Trichomoniasis is rightfully considered one of the urogenital infections, and untreated disease can lead to a number of complications. Most often, it is diagnosed in the fairer sex, since they undergo preventive examinations more often, and the signs of infection are pronounced.
This disease easily progresses to the chronic stage if treatment recommendations are not followed or if it is neglected. In this article we will talk about how you can become infected with trichomoniasis, how it manifests itself in women, the symptoms and treatment of this disease.
What is trichomoniasis and how can you get infected?
Trichomoniasis refers to diseases that are sexually transmitted (any variant - oral-vaginal, anal, anal-vaginal contact). It is caused by a protozoan single-celled parasite that is capable of living in anaerobic conditions, that is, without air. Every year, 170 million people around the world are diagnosed with the disease.
Trichomoniasis is transmitted only during sexual intercourse. Household transmission, that is, through contaminated towels, shared bed linen, wet swimsuits, and washcloths, is extremely rare. For optimal existence of Trichomonas, it is necessary that the pH of the environment (in women - vaginal contents) be 5.5 - 6.6.
https://youtu.be/XVbFKcW9kkc
Trichomoniasis of the vagina
In the general structure of STIs, the frequency of vaginal trichomoniasis or urogenital trichomoniasis is estimated at about 10%. Vaginal trichomoniasis is sexually transmitted and is usually combined with other STIs. Cases of non-sexual transmission are extremely rare.
Vaginal trichomoniasis and characteristics of the disease
When passing through the birth canal, newborns become infected with trichomoniasis from the vagina from a sick mother. Trichomonas invasion is facilitated by changes in the pH of the hormonal status and vagina. In epidemiological terms, it is Trichomonas carriers and patients with a sluggish inflammatory process, patients with strains that are resistant to metronidazole that pose a big problem.
What microbe affects the vaginal flora during trichomoniasis?
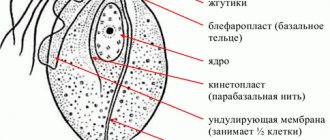
Trichomonas vaginalis - trichomoniasis of the vagina - belongs to the genus Trichomonas, family Trichomonadidae, phylum of protozoa and is a pear-shaped, single-celled organism up to 24 microns in size with an undulating membrane and flagella that ensure active movement. An axostyle, a supporting rod, passes through the entire body of the microorganism. Electron microscopy in the cytoplasm of Trichomonas to check for vaginal trichomoniasis shows round granules that form conglomerates near the nucleus, digestive vacuoles, a nucleus with the Golgi apparatus complex, sometimes containing phagocytosed bacteria. Trichomonas can exist not only in the flagellated vegetative pear-shaped form, but also in the amoeboid form, when the movements of the flagella are not visible, and the movement of the parasite itself occurs so slowly that it appears motionless. The parasite in the amoeboid form is distinguished by its larger shape and size up to 30 microns, repeating the relief of the epithelial cell on which Trichomonas parasitizes. It is capable of phagocytosing whole cells, but phagocytosis may be incomplete. With vaginal trichomoniasis, endocytobiosis is sometimes possible, and in particular with trichomonas-gonorrheal infection.
How does vaginal trichomoniasis develop?
Trichomonas in trichomoniasis usually affects only the squamous epithelium of the vagina. Getting into the cervical canal and the urethra, they spread, then along the mucous membrane and penetrate through the intercellular spaces into the subepithelial connective tissue, thus causing an inflammatory reaction with damage, affecting the glands and lacunae of the urethra, penetrating into the vagina, lymphatic vessels and crevices , move to the gonads and cause their inflammation.
Causes of trichomoniasis in women
- the period of menstruation and after its end (the acidity of the vaginal contents changes)
- abortion (consequences) and childbirth (mechanical protection is disrupted due to expansion of the cervical muscles)
- sexual intercourse (during orgasm, Trichomonas are “absorbed” into the uterine cavity)
Considering the duration of the disease and its symptoms, three forms of urogenital infection are distinguished:
- “fresh” trichomoniasis (acute, subacute and asymptomatic forms)
- chronic trichomoniasis (with minor clinical manifestations) – disease duration of 2 or more months
- trichomonas carriage (asymptomatic course and detection of trichomonas in vaginal leucorrhoea)
In only 10.5% of infected people, the disease occurs as a monoinfection, in other cases it is combined with gonorrhea, chlamydia, ureaplasmosis and other infections. This phenomenon is explained by the fact that Trichomonas are a “vessel” for other microorganisms (that is, they absorb them). The frequency of Trichomonas carriage reaches 2–41%, which is associated with the severity of immunity.
Diagnosis of trichomoniasis
Despite such a long and very detailed study of Trichomonas, the diagnosis of trichomoniasis still causes certain difficulties for doctors. All this is explained by the fact that trichomoniasis is often asymptomatic and takes quite a long time, so it is impossible to detect it without a variety of reusable laboratory tests. According to some doctors, this parasite is able to very successfully “hide” from specialists under the guise of blood and lymph cells, and change its shape, appearance and mobility.
Diagnosis of trichomoniasis before prescribing treatment
Trichomoniasis is usually diagnosed faster and easier in females due to the fact that the symptoms and signs of female trichomoniasis are more pronounced.
To correctly diagnose trichomoniasis, doctors carry out a comprehensive diagnosis, which includes various studies.
One of the first methods of diagnosing trichomoniasis is an examination and interview of the patient.
Often, a patient’s complaints about trichomoniasis are characteristic enough for an experienced specialist to suspect he has this disease. The doctor, for example, must clarify how long a patient with trichomoniasis has been experiencing pain or pain in the genital area, whether she has discharge, what it is, whether it is related to the onset of menstruation, and so on.
Examination and diagnosis for trichomoniasis
Examination of the patient for trichomoniasis is also a very important component of the first stage of diagnosis for trichomoniasis disease. So, when examining the genital organs, you can identify their inflammation and features of the discharge, which can be noticed even without a microscope or special equipment. During an examination for trichomoniasis, some specialists also check the acidity level of vaginal secretions. For example, trichomoniasis is characterized by a high pH.
Diagnosis of trichomoniasis also begins with light microscopy. During the first examination, the doctor takes a general smear to conduct a bacterioscopic examination. In men, prostate secretions and discharge from the urethra are taken for analysis; in women, discharge from the posterior vaginal vault is taken. This test for trichomoniasis is done immediately - the high mobility of oval microorganisms and the beating of Trichomonas cilia are very visible under a microscope. The result of such a test for trichomoniasis will be ready in 20 minutes. This type of diagnosis of trichomoniasis allows the doctor to determine the total amount of Trichomonas and the degree of inflammatory reaction of the mucous membrane.
First symptoms after infection
The incubation period of the disease is 4–14 days, that is, the first signs appear 4–5 days after infection. With trichomoniasis, symptoms depend on where the pathogen has entered and spread. Typically, the infection affects the vagina, urethra and cervix.
- A pathognomic sign of this infection is profuse vaginal leucorrhoea.
- The discharge is greenish or yellowish in color, foamy and profuse.
- In addition, vaginal leucorrhoea with trichomoniasis has an unpleasant odor; when gardnerellosis is added, the smell becomes fishy (see discharge with a fishy odor).
- Often the disease is combined with dyspareunia (pain during coitus).
- When the pathogen penetrates the urethra, urinary disorders appear (cutting, pain, burning during urination), frequent urge to urinate, which indicates the development of urethritis (see urethritis in women: symptoms and treatment).
- Also, all patients, without exception, complain of itching and burning in the vagina. redness and swelling of the vulva
- Rarely, but sometimes women complain of aching pain in the lower abdomen.
During a vaginal examination, a hyperemic vaginal mucosa is discovered, which is covered with abundant “foam” (vulvovaginitis), the cervix is softened and bleeds easily when in contact with the speculum (cervicitis). In addition, when vaginal leucorrhoea gets on the skin of the perineum and the medial surface of the thighs, it causes irritation and ulceration, which is manifested by ulcers and abrasions of various sizes. Trichomonas cervicitis is characterized by a colposcopic conclusion - “strawberry cervix”. When magnified, the cervix is visualized with numerous petechial (capillary) hemorrhages.
Oral trichomoniasis - symptoms and treatment
Trichomoniasis is a sexually transmitted disease that is transmitted both sexually and domestically. There are three types of trichomoniasis in humans: oral trichomoniasis - Trichomonas tenax, intestinal - Trichomonas hominis and genitourinary - Trichomonas vaginalis.
Oral trichomoniasis and its features
Trichomonas vaginalis can live outside the human body for several hours, so the possibility of infection through wet washcloths, underwear and towels prevails, but these are very rare cases. Trichomoniasis is also rarely transmitted through oral and anal sex. In women, oral trichomoniasis affects the vagina and urethra; in men, in addition to the urinary canal, it also infects the prostate gland.
Symptoms of oral trichomoniasis
Oral trichomoniasis, as a rule, does not manifest itself and does not survive in the genitourinary system. We can talk about vaginal trichomoniasis if the patient has symptoms: vaginal discharge is grayish-yellow and sometimes has an unpleasant odor, redness and itching of the genitals, pain during sexual intercourse and urination. As a rule, there are no symptoms of oral trichomoniasis in men, but burning and pain when urinating, discharge from the urethra, and symptoms of prostatitis are still possible. But the diagnosis of trichomoniasis can only be made based on the results of the analysis: PIF and PCR studies, as well as a general smear. For men, studies of discharge from the secretion of the prostate gland and urethra are needed, for women - discharge from the vagina. The incubation period for oral trichomoniasis is from 1 week to 1 month. If trichomoniasis is not treated, it can develop into chronic trichomoniasis and cause serious complications such as infertility and prostatitis in men and premature birth in women.
Prevention of oral trichomoniasis
Prevention and methods of preventing oral trichomoniasis are similar to methods of combating other sexually transmitted diseases:
1.
Safe sex.
2.
Immediately after sexual intercourse, wash the external genitalia with soap and water.
3.
Showering, genital douching and enemas after sexual intercourse.
4.
Use of spermicides during sexual intercourse.
True, the last three methods do not provide any special guarantees.
Treatment of oral trichomoniasis is purely individual and should be carried out comprehensively by a medical professional. As a rule, anti-trichomonas drugs are prescribed: octilin, metronidazole, furazolidone, tinidazole, nitazol, trichomonacid.
Signs of chronic trichomoniasis
Chronic trichomoniasis is a consequence of either ignoring the disease or the transition of the acute form to the chronic form if treatment for trichomoniasis in a woman and/or her sexual partner was not carried out. The chronic stage of trichomoniasis is characterized by a long course and periodic exacerbations. Relapses are promoted by:
- failure to comply with intimate hygiene rules
- menstruation
- sexual intercourse
- alcohol consumption
- decreased immunity (general diseases, hypothermia)
- hypofunction of the ovaries and other factors
Outside of exacerbation, trichomoniasis occurs with mild symptoms. Patients complain of an increase in the volume of vaginal leucorrhoea, slight discomfort in the vagina, especially during sexual intercourse. Exacerbation of the disease is similar to the clinical manifestations of acute trichomoniasis.
Symptoms
The incubation period for trichomoniasis in women varies from 3 days to one month, often 2 weeks. At this time, the pathogen only multiplies and does not cause any particular damage to the internal organs of the genitourinary system. Clinical manifestations are completely absent.
The first signs of the disease in the acute form:
- copious discharge of a foamy consistency of a yellowish or greenish tint - it is worth noting that discharge from trichomoniasis has a specific unpleasant odor of rotten fish;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- pain localized in the lower abdomen, spreading to the lower back;
- itching of the genitals of varying severity;
- discomfort during sexual intercourse;
- a slight increase in temperature to 37.5 degrees;
- pain and burning when emptying the bladder;
- the vagina swells and becomes bright red;
- the appearance of blood impurities in urine;
- sleep disorder;
- menstrual irregularities;
- general deterioration of health.
The duration of the first symptoms is 12–15 days, often ending with recovery against the background of timely treatment.
Symptoms of trichomoniasis in women
In cases of subacute course, the main difference in the clinical picture will be only an increase in the amount of vaginal discharge. In torpid trichomoniasis in women, the symptoms are erased, the disease becomes either chronic or trichomonas carriers.
The chronic course of the pathology during exacerbation has standard symptoms. During remission, external manifestations are not noted.
Why is trichomoniasis dangerous?
Chronic trichomoniasis can lead to the following consequences:
- female infertility - chronic inflammation of the uterine appendages (symptoms, treatment), obstruction of the fallopian tubes (treatment)
- sexual disorders (frigidity, anorgasmia)
- complications of pregnancy (miscarriage, premature birth, antepartum rupture of water, chorioamnionitis, intrapartum and antenatal fetal death)
- malignant process in the cervix (see signs of cervical cancer).
Today, scientists are conducting research and claim that Trichomonas can contribute to the occurrence of diseases such as diabetes, allergic manifestations, mastopathy and oncology of the female genital organs.
Preventive actions
After a woman undergoes a course of drug therapy, she needs to regularly take preventive measures aimed at preventing relapse or re-infection with trichomoniasis:
- The sexual partner must also undergo a course of treatment, after which he must undergo tests.
- Casual contact should be avoided and protected sex should be practiced.
- An extremely important point is maintaining personal hygiene.
- It is necessary to undergo preventive examinations with a gynecologist at regular intervals and take the tests prescribed by him.
https://youtu.be/xs0AedZPvcU
Treatment of trichomoniasis
Treatment of the disease is prescribed to both sexual partners, regardless of whether there are signs or symptoms of trichomoniasis in a man. First of all, you should avoid eating spicy food and alcohol for the period of treatment. It is also recommended to maintain sexual rest during therapy and until negative tests are obtained (to avoid reinfection).
For trichomoniasis, treatment in women with drugs is prescribed only by a doctor; self-medication is not allowed. Medicines must have an effect against anaerobic microorganisms. That is, agents from the 5-nitroimidazoles group are used. These include:
- Metronidazole and its derivatives (Trichopol, Flagyl, Tinidazole, Ternidazole, Ornidazole and others).
- All anti-Trichomonas drugs are effective only when administered systemically (orally) in conjunction with local therapy (Metrogyl vaginal gel). Suppositories for trichomoniasis are inserted intravaginally, one daily for 7–10 days. These can be: Terzhinan, Klion-D, Betadine and other suppositories.
- In case of existing contraindications to oral antrichomonas drugs, suppositories Osartsid or Oosarbon are prescribed, the components of which are osarsol (destroys the enzyme system of Trichomonas) and streptocide (anti-inflammatory effect).
Treatment regimens for trichomoniasis are different:
- trichopolum 0.5 g. (or metronidazole 0.25 g.) 1 tablet twice a day (or 2 tablets 2 times a day), course duration is 7 - 10 days
- Tinidazole 0.5 g. – single dose of 4 tablets
- fascigin 150 mg twice a day for a week
For chronic trichomoniasis, treatment is practically no different from the treatment of the acute stage. In addition to anti-trichomonas drugs, immunostimulants, vitamins and adaptogens (Aloe extract, Eleutherococcus tincture, Aralia tincture) are prescribed.
Control tests after suffering from trichomoniasis are taken three times after each menstruation for 3 months.
Case study: When I was doing my internship, a young woman was admitted to the gynecology department to terminate her pregnancy. The period at that time was already 14 weeks, and an abortion had to be done for medical reasons (mental retardation in the stage of debility). Her tests, of course, were not “oh”, but in the smear, and even more so: Trichomonas. None of the doctors wanted to take on such responsibility (both the term was long and trichomoniasis) and they sent an intern (me) to perform an abortion. The abortion was performed successfully, but! After an abortion, the “client” developed pelvioperitonitis with all the pronounced symptoms. She was then treated in hospital for a long time. She was discharged with recovery.
How to treat trichomoniasis?
Treatment of trichomoniasis primarily involves taking antibiotics, such as trichopolum or nystatin. However, it is worth mentioning that only a doctor can choose the correct dosage and calculate the duration of treatment.
In addition to antibiotics, antiprotozoal drugs produced in the form of oral medications are widely used to get rid of Trichomonas, these include, for example, tinidazole, ornidazole and metronidazole. Along with taking medications, maintenance therapy is usually prescribed - physiotherapy, immunotherapy, urethral instillations and prostate massage (in men).
There are also local remedies for the treatment of trichomoniasis, for example, vaginal suppositories or tablets, douching. But, when planning how to get rid of trichomonas using topical medications, you need to know that they only bring temporary relief, relieving acute symptoms. To completely get rid of trichomonas, complex therapy is necessary.
The effectiveness of treatment can only be checked by passing the appropriate tests, since the disappearance of symptoms does not mean that Trichomonas has completely disappeared. If Trichomonas is detected in one of the partners, then both must undergo treatment, even if the second partner does not have any symptoms of trichomoniasis. Sometimes after a course of treatment, symptoms may appear again after some time. Then the course of treatment must be repeated.
If, in the absence of sources of re-infection, the symptoms of trichomoniasis do not go away after taking medications, then the cause may be the insensitivity of this strain of trichomonas to the action of the drug. In this case, you just need to choose alternative therapy using a different drug.
Prevention measures
Prevention of trichomoniasis, like all urogenital infections, is as follows:
- having one permanent partner
- confidence in sexual partner
- use of barrier contraceptives (condoms)
- compliance with the rules of intimate hygiene (do not use other people’s underwear, towels)
- undergoing regular (at least twice a year) medical examination. inspection.
In case of accidental unprotected sexual intercourse, drugs such as Miramistin, Betadine can be used as an emergency prevention of infection; they reduce the risk of infection by 70% if the external genitalia and vagina are treated within 1-2 hours after coitus.
- To do this, inject 5 ml of Miramistin solution (no more) or Betadine (with a urological attachment) into the vagina, or douche with a weak solution of potassium permanganate (well dissolved to avoid burns). The external genitalia should be treated with an antiseptic - Chlorhexidine, Miramistin. Such procedures can be performed only in extreme cases, as an emergency measure, and should not be abused, since this is not a way to protect against STIs.
Possible complications
Lack of treatment for chronic trichomoniasis, as well as its acute form, is fraught with the development of unpleasant complications. The most common consequences:
- endometritis;
- adnexitis;
- salpingo-oophoritis;
- infertility;
- parametritis;
- abscess of Bartholin glands;
- tubo-ovarian abscess;
- pelvioperitonitis;
- vulvitis;
- salpingitis;
- urethritis;
- bartholinitis;
- cystitis;
- cervicitis;
- pyelonephritis.
In pregnant women, the consequences of infection include spontaneous abortion and premature labor.
What are Trichomonas?
Trichomoniasis is caused by a parasite called Trichomonas vaginalis. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that about 170 million people are diagnosed with the disease each year. The disease is widespread in developing countries. Trichomonas can survive for 24 hours in a humid environment, so there is a possibility of their transmission through the use of shared towels, washcloths, bathtubs, irrigation items, public toilets, etc. The disease most often affects sexually active people between the ages of 20 and 40 years.
What is Trichomonas in women, where do they come from? Trichomonas vaginalis is a parasitic microorganism that causes infection of the lower parts of the human genitourinary system.
There are more than 100 species of the genus Trichomonas, but only three are pathogenic to humans: Trichomonas hominis, Trichomonas tenax and Trichomonas vaginalis.
Trichomonas hominis lives in the gastrointestinal tract and causes diarrhea; It is more common in children than in adults, but its pathogenesis has not yet been studied.
Trichomonas tenax causes oral diseases. Its presence is sometimes detected in sputum during inflammation of the lungs or bronchi. Only Trichomonas vaginalis promotes the formation of inflammatory processes in the human genitourinary system.
T. vaginalis has a pear-shaped, oval, or less often spindle-shaped shape. Their size can range from 8 to 30 microns, and vary depending on the phase of clinical infection. Trichomonas feed on bacteria and fungi, but their main nutrient is glycogen from the epithelial cells of the genitourinary system. As a rule, infection with trichomonas vaginalis passes without characteristic signs. Symptoms of the disease appear when the infection becomes acute. The chronic form of the disease is more common and is accompanied by signs of weaker intensity.
How to cure trichomoniasis in women? It can be effectively treated with antibiotics. Even if there are no signs of the disease, an infected person can infect a sexual partner. Therefore, it is important that both partners undergo pharmacological treatment at the same time.
Is trichomoniasis transmitted through a condom? Proper use of condoms significantly reduces, but does not eliminate, the risk of infection or spread of Trichomonas.
Currently, metronidazole is most often used in the fight against trichomonas vaginalis, but in recent years there has been an increase in the number of strains resistant to this drug. Important questions also arise regarding immunology, complications during pregnancy, accurate diagnosis and public health control of this infection.
Article for you:
How to remove bumps after injections on the buttocks
The high incidence of transmission and serious complications associated with morbidity during pregnancy indicate the need for an epidemiological control program for this disease.