Indications for use
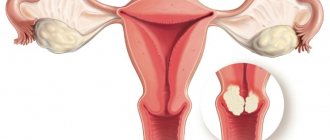
Removal of the cervix is an operation whose main purpose is to prevent the development of malignant transformations in the organ. Only the attending physician, based on advanced diagnostics, will be able to say whether this intervention is necessary or not. Indications for uterine amputation are:
- Hypertrophic changes in organ tissue - it sinks, becomes inflamed, and the functioning of the glands is disrupted.
- Growing polyps with endocervicitis in the chronic stage.
- Formation of malignant tumors in the initial stages.
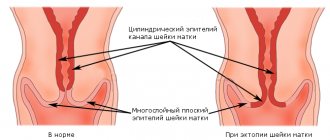
- Cervical canal dysplasia.
- Cervical erosion.
https://youtu.be/acBV2jVRShs
Possible complications: life after treatment
After surgical treatment, some complications may occur, which manifest themselves in the form of minor bleeding. Less commonly, wound infection or even sepsis may occur. To avoid sad consequences, all operated patients undergo mandatory routine examination after surgical treatment. Patients are usually prescribed antibiotics and some painkillers.
Advice: after surgical treatment, it is forbidden to have sex, take baths, swim in the pool, or lift weights for 1.5 months to avoid sutures coming apart and causing infection.
Soon after amputation of the affected cervix (1-1.5 months), the woman will be able to return to her usual lifestyle. It is imperative to undergo periodic examination by the treating gynecologist, and also to exclude the possibility of conceiving a child during the first 6 months after treatment.
We recommend reading: methods of cauterization of cervical erosion
Preparing for the intervention
Before the doctor sends a woman for surgery, it is necessary to conduct an extensive diagnostic examination. A biochemical blood test is performed to determine the rate of blood clotting. You will also need to undergo a chest x-ray. In order to exclude the possible formation of metastases in the lymph nodes, the woman undergoes MRI and CT. Before prescribing surgical intervention, it is necessary to completely cure infectious processes.
Before the operation, the woman is told in detail how the operation will take place, its features and possible complications. After this, she signs a paper according to which she confirms her awareness of the possible consequences. The woman is admitted to the hospital the day before the intended intervention. She cannot drink or eat for 6-8 hours. Some medications are also started at this time.
How long do women with uterine cancer live?
There is no clear answer to the question of how long women with uterine cancer live. This depends on many factors, the main one being the stage at which the cancer was diagnosed. The second factor is at what point treatment was started. Sometimes women who have been diagnosed with such cancer delay treatment, often not realizing that delay in such a case could cost them their lives.
Regarding the symptoms of the disease, only one thing can be said: the main sign that accurately indicates the presence of a tumor is uterine bleeding.
Must Read: Bone Cancer
If a patient experiences periodic uterine bleeding, this gives the doctor reason to assume that she has tumors in the uterine cavity and refer her for examination for the development of cancer.
To make a diagnosis, standard tests are prescribed:
- blood tests (general and biochemical);
- analysis of a smear taken from the cervical canal;
- standard gynecological examination;
- hysteroscopy aimed at obtaining tumor biomaterial;
- cytological examination of tumor biomaterial;
- ultrasound examination to confirm the presence of a tumor and determine its parameters.
Based on the data obtained, the doctor makes an accurate diagnosis and prescribes treatment.
Treatment for uterine cancer includes hormonal, radiation, chemical therapy and surgery.
Types of hysterectomy operations
Several techniques have been developed to remove the cervix. The choice of one or another method of operation is made by a surgeon based on diagnostic data. In this case, it is very important to assess the degree of pathological processes in the body. Today the following operations are used:
- Resection of the cervix is the removal of a functional part of an organ or its entirety. In this case, the specialist excises part of the parametrial tissue, but the fallopian tubes and ovaries are not affected. Thanks to this, reproductive ability is preserved.
- Laser excision is a modern method of surgical intervention in which the location of the tumor is cauterized with a special glow. The disadvantage of this operation is the formation of stumps on the cervix, which causes serious problems with fertilization. Because of this, laser excision is performed extremely rarely in nulliparous women.
- Cryodestruction is an operation in which the resulting tumor is exposed to liquid nitrogen. The affected tissue freezes and dies, as a result of which the neoplasm completely dies. An absolute contraindication to this method of treatment is the presence of inflammation in the uterus.
- The radio wave treatment method is the safest way to treat tumors in the uterus. New growths are destroyed under the influence of waves of a certain length, while the organ remains as intact as possible.
Carrying out the operation depending on the type and stage
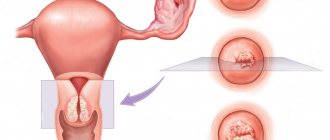
The uterus is a hollow organ, the anatomy of which is distinguished by the body (convex upper part) and the cervix (narrowed canal, thanks to which contact with the environment and the vagina occurs).
In the middle, the uterus is lined with endometrium, a type of epithelium. With an excess amount of estrogens and a number of other factors, the endometrium can grow and after a certain time undergo a malignant transformation. The mucous membrane of the cervix also has the possibility of degeneration. In some cases (about 20%), the malignant process does not affect the epithelium.
Similar degenerations occur after menopause, but in recent years there has been a trend towards an increase in the development of tumors among women of reproductive age. Removing a uterine tumor separately from the organ is not possible. The cancerous formation is excised along with all its surrounding tissues.
Oncology of the cervix is distinguished separately. This fact is associated with the high incidence of the disease. Treatment depends on the extent of the process.
Based on this, the types of cancer are distinguished:
- Pre-invasive (limited to epithelium);
- Microinvasive (the neoplasm is able to penetrate the mucous membrane, the tumor size is up to one centimeter in diameter);
- Invasive (the malignant process spreads to surrounding tissues).
Intervention depending on the stages:
- 1st stage. This stage allows organ-preserving operations.
- 2nd stage. Preserving the organ is possible, but involves great risks. At this stage, there is a possibility of the tumor penetrating into the lymph nodes and blood vessels, therefore, metastases are formed. The risk of preserving the uterus is quite high, so total removal is usually used. Such surgical treatment gives a high remission rate. Up to one hundred percent of women can live five years or more after undergoing surgery, as well as appropriate courses of radiation and chemotherapy.
- For invasive cancer, treatment occurs in a combined way - excision of the cervix (in later stages, along with the uterus, appendages and lymph nodes) in combination with radiotherapy. Survival over the next five years depends on the prevalence of the tumor, the presence of metastases and is about 40-80%.
- Endometrial cancer quite often develops together with cervical cancer. His treatment is removal of the uterus. The exception is the first stage, when the tumor has not yet spread beyond the body of the organ. In this case, it is possible to perform a subtotal hysterectomy (partial removal). In all other cases, for endometrial cancer (body of the uterus), complete amputation is performed, the exception being general contraindications to surgical intervention from other organ systems (disorders of the circulatory and cardiovascular systems). Surgical treatment should be carried out in combination with radio and hormonal therapy.
- Uterine sarcoma is a rare nonepithelial malignant tumor. The disease is characterized by severe course and treatment. In the first stages, combination therapy is carried out. And the affected organ must be amputated. In the final stages, large-scale irradiation is carried out followed by removal of the organ. The surgical intervention strategy depends on the aggressiveness of the tumor. Some types involve not only the removal of the uterus, ovaries and appendages, but also parts of the vagina. This treatment tactic is called Wertheim's operation. The prognosis, unfortunately, is less favorable than with other forms of oncology.
Recovery period
The recovery period after cervical surgery takes several months. Immediately after surgery, the patient remains in the hospital for about 1-2 weeks. All this time, the doctor monitors her condition and prescribes medications along the way. Quite often, patients experience apathy, lethargy, drowsiness, and fatigue. In the first few days, women complain of severe pain in the lower abdomen, which must be relieved with painkillers.
Also in some cases they develop reddish discharge. In such cases, it is necessary to begin therapy with antibacterial drugs that will help minimize the risk of developing a secondary infection. During recovery, the woman is fitted with a special urinary catheter. After discharge from the hospital, the patient must follow all the recommendations of the attending physician for several months. Among them:
- Ban on swimming in lakes, rivers, and pools.
- Refusal to visit the bathhouse and sauna.
- Quitting smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages.
- Abstinence from sexual intercourse.
- Prohibition on heavy lifting and physical activity.
- Ban on the use of tampons.
- Regular examinations with a gynecologist.
- The need for frequent walks in the fresh air.
Somewhere 1-2 months after the operation, the woman is scheduled for a follow-up examination with a gynecologist, which allows us to determine any complications or abnormalities. The specialist will take a smear for cytological analysis, perform an MRI and prescribe a colposcopy. Such studies allow us to determine how effective the surgery was. You will have to visit the doctor every 3 months for 5 years. This is necessary in order to diagnose a possible relapse in the early stages.
Is it possible to have a baby after surgery?
The main purpose of surgery to remove the cervix is to stop the pathological process. Such an event is aimed at minimizing negative consequences, as well as preserving reproductive ability. If the pathology can be diagnosed in the early stages, then the opportunity to have offspring still remains. However, pregnancy after removal of the cervix is almost impossible; this occurs only in 0.01% of cases.
Infertility is one of the common consequences of cervical cancer surgery. It may be caused by a narrowing of the cervical canal. Because of this, the uterus does not produce enough cervical mucus, which leads to obstruction of the fallopian tubes. In this case, natural conception is impossible; the only way out of the situation is artificial fertilization or insemination.
If a woman retains part of the cervical canal, she will become pregnant on her own. However, it will be quite difficult for her to bear the fetus: due to surgical intervention, the neck, which holds the developing child, is weakened. To maintain pregnancy, a woman has special sutures and a pessary placed on her uterus.
Surgical treatment
Surgery to remove cervical cancer can be performed using different methods, but the main task of each of them is the complete destruction of all atypical cells and affected tissue. If at least one cancer cell remains, relapse of the pathology becomes inevitable. For this reason, the combined method of surgery with radiation is popular. The latter procedure is carried out after surgery to destroy any remaining individual cancer cells.
Cryosurgery
This technique can be applied only at the earliest stage of development of the oncological process, namely zero. Also, the neoplasm should not be invasive; only in this case will cryosurgery or the freezing method with liquid nitrogen be effective.
The procedure involves placing a metal probe on the walls of the cervix and pumping liquid nitrogen through it. As a result of such manipulations, atypical cells are frozen.
Radiation therapy
This technique, like cryosurgery, can only be used at the zero, precancerous stage. For invasive cancer, the method will not be effective. A stream of laser beams is directed at the pathological tissue, thereby burning out the affected mucosa. The technique is also used to obtain material for histological analysis of the tumor.
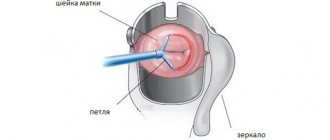
Conization
This involves removing a cone-shaped section of the cervix. This operation can be performed using a surgical scalpel, a thin wire with current, or cryoconization.
Treatment method
As the main treatment, conization can be carried out at the first stage of the disease, while allowing the woman to maintain reproductive function. Conization is also performed to clarify the diagnosis using a biopsy (pipe biopsy) and histological analysis, thereby determining the further type of treatment.
The procedure can be performed if the invasion of pathological tissue does not exceed 1 mm. The operation is organ-preserving and causes minimal harm to the woman.
Hysterectomy
Surgical intervention
Cervical cancer, surgery - hysterectomy involves removing the uterus and its cervix, but preserving nearby tissues and organs.
Saved:
- pelvic lymph nodes;
- ovaries;
- the fallopian tubes;
- sacrouterine ligaments.
Hysterectomy can be of three types:
- open - performed through an incision in the anterior part of the peritoneum;
- vaginal - when the uterus is removed through the vagina;
- Laparascopic hysterectomy is performed by puncturing the peritoneum with special instruments.
Possible complications
Usually, removal of the cervix for dysplasia does not cause any complications. However, in rare cases, a woman experiences consequences such as bleeding, purulent infections and sepsis. Also, due to unskilled actions of the surgeon, the death of the vaginal dome develops. To minimize the risk of complications, the operated patient should be regularly examined by a gynecologist after the intervention. It is also necessary to follow all the rules for restoring the body. Also, possible complications after surgery can provoke the development of:
- Reproductive dysfunction.
- Scarring of the cervix.
- Channel deformations.
- Scanty menstruation or its absence.
18+ Video may contain shocking materials!