What is polycystic disease
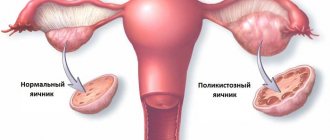
For various reasons, the follicle that matures in the ovaries does not open, releasing the female reproductive cell, but remains on the surface of the organ. The normal process of its release is disrupted due to an imbalance of hormones, in which the hypothalamus, thyroid gland, pituitary gland, and adrenal glands may be to blame. As a result, the surface of the ovary thickens and is strewn with small neoplasms - cysts. But ovulation does not occur.
In some cases, the disease may not make itself known. But sometimes polycystic ovary syndrome has clear and unique symptoms:
- The appearance of hair on the body, in places and quantities not typical for women, that is, above the upper lip, on the cheeks, chin, chest, limbs. On the head, the hair, on the contrary, thins out according to the male type. All this is caused by an excessive concentration of androgens, which, however, is not always recorded. But in 70% of cases, excess insulin is found in the blood, which provokes increased synthesis of male hormones;
- Persistent pain in the abdominal and pelvic area. It is caused by the enlargement of the ovaries and their pressure on surrounding tissues;
- The appearance of excess weight. A woman can gain up to a couple of tens of kilograms in a short time. This is due to increased estrogen production;
- Thickening of the ovarian membrane. It becomes denser, smoother, small cysts spread over the surface;
- Violations of the timing of the menstrual cycle and the nature of discharge. The effect of polycystic ovary syndrome on menstruation is due to the hormonal nature of the disease, despite the difference in the causes that cause it. The cycle goes astray, menstruation becomes, as a rule, scanty and more painful;
- Increased sebum production, which causes acne on the face, chest and back, increased oily hair;
- Difficulty conceiving or infertility. This symptom is a consequence of a violation of the cycle and the entire functioning of the reproductive system.
PCOS - clinical guidelines
With PCOS, which is also known as Stein-Leventhal syndrome, doctors insist on normalizing body weight and performing regular exercise. They help induce ovulation, increase menstrual cycle regularity, increase insulin sensitivity and reduce the occurrence of hirsutism. Often these procedures provide an opportunity to improve fertility. Effective therapy requires an integrated approach, therefore, when diagnosed with polycystic ovary syndrome, treatment involves the use of several techniques simultaneously.
How to establish a cycle with polycystic ovary syndrome?
This question often arises in women with polycystic disease. Delayed menstruation with PCOS is a common symptom that patients report as one of the first. At the same time, many do not know about the changes taking place in the gonads, mistaking the cycle failure for a temporary phenomenon. However, according to doctors, when diagnosing the disease at this stage and making a timely diagnosis of polycystic ovary syndrome, the treatment is much more effective.
Among the medications to normalize the cycle and eliminate delays, hormonal drugs and antiprogestins are used (used under the supervision of a doctor):
- Mifepristone;
- Misoprostol;
- Mifegin.
Stimulation of ovulation in polycystic ovary syndrome
When trying to figure out how to get pregnant with polycystic ovary syndrome, women learn about problems with ovulation. Its absence and irregularity are often an obstacle to motherhood. To eliminate the disorder, doctors prescribe measures to stimulate the process of follicles leaving the ovary. In this case, drugs based on gonadotropin are used. The response to sham is assessed every 5 days using ultrasound. Among the drugs used for the stimulation process are:
- Merional;
- Gonal;
- Menopur;
- Follitrope;
- Menogon.
Treatment of acne in polycystic ovary syndrome
If doctors explain to women in detail how to treat PCOS, few inform them how to cope with its unpleasant manifestations. Against the background of hormonal changes, patients are faced with acne, acne that appears due to excess oily skin. In most cases, after normalization of hormonal levels, such symptoms disappear without a trace. To eliminate these defects without waiting for the end of the course of treatment, you can use the following means:
- Tretinoin cream;
- Benzoyl peroxide.
Treatment of hirsutism in polycystic ovary syndrome
Excessive male pattern hair growth is often a consequence of hyperandrogenism. In this regard, when Stein-Leventhal syndrome is diagnosed, treatment is supplemented with special techniques aimed at reducing the intensity of hair growth on the body and face. For this purpose, the following procedures are prescribed:
- electrolysis;
- bleaching;
- epilation.
To treat hirsutism in women who are not planning pregnancy, hormonal drugs are used:
- Finasteride;
- Spironolactone;
- Nafarelin.
Should I wait until my period?
In the cycle, follicle-stimulating and luteinizing hormones, which are produced by the ovaries, play a decisive role. It is these organs that are mainly affected by the disease. Therefore, it is natural to doubt whether menstruation can occur with polycystic ovary syndrome.
In some cases, the presence of the disease can only be suspected by menstruation, since other signs are almost invisible. The work of the ovaries is disrupted, but does not stop completely, so polycystic disease, delayed menstruation and heavy bleeding between them are a common combination in the cycle.
Cycle length in polycystic disease
The main reason for menstruation to lag behind the usual schedule is the lack of the required amount of hormones. FSH and LH, which are necessary to start the process, must stimulate other substances for which the endocrine system is responsible. As a result of its malfunction, the proportions of hormones are disrupted, the follicle does not mature, remaining on the surface of the organ. Delayed menstruation with polycystic ovary syndrome can last from 2 weeks to several months. The paired organs do not have the ability to produce the estrogens necessary for the second stage of the cycle in sufficient quantities, since the female reproductive cell does not mature and the corpus luteum is not formed. The endometrium develops more slowly. The absence of menstruation can be so prolonged (up to several months) that a woman who is diagnosed for the first time cannot understand whether she has periods with polycystic disease.
The disease does not rank first in frequency among other gynecological ailments. But it can manifest itself even in adolescence if the girl has no sexual activity. And if the time has come, but after menarche she no longer has periods, polycystic disease is the first thing that can be assumed.
In adult women, the disease has slightly different causes than in adolescents. In addition to a decrease in the production of FSH and LH, an increase in prolactin is recorded during the examination. Normally, the hormone is synthesized in such quantities during pregnancy for subsequent milk production. Its high level is also observed during lactation. The more often the baby is put to the breast, the more hormone there is, and the first menstruation after birth is delayed. If polycystic disease is diagnosed and you have not had periods for a year, then the analysis will reveal prohibitive levels of prolactin, which suppresses them.
When your period comes on time
Sometimes it happens that when diagnosed with polycystic disease, menstruation is regular. And the problem is discovered almost by accident, when a woman consults a doctor about pain in her side during careless movement or during sex. There are no other symptoms of the disease, the weight remains at the same level, and there is no abnormal body hair. When diagnosed with polycystic ovary syndrome, regular periods occur when one of the paired organs is affected. The androgen level was slightly exceeded. But this is by no means a guarantee of monthly ovulation, as can be seen by measuring your basal temperature in the middle of the cycle. Its meanings will remain the same as before and after. Whereas normally, egg maturation is accompanied by an increase in basal temperature.
Presence and duration of the menstrual cycle in pathology of the appendages
Menstruation can be significantly delayed with polycystic ovary syndrome. This is explained by the fact that the body does not have enough hormones that are responsible for the formation and release of follicles. The endocrine system is responsible for such hormones. This means that if there are malfunctions in its functioning, they provoke a delay in the maturation of follicles, which accumulate on the surface of the ovaries, thereby forming cysts.
It is worth noting that with polycystic ovary syndrome, periods can be delayed from several weeks to 2-3 months. At this time, the organs do not produce the required amount of the hormone estrogen, as a result of which the egg does not mature and the corpus luteum does not form - ovulation does not occur.
Another reason for the absence of menstruation and disruption of the menstrual cycle may be a large amount of the hormone prolactin. In this case, we will talk about polycystic disease only when there is no breastfeeding and menstruation does not occur within a year. An increase in prolactin provokes polycystic ovary syndrome and causes disruptions in the menstrual cycle.
It should be noted that even with polycystic disease, menstruation can occur regularly. In such cases, the disease occurs without symptoms - hair throughout the body does not increase, menstruation is present, and body weight does not change dramatically. And only periodic pain during intimate relationships or sudden movements can prompt a woman to see a doctor. It is during a routine examination by a gynecologist that polycystic disease may be detected, in which menstruation is regular.
With polycystic disease, menstruation occurs if one of the ovaries is affected. The androgen hormone may be present in small quantities at this time. It is worth understanding that even under such conditions, ovulation may not occur on a regular basis, since negative processes in the body are already occurring, and it is difficult for one appendage to cope with the production of the necessary hormones for the maturation of the follicle and the release of an egg ready for fertilization.
Many women are interested in whether or not they have regular periods after childbirth. It is worth noting that after the birth of a child, the hormone prolactin is formed in the mother’s body to increase milk during breastfeeding, therefore, the more often a woman feeds the baby, the more this hormone becomes, and the longer there is no menstruation, since other hormones are suppressed during this period.
Is it necessary to provoke menstruation with polycystic disease?
Frequent delays force us to look for ways to induce menstruation with polycystic disease. When a diagnosis is made and there is no hirsutism or obesity, a specialist may recommend:
- Duphaston. This is artificially synthesized progesterone, which in the second half of the cycle is not enough for the development of the endometrium, and therefore the beginning of a new menstruation. Duphaston is taken from 14-16 days to 25-27, 1 tablet;
- Utrozhestan. A herbal analogue of Duphaston is also used to increase progesterone levels. It is more suitable for some women, as it causes almost no adverse reactions;
- Norkolut. The drug contains a progestin analogue, which reduces the tone of the uterus and affects the ovaries, inhibiting the development of the egg. Norkolut is taken 2 tablets for 7 days. After cessation, menstruation should come.
The nature of menstruation
Improper functioning of the ovaries, inhibition of the production of some hormones and an excess of others can give menstruation any character. But scanty periods with polycystic disease are the most likely development of the disease. The cause of such discharge is the lack of ovulation and endometrial depression caused by hormonal disorders. The egg does not mature, which gives the body a signal that there is no need to prepare for possible fertilization. Consequently, there is no reason for the endometrium to thicken and loosen to receive the fertilized egg. This means that its further development, when normally it becomes thinner and gradually but steadily separates the upper layer of cells, is also disrupted.
The underdeveloped endometrium in polycystic disease is excreted unevenly. Hormonal imbalance leads to its inability to grow and renew itself. Hence the scanty periods with polycystic ovary syndrome. All this together makes conception difficult or even impossible. Almost always during menstruation there is pain in the groin area, radiating to the lower back. Twitching sensations in the side and abdomen may remind you of the illness on other days.
Another feature that characterizes polycystic disease is spotting before menstruation. It is observed not immediately before menstruation, but a week or two before it. The disease is characterized by an increase in the amount of estrogen combined with a decrease in progesterone. The endometrium thickens from this influence, which causes the accumulated tissue to separate unevenly from time to time outside of critical days.
Vitamins
Along with the diet for PCOS, patients should take vitamin supplements, even in cases where the diet is rich in essential substances. Taking such drugs helps strengthen the immune system, increases the functionality of the body, which has a positive effect on stress resistance, and normalizes the levels of testosterone, androgen and insulin. In addition, many women with this syndrome have hypovitaminosis.
Vitamin E for polycystic disease is considered one of the most important substances for restoring the normal functioning of the reproductive system.
Just like B vitamins and ascorbic acid, it is classified as an antioxidant. Taking these substances promotes better cell regeneration, which leads to faster recovery. Ascorbic acid also helps cleanse the body of the final metabolic products of estrogen hormones.
It is definitely recommended to take medications that contain microelements - selenium, magnesium, zinc, chromium, calcium and others. There are a large number of such drugs, so the dosage should be selected according to the instructions.
Consumption of complex dietary supplements helps eliminate negative factors affecting health from the main treatment of the disease.
Treatment
Among other gynecological diseases, the syndrome is not the first in prevalence. But the disease is not one that can be brushed aside for a long time, suppressing the unpleasant symptoms with pills.
Persistence and joining forces with good specialists can defeat polycystic ovary syndrome; treatment can be complex and quite lengthy. They always start with taking hormonal drugs:
- Metformin, Siofor. These are medications that lower blood glucose levels. It would seem, what does polycystic disease have to do with it? But the fact is that hormonal imbalances inherent in diseases often make body tissues insensitive to insulin. Hence the increase in its concentration in the blood, increased appetite and obesity. Metformin controls excess sugar, reducing excessive food intake and weight. Often, 3-6 months of use of the product allows you to return the menstrual cycle to normal;
- Diana 35, Yarina, Zhanin, Marvelon, Logest. Oral contraceptives are based on estrogens and gestagens. They suppress the synthesis of male hormones, which are in excess in polycystic disease. To get rid of excess hair, contraceptives are supplemented with the antiandrogenic Veroshpiron and Flutamide;
- Bromocriptine. Prescribed to reduce the secretion of prolactin, reduces tissue swelling, especially in the mammary glands;
- Klostilbegit. Therapy with this drug stimulates ovulation. Its antiestrogenic properties after withdrawal have the effect of producing the necessary proportions of FSH and LH for follicle maturation and egg release. Clostilbegit is prescribed from days 5 to 9 of the menstrual cycle, 0.05 g for 3 months.
Surgery for polycystic disease
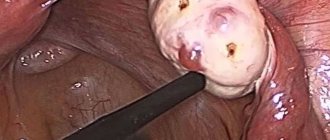
In the absence of the desired result from conservative treatment, the solution is surgery. Laparoscopy for polycystic ovary syndrome is the best option, combining effectiveness with the lowest cost for the patient. During general anesthesia, women make thin punctures in the abdomen through which instruments and a video camera are inserted. Depending on the existing picture of the disease, the surgical technique is selected. The ovaries are freed from the sclerotic membrane, and the resulting cysts are cut off. After this, follicles and female germ cells are able to develop normally.
Treatment methods for PCOS
Before starting therapy, doctors conduct a full examination of patients with polycystic ovary syndrome. Doctors pay attention to the number of cystic formations, their size, the patient’s age and concomitant pathologies. Traditional recommendations are:
- lifestyle changes;
- diet correction;
- normalization of body weight.
As for the impact directly on the cause of the disease, doctors initially try to normalize the patient’s hormonal levels. The use of combined oral contraceptives, gestagens and estrogens prevents the growth and further development of the cyst, helping to reduce its size.
If there are significant changes in the tissue of the gonads, partial resection of the ovaries is recommended. If the patient no longer plans to have children, complete removal of the gland may be recommended. Doctors determine how to cure polycystic ovary syndrome in a particular case exclusively individually, taking into account the specifics of the situation.
Polycystic ovary syndrome - treatment, drugs
The basis of drug treatment is hormonal drugs. Their goal is to normalize and restore the menstrual cycle, growth and formation of a dominant follicle. In order to reduce the risk of hyperplasia and endometrial tissue cancer, an intermittent course of progestins is prescribed: 5-10 mg of medproxyprogesterone acetate for 10-14 days, with an interval of 1-2 months. Instead, COCs that reduce estrogens in the blood can be used:
- Duphaston (one of the first to be used for polycystic ovary syndrome);
- Diana;
- Utrozhestan;
- Logest.
In addition to hormonal treatment, insulin sensitivity is often increased. As a result, Metformin is prescribed for PCOS. The dosage is determined individually. More often, doctors adhere to the following regimen: 500–1000 mg twice a day. This drug helps normalize menstruation, reduce the level of free testosterone and is used in cases of diabetes mellitus or ineffective hormonal therapy. Glucophage for PCOS is used as an alternative to pure metformin. In addition, use:
- Inositol
– in PCOS, it helps normalize the deficiency of B vitamins. - Fertina
- for PCOS it is used for the same purpose as Inositol.
Polycystic ovary syndrome - treatment with folk remedies
To reduce the symptoms that accompany polycystic ovary syndrome, doctors recommend using folk remedies. They do not help eliminate existing changes in the tissues of the gonads, but they can improve the general condition of a woman and relieve her of menstrual pain. An example is the following recipe.
Tincture of boron uterus
Ingredients:
- hogweed leaves – 50 g;
- vodka – 500 ml.
Preparation, use
- The raw materials are poured with vodka, the container is tightly closed and placed in a dark place.
- They insist for 1 month.
- Take 30–40 drops up to 4 times a day. The course of treatment lasts 3 weeks, after which they take a break for 1 week and, if polycystic ovary syndrome does not go away, treatment is continued.
Laparoscopy for polycystic ovary syndrome
When diagnosed with polycystic ovary syndrome, surgical treatment has been the main method of therapy for a long time. Previously, doctors began healing directly from the operation. Today, gynecologists with small cysts and a small number of them adhere to a conservative method, starting treatment with medications. However, in case of extensive damage to the ovaries, a large number of cysts, surgical intervention is resorted to.
Surgical treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome is carried out using laparoscopy. Through small punctures on the anterior abdominal wall, special instruments and a camera are inserted, under the control of which the operation is carried out. Depending on the clinic and the patient’s condition, the following methods are used:
- Decortication
involves removing the outer cortical layer of the ovaries, which stimulates ovulation. - Cauterization
- the cyst is incised and the fluid is drained. The ovaries acquire a physiological size. - Electrodrilling
is the removal of fluid from a cyst using a laser, which cauterizes its walls. - Wedge resection
- performed when changes affect part of the gland. Part of the organ is removed.
After treatment for polycystic ovary syndrome
If the treatment was conservative, that is, using hormonal drugs, the main thing that it gives is the restoration of cycle regularity. Menstruation comes on schedule after completing the course of pills, becomes less painful, and its volume corresponds to the average norm. You can find out about the presence of ovulation by measuring your basal temperature throughout the cycle. Maturation of the egg does not happen in each of them. But you shouldn’t expect quick results; therapy can last longer than six months.
Menstruation becomes more abundant, the cycle may shorten, as the organs, freed from cysts and dense membranes, begin to actively function. But the pain is noticeably reduced due to the normalization of hormonal levels and a decrease in the size of the ovaries and swelling. If you feel constant pain in the lower abdomen, you should consult a doctor to find out the reasons.
Menstruation in early or protracted polycystic ovary syndrome is not the only changing factor. But their negative changes pose the greatest danger to health. This is not only infertility, but also an increased likelihood of developing cancer of the reproductive system. Polycystic disease sometimes requires long-term treatment and patience. You should not be afraid of the scheduled operation; after it, the return of the appearance and functions of the body occurs much faster.
Before using any medications, you should consult a specialist doctor. There are contraindications.
For some reason, not all women clarify with the gynecologist those points that concern them most. This is especially true for polycystic ovaries. Most often, the doctor himself tells general information about the disease, but sometimes he is silent about such seemingly simple points. Next, we will talk about the mandatory diagnosis of hormonal levels, menstruation and ovulation in PCOS.
No. 1. What hormones should I take for polycystic ovary syndrome?
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a disease that is caused by a disruption in the production of sex hormones. Its first sign is an irregular cycle or complete absence of menstruation, as well as the inability to become pregnant with regular sexual activity.
If polycystic disease is suspected, a woman undergoes a number of diagnostic tests, including:
- Ultrasound. The ovaries are visualized as enlarged in size, their structure is heterogeneous due to the large number of small follicles (cysts) filled with fluid.
- Blood tests for hormones in PCOS. It is necessary to determine the level of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), testosterone, estradiol, progesterone, cortisol and prolactin.
In polycystic ovary syndrome, luteinizing hormone (LH) and testosterone levels are usually elevated, and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) levels are decreased. If a blood test is taken on days 18-21 of the cycle, then a reduced amount of progesterone can be diagnosed, since ovulation does not occur, the corpus luteum does not form, and it is this that produces progesterone.
Rupture of the dominant follicle and release of the egg
What is polycystic ovary syndrome?
Doctors call this condition polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). With PCOS, a large number of small bubbles called cysts appear in the ovaries. Due to these bubbles, the ovaries increase in size. With polycystic ovaries, their function is disrupted, ovulation (the release of an egg) does not occur, and an irregular menstrual cycle is observed due to hormonal imbalance.
What are the causes of polycystic ovary syndrome?
The causes of polycystic ovary syndrome are not yet clear. A woman suffering from polycystic disease has an increased level of testosterone (male sex hormone) in the blood, and an increase in blood glucose levels (due to immunity to the hormone insulin).
When do symptoms of polycystic ovary syndrome appear?
The first signs of polycystic disease may appear in adolescence, some time after the start of the first menstruation.
In some cases, a woman may not be aware that she has PCOS until she decides to have a baby. In this case, the first symptom of polycystic ovary syndrome may be infertility.
What are the symptoms of polycystic ovary syndrome?
Symptoms of polycystic ovary syndrome can vary from woman to woman, and it is not necessary for a woman with polycystic ovary syndrome to have all of the following symptoms at once:
- Irregular periods are the most common symptom of polycystic disease, which is usually the reason for visiting a gynecologist. Menstruation may come late, be absent for several months in a row, or, conversely, come 2-3 times a month.
- Unusual periods: too scanty, or vice versa heavy. The duration of menstruation is also variable: from 2 days to a week or even more
- Overweight and Obesity
- Excessive hair growth on the face and body
- Oily facial skin and acne
Is pregnancy possible with polycystic ovary syndrome?
Pregnancy with polycystic disease is possible, but often women suffering from this disease encounter great difficulties when planning a pregnancy.
With polycystic ovary syndrome, a woman’s body has a hormonal disorder (increased testosterone levels) that disrupts the functioning of the ovaries. If the ovaries are not working properly, they will not produce eggs. This is called non-ovulation, or anovulatory cycles. The main sign that you are not ovulating is an irregular menstrual cycle. In this case, the likelihood of becoming pregnant without treatment is very low. On our website there is a separate article devoted to the topic of pregnancy with polycystic ovary syndrome.
Can polycystic disease be dangerous?
Most often, polycystic ovary syndrome proceeds favorably and does not lead to the development of any complications. But there are some risks associated with this disease.
First of all, this is the risk of developing diabetes. In diabetes mellitus, blood glucose levels increase, which leads to serious metabolic disorders. Therefore, all women diagnosed with polycystic ovary syndrome are recommended to measure their blood glucose levels at least once a year.
In women over 30-35 years of age, polycystic ovary syndrome can lead to increased blood pressure (hypertension). Increased blood pressure, in turn, leads to heart disease.
If polycystic ovary syndrome is not treated, long-term hormonal disorders in the body can lead to the development of uterine cancer.
What tests need to be taken to diagnose polycystic disease?
If polycystic ovary syndrome is suspected, a woman is recommended to take a blood test for hormones.
Signs of polycystic ovary syndrome on ultrasound are: an increase in the size of the ovaries, thickening of their capsule and many cysts in the ovaries.
How to cure polycystic ovary syndrome?
There are several methods for treating polycystic disease, which are prescribed by the gynecologist depending on the patient’s age, symptoms and complications of the disease:
- Treatment with hormonal pills
- Treatment with surgery (laparoscopy)
- Treatment with diet
Treatment of polycystic disease with birth control pills
Hormonal birth control pills (Diane-35, Chloe, etc.) help regulate the menstrual cycle, as well as reduce hair growth on the face and body, normalize the condition of facial skin and get rid of acne. The choice of contraceptive pills is made only by the treating gynecologist.
Treatment of polycystic disease with surgery (laparoscopy)
If treatment with hormonal pills does not have any effect, then you may be prescribed a laparoscopy. Laparoscopy is an unusual operation, since to perform it the surgeon does not make incisions on the skin, but carries out all manipulations through small punctures in the skin. After surgery, these punctures heal very quickly and the risk of complications from laparoscopy is very small. Laparoscopy is performed under general anesthesia. Women are allowed to get up 8-12 hours after surgery and are discharged from the hospital after 1-2 days.
Diet for polycystic ovary syndrome
It may seem surprising, but even a simple diet for polycystic disease can lead to recovery. Moreover, the diet does not include any special ingredients and is therefore accessible to any woman. The main principle of the diet for polycystic disease is a healthy diet and low calorie content.
Overweight and obesity support polycystic ovary syndrome, since it is in adipose tissue that excess male sex hormones are produced. We remove adipose tissue and hormones return to normal.
So, if you are overweight, then think about your diet, create a healthy diet that is suitable for you and lose weight.
Read also: How to get pregnant with polycystic ovary syndrome?
No. 2. Does ovulation occur with polycystic ovary syndrome?
Polycystic disease is a hormonal disease in which the ratio of the sex hormones estrogen and progesterone is disrupted. In this regard, the formation of follicles on the ovaries increases several times. Using ultrasound, this condition is easily diagnosed - the ovaries become like blackberries.
Due to the fact that multiple follicles appear, the walls of the ovaries thicken. The dominant “vesicle” in which the egg matures is not formed at all, or the cell cannot break through its thick walls. Therefore, ovulation does not occur with polycystic disease.
Since there is no ovulation, symptoms appear such as changes in the menstrual cycle up to the complete absence of periods, the inability to get pregnant with regular sexual activity and the health of the partner. In the middle of the cycle, pathological discharge may be present. In some cases, women note nagging pain in the abdominal area. Apart from cycle disruption and problems with conception, there are no other symptoms.
Vitamin D for PCOS
Lack of cholecalciferol (which quickly disappears with regular sun exposure) is one of the causes of metabolic changes in polycystic ovary syndrome. Almost 50% of women with PCOS have a lack of vitamin D in their body.
Vitamin D is also found in food products, such as dairy products, eggs, cottage cheese, fish oil, etc.
Vitamin E in PCOS improves progesterone synthesis. Also, tocopherol eliminates hyperprolactinemia, is an antagonist of free radicals and therefore prevents the development of cancer. Vitamin E helps reduce menstrual pain when taken regularly.
How often should I take vitamin E if I have polycystic ovary syndrome? the average dosage is 15–25 mg tocopherol equivalents/day. For vitamin therapy for polycystic disease, the doctor prescribes dosages depending on the severity of the disease and hormonal imbalance. Usually vitamin E is taken throughout the monthly cycle, but in the second phase the amount is doubled.
A significant amount of tocopherol reduces blood viscosity and leads to bleeding, so it is dangerous to take it for a long time and uncontrollably.
Cyclovita for PCOS. Cyclovita is a compound of 12 vitamins, 5 minerals, rutin and lutein. It is designed to cover vitamin and mineral deficiencies throughout your periods.
Retinol is needed for the formation of sex hormones and normal reproductive function.
Vitamin B1 is involved in the regulation of all types of metabolism and improves the functioning of the endocrine system.
Vitamin B2 has a gonadostimulating effect and takes part in the metabolism of all estrogen-derived hormones.
Vitamin B6 eliminates progesterone deficiency.
Vitamin B12 normalizes ovulation.
Vitamin C takes part in the formation of estrogens and progesterone.
Tocopherol is needed for the formation of gonadal hormones and normalizes their ratio.
Cholecalciferol is needed for the proper functioning of the parathyroid glands.
Vitamin PP is involved in many metabolic processes.
Lutein contributes to the creation of the corpus luteum, which produces progesterone.
Folic acid has a gonadostimulating effect and regulates estrogen metabolism.
Calcium is needed for the production of sex hormones.
Rutin improves the condition of blood vessels.
Selenium helps normalize thyroid hormone levels.
Copper is an antioxidant, needed for the formation of collagen and elastin fibers.
Manganese is an important cell metabolite and is a free radical antagonist.
Iodine is needed for the functioning of the thyroid gland and the formation of its hormones.
Zinc is important for the synthesis and release of luteinizing and follicle-stimulating hormones.
No. 3. How to induce menstruation with polycystic ovary syndrome?
Menstruation with polycystic ovary syndrome often comes with a great delay, and may be absent altogether for several months. This is due to a lack of the hormone progesterone, which is responsible for the development of the uterine endometrium and the arrival of menstruation.
Therefore, in order to artificially induce menstruation, synthetic progesterone is needed. It is contained in the following drugs:
- Duphaston. It should be taken starting from days 14-16 of the cycle to days 25-17, one tablet. Usually your period comes on the 28th-29th day.
- Utrozhestan is a drug similar to Duphaston, only of plant origin. It is preferred more often, since it has virtually no contraindications and is suitable for most women.
- Norkolut is a drug containing a progestogen analogue. Reduces the tone of the uterus and affects the ovaries in such a way as to induce menstruation. You can start taking it at any time, 2 tablets for 7 days. After the end of the treatment, menstruation comes.
Irregular or absent periods in girls and women of childbearing age can be caused by medical or physiological problems, including pregnancy, PCOS, endocrine and gynecological diseases. Delay almost always causes unpleasant symptoms: nervousness, heaviness and aching pain in the lower abdomen.
If menstruation is absent for at least 3 months, a woman may be diagnosed with amenorrhea. If you are sure that your period did not come on time due to pregnancy, you can try to speed up its arrival using traditional methods. Most of these natural methods that can be used at home, unlike medications, act gently and gradually.
HOW TO STIMULATE MENSURES WHEN DELAYED
If the delay is not caused by pregnancy, menopause, early adolescence or postpartum recovery, you can try to induce menstruation using herbs, foods and other gentle remedies.
Vitamin C can stimulate periods if you are late without medication. It has the potential to influence progesterone and estrogen, which regulate the menstrual cycle. Like other antioxidants, ascorbic acid increases blood flow and microcirculation, which is especially important for smoking and obesity. In the second half of the cycle, it can be taken up to 500-1000 mg per day (with sufficient water).
You can also get vitamin C from food: red peppers, oranges, papaya, Brussels sprouts, broccoli, strawberries, tomatoes, grapefruits, kiwi, guava. Before taking large doses of ascorbic acid powder or tablets, make sure you are not pregnant.
- Herbs
Emmenagogues are herbs that stimulate menstruation. Such plants include parsley, ginger, rosemary, yarrow, and sage. Black cohosh, wild carrot seeds, wormwood, and juniper have a more pronounced effect. The most powerful herbal supplements that affect menstruation include angelica, celery seeds, mint, tansy, and asafoetida.
- Parsley
Using parsley you can induce menstruation if you are late. This plant is used as a folk remedy to stimulate the uterus and pelvic organs, which facilitates and speeds up the onset of menstruation. You can make tea from parsley. The recommended dose is 2 to 4 cups per day. Although this herb is quite safe, it is best to consult your doctor first. Parsley gently stimulates menstruation, usually with fewer side effects than stronger herbs.
Ginger tea helps stimulate the arrival of menstruation. Taking it 2-3 times a day will speed up the onset of bleeding for several days (it is not recommended to use it on an empty stomach). Start drinking ginger tea a week before your expected period and menstrual bleeding should begin within a few days. Ginger tea also helps treat period pain.
With proper nutrition, sodium intake (mainly salt) should be limited so that excess does not cause fluid retention in the body. To speed up the onset of menstruation, it is also recommended to eat foods such as mustard and red meat. These, as well as consuming enough calories, help increase body heat. Carotene-rich foods - peaches, eggs, apricots, carrots, spinach, pumpkin - are also recommended to speed up menstruation.