Symptoms of ovarian inflammation in women, treatment and prevention
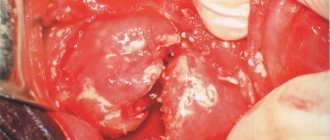
Inflammation of the ovaries (oophoritis) is a pathology in which the infectious process covers the female reproductive glands on one or both sides.
The disease is extremely rarely isolated. Most often, the inflammation spreads to the uterine (fallopian) tubes. Oophoritis is accompanied by dysfunction of the ovaries.
Without adequate timely treatment, the pathology can lead to decreased fertility (ability to conceive). Let's consider the directions of treatment and symptoms of ovarian inflammation in women.
Description of the disease
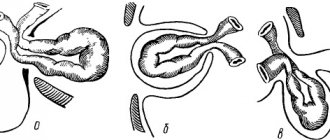
Inflammation of the ovaries, or oophoritis, can occur in several forms, differing in the severity of symptoms. All of them occur when the tissues of the appendage are damaged. This condition causes dysfunction of the ovaries, often resulting from adnexitis - inflammation of the fallopian tubes. A disease that simultaneously affects both the fallopian tubes and the appendages is called salpingoophoritis.
Quick elimination of the inflammatory process has virtually no effect on the functioning of the reproductive system. If it lasts for a long time, women consult a doctor if they are unable to conceive or develop symptoms of oophoritis. The prolonged presence of pathology in the body can lead to infertility, hormonal imbalance and other negative processes.
https://youtu.be/stVMtwF8ceM
Signs of various forms of inflammation
There are three forms of ovarian inflammation, namely acute, subacute and chronic.
The signs may be similar, but their severity varies.
Acute inflammation has pronounced symptoms. As a rule, it is at this stage that the patient decides to contact a specialist so that he can prescribe the appropriate treatment.
The symptoms here are as follows:
- pain in the lower abdomen. Localization can be on one or both sides. Sometimes the discomfort spreads to the groin area;
- headache , aches in muscles and joints;
- chills accompanied by fever;
- painful and frequent urination;
- metabolic disease;
- bleeding on days other than your expected period;
- pain during intimate contact;
- constant change of emotional state.
Attention! Often, palpation cannot be used for diagnosis, since pain and swelling are recorded.
Subacute inflammation mainly occurs in those suffering from tuberculosis. The signs of the disease are similar to those mentioned above, but they are much more difficult to determine.
Chronic inflammation occurs if the patient does not see a doctor or the prescribed treatment is not completed. Sometimes the disease worsens, but the condition is replaced by periods of temporary improvement.
Relapses do not occur if a woman complains only of pathological secretion or menstrual irregularities. The same symptoms are observed, for example, with gonorrhea. However, over time, adhesions form and the walls of the fallopian tubes thicken.
Useful video on the topic:
https://youtu.be/y7KxYjUw-vQ
Causes of ovarian inflammation in women
Most often, inflammation of the right or left ovary develops under the influence of infections that have penetrated the genital tract. There are other factors that contribute to the development of pathology - hypothermia, organ injury, inflammatory processes in the pelvis, other problems with the ovaries, etc.
Sexual infections
In the presence of genital infections, damage to the appendages is often accompanied by inflammation of other genital organs. The occurrence of pathology is possible when:
- unprotected sexual intercourse;
- lack of personal hygiene;
- uncontrolled vaginal douching;
- taking antibiotics;
- hormonal disorders;
- stress;
- decreased immunity.
Pathology usually occurs with severe infection, since the appendages are the last link in the spread of microorganisms to the rest of the genital organs.
The risk of infection increases in the presence of recent illnesses (colds, flu, acute respiratory viral infections), abortions, including spontaneous ones, childbirth, after diagnostic curettage of the uterus, or installation of an intrauterine device. These factors reduce the protective functions of the cervix and disrupt the production of mucus in the cervical canal. This decrease in body strength increases the likelihood of pathogenic microorganisms penetrating the appendages.
Types of infectious agents:
- chlamydia - often present in a latent form, manifesting itself when immunity decreases, their presence is not accompanied by acute symptoms;
- gonococci - in most cases, they affect only the lower part of the reproductive system, the infection multiplies more actively and causes ovarian disease when immunity declines;
- mycoplasmas are opportunistic bacteria, the spread of the infectious process is accompanied by symptoms when the body’s defenses are weakened;
- Trichomonas - can cause inflammation of the ovaries when the fallopian tubes are damaged.
In order for acute inflammation of the appendages to develop, prolonged and active reproduction of the infection is necessary.
Virus infection
The likelihood of developing this ovarian disease in women in the presence of viruses in the genital tract has not yet been proven. It is assumed that such an infection can cause inflammation both directly and indirectly, that is, as a result of damage to the uterus and its tubes.
Types of viruses:
- herpes simplex type 2 (genital) – enters the body through unprotected sexual intercourse, contact with the mucous membranes of an infected person, through household objects, a complete cure is impossible;
- Cytomegalovirus affects many organs and systems of the body and cannot be treated.
Viruses are present in the body asymptomatically almost all life, occasionally manifesting as exacerbations when immunity declines.
The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) does not cause disease directly. It indirectly affects the condition of the appendages by reducing the body's defenses and increasing the risk of infection with other viruses and infections.
Tuberculosis
Most often it affects the lungs, but can spread to other organs. Infection occurs through airborne droplets, through consumption of infected products and through contact with the skin of a sick person. With a low level of immunity, the risk of tubercle bacilli entering the body increases.
The infection enters the ovaries through the bloodstream. In this case, bilateral oophoritis usually develops. The disease is often asymptomatic and is detected only during a routine medical examination. This entails the development of complications in the functionality of the woman’s reproductive system.
Organ injury
The inflammatory process can occur as a response to a violation of the integrity of the appendages. Mechanical damage to the genital organs is possible in the following cases:
- blow to the stomach;
- penetrating injury to the area of the uterus and appendages;
- surgical intervention;
- gynecological procedures - abortions, curettage, installation of spirals.
Often the disease occurs because a woman has caught a cold in her ovaries by sitting on cold surfaces or dressing inappropriately for the weather.
Pathology does not occur in all cases of possible injury. If tissue integrity is compromised, the risk of its occurrence increases.
Diagnosis of inflammation of the ovaries and tubes
Salpingoophoritis is a very difficult disease to diagnose. The doctor must take into account a lot of data both from the anamnesis and from symptoms and data from laboratory and instrumental studies.
Anamnesis for diagnosis is important to indicate:
- abortions and childbirth with complications;
- manipulations performed in the uterine cavity, including curettage;
- use of intrauterine contraceptives;
- hysteroscopy;
- promiscuity;
- hysterosalpingography (a procedure in which an X-ray contrast agent is injected into the uterine cavity and tubes to determine possible narrowing of the tubes and the presence of space-occupying formations or other deformations in the uterine cavity).
From laboratory tests, it is important to study a general blood test to identify the fact of inflammation, as well as study discharge from the cervix, vagina, and urethra for the presence of pathogens, determining their type and sensitivity to antibiotics.
Ultrasound diagnostics does not provide enough information to make a correct diagnosis. The transabdominal method (ultrasound sensor on the abdomen) can only reveal some indicators that indicate a chronic process - adhesions, thickening of the tubes. It is also possible to detect fluid in the pelvis or tubes in severe forms of salpingoophoritis that occur with complications - pyo- and hydrosalpinx, pelvioperitonitis. CT and MRI make it possible to distinguish an inflammatory process from a tumor process.
Inflammatory process in neighboring organs
Inflammation in the pelvic area can spread to the appendages. The development of right-sided or left-sided oophoritis is provoked by pathologies in the following organs:
- colon;
- bladder;
- appendix;
- peritoneum.
Often, inflammation of the appendage together with a neighboring organ leads to the formation of adhesions, which complicates the treatment process, and in some cases requires surgical intervention.
Types of disease
Oophoritis occurs in several forms. They differ in the speed of development of symptoms and the intensity of their manifestation.
Spicy
Characterized by rapid development of disease symptoms. Acute oophoritis appears immediately after the end of the incubation period after infection or as a complication of other diseases. The intensity of the symptoms forces the woman to immediately consult a doctor.
Subacute
Most often occurs with tuberculosis. Signs of ovarian inflammation are less pronounced than in the acute form. They are often difficult to recognize due to the current underlying medical condition.
Chronic
A consequence of the course of acute or subacute forms of ovarian disease. The main reason for the appearance of a chronic type of pathology is incomplete, incorrect or absent treatment of the previous stages of the disease. It rarely occurs as an independent disease. It can be present for many years, occasionally manifesting itself with exacerbations. The latter are characterized by less intense symptoms than during the primary manifestation of the disease.
https://youtu.be/C5O6Ouaskos
General signs of inflammation of the appendages
The inflammatory process can be localized in the tube or ovary on only one side, but a bilateral form of the disease is more common. The pain appears from time to time or is constant. How strongly they are expressed depends on the degree of the inflammatory process.
The pain usually extends to the lumbar and sacral region and manifests itself in the lower abdomen. It intensifies when muscles tense during bowel movements or sex. Sometimes these unpleasant symptoms are accompanied by problems associated with urinary incontinence.
General signs of inflammation of the ovaries and tubes are associated with increasing intoxication of the body. Among them are the following manifestations:
- sleep disorders;
- increased fatigue, irritability;
- severe weakness, dizziness;
- increased body temperature;
- dry mouth;
- headaches, tinnitus;
- cardiopalmus.
In a laboratory blood test, changes in the leukocyte formula are noticeable - an increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and leukocytes.
The source of inflammation located in the ovaries and appendages leads to hormonal imbalance. This is expressed in a sharp change in a woman’s mood, a decreased desire to have sex, and during sexual intercourse – pain and lack of orgasm. The menstrual cycle is also disrupted: periods are too scanty or, conversely, too abundant and accompanied by severe pain.
Symptoms
The disease can occur without any symptoms. In other cases, the intensity of the symptoms of ovarian inflammation in women determines the method of treatment and the type of pathology.
Pain syndrome
Pain during the disease is localized in the lower abdomen.
Most often they are present during the acute course of the disease. Typically, the pain syndrome is aching, pulling in nature, and less often manifests itself as stronger sensations. This condition lasts from several days to several weeks. With timely treatment, the symptom that the ovaries have caught a cold goes away within the first week from the onset of the pathology.
With a chronic disease, the patient is periodically bothered by nagging and aching pain in the lower abdomen, sometimes radiating to the lower back.
Body temperature
Body temperature rises during the acute course of the disease. In other forms, it may reach low-grade levels. Elevated temperature is diagnosed with inflammation of the appendages, occurring against the background of other diseases that cause the appearance of this symptom.
Gastrointestinal tract dysfunction
Rarely accompanies the course of pathology. Possible signs of disruption of the digestive organs:
- diarrhea and frequent urge to defecate are a consequence of irritation of the intestinal walls by a source of inflammation and intoxication;
- nausea, vomiting - occur with severe pain in the lower abdomen, elevated body temperature, and accumulation of toxins in the body.
Therapy of pathology with antibacterial drugs often entails the appearance of their side effects - nausea, vomiting, diarrhea and heartburn.
Vaginal discharge
The most noticeable change in their character is when the genital tract is infected. When the ovaries become inflamed, yellowish or greenish discharge appears, containing impurities of pus and having an unpleasant odor. Their daily volume exceeds the standard norm, which forces the woman to use panty liners.
Sometimes bleeding may occur. Such a symptom of inflammation of the ovaries in women indicates a violation of the integrity of the tissues of the appendage, the acute course of the pathology. The presence of blood is insignificant; often such discharge has a reddish or brownish tint and is not abundant. Their presence is most likely accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen.
Irregularity of the monthly cycle
Violation of the functionality of the ovaries leads to a malfunction of all genital organs and the endocrine system of the body. This is primarily manifested by the irregularity of the menstrual cycle. Options for violations:
- complete absence of menstruation;
- lengthening or shortening the cycle;
- too much or scanty bleeding;
- painful periods;
- increase or decrease in the duration of menstrual bleeding.
Causes of cycle disruption:
- damage to the lining of the uterus or ovarian tissue;
- disruption of the ovulation process;
- lack of endometrial growth or hyperplasia;
- hormonal imbalance.
Most often, a disruption of the menstrual cycle due to oophoritis is accompanied by the inability to conceive for a long time.
Pain during intimacy
During the pathology, sexual intercourse may be accompanied by pain.
In this case, a woman may experience the following types of discomfort:
- sharp pain on the left or right side of the lower abdomen with active friction;
- discomfort in the appendage area throughout sexual intercourse;
- spotting immediately after intimacy;
- burning and itching – in the presence of pathogenic bacteria in the genital tract.
If pain occurs due to inflammation of the ovaries, it is better to stop sexual intercourse.
Hormonal imbalances
Normally, the epididymis produces estrogens and progesterone. These hormones are necessary for regular ovulation and control of the frequency of the menstrual cycle. Violation of their levels in women with inflammation of the ovaries provokes symptoms:
- lack of ovulation;
- irregular menstrual cycle;
- painful periods;
- impossibility of conception;
- deterioration of skin and hair condition;
- obesity or sudden weight loss;
- male pattern hair growth;
- fast fatiguability;
- mood swings.
Hormonal imbalance can only manifest itself as a lack of conception, so many women are unaware of its presence.
Infertility
Complete infertility occurs with a long course of the disease. Doctors make this diagnosis when there is no treatment for the disease or when the patient does not comply with all the rules of therapy. In most cases, infertility due to oophoritis is a temporary phenomenon. After eliminating the signs of inflammation of the appendages in women, reproductive ability returns.
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis, the patient needs to undergo a series of examinations. Diagnosis is aimed at determining the type of ovarian disease and the cause of its occurrence.
Patient interview
The gynecologist must interview the patient before the examination. The anamnesis is compiled based on the results of answers to the following questions:
- regularity of menstruation;
- age of onset of first menstruation;
- whether there is pain during bleeding;
- what is the nature of menstruation - scanty or heavy;
- whether there are problems with conception;
- whether there are symptoms of inflammation of the left or right ovaries;
- the presence of childbirth, abortion, spontaneous miscarriages;
- methods of contraception;
- whether the woman had other ovarian diseases.
If you are taking any medications, you should notify your specialist.
After filling out the patient’s questionnaire, the doctor begins the examination.
Gynecological examination
Study of the condition of the external and internal genital organs. A vaginal speculum is used for this. With oophoritis, the doctor can determine the following signs of the disease:
- swelling of the mucous membranes and vagina;
- the presence of pathological discharge with an unpleasant odor and impurities of pus;
- ulcerative lesions of the mucous membranes;
- redness;
- enlargement of the ovaries and their pain - determined by two-handed palpation.
At the end of the gynecological examination, the doctor takes a smear from the vagina.
Biomaterial research
A cervical smear is considered a mandatory type of diagnosis, which should be carried out for preventive purposes every six months. With the help of its examination under a microscope, the state of the vaginal microflora, the course of the inflammatory process, and the presence of sexually transmitted infections are determined.
https://youtu.be/YrL7KCF4iw4
Ultrasound
Using ultrasound, the condition of the appendages and adjacent pelvic organs that are susceptible to inflammation is assessed. Based on the diagnostic results, the following deviations from the norm are revealed:
- increase in the size of the appendages;
- smoothed surface of the ovaries;
- thickening of the fallopian tubes - diagnosed when they are inflamed;
- increased echogenicity of the organ;
- inflammatory process in the uterus.
When pathology is determined in only one appendage, the size of the second organ remains within normal limits.
For women who are sexually active, ultrasound is performed using the transvaginal method, that is, by inserting a sensor into the vagina. In girls and virgins, examination of organs occurs through the anterior abdominal wall.
Laparoscopy
A minimally invasive type of surgical intervention, which is often prescribed for diagnostic purposes.
It is carried out by making several punctures in the lower abdomen and introducing special devices into the abdominal cavity. Visualization of organs occurs through a laparoscope, which has a small video camera at the end. This method is highly informative. If pathologies that can be eliminated surgically are detected, the diagnostic study immediately proceeds to surgery.
Laparoscopy is performed only in the absence of accurate results from other research methods.
Treatment of inflamed ovaries
If all signs of inflammation are present, you should not heat the lower abdomen. Heat exposure promotes the spread of infection to neighboring organs. It is also not recommended to actively engage in sports or put stress on the body, since movement increases the pain - doctors advise lying down more and remaining still. You should temporarily avoid taking baths, especially with hot water, and only bathe in the shower.
A woman's cold can be treated at home. The specialist selects drug treatment depending on the type of pathogen. If bacteria are detected, antibacterial drugs are used; viral oophoritis can be overcome with immunity-boosting and symptomatic drugs.
Medicines against inflammation
Antibacterial drugs are prescribed based on the results of the analysis; medications are selected specifically according to the type of pathogen and depending on its resistance to drugs.
Ampicillin disrupts the synthesis of cell membranes and helps stop their development
Types of antibiotics:
| Name | Action |
| Ampicillin, Oxacillin, Norfloxacin (penicillin group) | They have a bacteriostatic effect, are the safest, and rarely have side effects. This pharmacological group of drugs is effective against gram-positive microorganisms, as well as meningococci, gonococci and spirochetes. They disrupt the synthesis of cell membranes of microorganisms and suppress their development. |
| Doxycycline, Minocycline, Metacycline, Amoxiclav (tetracycline series) | Preparations with a wide range of effects affect gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria, large viruses, and suppress the biosynthesis of microbial cell proteins in ribosomes. They act bacteriostatically. |
| Clarithromycin, Erythromycin (macrolides) | A class of antibiotics that suppress the development of gram-positive cocci, intracellular pathogens - chlamydia, mycoplasma. They are least toxic among other ABs, have a bacteriostatic effect, modulate immunity, and suppress the inflammatory process. |
| Clindamycin, Dalatsin, Zerkalin (lincosamides) | Suppress the growth processes of pathogenic cells, antibacterial drugs of a narrow spectrum of action, are used mainly against gram-positive microorganisms and some protozoa - toxoplasma, pneumocystis. |
| Metronidazole, Ornidazole, Tinidazole (nitroimidazoles) | Effective against anaerobes, causative agents of protozoal infections. Narrow-spectrum antibiotics. |
| Cefazolin, Cephasidime (cephalosporins) | Effective against anaerobes and cocci. |
Antibiotics are available in several forms: ointments, suppositories, tablets and solutions for injections. In gynecology, solutions and suppositories are used, while maintenance therapy with drugs containing fluconazole is prescribed to prevent candidiasis - Clotrimazole.
Vaginal suppositories for oophoritis:
- Depantol - allowed during pregnancy, has a bactericidal effect;
- Hexicon - suppresses the process of inflammation, not used during pregnancy, up to 12 years of age;
- Betadine – inhibits the growth of bacteria, viruses and fungi;
- Voltaren - heals mucous membranes, stops inflammation.
Hexicon suppresses ovarian inflammation
To reduce tissue hyperemia, antihistamines are used - Suprastin, Tavegil, Edem, Cetrin.
NSAIDs: Diclofenac, Nimid - relieve inflammation in soft tissues, reduce swelling, reduce pain.
Diclofenac - relieves inflammation and reduces swelling
According to indications, anti-adhesion drugs are prescribed, and when planning pregnancy, surgical removal of obstruction of the paired fallopian tubes.
Symptomatic therapy - analgesics to relieve pain, antispasmodics to eliminate muscle tension in the abdominal cavity and lower abdomen, antipyretics for increased body temperature and fever.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine will help relieve inflammation, reduce the severity of symptoms, and have a mild analgesic effect.
- Prepare 50 g of dried calendula, chamomile and immortelle. Mix, pour 1 liter of hot water, leave for at least half an hour. Drink 60 ml of tincture after meals for at least 30 days.
- Mix equal parts of knotweed, oak bark, nettle and centaury. Pour 200 g of this mixture into 1 liter of hot water and simmer over low heat for an hour. Then leave for another 5 hours, covered with a towel. Strain, take half a glass before meals for 15 days.
- 1 tbsp. l. dried boron uterus grass, pour 200 ml of hot water, leave for 2 hours. Then strain the infusion and take it as follows - half a glass three times a day after meals. Course – up to 1 month.
- 2 tbsp. l. dried goose cinquefoil pour 400 ml of hot water. After an hour of infusion, strain. The dosage regimen is half a glass 4 times a day for 15 days.
Dried calendula and chamomile for tincture against ovarian inflammation
You can make your own vaginal tampons for insertion at night:
- Melt the propolis over steam and cool to body temperature. Then soak a tampon made from a sterile bandage with it. Once the mixture has cooled, gently inject it overnight.
- Squeeze the juice from 1 head of garlic and 50 g of celandine leaves and stems. Mix fresh juice with 1 glass of water at room temperature. Gently soak a sterile bandage tampon and insert it into the vagina overnight.
- To impregnate tampons, you can prepare such a mixture. In a ratio of 5:2:3, take chamomile, dried oak bark and sage leaves. Brew in 300 ml of boiling water, strain, cool. Gently moisten a cotton swab or bandage and insert it inside overnight.
Douching with any decoctions and solutions for oophoritis is not recommended. This contributes to the spread of pathogenic microflora into the uterine cavity, which is fraught with additional infection.
How and how inflammation of female ovaries is treated
To quickly eliminate the pathology, it is necessary to prescribe a set of procedures. Treatment of ovarian inflammation in women includes taking medications, attending physiotherapy courses and using some traditional methods. Surgery is rarely used for this purpose.
Drugs
The type of medicine is determined by the cause of the development of the pathology. Drugs for the inflammatory process in the appendages:
- antibiotics (injections and tablets) – used in the presence of pathogenic microorganisms;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (tablets and suppositories) - reduce the source of inflammation, relieve pain;
- antipyretics (tablets) – necessary for high body temperature;
- immunostimulants (suppositories, tablets) – increase the body’s defenses and accelerate recovery;
- vaginal suppositories (anti-inflammatory or antiseptic) – eliminate the inflammatory process, destroy pathogenic microorganisms;
- vitamin complexes (tablets) – normalize the functionality of the ovaries, saturate the body with useful substances.
If the pathology is infectious, both partners should undergo therapy.
The duration of treatment for ovarian inflammation is 7-14 days. If the drugs are not effective, the therapeutic regimen is changed. Vitamins are taken for a longer period - up to 1-1.5 months.
Physiotherapy
Prescribed after relief of acute inflammation. Physiotherapy has positive effects:
- improvement of local blood circulation;
- pain relief;
- elimination of concomitant problems with the ovaries in women;
- preventing the development of adhesions;
- reduction of inflammation;
- restoration of the functionality of the genital organs.
To treat oophoritis, the following procedures are prescribed:
- magnetic therapy;
- mud therapy;
- hirudotherapy;
- phonophoresis;
- ultrasound;
- acupuncture;
- radon baths;
- electrophoresis.
Physiotherapy is carried out in a course of 5-10 sessions. They need to be visited every day or every 1-2 days. Sanatorium-resort treatment is considered optimal - this makes it possible to fully and comfortably complete the entire therapeutic course, improving women's health.
Operation
Surgical treatment for inflammation of the ovaries is extremely rarely prescribed. It is recommended for the following indications:
- the course of the adhesive process;
- tubo-ovarian abscess - accumulation of pus near the genitals;
- peritonitis - inflammation of the peritoneum;
- the presence of large cysts or tumors of the appendages;
- risk of ovarian rupture.
Treatment methods
How to treat inflammation of the ovaries is determined only by a gynecologist after the patient has completed all the necessary examinations. That is why, in order to make an accurate diagnosis, a woman must comply with all requirements before taking tests (for example, donate blood only on an empty stomach). Treatment for inflammation of the ovary (oophoritis) depends on the true cause of infection and the main pathogen. Therapy is carried out in several stages.
Acute oophoritis requires immediate hospitalization, antibiotics and painkillers. Antiviral agents and vitamins are also prescribed. Based on the test results, physiotherapy may be prescribed, which includes the following procedures:
- magnetic therapy;
- radon baths;
- phonophoresis;
- electrophoresis.
Chronic oophoritis requires long-term treatment. Initially, pain during inflammation of the ovaries is relieved, all microbial and inflammatory processes are eliminated, and body systems that have suffered from this disease (vascular, nervous, hormonal) are restored. The patient is strongly recommended to have a special massage and rest in a sanatorium-resort type place.
If a woman’s menstrual cycle is completely disrupted due to inflammation of the ovaries, then its restoration with the help of hormonal drugs is required. Most often these are birth control pills, for example, Regulon.
Unfortunately, almost every case of oophoritis results in the formation of adhesions in the pelvis. In this case, treatment for inflammation of the ovary should be not only medicinal, but also surgical. The patient has adhesions, inflamed appendage tissue and cystic neoplasms (if any) removed.
Pregnancy is not recommended for a woman with this disease. Absolutely all gynecologists say that you first need to cure the inflammation, and then prepare for conception. But if fertilization does take place, what should you do? You should immediately visit a gynecologist. He will examine the patient, prescribe tests and ultrasound diagnostics. Taking into account the location of the fetus and the advanced state of the disease, the doctor tells whether there is an ectopic pregnancy and whether the woman can give birth.
Possible complications
The risk of developing negative consequences for the body increases in the absence of full treatment or non-compliance with the rules of therapy specified by the doctor. Complications are also possible with a long-term course of chronic disease of the appendages.
Inflammation of the ovaries is dangerous for women due to the following consequences:
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract;
- inflammation of the bladder - cystitis;
- pyelonephritis - an inflammatory process in the kidneys, often a consequence of cystitis;
- irregular menstrual cycle;
- complete absence of menstruation;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- bilateral inflammation of the ovaries;
- spontaneous abortions;
- infertility;
- adhesions in the pelvis;
- ovarian dysfunction;
- formation of cysts and tumors on the appendages;
- purulent inflammation of the genital organs.
The likelihood of developing complications is determined by the patient’s age, her individual characteristics, the presence of gynecological pathologies and other chronic diseases.
Inflammation of the ovaries - treatment with folk remedies
You can also use traditional methods of treating ovarian inflammation.
Baths with the addition of juniper have a beneficial effect. Pour 5 kg of grass into a bucket of hot water and steep for two hours. Add the drug to a warm bath after it has been filtered.
Thanks to the use of folk remedies, it is possible to significantly improve the condition, improve the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, and reduce pain.
In the subacute stage, autohemotherapy, ultraviolet radiation, electrophoresis, and vibration massage are used under the control of clinical and laboratory data.
Correct use of these measures prevents the transformation of acute adnexitis into chronic inflammation of the ovaries and the creation of permanent changes in the form of adhesions, scars and sclerosis.
Pathology and pregnancy
The course of the disease negatively affects a woman’s reproductive abilities. This can cause difficulty in getting pregnant or complications during pregnancy.
Is pregnancy possible with oophoritis?
Most often, the ovary becomes inflamed at the same time as the fallopian tube.
Consequently, even in the absence of a violation of its functionality, the advancement of the egg to the uterus may be difficult. The situation is aggravated by the presence of adhesions and the chronic course of oophoritis. This reduces the possibility of conception and increases the risk of ectopic pregnancy or spontaneous abortion.
A miscarriage is possible even if the fetus is attached to the walls of the uterus, that is, in its natural position. This can be facilitated by a malfunction of the appendages and a decrease in the amount of hormones produced. Against the background of such a pathology, a child can be carried to term only by taking hormonal drugs prescribed immediately after conception.
Pathology during pregnancy
Pregnancy can occur against the background of existing oophoritis. The disease can develop after conception, at any stage of gestation. This is likely due to the following reasons:
- natural decrease in immunity;
- the presence of chronic gynecological pathologies;
- hypothermia;
- pressure on the ovary, subject to chronic processes, by the growing uterus.
Progressive inflammation of the appendages of an infectious nature can lead to infection of the fetus with pathogenic bacteria from the mother.
Oophoritis and pregnancy are compatible if the woman has regular medical monitoring.
But treatment is complicated by the inability to take most antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs. Their uncontrolled use can harm the unborn child. Strong drugs for ovarian inflammation during pregnancy are prescribed only in acute cases of the pathology. In other cases, the doctor allows you to take medications with a mild effect, which are completely safe for pregnancy.
Sexual life during illness
Sex during oophoritis is not prohibited. The exception is cases of pathology arising under the influence of sexually transmitted infections. Intimate life is permitted only after both partners have completed treatment and confirmed the absence of pathogenic microorganisms.
Sexual intimacy can cause a woman discomfort, sometimes severe pain.
In this case, you need to change your position. Positions with shallow penetration are considered the best option. If they are accompanied by unpleasant sensations, then sexual activity should be stopped for a while. It is also necessary to urgently end intercourse if bloody discharge from the vagina or acute, unbearable pain occurs.
Prevention
Many gynecological diseases are much easier to prevent than to cure. To do this, you need to follow all the rules of prevention:
- visiting a gynecologist every six months;
- use of barrier methods of contraception;
- daily personal hygiene – 2 times a day;
- timely treatment of all pathologies of the genital area;
- avoiding sitting on cold surfaces;
- organization of proper rest;
- balanced diet;
- regular walks;
- taking medications only as prescribed by a doctor.
Regular sex life has an important influence. It has a healing effect on a woman’s body, stimulating the production of sex hormones and improving local blood circulation. At the same time, one must not forget about the use of barrier contraceptives.
Ovarian inflammation is a disease that requires timely treatment. In the absence of medical intervention, it can develop into a chronic stage that is difficult to treat. For a successful recovery, a woman must follow all the recommendations of the gynecologist.