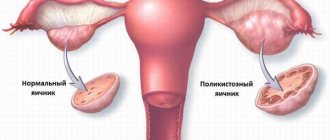
Polycystic ovary syndrome is a benign growth that results from disruption of the endocrine system.
The pathology can be congenital or occur after puberty. In some cases, polycystic disease acts as a primary disease, in others it forms as a complication after other inflammatory processes, especially chronic ones. The main problems of the disease are the inability of a woman to become pregnant and the high probability of relapse even after successful treatment.
Modern statistics indicate that polycystic ovary syndrome most often manifests itself in girls who have entered puberty. However, the disease can develop in women of any age. At a later age - during the menstrual pause - the so-called secondary polycystic ovary syndrome appears as a consequence of chronic female diseases. The disease must be properly treated, as it can threaten a woman’s health.
In addition, the formation of multiple cysts on the ovaries significantly reduces a woman’s ability to conceive and bear a child. But still, after competent and timely treatment of the disease and elimination of the problem, such a patient can carry and give birth to a healthy baby.
What it is?
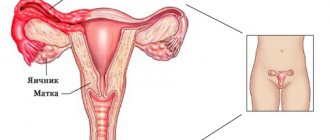
If you delve deeper into the term “polycystic”, the essence of the disease becomes clear: “poly” from the Latin “many”, “cyst” is a cavity formation filled with liquid contents. Therefore, in most cases, when establishing PCOS, the doctor means small cystic transformation of the ovaries, as a result of which their main function is disrupted and characteristic external signs of the disease appear.
The causes of polycystic ovary syndrome have not yet been established. Only some links in the development of the disease are known. Therefore, there is no radical therapy for it yet; all attempts to get rid of the disease come down to reducing the severity of symptoms, improving menstrual function and making it possible to get pregnant.
There are primary and secondary polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). If changes appear as a result of some other disease or while taking medications, polycystic disease is secondary. If the “fault” initially lies with the ovaries - primary.
To make a diagnosis of PCOS, a combination of at least two of the following symptoms is necessary:
- Irregular menstrual cycle - more than 35 days or with large intervals, for example, 21 days and then 35;
- Lack of growth and maturation of follicles - in this case, there is no ovulation according to the results of monitoring ultrasound of the ovaries and when plotting basal temperature charts;
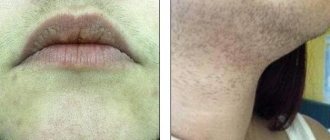
- Signs of increased male sex hormones - hair growth along the midline of the abdomen, above the upper lip, along the inner thighs, increased levels of adrenal hormones and androgens in the blood according to tests;
- Signs of polycystic disease according to ultrasound are the presence of nine or more follicles when examined along the periphery or throughout the entire area of the ovaries.
Similar terms to PCOS include the term "polycystic ovaries" and idiopathic (unknown cause) hirsutism.
Isolated polycystic ovaries. They are established if, against a background of complete health, ultrasound results reveal multiple follicles in the ovaries. At the same time, the woman has no problems with pregnancy, menstruation, and there are no signs of virilization (androgenization). The pathology does not require treatment. Idiopathic hirsutism. It is established if hair growth is recorded in the “male zones”, but when examining the level of sex hormones there are no problems, the ovaries are normal and there are no menstrual dysfunctions. Only cosmetic procedures and no other treatment are needed.
Considering that PCOS is not a fully understood pathology, there is a little confusion in making diagnoses. Only a specialist can understand the peculiarities of the functioning of a particular woman’s body.
About the syndrome
This gynecological disease occurs in women who have been diagnosed with endocrine infertility.
Due to the fact that polycystic ovary syndrome is manifested by a lack of ovulation, it is often impossible to get pregnant.
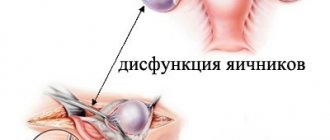
In this case, the maturation of the eggs does not occur completely, so the follicles stop developing, which is why multiple cysts appear.
Stein-Leventhal syndrome is observed in 5-10% of women, and it has a number of serious complications.
There are primary and secondary polycystic diseases. In the first case, the symptoms make themselves felt in the girl’s adolescence (at about 12-13 years old). The primary type is characterized by severe pathology and is very difficult to treat.
Secondary polycystic disease is most often diagnosed in middle-aged women who have given birth or are in the menopause stage. The main symptoms of this type of polyendocrine disorder are: excess weight, metabolic disorders, increased insulin in the blood, androgenemia and disruption of the pancreas.
Reference! If PCOS is suspected, it is necessary to simultaneously conduct examinations for other serious diseases, such as cancerous tumors and Cushing's syndrome. The fact is that they have similar manifestations, so the previously listed complications should be excluded.
Reasons for development
The etiology of polycystic disease has not yet been fully elucidated. But a number of features have been identified that accompany this condition:
- Excess of male sex hormones . Excessive concentration of male sex hormones in the blood can become a trigger in the development of polycystic ovary syndrome. In adipose tissue, androgens are converted into female sex hormones estrogens, which in turn stimulate the production of luteinizing hormone and suppress the production of follicle-stimulating hormone.
- Increased enzymatic activity in the ovaries . Some patients with polycystic ovary syndrome have increased activity of some enzymes and decreased activity of others. This imbalance in enzymatic activity leads to increased production of male sex hormones, which can lead to the formation of cysts in the ovaries.
- Pathologies of the pituitary gland . The pituitary gland produces key hormones that regulate follicular growth and ovulation. These are follicle-stimulating (FSH) and luteinizing (LH) hormones. With polycystic ovary syndrome, there is an increased level of LH, which leads to an increase in androgen production in the ovaries. The effect of LH also enhances growth hormone, and therefore increased concentrations contribute to the development of polycystic ovary syndrome.
- Insulin resistance . Many women with polycystic ovary syndrome and excess body weight also have resistance to the hormone insulin. When the body's cells are resistant to insulin, its concentration in the blood increases, which in turn stimulates the production of additional amounts of luteinizing hormone and androgens. Increased concentrations of insulin and androgens stimulate the growth of follicles, but none of them develop into a mature egg. Thus, their premature aging occurs, and the likelihood of cyst formation in the ovaries increases.
- Hereditary predisposition . There is evidence indicating the hereditary nature of the pathology. Of course, polycystic ovary syndrome is not inherited, but women who have direct relatives with this disease are at increased risk.
With polycystic disease, against the background of an excess amount of male sex hormones, the patient also experiences other problems associated with increased androgen activity. This is, for example, excess male pattern hair growth. A woman may experience acne and hair loss on her head.
Symptoms
Cystic ovarian degeneration has a number of symptoms, but there is no clear and unambiguous pattern of how the disease manifests itself. The main symptoms of polycystic ovary syndrome are as follows:
- increased size of the gonads (up to 10 cubic cm) and small cystic changes in the ovaries, detected by ultrasound diagnostics;
- not a single pregnancy recorded in the anamnesis (primary infertility of the patient);
- menstrual cycle disorders of various types (irregular, prolonged, heavy or scanty bleeding; cycle length more than 35-40 days);
- excess body weight and male distribution of body fat;
- in some cases, patients’ skin darkens in places (armpits, groin area, back of the head, inner thighs);
- high level of AMH (anti-Mullerian hormone).
Signs of polycystic ovary syndrome are usually accompanied by hormonal changes in the female body: increased levels of androgens cause increased hair growth in patients, especially on the legs, in the perineum, above the lip; there are bald patches on the sides of the forehead, on the top of the head; the skin is prone to oiliness, acne is visible; voice timbre is low. Polycystic ovary syndrome is accompanied by pain symptoms in the abdominal area (usually due to compression of neighboring organs by cysts), and hardening of the mammary glands. Pain with polycystic ovary syndrome is very similar to the condition with PMS: the stomach pulls, the nipples hurt, the body experiences fatigue. Some women experience sudden uterine bleeding: due to polycystic ovaries, estrogens act on the uterine mucosa for a long time, and since progesterone is low, the endometrium cannot withstand it and hyperplasias.
Symptoms
Due to the fact that with polycystic ovary syndrome, numerous pathological changes occur in a woman’s body, the clinical picture of the disease in question can be very different both in the set of clinical signs and in their severity. For example, some patients may not even be aware of their condition until they begin to actively look for the cause of infertility. In others, on the contrary, the symptoms are so pronounced that women seek medical help immediately after the first signs of the disease appear.
The main symptoms of polycystic ovary syndrome include:
- Inability to get pregnant.
- Menstrual irregularities – long delays and prolonged menstruation.
- Chronic pain in the lower abdomen, pelvic region, lower back.
- Overproduction of secretions by the sebaceous glands (this causes the skin and hair to become oily).
- Acne.
- Significant increase in body weight. Fat deposits appear mainly in the waist area (apple-type). The development of obesity in polycystic ovary syndrome is associated with impaired glucose tolerance and excess insulin in the blood.
- Constancy of basal temperature. Women who use natural methods of birth control or, conversely, who are trying to get pregnant, may note that the basal temperature does not change during the cycle, which indicates the absence of ovulation.
- Masculinization is the process of accumulation of male secondary sexual characteristics in a female individual. It manifests itself as the appearance of excess hair on a woman’s body and face, deepening of the voice and increase in muscle mass (development of secondary male sexual characteristics), changes in skin elasticity, acne, menstrual irregularities, increased libido, hair loss on the head, hair growth on body, face, pubis and clitoral enlargement. In some cases, the female genital organs can become very modified and become similar to the male penis.
If polycystic ovary syndrome occurs in childhood, then the first menstruation can occur as usual - at 12-13 years of age. At the same time, the correct menstrual cycle is not established. The girl has oligomenorrhea or amenorrhea, which indicates anovulation. During puberty, due to the high content of male sex hormones, the girl experiences hypertrichosis. If there is obesity, then, as a rule, it is of a classic nature with an even distribution of fat throughout the body. It is noteworthy that the presence of all these symptoms is not necessary for polycystic ovary syndrome. Also, symptoms may change with age. In particular, it is possible to reduce the number of acne. At the same time, the likelihood of obesity increases with age.
What symptoms indicate polycystic ovary syndrome?
The leading symptoms of PCOS are:
- menstrual irregularities (hypo-, oligo-, amenorrhea);
- primary infertility;
- hirsutism (increased hair growth);
- acne;
- obesity.
Cycle disruption
Menstrual cycle disorders are manifested by rare, short periods, which eventually turn into amenorrhea. Different types of PCOS have some features of cycle disorders.
- In the ovarian form of polycystic menarche at 12-13 years of age, oligomenorrhea occurs early, secondary amenorrhea is rare.
- The mixed form of PCOS is determined by late menarche (15-18 years), much more often accompanied by secondary amenorrhea.
- The central form is distinguished by later menarche (16-20 years), menstrual function is disrupted according to the type of hypooligomenorrhea with the transition to amenorrhea.
Reproductive dysfunction
Primary infertility is observed in ovarian and ovarian-adrenal forms of PCOS. In the central form, in addition to primary infertility, spontaneous abortions in early pregnancy, as well as secondary infertility, are common.
Hirsutism
Hirsutism is a hallmark symptom of PCOS. Excessive hair growth occurs in 70-90% of women. The main areas where excess hair is localized are: the area above the upper lip, the white line of the abdomen, the chin, the nipple area, and the limbs.
Acne as a sign of PCOS manifests itself in 50% of cases.
Obesity
Obesity manifests itself more clearly in the central variant of PCOS, less in the ovarian form, and is characterized by a uniform pattern across the female morphotype. Body weight in the mixed version usually remains within normal limits.
Photo: https://pixabay.com/photos/thick-overweight-obesity-weight-373064/
Pregnancy and polycystic disease
“I was diagnosed with polycystic ovary syndrome, can I get pregnant?” – this is the question that worries most patients. However, despite all the assurances of “competent” girlfriends and relatives, you should not give up on the desire to have children. Undoubtedly, getting pregnant in the presence of such a pathology is much more difficult, but still possible.
Obviously, not many people can easily fulfill their dream, but medicine does not stand still and today treatment of polycystic disease increases the chances of a long-awaited pregnancy. First, you need to restore the normal cyclicity of menstruation; for these purposes, combined-action oral contraceptives are often used. Then they stimulate ovulation with the help of antiandrogenic drugs - “Clostilbegit”, after which the most successful day for conception is determined, for this they use an ultrasound of the ovaries (the dominant follicle is detected). If fertilization is successful, in the first 3 months of pregnancy a woman must take progesterone medications to maintain the functions of the corpus luteum, and therefore pregnancy.
An example from practice: in a antenatal clinic, a woman with a diagnosis of polycystic ovary syndrome, which was confirmed by laboratory tests and ultrasound data, was observed for quite a long time. Until a certain time, she did not think about pregnancy and decided that pregnancy would happen by itself. However, on the threshold of her thirties, the issue of pregnancy came to the fore, and she asked for help. After a short course of therapy with oral contraceptives (about 3 months), Clostilbegit was prescribed. Pregnancy occurred with the first ovulation. Duphaston was also prescribed for 2 months, but during a gynecological examination it was determined that the pregnancy was not developing further, the uterus was behind the expected period, and there were periodic spotting.
Using ultrasound, the diagnosis was confirmed and curettage was performed. The patient disappeared from view for 2 years, but then returned with the decision to perform laparoscopic intervention. After passing the necessary examinations, she was referred for laparoscopic ovarian resection. After 4 months, pregnancy began, which proceeded relatively normally and ended with the birth of the long-awaited child.
Signs and symptoms of polycystic ovary syndrome
Symptoms of polycystic ovary syndrome are very varied and can resemble symptoms of other diseases. Another special feature is that it is not necessary for one woman to have all the symptoms at once.
Signs of polycystic ovary syndrome may not be noticeable for many years. Most often, a woman learns about her diagnosis only at the moment when she plans to become a mother.
The main symptom of polycystic ovary syndrome that forces you to see a doctor is the inability to get pregnant.
The most common causes and additional symptoms of polycystic ovary syndrome:
1. The menstrual cycle is unstable. Disturbances begin to appear from the moment of menstruation: an irregular cycle with scanty periods or, conversely, with prolonged bleeding.
Often, periods may be completely absent for several months. Due to hormonal imbalance, the endometrium of the uterus increases in thickness, but monthly rejection does not occur or occurs with a delay.
2. Pain in the abdominal area. The pain symptom may be constant. This is explained by enlargement of the ovaries and pressure on the pelvic organs.
3. Increase in body weight. The sign is not constant, but is observed in many women. Obesity is characterized by the “apple” type - the bulk of fat is located in the abdomen and waist.
Obesity is associated with excessive production of insulin - insulin increases appetite, a constant feeling of hunger does not leave a woman. Due to a sharp increase in weight, stretch marks (striae) appear on the skin of the body.
4. The appearance changes. Acne appears on the skin, hair and skin are oily, and oily dandruff is often detected. Girls and women find increased body hair in the genital area and on the legs.
The so-called female mustache appears above the upper lip. On the head, on the contrary, patchy hair loss (alopecia) may occur with the formation of bald patches. These changes indicate increased production of male hormones.
5. It is noted by increased pigmentation of the skin on the back, in the armpits.
6. On the part of the nervous system, irritability, drowsiness, and mood swings may be observed, i.e., symptoms reminiscent of PMS.
Health risks and complications
Women with PCOS are at increased risk of developing the following complications:
- Mammary cancer;
- Obesity;
- Insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes mellitus; high blood pressure;
- Thrombosis, thromboembolism, thrombophlebitis due to increased blood clotting;
- Dyslipidemia (metabolism disorders of cholesterol and triglycerides with the possible development of vascular atherosclerosis);
- Cardiovascular diseases, myocardial infarction, stroke;
- Endometrial hyperplasia and endometrial cancer due to the absence or irregularity of menstruation and the “accumulation” of non-exfoliating endometrium, as well as due to the absence or insufficiency of progesterone effects, leading to long-term hyperstimulation of endometrial cells unbalanced by progesterone with increased levels of estrogen.
Data from a number of researchers indicate that women with polycystic ovary syndrome have an increased risk of miscarriage or premature birth, and miscarriage. In addition, many women with this syndrome cannot conceive or have difficulty conceiving due to irregular menstrual cycles and absent or infrequent ovulation. However, with proper treatment, these women can normally conceive, carry and give birth to a healthy child.
Complications
Without adequate treatment, polycystic ovary syndrome can provoke undesirable consequences. These include the following:
- hypertonic disease;
- ischemia;
- heart and vascular diseases;
- arterial occlusions;
- cerebral hemorrhage.
Long-term use of hormonal drugs can cause mastopathy and cancer. The presence of polycystic disease often provokes symptoms of diabetes in pregnant women.
Polycystic ovary syndrome is a dangerous disorder that can become an obstacle to successful conception. In order for pregnancy to occur, it is very important to consult an experienced doctor. Thanks to strict implementation of his recommendations, it will be possible to carry and give birth to a healthy baby.
Diagnostics
Diagnosing polycystic ovary syndrome is a complex process. This is a whole complex of studies on the basis of which a diagnosis is made or refuted.
- The main criterion is infertility, due to rare ovulations or their complete absence. Women unsuccessfully try to get pregnant, years go by, but pregnancy does not occur.
- The second important indicator is the quantitative determination of female and male sex hormones in blood serum. Clinically, signs of increased androgens may not always appear, while laboratory testing may reveal their increase. It is also necessary to take tests for glucose and cholesterol.
- With a two-handed examination, the gynecologist can feel enlarged ovaries that are firm to the touch.
- An ultrasound examination will help to examine the structure of the ovaries. The doctor reveals the following ultrasound signs: the ovaries are enlarged, small follicles are visualized along the periphery of each, more than 10 in number.
- Sometimes laparoscopy may be performed. This study is carried out using a device called a laparoscope, which is inserted through a small hole in the abdominal wall. The laparoscope is able to examine the appearance of the ovaries: they are enlarged, their surface is covered with a white capsule, there are no signs of egg release on the surface of the capsule (point ruptures). Laparoscopy allows you to take a piece of tissue for histological examination during the examination, and is also one of the methods for treating polycystic ovaries.
The diagnosis is made only on the basis of several signs (the main ones are infertility, increased androgens and related symptoms). None of the signs in a single manifestation can confirm the disease.
Diagnostic methods
To identify pathology, you need to conduct a thorough diagnosis. To begin with, it is recommended to exclude other diseases that provoke cycle disorders and the development of hyperandrogenism.
The main diagnostic method is ultrasound, which allows you to detect small follicles. With the development of polycystic disease, more than 25 follicles may appear. With the help of laparoscopy, it is possible to identify the thickened surface of the white ovaries.
An increase in androgen levels in women is evidenced by acne, obesity, and hirsutism. To detect an increase in male hormones, clinical or biochemical tests are performed.
During the examination, the doctor must collect family history and general medical history of the patient. The gynecologist must also perform an examination, during which he examines the genitals for the presence of lumps and other abnormalities.
We also recommend viewing: The exact location of the prostate in a man
During the diagnostic process, blood pressure measurement is required. The doctor also prescribes a number of blood tests - cholesterol levels, hormones, glucose tolerance.
Transvaginal ultrasound can visualize the ovaries and determine the thickness of the uterine lining. After studying the information received, the doctor decides on the method of treatment for polycystic disease.
Treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome
Therapy for polycystic ovary syndrome is a complex multi-stage process of sequential restoration of the physiological parameters of the whole organism. Polycystic ovary syndrome is not only a gynecological disease, so treatment should also be aimed at eliminating those disorders that led to the development of ovarian pathology.
The scope of treatment measures is determined taking into account the severity of the process and the woman’s desire to become pregnant.
At the first , preparatory, stage of treatment, it is necessary to bring the patient’s weight to a physiological norm (in case of obesity). Diet therapy helps normalize fat metabolism, and the necessary physical activity restores carbohydrate metabolism. An individual nutrition plan and a set of physical exercises are drawn up for each patient, taking into account her physical characteristics and the severity of the disease. It cannot be said that this seemingly completely uncomplicated stage of therapy can be completed without difficulties and disruptions. If the effect is positive, weight loss not only improves external appearance and general well-being, but also contributes to a good psychological attitude of patients for subsequent treatment.
Elimination of hormonal disorders is carried out at the second stage of treatment for polycystic ovary syndrome. At this stage, it is necessary to restore the normal menstrual cycle, eliminate hyperandrogenism (hirsutism, acne, etc.), and bring carbohydrate and fat metabolism to physiological norms.
To correct the menstrual cycle in the treatment of infertility, hormonal drugs with a low estrogen content are used, since anovulation in polycystic ovary syndrome involves hyperestrogenism. Modern combined oral contraceptives (COCs) are successfully used in the treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome. Drugs such as Marvelon, Logest, Femoden, Janine and others, similar in composition, are prescribed in three-month courses followed by a month-long break. The treatment process is certainly monitored by determining the level of hormones in the blood and ultrasound.
The third stage of conservative treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome is carried out for women planning pregnancy. The essence of the treatment is to stimulate ovulation.
Disorders of carbohydrate metabolism are successfully eliminated with the help of hypoglycemic drugs. A good effect is observed after using the drug Metformin. Typically, Metformin for polycystic ovary syndrome is prescribed for one to two weeks, after which a decrease in the level of glucose in the blood of patients is noted. It has been established that Metformin in polycystic ovary syndrome slows down the processes of glucose absorption in the digestive tract, eliminates tissue insulin resistance and inhibits glucose synthesis in the liver.
Elimination of the phenomena of hirsutism is carried out with the help of antiandrogenic drugs. The drug Diane - 35 successfully copes with this task. The use of antioxidants (Methionine, Ascorbic acid, etc.) and vitamins, physiotherapy and therapeutic massage are of auxiliary importance.
It should be noted that the choice of treatment regimen, as well as drugs, depends on the purpose of therapy. If a woman complains of menstrual irregularities, hirsutism and other abnormalities, but does not plan to become pregnant, the treatment method chosen for her may differ from that if the woman wants to become pregnant. No single treatment regimen for polycystic ovary syndrome is universal. All drugs are selected only for each specific patient. There is no guaranteed time frame for recovery, just as there is no guarantee of recovery itself.
Treatment
Typically, treatment is selected to eliminate individual problems - excess weight, infertility, acne. It must be comprehensive.
Regulating the menstrual cycle
If a woman does not plan to become pregnant, her doctor may recommend birth control pills that contain small amounts of synthetic progesterone and estrogen. They help reduce androgen synthesis and provide a break from constant estrogen production. Thanks to this, the threat of endometrial cancer is reduced and pathological bleeding is corrected.
An alternative approach is to use progesterone for 10-14 days each month. In such a situation, treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome with duphaston is prescribed. Thanks to the use of this remedy, it is possible to restore regular periods and cope with bleeding. Also, duphaston for polycystic ovary syndrome prevents excessive tissue growth inside the uterus and is a reliable cancer prevention.
Doctors often prescribe metformin. This remedy helps reduce insulin levels. Thanks to its use, it is possible to improve ovulation and make the cycle regular. In addition, metformin helps slow the progression of type 2 diabetes.
Restoration of ovulation
For women who are planning a pregnancy, the doctor should select medications that will restore ovulation. Clomiphene citrate, which is an anti-estrogen, is suitable for this purpose. It is taken in the first part of the cycle. If this remedy does not produce results, the specialist also prescribes metformin.
If the combination of these drugs does not allow you to get pregnant, the doctor may recommend the use of gonadotropins - FSH and LH. These medications are administered by injection.
Reduced hair growth
In such a situation, a specialist may recommend birth control pills to reduce androgen synthesis. Doctors also often prescribe a drug called spironolactone. It blocks the effect of androgens on the dermis.
We also recommend viewing: What to do if an ovarian cyst bursts: consequences for the body
However, this substance can cause birth defects. Therefore, during the treatment period you need to carefully protect yourself. Spironolactone is not used during pregnancy or planning. Eflornithine cream will also help slow down hair growth.
Vegetation can be removed without medications. Effective methods include electrolysis and laser hair removal. The second method works well with dark hair, allowing you to cover large areas.
Surgical intervention
If, after using medications, the desired pregnancy does not occur, laparoscopy is performed. During this operation, the doctor makes an incision in the abdomen and places tubes equipped with a camera into it.
The specialist then inserts surgical instruments and uses current or laser radiation to burn holes in the follicles. This ensures the restoration of ovulation. However, after such an intervention only a temporary effect is achieved.
Weight correction
Losing weight helps manage hormonal changes and improve key health indicators. Thanks to this, the condition of diabetes, high cholesterol and increased blood pressure is normalized.
Reducing weight by just 5% allows you to restore the normal balance of hormones and increase the likelihood of successful conception.
Surgery
If conservative treatment is ineffective and the patient desires to become pregnant, surgical intervention is indicated. The operation is performed laparoscopically. The following surgical methods are used:
- Wedge-shaped resection of the ovaries (excision of up to 2/3 of the volume of the ovaries) - in this case, most of the gonads are removed, which stimulates the production of androgens, and with the elimination of hyperandrogenism, hormonal levels are normalized and ovulation occurs;
- Decortication of the ovaries (the dense tunica albuginea is excised, and the follicles are pierced with a needle);
- Endothermocoagulation (spot cauterization) of the ovaries.
It should be noted that the possibility of spontaneous ovulation after surgery decreases over time. That is, up to 75% of patients become pregnant in the first 3 months after surgery, up to 50% within six months after laparoscopy, and about 25% or less within 9 months. In this regard, the patient is prescribed ovulation stimulation immediately 3 months after the operation, if pregnancy has not occurred.
Diet
Nutrition provides the body with substances to produce the energy necessary for metabolic processes, for the restoration and synthesis of new cells in order to store reserve substances (fat in adipose tissue, glycogen in the liver).
Doctors recommend something like this for patients with polycystic disease:
- a hearty first breakfast approximately 30-40 minutes after waking up;
- light second breakfast;
- full lunch;
- multi-course dinner;
- light snack before bed.
Women suffering from polycystic ovary syndrome due to obesity should combine physical activity with a certain diet and diet:
- limiting the calorie content of food to 1200 - 1800 kcal per day with 5-6 meals a day;
- eating low-calorie foods (fruits, vegetables);
- increasing the protein content in the diet (fish, seafood, meat, cottage cheese);
- limiting carbohydrate foods (baked goods, sugar, jam, honey, sweet drinks);
- exclusion of animal fats and their replacement with vegetable ones. Daily fat intake is no more than 80 g;
- exclusion of spices, herbs, sauces, smoked and pickled foods;
- complete exclusion of alcohol;
- fasting days 2-3 times a week (apple, kefir, cottage cheese, vegetable).
If you have polycystic ovary syndrome, you will have to once and for all eliminate foods that contain large amounts of carbohydrates and cholesterol from your diet. This requirement is very categorical - the foods listed below cannot be eaten even sometimes and even if you really want to.
| Exclude products | Authorized Products |
|
|
After body weight returns to normal, the number and range of foods consumed can be expanded. However, if the patient returns to her previous diet, excess weight will quickly return. To get rid of obesity forever, you need to consume foods in such quantities that your body weight remains in a stable physiological state.
Physical activity (fitness, gymnastics) is a good addition to a balanced diet. For some patients, exercising just two hours a week along with a diet gives results similar to taking special weight loss pills. As with diet, intense exercise will help you shed extra pounds faster, but stopping exercise will bring back the excess weight. It is enough to look at former athletes to be convinced of this possibility. If a woman is not ready for constant physical activity, it is better to choose the optimal mode of physical activity for herself.
Stricter diets and increased physical activity help to quickly lose weight, but are not able to maintain it. This problem can be successfully solved only by the right way of life, not imposed from the outside, but consciously chosen by the woman herself.
Folk remedies
You should not expect to cure polycystic ovary syndrome using only folk remedies. But some prescriptions will increase the effectiveness of the main therapy.
- A mixture of herbs. These are the red brush and the hog queen. You need to take 40 g of crushed roots of the brush and the same amount of leaves of the hogweed, pour in 500 ml of alcohol or vodka. Let it brew for a week in a cool, dark place, then take one or two tablespoons three times a day.
- Nettle. Pour 10 g of dried leaves into a glass of boiling water and let stand for 20-30 minutes, then drink twice.
- Mumiyo. The mummy should be diluted to a paste with warm water. After this, apply a moderate amount to gauze and form a tampon. Leave overnight for 7-14 days.
- Dandelion root. It is necessary to grind the root to a powdery state and divide into portions of 2-3 g. Brew and drink instead of tea.
Treatment of PCOS in case of unwanted pregnancy
This therapy has mainly two goals:
- Reducing the risk of developing diabetes mellitus and other diseases associated with PCOS.
- Correction of the menstrual cycle and cosmetic disorders.
For these purposes, nonsteroidal and steroidal antiandrogenic drugs are used:
- “Flucinom”, “Flutamide”, “Flutaplex”, blocking androgen receptors of target tissues and affecting the synthesis and production of male sex hormones by the adrenal glands;
- “Spironolactone”, “Veroshpilaktone”, “Veroshpiron” - inhibit the synthesis of androgens in the ovaries;
- COCs (combined oral contraceptives) - lead to the reversal of symptoms caused by excess androgen levels; COC drugs of the latest generation, “Dienogest”, “Zhanin”, “Diane-35”, which have the most pronounced results of use, reduce the level of testosterone in the blood and increase the content of the sex-steroid gdobulin (SSB).
Methods of treatment when planning pregnancy
Conservative therapy can be carried out both to achieve a natural pregnancy and to obtain eggs for IVF for polycystic ovary syndrome.
In the presence of insulin resistance, therapy begins with the use of so-called sensitizers, that is, drugs that increase tissue sensitivity to insulin. If there is no effect, conservative combination therapy is carried out with drugs that reduce the production of androgens in combination with ovulation inducers.
Hyperstimulation of ovulation is carried out:
- first, with the help of “Clomiphene citrate” or its analogues—“Clostilbegit”, “Clomid”; these drugs are derivatives of synthetic non-steroidal estrogens;
- if there is no effect, human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), which contains FSH and LH, is added to “Clomiphene citrate”. It is obtained by isolation from the urine of postmenopausal women or synthetically (“Gonal - F”, “Luveris”, “Pregnil”, “Puregon”, “Ovitrel”).
The lack of results from the induction therapy is an indication for the use of surgical methods of treatment using the endoscopic method:
- Knife or laser wedge resection - excision of a segment of the ovary (2/3).
- Thermocautery - pathologically altered ovarian tissue is destroyed.
- Diathermocoagulation - applying small incisions to the cortex while simultaneously carrying out coagulation of small cysts.
- Decortication—a dense sclerocystic membrane is removed from the surface of the ovary.
Surgical resection of the ovaries for polycystic disease, compared with conservative methods, is the most effective: the restoration of menstruation occurs on average after 1 week, and ovulation is restored after 4-6 months.
Prevention and prognosis
It is impossible to completely cure PCOS, so the goal of treatment is to create favorable opportunities for pregnancy. When planning pregnancy, women diagnosed with polycystic ovary syndrome need to undergo a course of treatment to restore and stimulate ovulation. Polycystic ovary syndrome progresses with age, so the issue of pregnancy should be resolved as early as possible.
As in the case of the prevention of other gynecological diseases, the prevention of PCOS requires regularly scheduled consultations with a gynecologist. Polycystic ovary syndrome, detected in an early phase of development, allows timely correction of disorders to begin and avoid dire consequences, including infertility. Prevention of abortion, inflammatory and other diseases leading to impaired ovarian function is of great importance. Mothers of teenage girls should be interested in the “female” health of their daughters and at the first signs of polycystic ovary syndrome, immediately take them to a competent specialist.
Amenorrhea Menopause in women Endometriosis Adenomyosis of the uterus Colpitis Thrush in women