (through the vagina).
The first two methods are prescribed in the vast majority of cases, as they do not require long-term recovery and preserve the woman’s ability to bear her child.
Traditional treatment
Traditional methods of treatment for this disease should not be used; it is better to combine traditional medicine with proper nutrition and adequate exercise.
Treatment
Uterine fibroids have different symptoms and signs, and treatment is prescribed depending on the location of the tumors and their size. Often, when the patient reaches premenopausal age, therapy is not prescribed at all - after menopause and a decrease in hormonal levels, the development of the pathology stops.
Until recently, the only treatment for fibroids was hysterectomy - removal of the uterus. Today this procedure is used quite rarely. There are several main methods of treating fibroids that are used at different stages of the disease.
Drug treatment
Conservative drug treatment of the disease has several goals: reducing the amount of bleeding during menstruation, normalizing hormonal levels, slowing growth or reducing the size of tumors. The following drugs are used for this:
- Coagulants or hemostatics are medications that increase blood clotting. They do not directly affect tumors, but only reduce the amount of bleeding during menstruation.
Attention! Previously widely used drugs from the group of oral contraceptives have not proven their effectiveness in recent studies. Moreover, some of them can, on the contrary, cause tumor growth.
- Gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists are drugs that suppress hormone production. Significantly reduce the size of tumors – up to 50%.
The latter drugs are prescribed in a course, as they have a number of serious side effects and after the end of taking the disease, the development of the disease, as a rule, resumes. For this reason, hormonal therapy is most often prescribed to shrink swelling before surgery to minimize trauma.
Before use, be sure to consult your doctor. Any self-medication can be harmful
Surgery
Today, there are a number of minimally invasive surgical methods for treating tumors. The main indications for surgical intervention include:
- Excessive bleeding during menstruation and risk of anemia.
- Tumor growth in postmenopause.
- Severe pain.
Minimally invasive endoscopic surgeries include laparoscopy and hysteroscopy. Surgeries to remove tumors are performed using small punctures and a laparoscope or without incisions through the vagina using an endoscope. In extreme cases, when removing large tumors, abdominal surgery is used.
Attention! The maximum weight of fibroids extracted by specialists was 63 kg.
https://youtu.be/wwAfmUWbe9o
Arterial embolization
Fibroids are tumors that feed mainly from the uterine arteries. In this case, the uterus itself can be supplied with blood from other blood vessels. An extensive vascular network allows the organ to be fully supplied with blood even after blood flow through the main uterine vessels has stopped.
The essence of the method is that special balls - emboli - are inserted into the artery through a thin catheter, which selectively block the vessels feeding myomatous neoplasms.
Important! A small part of the emboli can penetrate the small vessels that supply the uterus. However, this does not affect the blood supply to the organ, since the proportion of these emboli is minimal, and the extensive network of arteries helps to quickly restore the blood supply to the organ.
After the cessation of blood supply to the myomatous nodes, the process of fibrosis begins - the replacement of smooth muscle tissue and connective tissue. The tumor lasts about a year and then disappears completely.
Treatment without surgery
FUS ablation is a method of minimally invasive surgery. In fact, this is an operation, only without incisions and punctures. The tumor is targeted using intense ultrasound. The procedure is carried out under the control of an MRI machine, and the specialist precisely affects the tumor, as if evaporating it.
Attention! This method is suitable for treating only tumors consisting predominantly of connective tissue.
Today, this is the least traumatic method of surgery. Allows operations to remove tumors without pain and hospitalization. It belongs to the category of organ-saving operations and allows patients not only to maintain health, but also to become pregnant.
Is treatment possible with folk remedies?
There are many traditional medicine recipes for treating tumors in the uterus. In particular, they include diet and intrauterine injections. However, there is no scientific evidence that they really help.
Before trying to cure uterine fibroids using folk remedies, it is strongly recommended to consult with your doctor.
Prevention
To prevent the development of fibroids, you should adhere to the following rules:
- Healthy food;
- do not have abortions;
- undergo regular gynecological examinations;
- treat inflammatory processes of the genital organs.
You should not refuse to have a child, the optimal age for this is considered to be 22-25 years old, and if possible, you should not give up breastfeeding, because this process reduces the risk of fibroids in the future.
Main symptoms and diagnostic signs of uterine fibroids
Uterine fibroids are one of the most common tumor diseases among women. It occurs mainly at the age of 30-45 years, the average frequency is 25:100. The peculiarity of uterine fibroids is that their symptoms and signs in the early stages are mild and nonspecific. But every woman should know them in order to notice the disease in time and begin treatment.
general information
Myoma is a benign neoplasm that is formed from abnormally overgrown myocytes (muscle cells) of the uterus. It is a knot of muscle and connective fibers, intertwined with a dense network of altered blood vessels. The size of fibroids can vary from a few millimeters to 7 cm. In 85% of cases, several nodes are formed (multiple form).
Uterine fibroids, the causes of which have not been reliably established, are a hormone-dependent pathology. Its growth is associated with a significant increase in estrogen levels. The main prerequisites for the development of neoplasms in women are:
- genetic predisposition;
- chronic inflammatory diseases of the genital organs;
- endocrine pathologies;
- abortions, traumatic births;
- use of intrauterine contraception and so on.
Characteristics of the clinical picture
In 25-30% of women, uterine fibroids progress very slowly and do not provoke any pathological manifestations in the early stages. Often, small nodes are discovered by chance during an examination by a gynecologist: they are detected by palpation examination or ultrasound.
What signs indicate the development of neoplasms? Multiple uterine fibroids, the symptoms of which begin to appear as the tumors grow, are accompanied by:
- disruptions in the menstrual cycle, menorrhagia;
- unpleasant sensations in the abdominal area;
- disturbances in the functioning of organs adjacent to the uterus;
- general deterioration of health associated with anemia.
In addition, if the node is damaged, severe pain and bleeding may occur.
The clinical manifestations of the disease in a particular patient are determined by factors such as:
- sizes and direction of growth of nodes;
- woman's age;
- concomitant diseases of the genital organs and endocrine glands.
Disruptions in the menstrual cycle
The cycle in women with fibroids can have different options: from a full cycle with normal periodicity to anovulatory with a disturbed rhythm. Menorrhagia and bleeding between monthly periods most often occur.
Menorrhagia is an increase in the duration (longer than 7 days) and volume (more than 100-150 ml) of menstrual flow, as well as the presence of clots in it. Intense monthly bleeding with fibroids occurs due to:
- endometrial growths;
- deterioration of the contractile properties of the myometrium (muscle fibers of the uterus);
- reducing tone and elasticity, as well as increasing the permeability of vascular walls;
- increasing the number of capillaries and venous plexuses;
- deterioration of blood flow from the uterus.
Menorrhagia most often develops with myomatous nodes of large diameter, which have a tendency to grow rapidly. If left untreated, heavy menstruation leads to anemia in women. It is important to see a doctor and undergo an ultrasound to find out the causes of menorrhagia.
Acyclic bleeding occurs due to irritation of the endometrium by the tumor. It can be abundant or insignificant. In the latter case, the patient is concerned about discharge mixed with blood.
Pain syndrome
Multiple small fibroids do not cause discomfort. A feeling of heaviness and pain occurs as the nodes grow. They are localized in the lower abdomen and lumbar region, intensifying during menstruation and sexual intercourse. The nature of the pain is pulling or cramping.
Discomfort with fibroids is caused by:
- increased tendency of the myometrium to spontaneous contraction;
- an increase in intravascular pressure in the walls of the uterus.
The growth of nodes can lead to a noticeable increase in abdominal volume.
Dysfunctions of neighboring organs
Difficulty conceiving and carrying a pregnancy to term
Impaired fertility with uterine fibroids is characterized by three aspects:
- The nodes provoke obstruction of the fallopian tubes. As a result, mechanical obstacles arise on the way of sperm to the egg, and the woman’s ability to conceive is reduced (completely lost).
- Large neoplasms negatively affect the course of pregnancy - they lead to increased uterine tone, fetal hypoxia, and increase the risk of placental abruption and miscarriages.
- Multiple fibroids make it difficult for the baby to pass through the birth canal. With such a diagnosis confirmed by ultrasound, a caesarean section is often resorted to.
Anemia and other manifestations
Heavy menstrual bleeding provokes anemia - a decrease in the concentration of hemoglobin in the blood. Its symptoms:
- dizziness;
- pallor;
- frequent headaches;
- general weakness;
- decreased performance.
The relationship between anemia and menorrhagia is indicated by the fact that treatment with iron-containing drugs does not produce a lasting effect. Chronic hemoglobin deficiency in women leads to a decrease in the supply of oxygen to tissues, as a result of which the functioning of the cardiovascular and other body systems is disrupted.
The clinical picture of uterine fibroids can be supplemented by such signs as:
- decreased tone of the heart muscle;
- arterial hypertension;
- worsening blood clotting;
- shortness of breath on exertion;
- tides.
Signs of an acute condition
If the fibroid is located on a narrow, long base (“pedicle”), it may be torsion. In this case, there is a risk of necrotization, inflammation or rupture of the node. Symptoms of tumor damage:
- Image by David Castillo Dominici at FreeDigitalPhotos.net
severe abdominal pain;
- bleeding;
- nausea, vomiting;
- bloating;
- hyperthermia
The patient needs urgent medical attention. In most cases, surgical treatment is performed - the node is excised by laparotomy. If the inflammatory process and thrombosis of small vessels have spread far beyond the tumor, the uterus is removed.
Features of the clinical picture depending on the location of the tumor
The manifestations of uterine fibroids and their treatment are largely determined by the location of the tumors. Tumors are classified into:
- intramural (interstitial, intermuscular) – formed in the thickness of the walls;
- submucosal (submucosal) - located on the inner surface of the uterus, growing towards the cavity;
- subserous (subperitoneal) - localized on the serous (outer) membrane, developing towards the peritoneum;
- cervical - found on the surface of the cervix;
- intraligamentous – located between the ligaments;
- mixed.
With significant sizes of interstitial fibroids, the following symptoms are observed:
- heavy monthly bleeding;
- pain during menstruation, which becomes constant over time;
- disturbances in the functioning of the intestines and bladder, if the node grows outward and displaces them.
Ultrasound can detect deformation of the uterus and changes in the location of the pelvic organs.
Submucosal fibroids are characterized by rapid development. Its symptoms:
- menorrhagia;
- acyclic bleeding with an unpleasant odor;
- anemia;
- painful cramps during menstruation;
- miscarriage.
Subserous and intraligamentary forms are asymptomatic because they do not affect the functions of the uterus. The first pathological signs appear when the tumor grows, which puts pressure on neighboring organs. The main ones:
- problems with emptying the bladder, cystitis;
- constipation, hemorrhoids;
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen.
Cervical nodes lead to deformation of the cervix. They provoke:
- difficulty conceiving;
- miscarriages;
- impaired blood supply to the pelvic organs;
- thrombosis of the veins of the lower extremities.
The influence of a woman’s age on the course of uterine fibroids
When considering the characteristics of the course of uterine fibroids in the age aspect, it is customary to distinguish:
- reproductive (15-45 years);
- premenopausal (46-50 years);
- postmenopausal period (over 51 years).
Characteristics of fibroids during childbearing age:
- formation of nodes at 30-33 years old, their slow increase;
- pain syndrome;
- heavy menstruation;
- increased frequency of cycles without ovulation;
- synchronous development of mastopathy;
- anemia;
- difficulties with conception.
Specifics of the disease in the premenopausal period:
- accelerated growth of nodes;
- uterine bleeding;
- chronic anemia;
- damage to tumors accompanied by acute symptoms;
- development of polycystic ovary syndrome;
- endometrial hyperplasia.
Features of fibroids in postmenopausal women:
- gradual reduction of nodes;
- occasional bleeding;
- cessation of bleeding and pain.
If tumor regression does not occur at this stage, the risk of oncological diseases of the reproductive organs increases, therefore surgical treatment is indicated.
Diagnostic criteria
Symptoms of fibroids in women are nonspecific: they are also characteristic of other pathologies (endometriosis, neoplasms in the ovaries). Only a gynecologist can make a diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment. A palpation examination of the uterus can suggest fibroids, but instrumental methods are more reliable. The main one is transabdominal or transvaginal ultrasound.
Echo signs of uterine fibroids:
- in the case of a nodular form – an increase and change in the contours of the uterus, visualization of one or several nodes of small (8-15 mm), medium (13-35 mm) or large (35-70 mm) sizes;
- in the diffuse form - focal heterogeneity of the myometrial structure, thickening of the walls of the uterus, a decrease in their echogenicity, preservation of the normal contour of the organ, and absence of deformation of the cavity.
General characteristics of nodes detected by ultrasound:
- oval or round shape;
- clear outlines;
- heterogeneity (heterogeneity of structure);
- vascularization (increase in the number of blood vessels);
- reduced acoustic activity.
Specific signs of myomatous tumors on ultrasound:
- intramural - found in the projection of the myometrium, do not change the shape of the organ;
- submucous - defined as oval-shaped objects against the background of the endometrium or uterine cavity, their structure is homogeneous, hypo- or isoechoic;
- subserous - create a tuberous outline of the organ and can shift its position.
In addition, the results of ultrasound are influenced by the tissue structure of neoplasms:
- fibroids (predominance of connective tissue) – light, hyperechoic nodes;
- leiomyomas (prevalence of smooth muscle fibers) are homogeneous, hypoechoic formations.
Multiple or single uterine fibroids in women are a disease that is asymptomatic in the early stages, but can lead to complications. The main ones are anemia, infertility, disorders of the urinary tract and intestines, and oncological pathologies. Proper treatment of small fibroids can slow down its growth and prevent negative consequences. You can detect a tumor in time by regularly visiting a gynecologist and performing an ultrasound of the reproductive organs.
Similar articles
besplodie911.ru
Reviews
Each patient has completely individual symptoms and signs. Here are the most common reviews about the manifestations of this disease.
Alisa, 28 years old.
I was diagnosed with uterine fibroids a year ago, there were no symptoms, I just decided to go for an examination with a gynecologist. Since I am on contraceptives, the doctor said that I don’t need to drink anything additional, just be observed;
Vera, 43 years old.
The problems started relatively long ago, but I still didn’t have enough time to visit a doctor. Bleeding periodically occurred, my lower back and lower abdomen hurt, but when my stomach began to grow, I got scared. It turned out that I had very large fibroids, and since I already have two children and don’t plan any more, I agreed to have the uterus removed. Now I’m getting ready, getting used to the idea;
Alexandra, 35 years old.
Due to heavy and painful periods, I went to the gynecologist. The doctor said that I have fibroids, because I want to give birth again, the doctor suggested a new treatment method - FUS ablation. After the procedure, myoma symptoms no longer bother me.
Is it possible to treat uterine fibroids without surgery?
In the case when a woman is approaching premenopause (see the first signs of menopause), the size of the fibroids is less than 12 weeks, it grows slowly and the woman is not bothered by the severe symptoms of uterine fibroids, then conservative treatment is possible, since with the onset of menopause in a woman, the growth of fibroids stops. Treatment of uterine fibroids without surgery involves the use of the following medications:
Combined oral contraceptives
These include the following combinations: desogestrel with ethinyl estradiol (Mersilon, Marvelon, Novinet), ethinyl estradiol with norgestrel (Ovidon, Rigevidon). These remedies effectively help reduce the symptoms of uterine fibroids, such as pain in the lower abdomen and bleeding. However, for the treatment of uterine fibroids in order to reduce its size, tablets of this group are not a priority, since they do not always lead to a reduction in nodes. Under the influence of such therapy, only nodes whose initial size did not exceed 1.5 cm can shrink in size.
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists
Drugs in this group include: triptorelin - (Decapeptyl, Diferelin, Decapeptil Depot), buserelin, goserelin (Zoladex), leuprorelin (Lucrin Depot). The disadvantage of using these drugs for the treatment of uterine fibroids is that after the end of therapy, the nodes can be restored in size, and long-term use of these drugs is not permissible, as it can lead to the development of osteoporosis and other consequences for the female body due to a lack of estrogen. Within six months of using these products, the size of fibroids can be reduced by 50%, and the intensity of fibroid symptoms can also decrease. These medications are often used to shrink uterine fibroids before surgery to reduce blood loss during surgery.
Antiprogestogens
Mifepristone (RU-486) is often used to treat uterine fibroids or as preparatory therapy before surgery. This remedy both eliminates the symptoms of fibroids and helps reduce the size of the nodes.
Antigonadotropins
Danazol (Vero-Danazol, Danazol, Danoval, Danol, Danogen), gestrinone (Nemestran). For uterine fibroids, treatment with these drugs is rarely used, since they cannot reduce the size of the nodes, but only help reduce the intensity of the symptoms of fibroids; moreover, they have a number of undesirable side effects, such as acne, voice changes, and hair growth on the body and face. These medications for fibroids can only be used if other treatments are ineffective.
Gestagens
The use of these drugs today is a controversial, open issue; some doctors consider their use unacceptable for uterine fibroids, especially a drug such as dydrogesterone (Duphaston). Others believe that its use is justified, since a lack of progesterone leads to the growth of fibroids. The effectiveness of using drugs such as nor-ethisterone (Primolut-Nor, Norkolut), medroxyprogesterone acetate (Depo-Provera, Provera), linestrenol (Escluton, Orgametril) for fibroids has not been proven, and the use of many gynecologists is not recommended. However, it is believed that their use is justified in cases of combination of fibroids and endometrial hyperplasia. The growth of fibroids is not caused simply by a lack or excess of a specific hormone, but rather by a general hormonal imbalance, so the use of these drugs should not be in all cases, but according to indications.
FUS ablation
FUS ablation is a relapse-free, non-invasive technique for eliminating myomatous nodes. A modern method of treating uterine fibroids without surgery, which involves evaporating the fibroids using an ultrasound beam. This procedure is performed with an ultrasound beam, which is precisely, focusedly directed to the location of the tumor; to more accurately aim the beam at the node, the surgeon uses MRI. The use of tomography also helps to monitor the degree of destruction and the degree of impact of the ultrasound beam on the tumor in real time.
Advantages of FUS ablation:
- No blood loss, anesthesia, or trauma
- Preservation of reproductive function, organ-preserving method
- High effect even with large nodes and multiple fibroids
- Significant reduction in the size of nodes, 2-3 times
- No side effects, no pain, no fever, no intoxication
- No relapses, treatment of symptoms of uterine fibroids
- The shortest recovery time, the possibility of performing the procedure on an outpatient basis
With this method of treating uterine fibroids, intensive infusion procedures are not required, there is no intervention in the body, since the procedure occurs remotely, the uterus is not injured, and there is no risk of developing infertility or miscarriage in the future. During FUS ablation, there should be no burning sensation of the skin, pain in the lower back, lower abdomen, or pain radiating to the leg.
Uterine fibroids and pregnancy
Manifestations of uterine fibroids in the early stages of pregnancy can be absolutely harmless if they are located away from the placenta, otherwise the growth of the formation can lead to spontaneous abortion.
In the 2nd and 3rd trimester of pregnancy, myomatous nodes, growing, can cause premature birth, as well as abnormal development of the fetus, in particular, cause deformation of the skull bones and torticollis. Large fibroids can cause oxygen starvation in a child.
If, over the course of 9 months, fibroids did not cause problems for either the expectant mother or the fetus, then during childbirth, if the fetus is malpresented, it can still lead to complications in the birth process. In such cases, a cesarean section with simultaneous removal of fibroids is indicated.
Symptoms of uterine fibroids in the early stages
Content
Symptoms of uterine fibroids in the early stages are best diagnosed by a gynecologist. These may be minor compactions of the outer layer of the myometrium or nodules. Their treatment is more effective the sooner the patient seeks help.
At first, the disease is almost invisible
The peculiarity of fibroids is that it is difficult for a woman to detect its symptoms in herself in the very first stages. This benign disease directly depends on hormonal levels, therefore, most often, some disruptions in the menstrual cycle or deterioration in general condition are attributed to other diseases. However, in the early stages, you can consider some signs of a female illness:
- Bleeding, heavy menstruation. Even if the norm is considered to be 3-5 days (discharge), you should focus on individual indicators. If previously the patient had only 3 such days, but now has 5, this is already a reason to contact a specialist. Or vice versa - the usual 5-6 days of menstruation last no more than 3-4 days. You should be wary of discharge with clots, copious amounts. Such blood loss can even lead to anemia (lack of iron in the blood).
- No pain. It happens that uterine fibroids are difficult to diagnose precisely because of the absence of pain, but this does not mean that there is no tumor. The cycle can also remain familiar. This is the danger of the disease, which is often found in more advanced forms. But due to the fact that the contour of the uterus can change, intestinal dysfunction sometimes occurs in the form of constipation and flatulence. This is due to the fact that the reproductive organ begins to take up more space in the abdominal cavity, putting pressure on the intestines. For the same reason, frequent urge to go to the toilet is possible. Urination becomes difficult, the urge becomes more frequent.
- Painful sensations during sexual intercourse. Perhaps these symptoms are related to erosion, are associated with cystitis or other abnormalities in the woman’s body, but there is a high probability of the occurrence of benign formations of the uterus.
- Change (enlargement) of the abdomen. It seems that it is getting larger due to the extra pounds gained, which may also be due to a hormonal imbalance that triggered the appearance of nodes or tumors.
- Pain in the lower abdomen and lower back can also be a sign of uterine fibroids. Periodically occurring pain syndrome that is unstable in nature should be a reason to contact a gynecologist. Severe pain during PMS is not the norm. Acute pain will indicate the progression of a common female illness.
- Liver problems. This organ is involved in the formation and distribution of hormones. Liver dysfunction in almost all cases leads to hormonal imbalance.
- Pain in the heart, cardiac muscle tone. At first glance, there is nothing in common. On the other hand, hormonal imbalances affect not only the reproductive organs, but also other systems.
These are common symptoms, but they may differ depending on the location of the fibroids. It is important to visit a female doctor on time and not be afraid. A benign uterine tumor does not always turn into a malignant tumor (only in 5% of cases, provided that the fibroid is not treated).
One should be wary of the fact that the disease can lead to infertility.
Before treating a common disease, it must be diagnosed. In addition to the standard signs and deterioration of well-being the day before, during and after menstruation, there are other manifestations.
It is important to remember that myometrial tumors tend to appear in places of the uterus that are not immediately noticeable. The symptoms of this disease may differ depending on the location of the tumors:
- With interstitial fibroids (when tumors arise inside the muscle layer), there may be an increase in body temperature and bleeding in the middle of the cycle (many perceive them as premature menstruation). Possible pain on the eve of menstruation (acute, unbearable).
- With the subserous (subperitoneal) type of fibroids, problems with conception or miscarriages are observed.
- Submucosal tumor (pedunculated, with processes), as well as intraligamentary forms, are also characterized by cramping pain in the lower abdomen and problems with bearing a child.
- The cervical type of uterine fibroids is characterized by such symptoms as general weakness, pallor (due to anemia), dizziness and headaches.
Certain types of fibroids can provoke spontaneous miscarriage even after 11 weeks, when the developing placenta can touch a benign neoplasm.
During conception, and sometimes during pregnancy itself, some uterine fibroids do not interfere with either the fetus or the expectant mother. Their presence can cause harm in the postpartum period (even during childbirth - the presence of some types of fibroids is a direct indication for a cesarean section). But, in any case, before planning conception and during each trimester, pregnant women are prescribed an ultrasound, which helps not to miss the first symptoms of the disease.
Diagnosis and treatment of the disease
If a woman doubts that the ongoing health problems are symptoms of a disease of any other organ, but not from the reproductive system, it is better to exclude the possibility of this particular illness by contacting an antenatal clinic.
Diagnostics
In the first stages of fibroid development, they help diagnose it:
- Annual examinations (scheduled), which are recommended to be carried out 2 times a year or at least once every 9 months (it is during this period that fibroids, like other abnormalities, can be found and effective treatment applied). A possible enlargement of this reproductive organ or a change in its contours will definitely be detected by a specialist by touch.
- During the examination, the doctor also asks relevant questions, after which more specific methods for detecting the disease may be prescribed.
- For example, ultrasound (ultrasound examination). It is carried out both through the abdominal cavity (especially for girls who are not sexually active) and transvaginally. The main goal is to detect and not miss the first symptoms of benign uterine formations. The advantage of this method is the detection of nodes at the very initial stage, when they cannot be noticed during a medical examination.
- Histological examination, when a part is pinched off from the tumor for further (laboratory) study. At the same time, tests are taken to determine the presence of urogenital infections, which could indirectly contribute to the onset of the disease.
To diagnose the disease at the very initial stages, an examination by a gynecologist and an ultrasound of the pelvis will be sufficient.
After this, the specialist can begin therapy. Fibroids can be treated with hormonal drugs.
Treatment
The use of folk remedies is ineffective (since the disease is hormonal in nature and must be treated with conservative drugs containing one or another hormone or a “blocker” of a hormone that exceeds the norm in a woman’s body).
They are conventionally divided into different groups:
- Androgenic group. The drugs can reduce the size of fibroids.
- The gestagen group, for example, is attributed to patients in order to restore the process of normal growth of the uterine endometrium. This tissue undergoes the most changes during the appearance of fibroids.
- Combined contraceptives taken orally. The main goal of this therapy is to stop the growth of fibroids (tumors).
There are more progressive drugs to get rid of the disease. An experienced female doctor, when attempting to treat fibroma with hormonal drugs, takes responsibility for prescribing medications. If you correctly follow the gynecologist’s recommendations, you can not only get rid of the disease at the very first stages of fibroma development, but also:
- Increase your chances of a successful pregnancy.
- Successful delivery (naturally).
- Preservation of the reproductive system, which helps a woman maintain the hormonal levels necessary for the body even after menopause.
Contacting a gynecologist (examination) will help prevent the risk of fibroids. The first signs cannot be ignored.
Women's illness is underestimated: a quarter of all gynecological diseases are caused by benign formations in the uterine area.
Myoma is only a consequence of the fact that there are serious problems in the body. The sooner the gynecologist begins to treat her, the better for the woman’s health.
We recommend reading:
matka03.ru
Hormonal games
Gynecologists today can offer 2-3 options for treating fibroids. If nodules are detected at the initial stage, then you can try antihormonal therapy. The essence of the method is as follows: with the help of hormonal drugs, temporary menopause is created. Fortunately, doctors are able to completely control this process: after the course of medication is consumed, reproductive function resumes in about two months. If hormonal therapy is chosen correctly and the treatment is successful, uterine fibroids stop growing and begin to decrease in size.
| Interesting! | |
| One of the factors in the development of uterine fibroids, according to scientists, is irregular sex life, especially after 25 years. In addition, it has been found that women who have problems achieving orgasm develop fibroids more often than others. | |
But, as you know, playing with hormones does not go unpunished. Women who are prescribed anti-hormonal therapy are likely to experience certain symptoms of menopause: “hot flashes”, or, scientifically, vegetative crises, headaches, sleep disorders, depressed mood or aggression, a sharp decrease in libido, joint and muscle pain, dryness of the vaginal mucosa and discomfort during sexual intercourse, changes in the condition of the skin and hair (loss of hair on the head and increase in hair on the body), reduction in the size of the mammary glands. Of course, it is unlikely that any single woman will experience the full range of troubles described, but some variants of discomfort are guaranteed.
After treatment, maintenance therapy is required, which consists of taking hormonal contraceptives. So it will be quite difficult to return your hormonal levels to their natural state and level out your psychological state.
If the situation is a little more advanced, the gynecologist will most likely offer the patient the procedure of conservative myomectomy (surgical removal of nodes while preserving the uterus itself). Myomectomy has its advantages and disadvantages: any surgical intervention is a serious stress for the body, but if the uterus is preserved, it remains possible to give birth to a child. If removal of the nodes is no longer possible, until recently, a hysterectomy operation, that is, complete removal of the uterus, was inevitable.