Common dermatological problems and causes
The skin protects the entire body, affects the process of thermoregulation and metabolism. Different skin problems are localized in different parts of the body. You need to understand that many skin diseases go away with almost no symptoms and can be easily gotten rid of.
Exogenous factors include those that affect the body from the outside. All these reasons can be divided into several types:
- mechanical influence;
- influence from temperature changes;
- chemical exposure;
- exposure to bacteria and parasites.
For example, mechanical damage occurs due to friction of the skin with any materials. For this reason, dermatitis or hemorrhages often appear. Thermal injuries occur due to excessive exposure of the skin to low or high temperatures. Dermatoses appear as a result of chemicals. For example, this happens in adults who are forced to work with chemicals (doctors, technologists). Pyoderma, skin tuberculosis, leprosy are often due to harmful bacteria.
Dermatosis
Pyoderma
Skin tuberculosis Leprosy
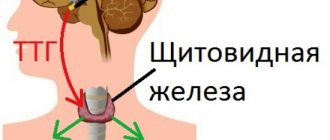
Skin problems are often due to endogenous causes. The functioning of the endocrine glands may change or excessive pigmentation may appear. Dermatological diseases can also be caused by problems in the central or peripheral nervous system.
Common skin diseases:
- Acne – among skin diseases, this problem occupies a leading position. Most often it occurs in adolescence. But in the absence of proper care, it can develop into a chronic form.
- Eczema and atopic dermatitis often occur in children. They suffer from severe itching. A common cause of this disease is an allergic reaction of the body.
- Herpes – There are different forms, but the most common form is herpes simplex.
Types and subtypes of skin diseases
Fungal skin infection.
A type of skin ailment caused by fungi that parasitize the skin and are of plant origin. They often affect:
- nail plates, hair and skin;
- the upper stratum corneum of the skin, causing it to become red.
Diseases of this type include:
Scab is a disease caused by a fungus that affects the hair, internal organs and nails. The disease is indicated:
- hair loss;
- small reddish spots.
Microsporia , or otherwise ringworm, is a disease often transmitted to humans from sick animals.
The disease is indicated by mild itching, red spots that have clear boundaries with a slight elevation above the skin.
Note! The listed skin diseases are contagious and are transmitted through infection from another person.
Pustular skin lesion.
This type of disease is caused by staphylococci and streptococci, as well as infection as a result of hypothermia and the presence of psychological trauma.
Diseases of this type include:
Pustular rash, which can be of an infectious, non-infectious or allergic nature.
Boils are indicated by a dense infiltrate, with further opening of the pustule, discharge of pus and subsequent scarring.
Leprosy.
This disease, better known as leprosy, has a chronic course of the disease with changes of a mutational nature, which mainly affect the mucous membrane of the skin. It has a latent period from 12 months to 10 years.
Symptoms after a latent period reveal themselves - bleeding from the nose, dry mouth, swollen lymph nodes.
Skin tuberculosis – this type of disease most often affects people with existing pulmonary tuberculosis.
The symptoms of this disease are due to:
- spread of spots on the skin;
- tubercles;
- sores.
If the disease is not completely cured, it leads to the process of scarring of existing ulcers on the skin.
Types of diseases originating from animal parasites.
Pediculosis , or in other words - phthiriasis, is a disease that can be easily cured .
Scabies is a disease caused by a scabies parasite in the form of a mite. Has symptoms:
- gray rashes about 3 mm in size;
- possible blisters on the skin;
- red nodules or watery crusts.
Important! It is necessary to undergo treatment in a timely manner so that the disease does not develop into eczema.
Eczema.
Acute and chronic skin disease. Eczema is indicated by the following symptoms:
- swelling of the skin;
- redness of the epidermis;
- reddish nodules, which subsequently burst and form a weeping surface - erosion;
- itching - constant and severe.
Treating eczema is a long and difficult process.
Psoriasis.
The disease has another name - scaly lichen. The disease is characterized by a chronic form, with characteristic rashes in the form of papules.
Lichen.
Lichen rosea - has an acute course of the disease along with inflammatory and painful processes.
Symptoms manifest themselves:
- flaky red spots;
- seasonal course of the disease (manifesting in autumn and spring).
Lichen red - has a chronic course of the disease.
The disease is caused by the following symptoms:
- rashes similar to nodular rash;
- severe itching.
Diseases of the skin glands.
Seborrhea – manifested by excessive secretion of sebum from the sebaceous glands. Affects the scalp (hair loss).
Acne is characteristic of adolescence, and is also another sign of existing seborrhea.
In addition, acne can occur due to an imbalance in the sweating process as a result of stressful situations and other severe psychological shocks.
Acne: causes and treatment
Photo and description of acne.
This disease begins due to blockage of the sebaceous glands and inflammation of the hair follicles. There are many reasons for the appearance of skin rashes. Dermatologists note that this can occur at any age. Acne is characterized by open or closed comedones, papular acne and nodular formations.
Why do rashes appear?
Acne can be caused by problems with two hormones: testosterone or progesterone. Testosterone is a male hormone. With excessive synthesis of this hormone, the work of the sebaceous glands increases, as a result of which too much sebum is released. It leads to the development of bacteria. Progesterone is also produced in both men and women. Significantly increases the work of the sebaceous glands, and with an excess of the hormone, the skin becomes swollen and less elastic. It is because of a sharp surge in hormones that acne appears in teenagers. Although other factors also play a role.
Scleroderma
Dermatology combines in this group skin diseases accompanied by thickening of the connective tissue and skin. The causes of skin diseases in this group have not been established, but some genetic disorders increase the risk of developing scleroderma.
Focal
Skin diseases are divided into linear and plaque. With a plaque manifestation, round seals with a purple rim appear on the skin. Multiple or single lumps appear on the face, trunk and limbs. With a linear disease, seals appear on the skin in the form of stripes. Often the muscles and bones in the affected area are involved in the pathological process, which results in limited development and functionality of these areas. The disease is often diagnosed in childhood and adolescence.
Causes of herpes and its treatment
To date, doctors have not found an ideal remedy to combat herpes. The cause of this problem is a virus. A significant amount of time may pass after it arrives and before it manifests itself. The stimulus for external manifestations can be stress or weakened immunity.
There are 3 routes of infection: airborne, household contact and sexual transmission. And the incubation period takes from 2 to 7 days (depending on immunity). Herpes affects almost the entire population on Earth. However, not everyone has it actively. The weaker the immune system, the higher the chances of getting this disease. Genetic predisposition also plays a role. An interesting fact is that most children become infected through airborne droplets. And many people become infected with herpes while breastfeeding.
Basic principles of treatment
Medicines developed on the basis of abnormal nucleotides can be easily purchased at any pharmacy. Most often they come in the form of an ointment. Abnormal nucleotides as a means of combating herpes were developed more than 20 years ago. They are especially effective in the early stages. Of course, it is not possible to completely get rid of herpes, but it is quite possible to forget about its manifestations.
A person may experience persistent colds on the face. In this case, the entire treatment process should be entrusted to doctors. The immunologist will prescribe all the necessary tests and, based on them, select a course of therapy.
Diseases with rash: where is it localized?
- Lichen versicolor - belongs to the category of keratomycosis. The fungus that causes it can remain in an inactive form for a long time; the disease most often occurs due to a deterioration of the immune system. It consists of multiple pink spots on any part of the body, which gradually acquire a dark brown color and disappear altogether. In some cases, peeling and itching are noted.
- Nodular trichosporia or piedra. The fungus affects the hair on the body and head without causing hair loss. Externally it appears as a black or white rim around the hair. As a rule, it occurs in a chronic form and is subject to long-term treatment.
- Trichophytosis. Unlike the above-mentioned diseases, the fungus affects the deeper layers of the skin, provoking inflammatory processes. You can become infected from a sick person or animal. Trichophytosis can be superficial, infiltrative and suppurative. The latter is the most severe and can cause severe, infectious complications. It is characterized by the appearance of pink or red spots, which subsequently become crusty.
- Microsporia. The symptoms are very similar to trichophytosis, but the spots are smaller in diameter. The disease can affect the hair. The source of this type of mushroom is often sick animals. And it is mainly children who become infected.
- Mycosis. The penetration of the fungus is facilitated by open wounds, abrasions and cracks. In addition to damage to the skin, nails are also often affected. At the same time, they crumble or become rough, change shape and color. To recover, you must wait until the affected plate is completely cut off. One of the most severe varieties is considered to be deep mycosis, in which the fungus enters the circulatory and lymphatic systems, provoking the development of secondary diseases.
- Candidiasis. This is a type of fungal skin disease that mainly affects the mucous membranes, as well as internal organs. Most often the oral cavity, pharynx, genitals, and skin folds are affected.
The microscopic scabies mite causes scabies. The pathogen multiplies very quickly, and the disease also develops rapidly. The main distinguishing features are numerous small white dots and severe itching. The herpes virus causes the disease of the same name.
Whatever the type of skin disease, it is not recommended to treat it on your own, since there are certain approaches to treating this or that disease. And if you solve the problem yourself, you can only harm the skin, which will subsequently lead to even greater troubles.
- Psoriasis. This is one of the most mysterious skin diseases, the causes of which have not yet been precisely established. The only thing known is that the earlier psoriasis appears in a person, the worse it goes. The main symptoms are the appearance of peeling and inflammation on the skin. It often happens that the disease seems to have passed, but after some time it recurs again, and treatment has to be started again. There are three stages of psoriasis - progressive, stationary, recurrent. If we talk about treatment, it mainly takes place when prescribing external ointments, which include ichthyol, menthol, tar, various alkalis, sulfur, etc. In addition, the patient is prescribed a complex of vitamins that are necessary for the body. This or that type of treatment or ointment should be chosen only by a doctor who will do this based on individual characteristics, as well as the degree and progression of the disease
- Fungal diseases. Fungi are common causative agents of skin diseases. They love dampness and warmth very much, and therefore reproduce very well on human skin. You can catch a fungal disease in a swimming pool, bathhouse, shower cabins in sports halls, etc. There are a lot of places. And since they spread very quickly, it sometimes becomes simply impossible to protect the body. Curing a fungal disease is sometimes not so easy. It seems that the disease has gone away, but in fact it has “subsided” for an indefinite period of time
- Candidiasis. Of course, this is a fungal disease, but it is isolated separately due to the difficulty of treatment, as well as due to its very rapid spread in the body
- Herpes. Quite often you can find herpes in people of different ages. This disease does not have any age restrictions. It is transmitted through saliva or sexual intercourse. There is an opinion that you can become infected with herpes in early childhood, and at the same time it will worsen only at that moment (that is, make itself felt) when the immune system is weakened (during the flu, ARVI, etc.). Herpes manifests itself as rashes on the skin, mainly on the lips. A person can fall asleep completely healthy and wake up with an ugly blister. Herpes is usually treated with tetracycline, as well as antiviral drugs.
- Warts. The causative agent of this disease is Panil, a human lomatosis virus. Warts do not look very aesthetically pleasing, which is why, as soon as a person notices it on himself, he tries to get rid of it immediately. Cryotherapy is the best way to get rid of a simple wart. It often happens that if you remove just one or two warts, the rest will disappear on their own. Of course, in most cases people have simple warts, but sometimes they also have genital and plantar warts, which are a little more difficult to get rid of
- Acne. One of the most common skin diseases is acne. They cause great discomfort, as they mainly affect the skin of the face and look ugly. Acne in most cases appears due to problems with the intestines, as well as as a consequence of hormonal imbalance. That is why it is worth establishing the exact cause of acne, and only then starting treatment. In order to prevent the appearance of a rash, it is necessary to carefully monitor your skin and follow all the rules of personal hygiene.
Skin diseases occur in almost every second person on earth, which is why a lot of time is spent studying them. If you suddenly notice any changes, growths, or redness in yourself, then there is no need to delay. It is necessary to immediately contact a specialist, because if you start treatment on time, you can avoid unpleasant consequences!
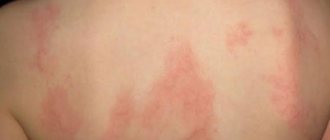
The most common types of skin diseases are urticaria, lichen, ulcers and psoriasis. The causes of some skin diseases are well studied, but the factors that trigger the development of others are still unknown, which complicates their treatment. There is a theory of the hereditary genesis of such diseases, but this has not yet been scientifically confirmed.
The acute form of urticaria lasts from several hours to several weeks; the chronic form, as a rule, lasts for several years.
The causes of this skin disease can be physical (sun, cold, water) or (insect bites, pollen, dust, medications, food) factors.
What other skin diseases are there, and what signs do they manifest?
The typical form of lichen planus is characterized by small, up to 2 mm in diameter, whitish-pearl or grayish-white nodules that merge with each other, forming a mesh, lines, arcs, a fancy pattern of lace or fern leaves.
Look at the photo of this type of skin disease: nodules often appear on symmetrical areas of the body (hands, feet, wrists, ankles, legs) and are accompanied by intense itching.
Also a symptom of the skin disease lichen planus is a whitish coating on the mucous membrane of the mouth and lips. Sometimes papules are located on the scalp, genitals and back. The nodules can remain on the skin from several weeks to several months, leaving persistent brown pigmentation of the skin after disappearing.
The cause of the development of lichen planus is still unknown. The first clinical manifestations of the disease occur between the ages of 30 and 60 years.
An ulcer is a type of skin disease in humans that is a deep inflamed defect in the epithelium of the skin or mucous membrane and underlying tissues. Ulcers occur as a result of infection, mechanical, chemical or radiation damage, but most often as a result of impaired blood supply and/or innervation.
Ulcers are usually very painful and prone to infection. Treatment should primarily be aimed at the cause of the ulcer, and also include long-term use of local remedies.
Trophic leg ulcers are a common collective term in clinical practice, which does not have a register in the international classification of diseases. But, like thousands of years ago (this form of pathology was noted in Ancient Egypt, among the dynasties of the pharaohs), it still exists today.
Trophic ulcers on the lower extremities are the result of various diseases in which the local circulation of arterial or venous blood and lymph is disrupted. In addition to these factors, the appearance of trophic ulcers can be caused by various injuries to the skin, soft tissues and peripheral nerves.
As a rule, ulcers form in the lower third of the limb and on the protruding part of the ankles. Ulcers caused by impaired venous circulation are relatively painless and are a consequence of varicose veins or a complication of phlebitis. High blood pressure and cholesterol levels in the blood, diabetes mellitus, and smoking can lead to the formation of painful trophic ulcers due to impaired arterial circulation.
Having identified the symptoms of this skin disease, treatment begins with addressing the cause of the ulcer. Then cleansing, disinfection, appropriate bandage, and sometimes skin grafting are performed. Treatment is possible only in a clinical setting.
Prevention of skin diseases
There are different types of skin diseases. Therefore, it is advisable to talk about their treatment only after a thorough diagnosis of the body. But since the skin takes part in the metabolic processes of the whole body and performs a protective function, it is necessary to take this issue seriously.
There are a number of basic recommendations for preventing skin problems. You need to carefully select cosmetics. They should not violate the water-lipid barrier. Otherwise inflammation will begin. In addition, existing chronic skin diseases are exacerbated.
Facial skin diseases are often the result of improper care. This problem is especially acute in adolescence. In the absence of proper hygiene procedures, bacteria actively develop. Pyoderma or other diseases may begin.
It is important to avoid stress and saturate the body with sufficient oxygen. Regular exercise or meditation in the fresh air are suitable for this. It is worth paying attention to your diet. A deficiency of vitamins and microelements immediately affects the condition of the skin. And with poor nutrition, toxins accumulate in the body, which leads to acne.
And more individual recommendations can be obtained from specialists.
Main symptoms
Characteristic symptoms of skin diseases are the following:
- the appearance of nodules, rashes, redness and other signs of skin disorders;
- itching, which becomes stronger as the disease progresses;
- burning and tingling sensation;
- the appearance of scales on damaged areas of the skin.
Local symptoms of diseases may vary. Almost all dermatological ailments are accompanied by insomnia, which occurs as a result of discomfort, itching and burning.
Hygiene measures for bacterial infections
Hygiene is very important for bacterial infections. Hygiene measures consist of brushing the nails using antiseptic solutions. While taking a bath, 1-2 tablespoons of these solutions are added to the water to disinfect the entire body .
The nose is regularly treated with antibiotics such as soframycin .
By following these measures, you can avoid relapses with furunculosis .
Share link:
Treatment of bacterial infections
Mainly, the treatment of all skin bacterial infections consists of antibiotic therapy , immediately after identification of the causative agent of the disease.
Macrolides are prescribed against staphylococcal infections .
Less commonly used for their treatment are quinolones , which may cause side effects:
- tendon inflammation;
- sensitivity to light.
To treat streptococcal infections, penicillin injections are used in large doses for 8 days. Treatment continues with oral penicillin. Before prescribing penicillin to patients with streptococcal infections, it is checked if they are not allergic to this drug.
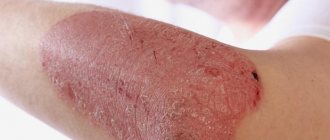
Eczema
Eczema
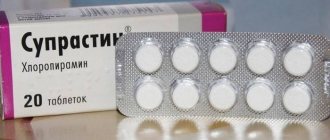
Eczema, like psoriasis, is chronic and is an inflammation of the outer layers of the skin. The causes of this dermatosis are usually associated with heredity or exposure to harmful chemicals on the skin. There are different types of eczema: seborrheic, true, microbial, occupational, etc. The main symptoms of this disease are visible to the naked eye. This is redness of the skin, its constant wetting or, conversely, excessive dryness, detachment of skin scales, unbearable itching. Periods of exacerbation of eczema are usually replaced by periods of remission of the disease, when there is an almost complete disappearance of its main symptoms. However, under certain circumstances, redness and flaking of the skin returns again. If you suspect the presence of eczema, it is recommended to consult a dermatologist, since only a doctor can choose the correct treatment for each individual case. Therapy for eczema involves the patient following a special diet, local application of special ointments that help relieve symptoms, and taking medications prescribed by a dermatologist in the form of tablets or injections. In extreme cases of eczema, when there is a threat of the disease spreading to the entire surface of the patient’s body, hormone-based medications are indicated. As an addition to the main treatment, antihistamines (Zyrtec, Suprastin) can also be prescribed.
ICD-10 code
In medicine, the disease is classified as a group of pathologies with the name: “Urticaria and erythema” ( L50-L54 ).
- For example, erythema nodosum of the lower extremities has code L52. It often occurs against the background of streptococcal, staphylococcal or fungal infections, tuberculosis or syphilis.
Erythema nodosum: photoWith this disease, the area of the ankle joint is affected; multiple nodular formations (from 50 mm to 10 cm in diameter in the walls of blood vessels) are visible on it.
- Erythema multiforme exudative is coded L51. This disease is acute and most often manifests itself in spring and autumn, developing against the background of allergies and autoimmune diseases. This form affects the feet, hands, elbows, knees, and mucous membranes of the oral cavity and genitals. Sometimes the disease has a moderate course and is limited to the occurrence of a few redness of the skin, and sometimes it is total in nature, in these cases the papules quickly spread throughout the body, blisters may appear and burst, microcracks and bloody crusts may appear on it.
- The ring-shaped form of the disease (L53) occurs with the formation of round-shaped spots (5-10 cm in diameter) on the body, often merging with each other, and occurs due to poisoning of the body or abuse of drugs.
Some types of erythema (burn (L59), erythema toxicum of the newborn (P83.1), erythema infectiosum of childhood (B08.3)) are not included in this group and are classified elsewhere.
For example, neonatal erythema toxicum is an infant disease. It appears in the first month of a child’s life as an adaptive reaction to external conditions and disappears without treatment as the child’s body adapts. An erythematous rash forms on the flexor surfaces of the arms and legs, abdomen, buttocks and back of the baby.
Scabies
Scabies is a skin disease that is caused by the active activity of the scabies mite. There are several types of scabies: typical, nodular, complicated, and so on. The main symptom is the appearance of a red, often watery rash on the skin (mainly between the fingers and on the sides of the palms). Usually accompanied by severe itching, which intensifies during sleep (the period when the mite is especially active). Scabies can also be distinguished by the nature of the localization of the rash: pimples on the skin are usually located in pairs.
Infection occurs through direct contact with the patient’s skin and personal belongings. The disease often does not manifest itself in the first days after infection, because the incubation period is 7-10 days.
To prevent complications such as a purulent infection (which can develop from scratching the rash), it is necessary to use soothing agents and control the itching.
The disease is diagnosed by visual examination by a dermatologist and examination of the mite and scraping. Scabies is treated externally with special preparations, along with which the doctor can individually prescribe general treatment with immunomodulators and sedatives. It is recommended to thoroughly wash and iron things that the patient comes into contact with.
Analyzes
To confirm the diagnosis, the patient must undergo the following tests:
- bacteriological culture;
- general blood analysis;
- Analysis of urine;
- stool analysis;
- examination of gastric secretions;
- tests for allergic reactions;
- chest x-ray.
Thanks to the detailed examination method, it is possible to make a diagnosis as accurately as possible. In some cases, additional studies are required, which include serological (detection of antigens and antibodies in the blood), pathomorphological (biopsy), microscopic (examination of a smear under a microscope).
Features of treatment
When prescribing treatment, it is important to understand that it is necessary, first of all, to eliminate the cause of the disease, and only then begin to treat the symptoms. It should also be remembered that some pathologies have a chronic course. Thus, having gotten rid of the signs of the disease, after a period of remission one can again expect an exacerbation.
Complex treatment involves the following:
- use of local and general medications;
- traditional medicine (act as an additional therapy);
- proper nutrition;
- physiotherapy.
It is worth noting that some pathologies can be cured on their own, without the use of medications and folk remedies.
Treatment of atonic dermatitis in adults
As you can see, the clinical symptoms are not much different from those in babies. All the same blistering rashes with unbearable itching, deterioration in general condition. Rapid attachment of a secondary infection with purulent discharge from the wound eroded surface of the opened papules.
Treatment of atonic dermatitis in adults must be carried out comprehensively. To begin with, it is important to determine the state of the immune system.
Often, against the background of such skin pathologies, reactive arthritis develops. Moreover, small articular joints in the spinal column can be affected, which entails an incorrect diagnosis of osteochondrosis.
Meanwhile, the principle of treatment is radically different. Therefore, be careful.
If you have strange itchy blisters on your skin, and after 10-14 days your back hurts (the rash may go away without a trace by this time), then tell your doctor. And do a blood test that will show the state of your immune system.
Treatment of atonic dermatitis in adults and children includes three areas:
- local impact to prevent infection and accelerate epithelial regeneration;
- general desensitization with the help of antihistamines: Suprastin, Claritin, Cetrin, Pipolfen, Loratadine, etc.;
- restoration of the immune system: taking immunomodulators and restorative vitamin-mineral complexes.
Acne vulgaris
Purulent inflammation of the hair follicle and the sebaceous gland itself. Often caused by a staph infection. Usually the rashes are observed on the face, chest, and back. The course of the facial disease: the appearance of blackheads - comedones, then the appearance of a painful red nodule, after which - the formation of a purulent pustule.
With infections, necrotic acne is possible, in which necrosis progresses deep in the element. In this case, after healing, a scar forms. The spread of the process increases the risk of abscesses and acne conglobata.
Important! Viral skin diseases occur in 3-4% of adult patients and in up to 10% of children.
Atopic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis in children is a chronic, genetically determined inflammatory skin disease.
The first and most important reason for the onset of the disease is genetic predisposition (relatives suffering from various allergies);
Important! Atopy is the tendency of a child’s body to develop allergies. You can read about the treatment of allergies in our article.
- Increased hyperreactivity of the skin (increased sensitivity to external factors).
- Disruption of the child's nervous system.
- Using tobacco products in the presence of a baby.
- Bad ecology.
- Food contains a lot of dyes and flavor enhancers.
- Dry skin.
Important! This type of dermatitis affects children under 12 years of age; at older ages it is extremely rare.
With atopic dermatitis, the child’s skin becomes dry, begins to peel, and a rash appears in spots, especially in certain places: on the face, neck, on the bends of the elbows and knees. This disease has a wave-like course, periods of remission (extinction of symptoms) are replaced by periods of exacerbation.
Diagnostics
Diagnosing one of the many types of erythema is quite difficult, since the characteristic redness of the skin and accompanying symptoms are characteristic of many diseases. For example, with scarlet fever, rubella or measles. After making a preliminary, primary diagnosis, the dermatologist prescribes specific tests:
- a serological test to detect the presence of antibodies to the virus that causes the disease;
- general blood test to determine the number of formed elements;
- allergy tests;
- taking exudate from pustules, if any.
It is also necessary to first exclude physiological causes of erythema and perform a differential diagnosis.
Toxidermy
- a disease of an allergic nature. As a rule, it manifests itself in the form of damage to the skin and mucous membranes. Often localized on the skin of the hands. This is usually a reaction to drug allergens. Manifestations of the disease occur after the allergen enters the body through injections or the digestive tract, sometimes through inhalation.
There are two forms of toxicoderma: fixed and widespread. The first is characterized by the appearance of red spots on the hands (usually raised above the surface of the skin), which are subsequently covered with a brown crust, or a watery bubble forms in the center, which bursts under mechanical stress. Symptoms disappear after stopping the drug that causes the allergy.
Common toxicoderma manifests itself more pronouncedly: not only the skin, but the entire body suffers. There may be an increase in temperature, irritability, nervousness, problems with the digestive and respiratory systems. This is a more severe form of the disease: skin lesions can develop into Lyell's syndrome - the appearance of blisters with serous contents on the skin, which burst and leave behind extensive bright red ulcers. It is important to ensure the sterility of the area of skin lesions and hospitalize the patient, because with this form of dermatitis there is a high probability of blood poisoning.
Please note: if symptoms of this disease appear, you should immediately consult a doctor!