What is cervical atresia
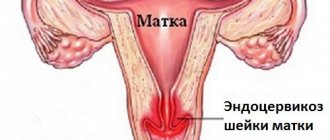
The term atresia or stenosis of the cervical canal refers to an anomaly in the structure of the cervix, consisting of narrowing or complete obstruction of the cervical canal. In the medical literature, the term means complete fusion of the walls of a hollow organ. Atresia can be partial or absolute. If the canal is not passable along its entire length, its complete fusion is diagnosed. If pathology is observed in the area of the external or internal pharynx, partial stenosis is diagnosed.
The main task of the gynecologist is to distinguish stenosis and atresia of the cervical canal from stricture. With stricture, cervical obstruction occurs due to scar deformities. The disease is detected based on the patient’s complaints and simple diagnostic procedures. The diagnosis of complete stenosis is determined when it is impossible to enter the uterine cavity with a probe with a diameter of 12 mm. The main danger of such a deformation is that it may have an oncological basis. To exclude the possibility of developing cancer, the patient undergoes an endometrial biopsy.
If the woman does not have atypical cells or negative symptoms, surgery is performed. It is worth noting that stenosis detected during menopause cannot be treated; patency of the cervical canal is restored only to women of childbearing age. In some cases, pelvic ultrasound and MRI are performed to diagnose the disease. It should be taken into account that atresia may be accompanied by structural disorders of the genitourinary system. To clarify the diagnosis, urethrocystoscopy is performed.
In medical practice, a distinction is made between acquired and congenital atresia. With congenital pathology, fusion of the cervical canal occurs at the stage of embryonic development. The reasons that provoke such deformation are as follows:
- infection of a pregnant woman with toxoplasmosis, chlamydia or syphilis;
- taking certain medications in the first trimester of pregnancy;
- exposure of a woman to ionizing radiation.
With congenital fusion, the symptoms do not bother the woman until puberty, or more precisely, until the first menstruation. Acquired atresia appears due to age-related changes or due to injuries to the cervical canal. Normally, the menopause period is accompanied by a significant decrease in the size of the uterus and cervix, a change in the structure of all tissues and organs that provide reproductive function. Such changes occur against the background of the cessation of estrogen secretion and cell insensitivity to follicle-stimulating hormone. Against the background of a decrease in the intensity of production, thinning of the epithelium occurs, resulting in a partial narrowing of the lumen of the canal. Over time, the stenosis progresses and complete fusion occurs.
The main causes of atresia that manifests itself during reproductive age may be the following:
- transferred electrocoagulation of the canal;
- chemical treatment of the cervix;
- violation of curettage technology during abortion;
- complicated course of endometritis or endocervicitis;
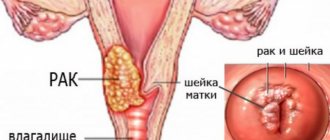
- cancer of the cervix or uterine body;
- consequences of past infections (tuberculosis, gonorrhea, chlamydia).
When atresia of the cervical canal appears in a woman, menstrual bleeding stops or its intensity significantly decreases. Such a symptom should be a cause for concern; the girl should urgently consult a doctor. The main danger is that menstrual blood accumulates in the uterine cavity and can cause infection.
The video and photos in this article will help the reader understand exactly how the operation occurs.
METHODS FOR DIAGNOSIS OF CERVICAL STENOSIS
- History taking and physical examination. The doctor will ask about your past menstrual cycles, family medical history, and symptoms you have, which will help him evaluate your condition.
- A hysterosalpingogram is one of the methods of X-ray examination of the uterus and fallopian tubes in real time. If the patient has a significant narrowing of the endocervical canal (its normal diameter: 0.5-3.0 cm), or complete obliteration of the cervix, insertion of a hysterosalpingographic catheter may be complicated. In such cases, additional devices are used: such as a uterine probe or a small dilator.
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs. Although the stenosis itself is difficult to see, visualization of surrounding tissue in the appropriate location may indicate associated stenosis, especially if it is complicated by proximal dilatation of the female genitalia.
What is dilation, or bougienage, of the cervical canal?
Expansion or bougienage of the cervical canal is a surgical operation performed to eliminate narrowing or fusion. The disease occurs in women of reproductive age due to various reasons, but often narrowing occurs due to curettage or age-related changes. The infection has a negative effect on the condition of the cervix. Patency is restored with the help of a simple manipulation, which is carried out using a special instrument called a bougie.
Bougienage is the only way to get rid of pathologies that limit a woman’s ability to conceive. This type of operation can be performed during menopause, but the procedure is done at the request of the woman. Reviews from patients who have undergone bougienage describe this procedure as painful, but this is not always the case. The main thing is to choose a good medical center. The manipulation is always carried out under anesthesia; doctors use equipment that significantly reduces the patient’s time in the hospital.
Attention! You cannot refuse the intervention. Against this background, the risk of developing inflammatory and cancer diseases increases. When the canal is completely closed, infertility is likely to develop.
Expansion of the cervical canal of the uterus can be done by acute or blunt means. The most common way is to use special dilators. The essence of the method is that devices with different diameters are inserted into the channel one by one. The size is gradually increased by 0.5 - 1 mm.
The procedure is carried out as follows:
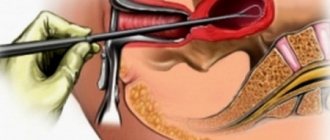
- The cervix is processed and exposed using speculum.
- Using bullet forceps, grab the front lip and move it towards the entrance to the vagina.
- The cervical canal is wiped with an alcohol solution.
- After fixing the vaginal part, a uterine probe is carefully inserted into its cavity, the position and size of the uterus is determined.
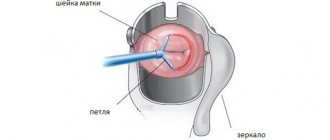
- The surgeon holds the bullet forceps with his left hand and begins to expand the canal.
- Hegar dilators are alternately inserted into the canal towards the uterine cavity, taking into account its location. Dilators should be inserted slowly; with physiological anteflexion of the uterus, the handle should be lowered down.
- The end of the dilator should go beyond the internal os, but you need to control the process so that the device does not reach the bottom of the uterus.
The first numbers of dilators with partial fusion are found quite freely. As the diameter increases, resistance is felt in the internal throat. At this moment, the gynecologist should work carefully, without making sudden movements. You need to remove the dilator slowly and immediately insert the next one, not allowing the internal pharynx to contract. If one of the next expansion tubes cannot be passed through the internal throat, insert the previous one and leave it in the canal for several minutes. The procedure is carried out very carefully without sudden, violent movements.
When is the procedure prescribed?
Manipulation to expand the cervical space is performed under general anesthesia in a clinic equipped with modern equipment. Highly qualified and experienced specialists can save the patient from the development of the inflammatory process, as well as oncological pathologies.
Surgical measures are prescribed for the following pathological conditions:
- diagnosis of stenosis, which is manifested by partial narrowing of the canal lumen;
- detection of impaired blood flow from the uterine cavity;
- the inability to become pregnant for a woman of reproductive age due to stenosis.
The ineffectiveness of conservative therapy when stenosis progresses to atresia is due to the fact that the pathology is not usually detected at an early stage. If the narrowness of the cervical canal, as a consequence of postoperative swelling of the mucous membrane, can be diagnosed in time, treatment takes place without surgery. The doctor prescribes medications, supplementing the treatment regimen with douching with decongestants (solutions) when refusing sexual relations.
Various factors, including congenital ones, can lead to complete or partial closure of the cervical walls.
In the case of a congenital anomaly of the cervix, the operation of bougienage of the cervical canal is recommended to be performed before the girl enters the period of her first menstruation.
Most often, the need for surgical intervention on the cervical segment of the neck is associated with certain situations:
- the presence of sexually transmitted infections (toxoplasmosis, chlamydia, herpes, syphilis);
- long-term use of medications;
- poor quality of curettage (diagnostic or therapeutic);
- hypertrophic scarring of tissue;
- congenital abnormal structure of the cervix;
- medical disposal of pregnancy (abortion);
- cauterization of the uterine epithelium (electrocoagulation);
- development of endocervicitis or endometritis, oncology;
- exposure to ionizing radiation.
Externally, a gynecological anomaly may not manifest itself in any way, but over time, due to impaired outflow, menstrual blood accumulates in the uterine cavity, signaling cramping pain in the lower abdomen during menstruation. Narrowing of the cervical canal makes it impossible to perform planned diagnostic procedures. Then the gynecologist prescribes bougienage using metal dilators of different diameters.
A technique for expanding the narrowed cervical canal was proposed by the German physician Alfred Hegar back in the second half of the 18th century. A set of instruments (bougies) was named after the surname of the obstetrician, consisting of 19 dilators with increasing diameter increments of 0.5 mm.
Indications for intervention
The list of main indications for intervention and expansion of the cervical canal includes the reasons that provoke pathological narrowing or overgrowth. This list includes the following conditions and diseases:
- infectious pathologies;
- taking certain medications for a long time;
- contact with ionizing radiation;
- poor quality of the procedure for curettage of the uterine cavity;
- cauterization of polyps or cervical erosion;
- consequences of obliteration;
- cervical cancer;
- late term abortion;
- endocervicitis;
- hypertrophic scarring.
Causes
This pathology can be congenital or acquired. It manifests itself as a consequence of abnormal development of the genital organs, infectious and inflammatory diseases of the cervix, injuries and medical interventions. There are fusions of the entire cervical canal and its separate part. These processes are called:
- Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the CD - endocervix.
- Curettage of the uterine cavity for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.
- Menopause (spontaneous infection due to hormonal changes in the body).
- Treatment of cervical erosion with chemicals.
- Radioactive exposure.
- Malignant and benign neoplasms of the cervix.
- Scar changes due to electrocoagulation and other surgical interventions.
- Endometriosis of the cervix.
In reproductive age, complete atresia of the central circulation leads to hematometra (filling of the uterus with menstrual blood), hematosalpinx (blood in the fallopian tube), peritonitis, partial ones can cause infertility.
How does the intervention work?
The bougienage procedure is carried out in a hospital setting under general anesthesia. Local anesthesia is used less frequently because it is considered ineffective. The type of anesthesia is determined by the doctor after a complete examination of the woman. The surgical technology involves the introduction of special instruments into the cervical canal.
Attention! Without anesthesia, the patient will feel pain, and the risk of injury to the mucous membranes due to sudden movements will increase.
The diameter of the bougie increases gradually; if the technology is not followed, cervical rupture is likely. In case of accidental injury, the risk of re-occlusion of the cervical canal increases. Correctly performed dilation guarantees the absence of complications. Bougienage is prohibited if the fusion occurs against the background of a malignant process. In this case, radical operations are used. Bougienage is not performed if a woman has had false amenorrhea for 6 months. Hormonal testing can help detect this condition. In this case, plastic canalization of the cervix is performed.
After the operation, the woman can go home, but sometimes the doctor recommends staying in the hospital. This condition reduces the likelihood of bleeding. Outpatient treatment is acceptable in the absence of pathologies of the heart and blood vessels. Local anesthesia is used if general anesthesia cannot be administered.
How is it carried out?
Surgical intervention to expand the cervical canal and restore its normal patency is done within the walls of a medical institution. On the eve of the operation, which is performed on an empty stomach, the patient must independently remove vegetation from the outer surface of the genital organs. The choice of type of anesthesia is determined by the degree of stenosis of the cervical lumen; the dilation procedure itself does not take more than 30 minutes.
The algorithm for bougienage of the cervical canal space is as follows:
- the patient, seated in a gynecological chair, is administered intravenously with drugs individually selected for anesthesia;
- the outer surface of the genital organs is treated with an antiseptic while maintaining maximum sterility to prevent infection;
- the surgeon inserts a spoon-shaped speculum into the vagina, providing free access to the cervix;
- the uterus is fixed using bullet forceps by the anterior lip of the cervix to straighten the uterine canal;
- A button-shaped probe with a diameter of the working part of 3.5 mm helps to determine the direction of insertion of the bougie; if necessary, take a probe with a smaller diameter;
- the expansion process begins with the use of the narrowest bougie, which is successively replaced by wider nozzles;
- at the stage of completion of the operation, the widest rod (Heger bougie No. 11) is left inside the space of the cervical canal for some time;
- The gynecological bougienage procedure is completed with sanitation with an antiseptic solution.
If the cervical canal becomes infected, complicated by an inflammatory process, additional curettage will be required to remove the purulent secretion.
Thanks to the procedure of sufficient expansion of the cavity, this is not difficult.
A gradual impact on the space of the intracervical tract during surgery allows minimizing the threat of tissue rupture, which ensures their rapid regeneration. After surgical manipulation under general anesthesia, the patient is discharged from the hospital the next day.
In case of minor fusion of the canal segment, it is possible to prescribe an operation without general anesthesia, but only under local anesthesia using an antiseptic and internal spraying of lidocaine. The gradual expansion procedure for partial stenosis follows a similar scenario, and the woman can go home after just a few hours.
Preparation for the operation
To reduce the risk of complications, a woman needs to undergo a series of preparatory examinations. They are needed not only to confirm the diagnosis, but also to establish the general state of health. The set of diagnostic measures includes:
- general blood analysis;
- blood chemistry;
- test to detect sexually transmitted infections;
- test for HIV, syphilis, hepatitis B and C;
- blood clotting test;
- colposcopy;
- microscopy of vaginal and cervical smears;
- electrocardiogram;
- fluorogram;
- probing;
- bacterial culture from the vagina;
- Ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs.
The woman should visit an anesthesiologist. On the day of the operation, drinking water and food is prohibited. The prohibition is due to the fact that nausea and vomiting may occur during intravenous anesthesia. The cost of the procedure differs in many clinics. When choosing a medical center, you need to take into account its reputation and the qualifications of its doctors.
Diagnosis and symptoms
Depending on the severity, cervical stenosis may be detected when symptoms are examined, or it may not be obvious until fertility testing or treatment. Possible symptoms:
- Abnormal menstrual bleeding
- No period or very light spots
- Intense menstrual cramps
If these symptoms occur after cervical surgery, cervical stenosis is strongly suspected.
Infertility is also a possible symptom.
During a fertility test, cervical stenosis may be suspected if there is difficulty with hysterosalpingography. This is a special x-ray that transfers dye into the female reproductive system through the cervix upward. Typically, the catheter is placed inside the outer cervix. The dye is released, and then the doctor takes an x-ray, which should show whether the fallopian tubes are open and the shape of the uterine cavity.
However, if the catheter cannot be placed, there is pain, or the dye does not pass past the cervix, a stenosis problem may occur. If this occurs, a hysteroscopy is usually ordered. This fertility test can also be used to possibly correct cervical stenosis.
It is possible that stenosis can be detected during the treatment itself.
Also, a problem with cervical stenosis can arise if there are problems with the placement of the catheter for insemination or embryo transfer.
Period after surgery
After the operation, the woman can return to normal life within 2 weeks. During this period, all pain completely disappears. If the pain intensifies within 14 days, you should consult a doctor immediately. There is a risk of infection. During postoperative treatment, a woman is advised to take anti-inflammatory drugs and use suppositories that have wound-healing properties.
Attention! Such drugs are prescribed by a gynecologist, taking into account the general state of health and tolerability of individual medications.
You should consult a doctor in the following cases:
- bleeding from the vagina and excessive secretion of mucus from the genitals;
- pain in the abdomen and lower back does not go away within several days;
- body temperature rises.
To prevent the development of negative consequences after probing the canal, the patient is advised to take antibiotics.
Rehabilitation
The duration of recovery after bougienage of the Central Committee is about fourteen days. During this time, it is not recommended to have sex, lift weights, engage in active sports, or visit open and closed reservoirs, saunas, and beaches.
For a week after the intervention, it is necessary to take antibacterial drugs to prevent infectious complications. Anxiety is caused by fever, pain in the lower abdomen, moderate and heavy bleeding from the genital tract. In this case, it is recommended to consult a doctor. Complications of bougienage can include inflammatory processes, bleeding, perforation (injury) of the organ.
How to prevent overgrowth
Compliance with the following rules helps prevent the development of the problem:
- timely treatment of various inflammatory processes affecting the central canal and cervix;
- regular visits to the gynecologist to identify inflammatory processes and malignant neoplasms;
- prevention of unwanted pregnancy, reducing the frequency of abortions;
- refusal of self-medication;
- compliance with the rules of a healthy lifestyle;
- the use of barrier methods of contraception to prevent bacterial infection.