Adrenogenital syndrome is a hereditary disease of the adrenal glands, in which steroidogenesis is impaired due to the functional failure of enzymes. Manifested by virilization of the genitals, masculine-like physique, breast underdevelopment, hirsutism, acne, amenorrhea or oligomenorrhea, infertility. During the diagnosis, the levels of 17-hydroxyprogesterone, 17-ketosteroids, androstenedione, ACTH are determined, and an ultrasound of the ovaries is performed. Patients are prescribed hormone replacement therapy with glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, estrogens in combination with androgens or new generation progestins. If necessary, genital plastic surgery is performed.
What is adrenogenital syndrome
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is the most common type of verulizing pathology. Adrenogenital syndrome is a disease that is known to world medicine as Apère-Gamay syndrome. Its development is associated with increased production of androgens and a marked decrease in the levels of cortisol and aldosterone, which is caused by congenital dysfunction of the adrenal cortex.
The consequences of deviation can be serious for a newborn, since the adrenal cortex is responsible for the production of a huge amount of hormones that regulate the functioning of most body systems. As a result of pathology in the child’s body (this can be observed in both boys and girls), there are too many male hormones and very few female ones.
Complications
The disease can lead to dehydration. This is due to the fact that with this disease, the substance that is responsible for maintaining fluid in the body ceases to be produced. One of the main complications of this disease is the development of infertility. With timely treatment, reproductive function can be improved and the development of infertility can be prevented. For this purpose, the drug “Prostatilen AC” is prescribed. It is sold in the form of rectal suppositories and is intended to maintain men's health. The medicine has an anti-inflammatory effect, eliminates pain, prevents the formation of blood clots and normalizes the production of prostate secretions. The drug improves sperm quality, increases testosterone levels in the blood and normalizes sexual function. Complications of this disease include progressive adrenal insufficiency. In this regard, it is extremely important to detect the disease in a timely manner for its further treatment.
Inheritance type
Each form of the disease is associated with genetic disorders: as a rule, anomalies are hereditary and pass from both parents to the child. More rare are the cases when the type of inheritance of adrenogenital syndrome is sporadic - it occurs suddenly during the formation of an egg or sperm. Inheritance of adrenogenital syndrome occurs in an autosomal recessive manner (when both parents are carriers of the pathological gene). Sometimes the disease affects children in healthy families.
Adrenogenital syndrome (AGS) is characterized by the following patterns that affect the likelihood of it affecting a child:
- if the parents are healthy, but both are carriers of the StAR gene deficiency, there is a risk that the newborn will suffer from congenital adrenal hyperplasia;
- if a woman or man is diagnosed with the syndrome, and the second partner has normal genetics, then all the children in their family will be healthy, but will become carriers of the disease;
- if one of the parents is sick and the other is a carrier of adrenogenetic pathology, then half of the children in this family will be sick, and the other half will carry the mutation in the body;
- if both parents have the disease, all their children will have similar abnormalities.
General information
Adrenogenital syndrome is divided into a congenital form, which is considered classic , and non-classical mild forms, which include postpubertal and pubertal . They are classified depending on hyperandrogenism and the level of C21-hydroxylase deficiency. With this disease, the adrenal glands produce an excessive amount of androgens , while the hormone gonadotropin is released in insufficient quantities.
As a result, a significant disruption of the subsequent growth of follicles, as well as their maturation, occurs in the ovaries. The main cause of adrenogenital syndrome is considered to be a congenital deficiency of an element such as C21-hydroxylase, a special enzyme involved in the synthesis of androgens produced in the adrenal cortex. This enzyme is formed in sufficient quantities under the influence of a gene that is located in the short arm of the autosome - a pair of the 6th chromosome . As a rule, the inheritance of this disease is autosomal recessive. If there is only one pathologically altered gene in the body, the disease may not develop, and only when the pathological genes are in different pairs of chromosomes can adrenogenital syndrome develop.
Forms
Androgenetic disease is conventionally divided into three types - virile simple, salt-wasting and post-pubertal (non-classical). The varieties have serious differences, so each patient requires a detailed diagnosis. How do forms of adrenogenital syndrome manifest themselves:
- Viril form. It is characterized by the absence of signs of adrenal insufficiency. The remaining symptoms of AHS are fully present. This type of pathology is extremely rarely diagnosed in newborns, more often in adolescents (boys and girls).
- Salt-wasting type. Diagnosed exclusively in infants during the first weeks/months of life. In girls, pseudohermaphroditism is observed (the external genitalia are similar to male ones, and the internal genitalia are female). In boys, salt wasting syndrome is expressed as follows: the penis is disproportionately large relative to the body, and the skin of the scrotum has a specific pigmentation.
- Non-classical look. The pathology is characterized by the presence of unclear symptoms and the absence of pronounced adrenal dysfunction, which greatly complicates the diagnosis of AGS.
Manifestations of pathology depend on the form of AGS
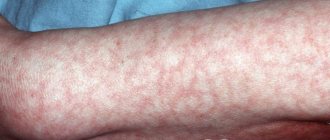
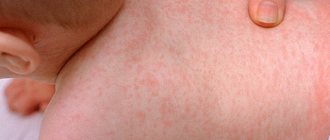
- Classic. The vulva in babies is formed according to the heterosexual type: the clitoris is enlarged, and the labia have the appearance of a scrotum. Upon reaching the age of two years, children of both sexes begin to experience signs of puberty: the appearance of hair in the armpits and groin, a change in the timbre of the voice, the appearance of roundness on the hips and chest, acne.
- Salt-wasting. In addition to the symptoms described above, there are signs of adrenal insufficiency. Moreover, this happens already in the first few days after the baby is born. With the salt-wasting form of adrenogenital syndrome, symptoms such as vomiting, loose stools appear, small patients quickly lose weight, there is a decrease in blood pressure and an increase in the number of heart contractions. As a result, the heart muscle may stop working due to too much potassium in the blood.
- Postpubertal. Signs characteristic of puberty appear in the third year of life. In babies, menstrual function is disrupted, and cysts appear on the ovaries.
Having learned about the main symptoms of adrenogenital syndrome, parents will be able to promptly identify the pathology and seek help from specialists.
Adrenogenital syndrome - causes
Congenital adrenal dysfunction is explained only by the manifestation of a hereditary disease, so it is impossible to acquire or become infected with such a pathology during life. As a rule, the syndrome manifests itself in newborn babies, but AGS is rarely diagnosed in young people under 35 years of age. At the same time, such factors as taking potent drugs, increased background radiation, and side effects from hormonal contraceptives can activate the pathology mechanism.
- List of orphan diseases and drugs
- What diseases are inherited - list, classification, genetic tests and prevention
- Analysis of total and free testosterone - indications for performance, the norm in men and women, reasons for deviations
Whatever the stimulus for the development of the disease, the causes of adrenogenital syndrome are hereditary. The forecast looks something like this:
- if at least 1 parent in the family is healthy, the child will probably be born without pathology;
- in a couple where one is a carrier and the other is sick with AGS, in 75% of cases a sick child will be born;
- carriers of the gene have a 25% risk of having a sick child.
Prognosis and prevention
The prognosis for timely detection of adrenogenital syndrome and adequately selected therapy is favorable. Even in patients with significant virilization of the genitals after plastic surgery, normal sex life and natural childbirth are possible. Hormone replacement therapy for any form of AGS promotes rapid feminization - the development of the mammary glands, the appearance of menstruation, normalization of the ovarian cycle, and restoration of generative function. Prevention of the disease is carried out at the stage of pregnancy planning.
If cases of such pathology have been observed in the family, a consultation with a geneticist is indicated. Carrying out an ACTH test for both spouses makes it possible to diagnose heterozygous carriage or latent forms of adrenogenital disorder. During pregnancy, the syndrome can be detected by the results of a genetic analysis of chorionic villi cells or the contents of amniotic fluid obtained by amniocentesis. Neonatal screening, carried out on the 5th day after birth, is aimed at identifying increased concentrations of 17-hydroprogesterone for quick selection of therapeutic tactics.
(
1 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5)
Symptoms
AHS is not a deadly disease, but some of its symptoms cause serious psychological discomfort to a person and often lead to a nervous breakdown. When diagnosing a pathology in a newborn, parents have the time and opportunity to help the child with social adaptation, and if the disease is detected at school age or later, the situation can get out of control.
The presence of AGS can be determined only after molecular genetic analysis. Symptoms of adrenogenital syndrome that indicate the need for diagnosis are:
- non-standard pigmentation of the child’s skin;
- steady increase in blood pressure;
- low growth inappropriate for the child’s age (due to the rapid completion of the production of the corresponding hormone, growth stops early);
- periodic seizures;
- digestive problems: vomiting, diarrhea, severe gas;
- in girls, the labia and clitoris are underdeveloped or, on the contrary, have increased sizes;
- in boys, the external genitalia are disproportionately large;
- girls with AGS experience problems with menstruation, conceiving a child (infertility often accompanies the disease), and bearing a fetus;
- Female patients often experience male-pattern hair growth on the genitals; in addition, growth of mustaches and beards is observed.
Symptoms of the disease
Virile and salt-wasting forms of the disease are formed in the prenatal period of development and appear after the birth of the child. Their main symptom is virilization of the external genitalia. In girls, the clitoris becomes large in size, it looks like a male penis, and the labia are also increased in size. In boys, the penis also enlarges, and pigmentation of the scrotum occurs.
The disease can be recognized by the following signs:
- predominance of masculine traits;
- strong pigmentation of the genitals;
- early hair growth in the pubic area and armpits;
- skin rashes.
Along with this, severe somatic disorders occur, which in some cases lead to death. In this case, adrenogenital syndrome has the following symptoms: severe diarrhea and vomiting, which lead to dehydration; convulsions. Children with this pathology have adrenal insufficiency. Adrenogenital syndrome in newborns is manifested by such signs as vomiting, acidosis, adynamia, sluggish sucking, and hyperpigmentation.
Adrenogenital syndrome in newborns
The disease can be detected at an early stage in newborns, which is associated with neonatal screening on the 4th day after the birth of the child. During the test, a drop of blood from the baby's heel is applied to a test strip: if the reaction is positive, the child is transferred to an endocrinology clinic and re-diagnosis is performed. Once the diagnosis is confirmed, treatment for AGS begins. If adrenogenital syndrome in newborns is detected early, then therapy is easy; in cases of late detection of adrenogenetic pathology, the complexity of treatment increases.
In boys
The disease usually develops in male children from the age of two or three. Increased physical development occurs: the genitals enlarge, active hair growth occurs, and erections begin to appear. In this case, the testicles lag behind in growth, and subsequently stop developing altogether. As in girls, adrenogenital syndrome in boys is characterized by active growth, but it does not last long and in the end the person still remains short and stocky.
For girls
Pathology in girls is often expressed immediately at birth in the virile form. False female hermaphroditism, characteristic of AGS, is characterized by an increased size of the clitoris, with the opening of the urethra located directly under its base. The labia in this case resemble in shape a split male scrotum (the urogenital sinus is not divided into the vagina and urethra, but stops developing and opens under the penis-shaped clitoris).
It is not uncommon for adrenogenital syndrome in girls to be so pronounced that at the birth of a baby it is difficult to immediately determine its gender. During the period of 3-6 years, the child actively grows hair on the legs, pubic area, and back, and the girl becomes very similar in appearance to a boy. Children with AHS grow much faster than their healthy peers, but their sexual development soon stops completely. At the same time, the mammary glands remain small, and menstruation is either completely absent or appears irregularly due to the fact that the underdeveloped ovaries cannot fully perform their functions.
- Cortisol - what is it, the level of the hormone in the blood. Cortisol levels in women and men
- Antiphospholipid syndrome - what is it? Diagnosis, tests and clinical recommendations for ATP syndrome
- Endocrinologist - who is he and what does he treat? An endocrinologist will help with diseases of the endocrine system
Symptoms of the disease
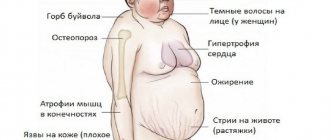
Signs of the described problem can be identified immediately after childbirth. Babies with AGS differ from others by having too much body weight and rather large stature. Their body appears elongated. In some cases, a child's growth may stop abruptly at age 11–12, and he will remain that way for the rest of his life. In girls, the disease causes changes in the vulva. The clitoris takes on a penis-like appearance. Internal organs continue to develop normally, although atrophy may occur over time. Despite all this, menstruation is either disrupted or completely absent. Breasts may also stop developing. Masculinization is accompanied by abundant hair growth in babies.
Diagnosis of adrenogenital syndrome
The disease can be detected using modern hormonal studies and visual examination. The doctor takes into account anamnestic and phenotypic data, for example, hair growth in places atypical for a woman, development of the mammary glands, male body type, general appearance/health of the skin, etc. AHS develops due to a deficiency of 17-alpha-hydroxylase, so the patient’s blood can monitor the level of the hormones DHEA-S and DHEA, which are precursors of testosterone.
Diagnosis also includes a urine test to determine the 17-KS level. A biochemical blood test allows you to determine the level of hormones 17-OHP and DHEA-S in the patient’s body. Comprehensive diagnostics, in addition, involves studying the symptoms of hyperandrogenism and other disorders of the endocrine system. In this case, the indicators are checked twice - before the test with glucocorticosteroids and after it. If during the analysis the hormone level is reduced to 75% or more, this indicates the production of androgens exclusively by the adrenal cortex.
In addition to hormone tests, the diagnosis of adrenogenital syndrome includes an ultrasound of the ovaries, in which the doctor determines anovulation (it can be detected if follicles of different levels of maturity are observed, not exceeding preovulatory volumes). In such cases, the ovaries are enlarged, but the volume of the stroma is normal and there are no follicles under the organ capsule. Only after a detailed examination and confirmation of the diagnosis begins treatment of adrenogenital syndrome.
Diagnosis and treatment
If a newborn has symptoms of adrenogenital syndrome, then he undergoes a comprehensive examination.
Doctors prescribe level tests:
- 17-hydroxyprogesterone;
- androstenedione;
- dehydroepiandrosterone;
- renin;
- adrenocorticotropin.
Sometimes a special test with adrenocorticotropin is required.
Currently, molecular genetic diagnostic methods are being introduced into practice. They allow direct detection of a significant gene defect.
Diagnosis of adrenogenital syndrome (non-classical form) in adults is the task of gynecologists and endocrinologists. Doctors take into account the level of 17-hydroxyprogesterone, examination data, and obstetric history.
Treatment of adrenogenital syndrome depends on the form. Doctors use glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids. Sometimes surgical interventions are required (for plastic surgery of the external genitalia).
In women with the non-classical form, treatment of adrenogenital syndrome is carried out only in cases of severe cosmetic problems and infertility.
Adrenogenital syndrome - treatment
ABC is not a fatal pathology with a lethal outcome, so the likelihood of developing irreversible changes in the patient’s body is extremely low. However, modern treatment of adrenogenital syndrome cannot boast of its effectiveness and efficiency. Patients with this diagnosis are forced to take hormonal medications for life to compensate for the deficiency of glucocorticosteroid hormones and to combat feelings of inferiority.
The prospects for such therapy remain unexplored, but there is evidence that there is a high probability of developing concomitant AGS pathologies of the heart, bones, blood vessels, gastrointestinal tract, and cancer. This explains the need for people with adrenal cortex dysfunction to undergo regular examinations - x-rays of bones, electrocardiogram, ultrasound of the peritoneum, etc.
Classification
As mentioned above, androgenital syndrome has three forms.
- Salt-wasting disease is characterized by a severe course and can appear in the first year of a baby’s life. He will experience gross disturbances in the anatomy of the external genitalia. 21-hydroxylase has an activity of no more than 1%. The disease is accompanied by convulsions, pigmentation of the skin, and vomiting. If treatment is not started, children die at an early age.
- Verile (classical) course is not as severe as the previous option. Changes in the structure of the genitals are also observed. 21-hydroxylase has an activity of 1–5%. The patients showed no signs of adrenal insufficiency.
- Non-classical (post-pubertal) is one of the most favorable forms of AGS. Its symptoms appear during puberty and reproductive age. The genitals have a normal appearance. 21-hydroxylase has an activity of 20-30%. In most cases, the diagnosis is made when problems with conception occur.
Pathogenesis of CDCN
The mechanism of development of the most common variant of adrenogenital syndrome with a defect in the CYP21-B gene is based on the feedback principle. Its initial link is a deficiency of steroids - cortisol and aldosterone. The failure of hydroxylation processes is accompanied by an incomplete transition of 17-hydroxyprogesterone and progesterone to 11-deoxycortisol and deoxycorticosterone. As a result, the secretion of cortisol decreases, and to compensate for this process, the synthesis of ACTH, a hormone that causes compensatory hyperplasia of the adrenal cortex to stimulate the production of corticosteroids, is increased in the pituitary gland.
At the same time, the synthesis of androgens increases and visible signs of their influence on sensitive tissues and organs appear. With a moderate decrease in enzyme activity, mineralocorticoid deficiency does not develop, since the body's need for aldosterone is almost 200 times lower compared to cortisol. Only a deep gene defect causes severe clinical symptoms, which manifest themselves from an early age. The pathogenesis of the development of the disease when the structure of other DNA sections is disrupted is similar, but the trigger point is disturbances in other parts of steroidogenesis.
Surgery
In cases of severe false hermaphroditism, hormones are prescribed and surgery is performed to correct the external genitalia. Sometimes the help of a psychotherapist may be needed. This usually happens when the congenital disease was not diagnosed at an early age, and the girl was raised as a boy in the family. In some cases, doctors remove the uterus and its appendages in order to preserve the civil male sex, but this decision must be made by the patient himself.
Surgery is aimed at resection of the clitoris, dissection of the sinus and formation of the vaginal opening. If a secondary infection develops, the dosage of medications is increased.
Thus, the treatment tactics for different forms of the disease depend on the patient’s age, the nature of the disorders, and the time of diagnosis of the pathology. Doctors recommend starting therapy as early as possible to reduce the risk of complications.
Prevention
As such, there are no drugs that prevent the development of adrenal cortex dysfunction. All that parents can do to protect their family from this terrible disease is to undergo timely genetic counseling. To identify abnormalities in the body, special tests are prescribed. It would not hurt to visit an endocrinologist if there have been cases of diseases of the endocrinological system in the family. The genetics of adrenogenital syndrome are revealed after the birth of the baby. To detect it, you need to conduct a full examination of the baby, this will allow you to be confident in the state of his health. To protect yourself from developing the disease, you need to be examined by a doctor on an ongoing basis.
Characteristics of the pathology
Adrenogenital syndrome (AGS) is a hereditary adrenal hyperplasia, which is accompanied by excessive synthesis of androgens.
The disease affects both women and men, but in most cases the fair sex suffers from it. In 90% of patients with adrenogenital abnormalities, a mutation of the gene responsible for the production of the enzyme 21-hydroxylase and corticosteroids is detected.
Hormonal imbalance occurs during fetal development and is detected from the moment of birth. Due to insufficient synthesis of cortisol, the concentration of androgens in patients increases. The main clinical manifestation of adrenogenital disorders is pronounced virilization of the genital organs. Newborn girls show signs of female pseudohermaphroditism.
In classical (congenital) forms of fermentopathy, the prognosis depends on the timeliness of diagnosis and the quality of replacement therapy. Long-term hyperandrogenism increases the risk of developing cosmetic defects, which impairs psychosocial adaptation. In case of adequate treatment of women with classic forms of adrenogenital abnormalities, pregnancy may occur.
Treatment methods
Hormone replacement therapy is the main method of correcting inherited adrenal dysfunction. In a situation where a patient with a latent form of adrenogenital syndrome has no reproductive plans, menstruation is rhythmic, and skin manifestations are minimal, corticosteroids are not used. In other cases, the choice of treatment tactics depends on the form of the disorder and the patient’s complaints. As a rule, glucocorticosteroids are complemented by other drugs and surgical methods selected according to the specific therapeutic goal.
Restoring fertility function
If there are reproductive plans, the woman is prescribed hormone therapy. Glucocorticosteroids are taken strictly under medical supervision. Hormonal treatment continues until the menstrual cycle is completely restored and pregnancy occurs. Sometimes ovulation stimulants are additionally prescribed. To avoid miscarriage, corticosteroids are taken until the 13th week of gestation. In the first trimester, women with adrenogenital abnormalities are recommended to take estrogens. In the second and third - progesterone analogues without androgenic effect.
Correction of virilization
If the patient does not plan to have children, but still wants to get rid of hirsutism, acne, and normalize the menstrual cycle, it is advisable to use drugs with antiandrogenic effects, oral contraceptives with the latest generation of gestagens. The therapeutic effect is achieved 3–6 months after the start of treatment for the syndrome. At the end of the course, the symptoms of adrenogenital disorder return.
Treatment of false hermaphroditism
Patients with such manifestations of the syndrome are prescribed hormone therapy. Then surgical correction of the shape of the genital organs is performed - opening of the urogenital sinus (introitoplasty), clitorotomy. In case of salt-wasting adrenogenital syndrome, in addition to glucocorticosteroids under the control of renin activity, mineralocorticoids are used with increasing dosages in the event of intercurrent diseases.
What disorders occur in the body during AGS?
In 90% of cases, the occurrence of AGS syndrome is caused by a lack of production of the enzyme 21-hydroxylase. Clinically, there are three main forms of this disease:
— Viral – more common in girls, it begins to develop even during pregnancy. After birth, the baby has an abnormal structure of the labia. If the form of the disease is more complex, it may be difficult to determine gender. At older ages, females are characterized by masculinization. It manifests itself in a low timbre of the voice, muscularity and an enlarged clitoris. The internal genital organs (uterus and ovaries) are usually developed normally.
- Salt wasting - the manifestations of the disease are similar to intestinal disease and occur due to an imbalance in the water-salt balance. Due to a lack of the hormone aldosterone, the return of salt through the kidneys into the bloodstream is difficult. The disease is accompanied by vomiting and loose stools. Symptoms of adrogenital syndrome are often confused with those of food poisoning.
- Hypertensive - with this form of the disease, blood pressure rises sharply, the function of the heart and cerebral circulation are disrupted. Difficult to treat with medication.
The salt-wasting type is the most complex form of the disease. If the diagnosis is not made in a timely manner, the patient may die. The salt-wasting form of AGS can develop into a severe form of adrenal insufficiency and lead to a crisis state of the body, which is characterized by cyanosis of the extremities, loose stools, nausea, and severe vomiting.
Children in this condition lose water very quickly. The skin becomes dry, blood pressure decreases, and the pulse quickens. An attack of adrenal insufficiency threatens the child’s life and requires immediate assistance.
What disorders occur in the body during AGS?
Diagnostic measures
Diagnosis of adrenogenital syndrome includes the use of several techniques:
- Ultrasound and CT scan, the results of which show that the adrenal glands are enlarged in size, and the uterus in females is lagging behind in development.
- Laboratory analysis of blood and urine, which shows an increase in the concentration of testosterone, DAE, FSH and LH, renin.
- ACTH test, where the concentration of cortisol decreases.
- Testing blood serum for androstenedione content.
- Measuring basal temperature.
Treatment of urogenital disorders
If the cause of urogenital disorders lies in a deficiency of estrogenic influences, then it is necessary to select adequate estrogen therapy . The use of local forms of estriol in the form of suppositories, ointments and gels is very effective. Unlike other types of estrogens, estriol “works” in the tissues of the genitourinary tract for only 2-4 hours and has no effect on the myometrium and endometrium. According to numerous studies, estrogen replacement therapy using vaginal administration of drugs containing estriol (for example, Ovestin) leads to an improvement in the condition of the mucous membranes of the urethra and vagina, an increase in the number of lactobacilli, a decrease in the pH environment of the vagina and helps eliminate infection.
In severe cases, surgical treatment can be used to correct urinary incontinence and pelvic organ prolapse.
Don't let your illness reduce your quality of life! Entrust the prevention and diagnosis of urogenital disorders to professionals! At MedicCity, the professional experience of the best gynecologists and other medical specialists is at your service!
Severe complication
The most severe complication of the disease is acute adrenal insufficiency, which is accompanied by blueness and coldness of the extremities, hypothermia, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea. At the same time, adrenogenital syndrome in boys and girls often leads to dehydration, dry skin, sharpening of facial features, retraction of the fontanelle, palpitations and decreased blood pressure. This condition is life-threatening, so it is important to provide prompt medical attention.
Therapy
Adrenogenital syndrome is treated in the form of hormone replacement therapy, which is aimed at replenishing the lack of steroids. Hormone treatment is not used in the absence of skin rashes, a normal menstrual cycle, and in the absence of planning pregnancy in the future. In other cases, therapy will depend on the manifestation of symptoms, the form of the disease and the degree of its manifestation. Usually, other medications are prescribed along with the use of hormones.
If a woman plans to have a child, she should take glucocorticosteroids until pregnancy occurs. Therapy can be supplemented with drugs that stimulate ovulation. To reduce the risk of miscarriage, hormones should be taken until the thirteenth week of pregnancy.
A doctor may prescribe oral contraceptives if a woman is not planning a pregnancy, but complains of menstrual irregularities and skin rashes. Treatment in this case lasts up to six months, after which it is recommended to carry out hormone replacement therapy.
Causes of the disease
This disease is solely the result of defects in DNA molecules. According to experts, this condition can occur due to the inheritance of a defective gene, or as a result of serious illnesses, stress, or the wrong lifestyle of a pregnant girl.
The reasons for the acquired type of disease lie in the fact that the body has minor gene damage since birth, and at the time of strong aggressive factors, the adrenal glands begin to fail.
Such aggressive factors that increase the load on the adrenal glands include:
- Severe infectious or bacterial disease.
- Bad habits.
- Severe stress or psychological illness.
- Chronic diseases without proper treatment.
All this leads to an increased load on the organ, which is gradually depleted.
Characteristics of the problem
Adrenogenital syndrome is a congenital pathology characterized by a disorder of the adrenal cortex, in which the production of enzymes responsible for the synthesis of steroids is disrupted. With this disease, sexual dysfunction occurs.
According to statistics, the pathology is most often found among representatives of Jewish nationality (19%), among Eskimos the disease is diagnosed in one case out of two hundred and eighty-two, and among Caucasians - 1:14,000.
Adrenogenital syndrome has an autosomal recessive mode of inheritance. If both parents have this pathology, then the probability of having a child with a defect is 25%. When one of the parents is a carrier and the other is sick with this disease, the risk of having a child with congenital anomalies increases to 75%. In the case where one of the parents does not have this pathology, the symptoms of the disease will not appear in the child.
Congenital adrenogenital syndrome is characterized by impaired production of enzymes that are responsible for the synthesis of steroids. As a result, there is a decrease in the production of corticosteroids (cortisol and aldosterone) and a simultaneous increase in androgens due to an increase in the level of ACTH hormone, which causes hyperplasia of the adrenal cortex as a compensatory mechanism to normalize the production of steroids. All this leads to the appearance of symptoms of the disease at an early age.
Thus, adrenogenital syndrome, the pathogenesis of which is described above, is associated with gene mutations that lead to impaired cortisol production.
Often the disease begins to manifest itself after severe stress, trauma, that is, conditions that provoke severe tension in the adrenal cortex.
Normal level of 17-OH-progesterone in the blood
| Group | Period | Value, ng/ml |
| Boys | 1 -3 months | Until 13.7 |
| Girls | 2.40-9.70 | |
| Children | over 3 months | 0.17- 1.70 |
| Men | Constantly | 0.50-2.10 |
| Women | 1st phase of the cycle | 0.10-0.80 |
| Phase 2 of the cycle | 0.60-0.23 | |
| In menopause | 0.13-0.50 | |
| Pregnancy | 2.00-12.00 |
Urine for 17-ketosteroids produced by the adrenal glands and gonads. With genital syndrome, the concentration of these substances can be increased by 6-8 times. For a more accurate diagnosis of the disease, a test with prednisolone is performed, in which the content of 17-KS is reduced by more than half.
Diagnostics
Making a diagnosis for antenatal types of AGS with characteristic changes in the genital organs is not difficult and is carried out immediately after birth. In doubtful cases, karyotyping is used to confirm the female karyotype (46XX). The diagnostic search becomes more important in cases of late clinical onset or latent course with minimal external manifestations of virilization. In such situations, the following laboratory and instrumental methods are used to identify adrenogenital syndrome:
- Level of 17-OH-progesterone
. High concentrations of 17-hydroxyprogesterone, which is a precursor to cortisol, are a key sign of 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Its content is increased 3-9 times (from 15 nmol/l and above). - Steroid profile (17-KS)
. An increase in the level of 17-ketosteroids in the urine of women by 6-8 times indicates a high content of androgens produced by the adrenal cortex. When performing a prednisolone test, the concentration of 17-KS decreases by 50-75%. - Androstenedione content in blood serum
. Increased levels of this highly specific laboratory diagnostic method confirm the increased secretion of precursors of male sex hormones. - Blood ACTH level
. Classic forms of the disease are characterized by compensatory hypersecretion of adrenocorticotropic hormone by the anterior pituitary gland. Therefore, in virilizing dysfunction syndrome, the indicator is increased. - Ultrasound of the ovaries
. In the cortex, follicles are identified at different stages of maturation, not reaching preovulatory sizes. The ovaries may be slightly enlarged, but no stromal proliferation is observed. - Measuring basal temperature
. The temperature curve is typical for the anovulatory cycle: the first phase is extended, the second is shortened, which is due to the insufficiency of the corpus luteum, which is not formed due to the lack of ovulation.
The salt-wasting variant of AGS is also characterized by an increased concentration of renin in the blood plasma. Differential diagnosis of adrenogenital disorders that arise during puberty and childbearing age is carried out with polycystic ovary syndrome, ovarian androblastomas, adrenal androsteromas, virile syndrome of hypothalamic origin and constitutional hirsutism. In difficult cases, endocrinologists, urologists, and geneticists are involved in diagnosis.