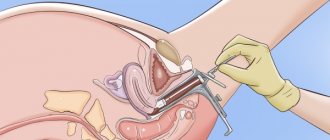
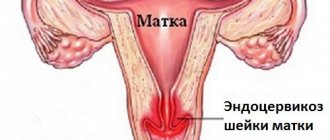
Uterus
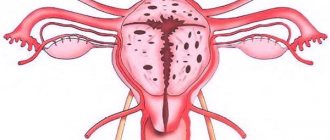
located in the pelvic region in front of the rectum and behind the bladder.
It is a hollow organ lined internally with endometrium. The cervix is located in the lower third of the uterus and opens into the vagina. Cervical cancer
affects both young and mature women and is often asymptomatic at the onset.
Cervical cancer (the appearance of abnormal cells) is one of the cancer diseases that claims the most lives among women. It can be considered one of the main problems of women's health. This disease is the most common cause of death among women aged 25 to 60 years. In terms of frequency, cervical cancer occupies an intermediate position between uterine cancer and ovarian cancer.
The uterus consists of two parts
: the body located above, in which the baby is born, and the cervix, located at the lower end of the uterus. The cervix connects her body to the vagina.
Cervical cancer
develops gradually. In the early stages, some cells undergo changes and turn into precancerous cells, from which cancer cells are subsequently formed. This transformation can take several years, although sometimes it occurs at a rapid pace. In some women, the precancerous condition may disappear without any treatment. However, it is impossible to prevent precancerous cells from turning into cancer cells without treatment.
Cervical cancer is the leading cause of death in women aged 25 to 60 years. Its development can be prevented through timely diagnosis, which only requires a smear ( Pap test)
).
Causes
The age group of patients susceptible to cervical cancer is 20-40 years. Pathology is detected mainly in the later stages, which is explained by the absence of pronounced symptoms. It is possible to make a timely diagnosis of cervical cancer only when a woman undergoes regular preventive examinations with a gynecologist.
Why cancer cells form is not known for certain. There are a number of factors, the presence of which increases the likelihood of developing uterine cancer; in their presence, a woman should visit a doctor at least 2 times a year for prevention.
Oncology can be caused by:
- The presence of human papillomavirus. Most patients diagnosed with a tumor have HPV.
- Long-term use of hormonal drugs. The likelihood of cancer of the uterus and cervix increases with long-term use of oral contraceptives, when the course of treatment lasts from 5 years.
- Age-related changes. The risk of developing cancer of the reproductive system increases after 40 years of age. In women, this trend is explained by the period of menopause, when hormonal changes occur, immunity decreases, and chronic diseases worsen.
- Promiscuous sex life.
- Early intimacy.
- Smoking. Cervical cancer is often diagnosed in women who have such a bad habit. Cigarette smoke contains toxic substances and carcinogens that have a toxic effect on the entire body and especially on the female reproductive system.
Pathology has a genetic predisposition. If there have been cases of cancer of the reproductive system among close blood relatives, the likelihood of the disease increasing significantly.
Symptomatic picture
Uterine cancer is dangerous because it does not manifest itself in any way at an early stage, when the disease can be cured using non-surgical methods and complications can be prevented. When a woman exhibits a certain clinical picture, this indicates that the pathological process is actively developing. General signs of oncopathology:
- general weakness, fatigue, apathy;
- constantly elevated body temperature up to 37°;
- signs of anemia - lethargy, headaches, refusal to eat;
- uterine bleeding;
- pain in the pelvic area;
- disruption of the menstrual cycle;
- increase or decrease in blood volume during menstruation;
- pain during sex;
- sudden loss of body weight;
- severe swelling of the lower extremities.
The discharge is often bloody. They occur in the middle of the cycle, mainly after sex or active sports. The fluid coming out of the vagina may be yellow or green. The discharge has a different consistency - watery, thick. The smell of the discharge may be absent altogether or may be quite strong and unpleasant. As the tumor develops, the smell becomes stronger and more offensive.
Cervical cancer causes pain that is localized in the pelvic area. The woman feels pain in the sacrum, lower back, and hips. When a malignant tumor develops, a woman experiences pain in the rectum during bowel movements. Features of pain with cervical cancer are the inability to relieve it with painkillers.
Over time, cancer cells from the uterine cavity spread to the organs of the genitourinary system, which provokes the development of the corresponding clinical picture. If the tumor affects the bladder, problems with urination occur, there is blood in the urine, and the lower abdomen hurts. When cancer cells penetrate the rectum, frequent constipation appears and the process of intestinal motility is disrupted, accompanied by a corresponding symptomatic picture.
Diagnostics
If cervical cancer is suspected, a comprehensive examination is required. The doctor will tell you what diagnostic measures will need to be taken in case of illness after examining the woman and studying her medical history. In many cases, the tumor is detected during a routine examination by a gynecologist. Diagnosis of cervical cancer includes a series of laboratory examinations and instrumental methods.
Lab tests
The first blood test to be taken for cancer is a general blood test with determination of its biochemistry. Decoding the results shows the general condition of the body, the presence of abnormalities in the functioning of internal organs that can be caused by tumors. They resort to a general analysis immediately, and it is better to donate blood before visiting a doctor, so that you can come to the appointment with the results in hand.
To determine the stage of an oncological tumor, a blood test is performed to identify a tumor marker - squamous cell carcinoma. Its presence indicates the development of pathology, and the stage of the tumor process is determined by the concentration of this blood parameter.
Smear analysis and cystoscopy
A blood test to determine the human papillomavirus is a mandatory diagnostic step. To conduct a test for cervical cancer, a smear is taken from the cervical canal. If tests show the presence of cancer, instrumental diagnostic methods are prescribed.
Screening
What is the name of the analysis? This test is called cervical cancer screening - it is a laboratory test of a smear from the cervical canal. The recommended time for collecting a tissue sample to obtain an informative result is the middle of the menstrual cycle.
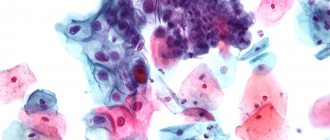
Among all screening methods, preference is given to the Papanicolaou method. This test for cervical cancer detects in the smear the presence of altered cells of the cervical canal mucosa, cancerous structures, dysplasia and other pathological processes.
Cytology
Among all the cytological techniques used in diagnosis, liquid-based cytology of the cervix is the most accurate. The method involves laboratory examination of a smear from the cervical canal. The analysis reveals the presence of cancer cells and determines the stage of development of the disease.
The smears are examined under a microscope. Diagnosis of uterine cancer using liquid cytology reveals cancer in the early stages, so it is recommended for prevention purposes at least once a year.
Instrumental research methods
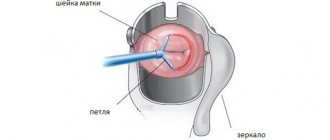
Diagnosis of cervical cancer begins with a visual examination of the patient in the gynecological chair. Upon examination, a change in the color of the mucous membrane of the cervical canal and the formation of lesions are visible. Invasive cancer is clearly visible using gynecological mirrors. Additional diagnostic methods to clarify the diagnosis and determine the stage of development of the disease, the presence of complications - biopsy, colposcopy, ultrasound, MRI, CT.
Colposcopy
It is possible to see cancer on the cervix in the early stages only using a colposcopic procedure. A colposcope is a device that magnifies the image several times. During colposcopy, a biopsy is performed - taking samples of biological material for further laboratory study.
Biopsy
The biopsy procedure has several methods:
- Loop - taking a tissue sample using electric current resection. The method is rarely used due to the high risk of soft tissue damage.
- Cryoconization is the detachment of soft tissues by cauterizing them with liquid nitrogen.
- The radio wave biopsy method involves cutting a tissue sample with a radio knife.
Among all methods of diagnosing cancer, biopsy is of utmost importance, as it shows highly accurate results. A laboratory examination method shows the stage of cancer, the presence of complications and metastases.
Ultrasound
How to determine cervical cancer using the simplest and most accessible method? Using ultrasound. The main method of ultrasound of the pelvic organs and uterine cavity is transvaginal.
During the diagnosis, changes in the soft structures of the cervical canal are revealed, and the focus of the oncological tumor is visible. If we analyze all the reviews from women, it was through a routine ultrasound of the pelvic organs that they were diagnosed with cervical cancer.
MRI and CT
Methods of examining the uterus such as MRI and CT are as informative as possible. They show all changes in the organs of the reproductive system and help identify metastases. Magnetic resonance examination is carried out to clarify the diagnosis and is not the primary research method.
Exceptions are cases when a woman has signs indicating uterine cancer, but other instrumental techniques do not visualize the tumor. The disadvantage of using an MRI for cervical cancer is that the tumor visible on the image may not always be visible due to its resemblance to fatty tissue.
Computed tomography is important for determining effective therapy for cervical cancer. The examination is carried out more than once during treatment to monitor positive dynamics.
What is a survey?
A precancerous condition is considered a harbinger of the development of a malignant neoplasm. It must be identified in a timely manner. Today this is more than possible, since you can be tested for cancer both in a regular clinic and in a specialized center.
To more accurately identify pathology, the most modern equipment is currently used, and highly qualified specialists work. The examination usually lasts one to two days.
It is carried out on an outpatient basis under the careful supervision of a doctor. In accordance with the results of the examination, the patient receives complete information about the state of his health. The specialist will also answer all your questions.
If necessary, treatment is immediately prescribed, the patient receives instructions and recommendations. How much does it cost to get tested for cancer? Prices for the study depend on the list of tests and diagnostic measures recommended by the doctor. On average, a general examination costs from 1.5 to 3 thousand dollars.
Treatment methods for cervical cancer
The main method of treating oncological pathology is radiation therapy. Depending on the severity of the clinical case and the presence of complications, this type of therapy may be the only one or it may be used before surgery.
Chemotherapy for uterine cancer is used extremely rarely and only as an auxiliary technique before surgery, or to enhance the therapeutic effect of radiation.
Types of surgical intervention:
- Conization is the resection of areas of soft tissue of an organ damaged by the tumor. It is used only in severe stages of cancer, mainly in women who have given birth, as it can lead to a number of complications, including infertility.
- Extirpation of the extended type is an operation to remove the uterine cavity and other organs of the reproductive system affected by the pathological process. This is a very complex operation, which is used in extreme cases when there is a high risk of metastases spreading. Resection of the uterus is an extreme but necessary measure. It is used when other methods do not give positive dynamics, and the cancer progresses.
After treatment, the woman needs to be examined regularly. In cases where the uterus has not been removed, there is a possibility of recurrence. Over the next 2 years after therapy, it is necessary to be examined at least once every 3 months. In the future, examinations by a gynecologist should be carried out every six months.
Why does antigen level increase in carcinoma?
An upward deviation from the norm of the SCC antigen indicates the progression of the tumor, the spread of metastases to the lymph nodes and other neighboring organs and tissues. In addition, the amount of antigen in the blood may be increased if:
- ineffectiveness of the therapy, when there is a high probability of subsequent relapses;
- development of benign pathology, or psoriasis, eczema, pemphigus, non-tumor diseases in the lungs: tuberculosis, sarcoidosis, exudative pleurisy or renal, liver failure.
The antigen for squamous cell carcinoma scca is also present in the body of a healthy person, but should not exceed 2.5 mg/l. As the tumor grows, the number of tumor markers will steadily increase. Carcinoma is fraught with relapses already at stages 1-2, so only regular determination of the antigen in the blood every 2-3 months will allow doctors to predict the course of the tumor and prevent relapses when primary clinical manifestations appear.
Exceeding the level indicates the development of oncological processes, as well as the release of glycoproteins from the epithelial layer of the cervix during the development of carcinoma.
The scc antigen is a tumor marker or detector for a squamous cell tumor, as it develops, the level of antigen in the blood increases sharply or when a protein is released - a protein from the epithelial layer of the cervix. At the same time, the level of ESR in the blood increases. Although it is impossible to make an accurate diagnosis using the SCC test alone. SCC level increases when:
- psoriasis;
- renal failure;
- gynecological diseases.
The squamous cell carcinoma antigen may indicate cervical cancer or other types of cancer.
SCC tumor marker is a tumor marker that is a kind of detector of cancer or squamous cell oncology that has a tendency to grow invasively. During this process, the tumor invades surrounding tissues and regional lymph nodes. The SCC tumor marker is also present in a healthy human body, only in small quantities. Its level increases with the development of cancer.
Experts say that thanks to the antigen of squamous cell carcinoma, it is possible to establish the development of neoplasms of the cervix, ear, esophagus, nasopharynx, lungs, etc.
Normal levels are up to 2-2.5 ng/ml; according to some data, even below 1.5 ng/ml
It should be noted, however, that this is the standard range of values accepted by most researchers. Adopting strict standards is not possible because some patients with squamous cell carcinoma have low blood antigen concentrations (below the acceptable upper limit of normal) even as the disease progresses. And vice versa - not every patient who shows an increase in antigen levels above the standards reveals the presence of oncological pathology.
Reviews
Women diagnosed with cervical cancer, who detected the pathology in a timely manner, say:
Ksenia : “I was lucky that my cervical cancer immediately began to manifest itself. My lower back hurt constantly, there was pain during sex, and spotting often occurred. Before going to the doctor, I did an ultrasound, but the examination showed nothing. And during the examination, the doctor immediately made a diagnosis and prescribed tests. An MRI turned out to be the most accurate; a tumor was immediately detected. It’s good that it was the initial stage, treatment was carried out only with radiation therapy. Now every 6 months you need to go for an examination with a gynecologist, as there is a possibility of relapse.”
Marina : “I have a cervical tumor, which, as it turned out, was already 4 cm, did not manifest itself at all. I came for a routine examination, it turned out that it was the first stage. I was tested for tumor markers and cytology, the diagnosis was confirmed. Treatment is radiation therapy. I’ve been in remission for 3 years already.”
Oksana : “My grandmother and mother had cervical cancer in my family, so I took a tumor marker test every year, and also had an ultrasound. At the last test, an elevated tumor marker was discovered, an ultrasound showed a small tumor, and a diagnosis was made of cervical cancer, stage 1. I started treatment right away, but radiation therapy didn’t help me much; the cancer went into remission for six months and progressed again. They did conization, and after that, irradiation. The remission has been going on for a year now.”
How is the SCC tumor marker tested?
A blood sample is taken from a vein into a tube containing EDTA. No special preparation is required. The antigen is found in sweat, saliva and other bodily secretions. Thus, contamination of the test material with them (for example, saliva splashes) can cause a false reading of elevated values.
Elevated SCC concentrations do not always indicate cancer
In addition, elevated SCC levels may indicate: benign tumors of the head and neck, as well as numerous non-tumor diseases, such as psoriasis or kidney disease. Slightly elevated levels may also occur in patients with inflammatory lung diseases.
SCC tumor marker concentrations may also increase during radiation therapy.